Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2022-10-12 at 9.42.50 PM
Uploaded by
nathanielOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screenshot 2022-10-12 at 9.42.50 PM
Uploaded by
nathanielCopyright:
Available Formats
Left Anterior Fascicular
Block (LAFB)
John Larkin and Robert Buttner ●
Feb 7, 2021
HOME ECG LIBRARY ECG DIAGNOSIS
ECG Library Homepage
ECG criteria
Left axis deviation (usually -45 to -90
degrees)
qR complexes in leads I, aVL
rS complexes in leads II, III, aVF
Prolonged R wave peak time in aVL >
45ms
aVR
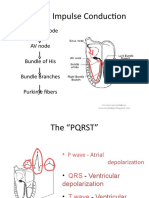
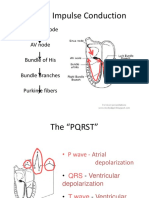
The
Scroll to annotate: Left Anterior Fascicular Block
(LAFB)
Typical ECG of LAFB, demonstrating:
rS complexes in leads II, III, aVF, with small R
waves and deep S waves
qR complexes in leads I, aVL, with small Q
waves and tall R waves
Left Axis Deviation (LAD): Leads II, III and aVF
are NEGATIVE; Leads I and aVL are POSITIVE
Associated features include:
QRS duration normal or slightly prolonged (80-
110ms)
Increased QRS voltage in limb leads
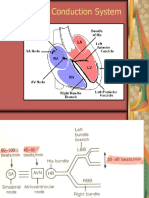
Electrophysiology
In LAFB, impulses are conducted to the left
ventricle (LV) via the posterior fascicle, which
inserts into the inferoseptal wall of the LV along its
endocardial surface
Depolarisation spreads from endocardium to
epicardium and thus the initial vector is
directed downwards and rightwards, towards
inferior leads. This produces small R waves in
leads II, III and aVF, and small Q waves in leads
I and aVL
The major wave of depolarisation is slightly
delayed and spreads upwards and leftwards,
producing tall R waves in left-sided leads and
deep S waves in inferior leads
This overall delay of approximately 20ms
(compared with normal simultaneous
conduction via both fascicles) results in a
slight widening of the QRS
Because impulses reach the left-sided leads
later than normal, there is an increase R wave
peak time in aVL (time from onset of QRS to
peak of R wave)
,
aVR JU aVl
LeadI
V6
V5
VIl
LeadIll LeadIl
aVF
Sequence of conduction in LAFB
1. YELLOW line: Impulses are conducted to the
left ventricle via the posterior fascicle
2. RED arrow: Initial depolarisation vector is
directed towards inferior leads
3. BLUE arrow : Major depolarisation vector,
which is slightly delayed, is directed towards
left-sided leads
ECG Morphology
aVR
AVI
AVE
Is
qR complexes
qR complexes in lateral limb leads, and rS
complexes in inferior leads
Left Axis Deviation (LAD)
Left Axis Deviation (LAD)
Leads I and aVL are POSITIVE;
Leads II, III and aVF are NEGATIVE
Prolonged R-wave peak time
Prolonged R-wave peak time
Prolonged R-wave peak time (= the time from
onset of the QRS to the peak of the R wave) in
aVL > 45 ms
Examples of LAFB
Example 1
Left axis deviation
qR complexes in I, aVL
rS complexes in II, III, aVF
Prolonged R wave peak time in aVL
Increased QRS voltage in limb leads
Example 2
Left axis deviation
qR complexes in I, aVL; rS complexes in inferior
leads
Prolonged R wave peak time in aVL
Slightly prolonged QRS duration
Example 3
Handy Tips
In LAFB, the QRS voltage in lead aVL
may meet voltage criteria for LVH (R
wave height > 11 mm), but there will
be no LV strain pattern.
