Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modern Money Forms
Uploaded by
Kajal RanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modern Money Forms
Uploaded by
Kajal RanaCopyright:
Available Formats
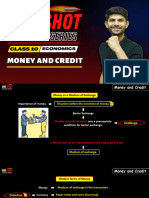
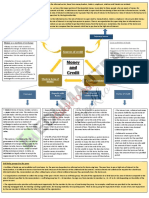
MODERN FORMS OF MONEY
(Money is something that can act as a medium of exchange in transaction)
CURRENCY DEPOSITS AND BANKS
(Modern forms of money include currency, paper notes and Is another form, in which people hold money – as deposited
coins.) with banks.
It is accepted as a medium of exchange because the People deposit extra cash with the banks by opening a bank
currency is authorised by the government of the country. account in their name.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues currency notes on behalf Banks accept these deposits and also pay an amount as
of the central government. interest on the deposits.
The law legalises the use of ‘rupee’ (` ) as a medium of People also have the provisions to withdraw the money as
payment that cannot be refused in settling transactions in and when they require.
India.
Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn
Therefore, the ‘rupee’ (` ) is widely accepted as a on demands, they are known as demand deposits.
medium of exchange.
Payment through cheque, the payer, who has an account
LOAN ACTIVITIES OF BANKS
Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves.
For example: Banks in India these days hold about 15% of their deposits as cash. This is kept as provision to pay
the depositors who might come to withdraw money from the bank on any given day.
Since, on any particular day, only some of its many depositors come to withdraw cash, the bank is able to manage with
this cash.
Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans.
Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
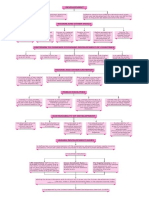
TWO DIFFERENT CREDIT SITUATIONS
Credit (loan) refers to an agreement in which the lender supplier the borrower
with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment.
The obtained credit to meet the In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production.
working capital needs of a production.
Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan
The credit helps to meet the ongoing after harvest.
expenses of production, complete
production on time and thereby
increase in the earnings.
Repayment of the loan is crucially dependent on the income from farming.
Credit therefore, plays a vital and
positive role in this situation. Credit in this case pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very
painful.
Whether credit would be useful or not, therefore depends on the risks in the
situation and whether there is some support in case of loss.
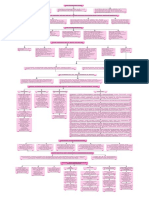
FORMAL AND INFORMAL SEC T OR CREDIT IN INDIA
FORMAL SECTOR INFORMAL SECTOR
The former are loans from banks and cooperatives. The informal lenders include moneylenders, traders,
employers, relatives, friends, etc.
The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of
formal sources of loans. There is no organisation which supervises the credit
activities of lenders in the informal sector.
The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to
They can lend at whatever interest rate they choose.
cultivators, small scale industries, to small borrowers, etc.
There is no one to stop them from using unfair means to
Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on get their money back.
how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate,
etc.
The cost to the borrower of informal loans is much
higher as no record of the transactions are kept and
poor are harrassed.
You might also like
- Notes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsDocument9 pagesNotes - Money & Credit - Class X - EconomicsabhinavsinghbaliyanraghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument2 pagesMoney and CreditChris JudeNo ratings yet
- 3 Money and CreditDocument5 pages3 Money and CreditRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- MONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapDocument49 pagesMONEY & CREDIT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-Mapnimit jaiswalNo ratings yet
- MONEY X EconomicsDocument7 pagesMONEY X EconomicsAvika SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.money and CreditDocument18 pages1.money and CreditNandita KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit One ShotDocument13 pagesMoney and Credit One Shotmrsnightmare76No ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument7 pagesMoney and Creditraimaali220077No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document98 pagesChapter 1Om Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument3 pagesMoney and CreditMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Money and CreditDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Money and CreditKiran shukla100% (1)
- Money and Credit NotesDocument3 pagesMoney and Credit NotestanishqNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit Class 10Document27 pagesMoney and Credit Class 10amritadevi121979No ratings yet
- Money - Credit Class 10Document1 pageMoney - Credit Class 10Legendary Pokemon Blaster 2406No ratings yet
- 9.banking ServicesDocument26 pages9.banking Servicessaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Banking LawDocument16 pagesBanking LawGarima SambarwalNo ratings yet
- Eco AssignmentDocument14 pagesEco Assignmentbeast auraNo ratings yet
- Eco PPT (Vardan)Document8 pagesEco PPT (Vardan)Samriddhi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Banking SystemDocument12 pagesBanking SystemDilip RCNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Eco Money & CreitDocument5 pagesClass 10 Eco Money & CreitPrarthna AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & BeyondDocument5 pagesFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Money & Credit - Mind MapDocument2 pagesMoney & Credit - Mind MapMohd RazaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Study Notes on Money and Credit ChapterDocument6 pagesClass 10 Study Notes on Money and Credit ChapterAavy MishraNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit NotesDocument4 pagesMoney and Credit Notesadityamanjhi108No ratings yet
- Economics - Money and CreditDocument1 pageEconomics - Money and CreditGg YyNo ratings yet
- 32 Nature and Scope of BankingDocument20 pages32 Nature and Scope of Bankingpatilamol019100% (1)
- Money and Credit Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 3 (PDF)Document9 pagesMoney and Credit Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 3 (PDF)jangdesarthakNo ratings yet
- Money ND CreditDocument28 pagesMoney ND CreditSanchita JianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Money and Credit: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science EconomicsDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - Money and Credit: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science EconomicsWIN FACTSNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Notes on Money, Credit and BankingDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Notes on Money, Credit and BankingADWIN JESUSSTONNo ratings yet
- MoneyCreditDocument4 pagesMoneyCreditNisha SinghNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER Two Money and BankingDocument8 pagesCHAPTER Two Money and Bankingananya tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Economics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditDocument3 pagesEconomics, Chapter 3 Money and CreditshambhaviNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument5 pagesMoney and CreditAYUSH DEYNo ratings yet
- BM - Ref Note 1Document4 pagesBM - Ref Note 1Karan TrivediNo ratings yet
- Banking Principles and ProceduresDocument39 pagesBanking Principles and ProceduresEyob FekaduNo ratings yet
- Why banks exist and ration creditDocument5 pagesWhy banks exist and ration creditNguyễn Đường Phương NgọcNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Eco Chap 3 Money and CreditDocument42 pagesClass 10 Eco Chap 3 Money and CreditDNo ratings yet
- SST - Revision (Economics)Document45 pagesSST - Revision (Economics)RSNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 3 Handwritten Notes Money and Credit EconomicsDocument11 pagesEconomics Chapter 3 Handwritten Notes Money and Credit EconomicsRenu Yadav100% (1)
- 2019 Batch OnwardsDocument97 pages2019 Batch OnwardsPavan ChinnikattiNo ratings yet
- Ibfs Unit 3Document9 pagesIbfs Unit 3220106062No ratings yet
- Basics of Banking: Understanding the Core PrinciplesDocument12 pagesBasics of Banking: Understanding the Core PrinciplesriyabhasinNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit - Shobhit NirwanDocument11 pagesMoney and Credit - Shobhit Nirwansannigrahipriyanshu08No ratings yet
- 10-Money and Credit NotesDocument6 pages10-Money and Credit NotesNagulan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Personal Loans Offered by Public AND Private Sector Bank"Document49 pagesPersonal Loans Offered by Public AND Private Sector Bank"revahykrish93No ratings yet
- Loan and AdvancesDocument9 pagesLoan and AdvancesSumit NaugraiyaNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingpptDocument19 pagesMoney and BankingpptSania ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Money and CreditDocument14 pagesMoney and CreditAbhimanyu Chauhan72% (57)
- Business Services Part 2Document11 pagesBusiness Services Part 2Santa GlenmarkNo ratings yet
- Retail: Business LoanDocument6 pagesRetail: Business LoanVinayak ShetNo ratings yet
- 1.bcredit Creation by CLDocument4 pages1.bcredit Creation by CLBoobalan RNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument5 pagesBankingManya JainNo ratings yet
- Loans & Advances Study at Ujjivan BankDocument75 pagesLoans & Advances Study at Ujjivan Banksachin mohanNo ratings yet
- Money & Credit SlideDocument64 pagesMoney & Credit SlideFREE FIRE SHORT VIDEO'SNo ratings yet
- Loans& AdvancesDocument80 pagesLoans& AdvancesSatyajit Naik100% (2)
- Insider's Keys: To The Best Rates And Terms On Your Next Mortgage, #1From EverandInsider's Keys: To The Best Rates And Terms On Your Next Mortgage, #1No ratings yet
- Class 10 Flow Chat 4Document1 pageClass 10 Flow Chat 4Kajal Rana100% (1)
- Global Business Environment Mcqs With Answers - Set2: EguardianDocument143 pagesGlobal Business Environment Mcqs With Answers - Set2: EguardianKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Economics Chapter 3Document2 pagesXam Idea Economics Chapter 3Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- (Note: This Chapter Is To Be Done As Project Work) : Consumer and The ProducersDocument1 page(Note: This Chapter Is To Be Done As Project Work) : Consumer and The ProducersKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Flow Chat 4Document1 pageClass 10 Flow Chat 4Kajal Rana100% (1)