Related Topics
Left bundle branch block LBBB
Right Bundle Branch Block RBBB
Left anterior fascicular block LAFB
Left posterior fascicular block LPFB
Interventricular Conduction Delay IVCD
Bifascicular block
Trifascicular block
Complete Heart block CHB
Advanced Reading
Online
Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Yellow Belt online
course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Blue Belt online
course: Learn to diagnose any rhythm problem.
Medmastery
Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG
Waves
Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
Textbooks
Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ.
Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and
Critical Care. 2e, 2019
Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram
in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical
Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
Hampton J. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e,
2014
Brady WJ, Truwit JD. Critical Decisions in
Emergency and Acute Care
Electrocardiography 1e, 2009
Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s
Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult
and Pediatric 6e, 2008
Mattu A, Brady W. ECG’s for the Emergency
Physician Part I 1e, 2003 and Part II
Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and
Acute Care 1e, 2004
Smith SW. The ECG in Acute MI. 2002 [PDF]
LITFL Further Reading
ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals,
Segments and Clinical Interpretation
ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation
in clinical context
ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball –
ECG Clinical Cases
100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for
examination practice
ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best
of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Electrocardiogram
EKG Library
John Larkin
Emergency Medicine Specialist MBChB FRCEM
FACEM. Medical Education, Cardiology and
Web Based Resources | @jjlarkin78 | LinkedIn |
Robert Buttner
MBBS (UWA) CCPU (RCE, Biliary, DVT, E-FAST,
AAA) Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine
Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia.
Special interests in diagnostic and procedural
ultrasound, medical education, and ECG
interpretation. Editor-in-chief of the LITFL ECG
Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner
Leave a Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how
your comment data is processed.
Subscribe to LITFL via Email
Subscribe
#FOAMed Medical Education Resources
by LITFL is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
International License. Based on a work
at https://litfl.com
About • Authors • Analytics • Contact
Cookies • Disclaimer• Privacy
Blog Stats
120,954,920 visitors
LITFL posts by EMAIL or RSS
FFFF by EMAIL or RSS
You might also like
- ECG WorldDocument139 pagesECG WorldsatyaNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction AbnormalitiesDocument9 pagesECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction Abnormalitiesradha1000100% (1)
- Advanced ECG Interpretation: Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN, CCRNDocument76 pagesAdvanced ECG Interpretation: Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN, CCRNI Putu SastrawanNo ratings yet
- P Wave Abnormalities and Their ECG SignsDocument10 pagesP Wave Abnormalities and Their ECG SignsAida UzunovicNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument48 pagesECG InterpretationKervayse St.ClairNo ratings yet
- ECG and ArrhythmiasDocument25 pagesECG and ArrhythmiasRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation UnismaDocument178 pagesECG Interpretation UnismadefinaNo ratings yet
- The 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideDocument31 pagesThe 12-Lead EKG: A Step-by-Step GuideJay JiangNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- Advanced Ecg InterpretationDocument88 pagesAdvanced Ecg Interpretationmiguel1123No ratings yet
- Critical Care: ElectrophysiologyDocument180 pagesCritical Care: ElectrophysiologyArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anas Yasin - MDDocument58 pagesDr. Anas Yasin - MDMahfouzNo ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction and ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction and ECG InterpretationIndra ToshiwayNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SDocument98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SAdinda GupitaNo ratings yet
- EKG Self Study GuideDocument40 pagesEKG Self Study GuideArgee AlonsabeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentDocument54 pagesDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentadela_97line100% (2)
- Advanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineDocument88 pagesAdvanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineRoroNo ratings yet
- Krishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesKrishnan - EKG Basics Lecture NotesanishdNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument83 pagesECG InterpretationJuana Maria Garcia Espinoza100% (2)
- ElectrocardiogramDocument52 pagesElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approach To ECGDocument12 pagesSystematic Approach To ECGAmr El TaherNo ratings yet
- Diastolic DysfunctionDocument6 pagesDiastolic DysfunctionMarina SecureanuNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG: DR Subroto Mandal, MD, DM, DC Associate Professor, CardiologyDocument206 pagesBasics of ECG: DR Subroto Mandal, MD, DM, DC Associate Professor, CardiologyRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aqa A2 Biology LDRDocument21 pagesAqa A2 Biology LDRjames100% (4)
- Angina Case Study PDFDocument10 pagesAngina Case Study PDFKEERTHANA PMNo ratings yet
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachFrom EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo ratings yet
- Lectro Ardio Raphy: by Dr. Omprakash Sah Medical Officer NAMS, Bir HospitalDocument162 pagesLectro Ardio Raphy: by Dr. Omprakash Sah Medical Officer NAMS, Bir HospitalAjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215No ratings yet
- Advanced ECG Interpretation (PDFDrive)Document30 pagesAdvanced ECG Interpretation (PDFDrive)hendratj90No ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersDocument73 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersIndra ToshiwayNo ratings yet
- Didactics ECGDocument87 pagesDidactics ECGGenesis Poblacion100% (1)
- Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB) - LITFL - ECG Library DiagnosisDocument1 pageLeft Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB) - LITFL - ECG Library DiagnosisemmyNo ratings yet
- Bloqueos Intraventriculares ECG UpToDateDocument16 pagesBloqueos Intraventriculares ECG UpToDateMoctezuma VeraNo ratings yet
- ECG - Systematic-ApproachDocument12 pagesECG - Systematic-ApproachMicael MendesNo ratings yet
- Left Posterior Fascicular BlockDocument4 pagesLeft Posterior Fascicular BlockFathimah afifah zahrahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentDocument54 pagesDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentacha kyungsooNo ratings yet
- Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Padjadjaran University School of Medicine Hasan Sadikin Hospital BandungDocument61 pagesDepartment of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Padjadjaran University School of Medicine Hasan Sadikin Hospital BandungMuhammad AmrieNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture: Waveforms, Leads and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesECG Lecture: Waveforms, Leads and ApplicationsSalah Salah 201-901-341No ratings yet
- EKG Siklus Jantung dan Pembacaan Hasil EKGDocument64 pagesEKG Siklus Jantung dan Pembacaan Hasil EKGSeptiani HasibuanNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation Guide for Abnormal Heart RhythmsDocument98 pagesECG Interpretation Guide for Abnormal Heart RhythmsMaylisa ManurungNo ratings yet
- ECG-Guided Localization of RVOT and LVOT ArrhythmiasDocument46 pagesECG-Guided Localization of RVOT and LVOT Arrhythmiaskrisna129No ratings yet
- Anatomi 1Document54 pagesAnatomi 1Fany LainamaNo ratings yet
- 5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersDocument48 pages5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersQusai Ibraheem100% (1)
- ECG Conduction Abnormalities: LPFB, Bifascicular BlocksDocument1 pageECG Conduction Abnormalities: LPFB, Bifascicular BlocksLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG 11 hikDocument21 pagesECG 11 hikmdee02031999mNo ratings yet
- 15.2. ECG 2 (Chambers Enlargement)Document149 pages15.2. ECG 2 (Chambers Enlargement)mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Common ECG Lead Placement Errors. Part II: Precordial MisplacementsDocument5 pagesCommon ECG Lead Placement Errors. Part II: Precordial Misplacementsmec17No ratings yet
- Electrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idDocument12 pagesElectrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idlemon kyuteaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Ecgs in Management of CV DiseasesDocument50 pagesImportance of Ecgs in Management of CV DiseasesPragnesh ShahNo ratings yet
- DASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanDocument68 pagesDASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanElsa TjahyaNo ratings yet