- 00 Flow Chart201907051111471562325107Document1 page00 Flow Chart201907051111471562325107Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- 00 Flow Chart201907050701491562310109Document1 page00 Flow Chart201907050701491562310109Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- 00 Flow Chart201907051111471562325107Document1 page00 Flow Chart201907051111471562325107Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Flow ChatDocument1 pageClass 10 Flow ChatKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- 00 Flow Chart201907050701491562310109Document1 page00 Flow Chart201907050701491562310109Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Je 0 Jvo BHL NW 3 NPRESv 2 HDocument12 pagesJe 0 Jvo BHL NW 3 NPRESv 2 HKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment (International Business) McqsDocument11 pagesBusiness Environment (International Business) McqsMinku RanaNo ratings yet
- Mental Ability, Reasoning, Computers and English Sample Questions for Class 6Document6 pagesMental Ability, Reasoning, Computers and English Sample Questions for Class 6sarthak kothariNo ratings yet
- Economics in 40 charactersDocument89 pagesEconomics in 40 charactersKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Strategy & Content For Essay PaperDocument15 pagesStrategy & Content For Essay PaperPraveen NairNo ratings yet
- Amendments 4yrs CourseDocument6 pagesAmendments 4yrs CourseKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- PN Regarding Result Declared 7-3-18Document11 pagesPN Regarding Result Declared 7-3-18Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Common Ordinance For 3 Year CoursesDocument3 pagesCommon Ordinance For 3 Year CoursesKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter1 PDFDocument60 pages09 Chapter1 PDFMonica MckinneyNo ratings yet
- Transport & Logistics: Pioneering Tomorrow's Innovations TodayDocument3 pagesTransport & Logistics: Pioneering Tomorrow's Innovations TodayKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- PN Regarding Result Declared - 22!3!18Document19 pagesPN Regarding Result Declared - 22!3!18Kajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Science ModuleDocument67 pagesScience ModuleKajal RanaNo ratings yet
- Last Modified On: 07-06-2014 No of Times Modified: 1Document2 pagesLast Modified On: 07-06-2014 No of Times Modified: 1mankm21No ratings yet
- Rtgs and NeftDocument31 pagesRtgs and NeftPravah Shukla100% (5)
- Indian EconomyDocument19 pagesIndian EconomyGanesh MallickNo ratings yet
- Understanding India's Debt MarketDocument13 pagesUnderstanding India's Debt MarketAnil AkgNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 (Introduction)Document6 pagesChapter - 1 (Introduction)Tanmay Sarkar100% (1)
- FDI in Retail Sector in IndiaDocument38 pagesFDI in Retail Sector in Indiajagdish91No ratings yet
- Term Paper On Bank ManagementDocument5 pagesTerm Paper On Bank Managementafdtliuvb100% (1)
- Home First Finance Company India LimitedDocument8 pagesHome First Finance Company India LimitedRAROLINKSNo ratings yet
- Blackbook-Project-On-Research-On-Credit-Risk-Management 2021 04 05 16 04 03796Document84 pagesBlackbook-Project-On-Research-On-Credit-Risk-Management 2021 04 05 16 04 03796Prashant VaraleNo ratings yet
- Audit of Banks ReportDocument7 pagesAudit of Banks ReportANMOL GUMBERNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument20 pagesIndian Banking Structureneha16septNo ratings yet
- A Role of Foreign Banks in IndiaDocument6 pagesA Role of Foreign Banks in Indiak gowtham kumarNo ratings yet
- MCOM MCQ PDF Sample PapersDocument26 pagesMCOM MCQ PDF Sample PapersAvi DVNo ratings yet
- 2017recoverycirculars2017recovery2017016 PDFDocument100 pages2017recoverycirculars2017recovery2017016 PDFDeepak Tandon100% (1)
- Cca Questions All Merged by VKG PDFDocument75 pagesCca Questions All Merged by VKG PDFabhishekNo ratings yet
- Non-Face to Face Customer KYC GuidelinesDocument100 pagesNon-Face to Face Customer KYC GuidelinesTarang100% (1)
- April Current AffairsDocument80 pagesApril Current AffairsAshok YadavNo ratings yet
- A Project On M.P of RbiDocument37 pagesA Project On M.P of RbiUmesh Soni100% (1)
- PM RBI Grade B CA Compilation PDFDocument47 pagesPM RBI Grade B CA Compilation PDFRavi KiranNo ratings yet
- 05.ca May-2019Document48 pages05.ca May-2019sreeNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999Document20 pagesForeign Exchange Management Act 1999Ishpreet Singh BaggaNo ratings yet
- 1Document13 pages1ASHISH JEENANo ratings yet
- Gyanm June 13Document21 pagesGyanm June 13Shailesh KamathNo ratings yet
- Forex Management-StructureDocument9 pagesForex Management-StructureV.AnnapurnaNo ratings yet
- Thesis TELECOM MOBILE SECTOR PreetkanwalDocument326 pagesThesis TELECOM MOBILE SECTOR PreetkanwalAkshat Shukla67% (3)
- Format of Pil in SC - PDF - Upload-380316Document30 pagesFormat of Pil in SC - PDF - Upload-380316nokav64141No ratings yet
- Ey Private Credit in India v1Document18 pagesEy Private Credit in India v1Naman JainNo ratings yet
- Memorandum To RBI On Banking Charges-FinalDocument7 pagesMemorandum To RBI On Banking Charges-FinalMoneylife FoundationNo ratings yet
- Business Quiz: A: Organization of The Petroleum Exporting CountriesDocument53 pagesBusiness Quiz: A: Organization of The Petroleum Exporting CountriessoumitrabehuraNo ratings yet
- HOMELOANSanctionLetter PDFDocument5 pagesHOMELOANSanctionLetter PDFanon_311324903No ratings yet