- Bullous ImpetigoDocument4 pagesBullous Impetigorostikawaty.A.sudirjaNo ratings yet
- ECG Conduction Abnormalities: LBBB, Incomplete LBBB, LAFBDocument1 pageECG Conduction Abnormalities: LBBB, Incomplete LBBB, LAFBLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG Laboratory Activit1Document9 pagesECG Laboratory Activit1Leiraset WuNo ratings yet
- The Normal Adult ECGDocument84 pagesThe Normal Adult ECGkimiastroNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: RR Interval Heart RateDocument66 pagesECG Interpretation: RR Interval Heart RateRoxana NegureanuNo ratings yet
- Bundle Branch Blocks and Hemiblocks ExplainedDocument29 pagesBundle Branch Blocks and Hemiblocks ExplainedmNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument18 pagesEcgmyla adapNo ratings yet
- C2 Lab 1xbnmvncmxcDocument51 pagesC2 Lab 1xbnmvncmxcanaNo ratings yet
- ECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieDocument60 pagesECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation GuideDocument50 pagesECG Interpretation GuideJake MillerNo ratings yet
- ECG Made EasyDocument82 pagesECG Made EasyBobby SodhiNo ratings yet
- LAFB ECG SignsDocument4 pagesLAFB ECG SignsFathimah afifah zahrahNo ratings yet
- 353Document51 pages353AdamilzaryFikryNo ratings yet
- Guyana Tuberculosis Manual FINALDocument175 pagesGuyana Tuberculosis Manual FINALnathanielNo ratings yet
- Neumonía IdsaDocument23 pagesNeumonía IdsaCarolina MoralesNo ratings yet
- Guyana Diabetes Guidelines 26-Jun-23 FinalDocument20 pagesGuyana Diabetes Guidelines 26-Jun-23 FinalnathanielNo ratings yet
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign International.15Document67 pagesSurviving Sepsis Campaign International.15Tanawat SingboonNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-12 at 6.03.41 PMDocument16 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-12 at 6.03.41 PMnathanielNo ratings yet
- Theory Examination QuestionsDocument8 pagesTheory Examination QuestionsnathanielNo ratings yet
- Prognosis ExampleDocument13 pagesPrognosis ExamplenathanielNo ratings yet
- 4 5931499803149076504 PDFDocument126 pages4 5931499803149076504 PDFCristianAltunaSotomayorNo ratings yet
- IDSA + Soft Tissue Infections (2014)Document43 pagesIDSA + Soft Tissue Infections (2014)nathanielNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Anatomy: Obstetrician & GynecologistDocument31 pagesObstetric Anatomy: Obstetrician & GynecologistnathanielNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document1 pagePaper 2nathanielNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobinopathies in Pregnancy by DR BialaDocument8 pagesHemoglobinopathies in Pregnancy by DR BialanathanielNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For DR DoobayDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For DR DoobaynathanielNo ratings yet
- Committee Opinion List of Titles — March 2019Document11 pagesCommittee Opinion List of Titles — March 2019nathanielNo ratings yet
- Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)Document3 pagesLeber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)nathanielNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesMicroscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionnathanielNo ratings yet
- Sexual Offences Act PDFDocument102 pagesSexual Offences Act PDFnathanielNo ratings yet
- RetinoblalastomaDocument11 pagesRetinoblalastomanathanielNo ratings yet
- Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)Document3 pagesLeber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)nathanielNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Action Potential: Aswin R. MDocument53 pagesCardiac Action Potential: Aswin R. MRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Human Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test BankDocument22 pagesHuman Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (32)
- Adrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument18 pagesAdrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDrFarah Emad Ali100% (1)
- Biomedical Instruments: Classification of Biomedical EquipmentsDocument85 pagesBiomedical Instruments: Classification of Biomedical EquipmentsDuy DươngNo ratings yet
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy - Google SearchDocument1 pageLeft Ventricular Hypertrophy - Google SearchZsa Zsa OllyviaNo ratings yet
- Aspire Business School-Term Exam1: BiologyDocument20 pagesAspire Business School-Term Exam1: BiologyAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- Are you allergic to mornings? How your genes affect being a morning or night personDocument2 pagesAre you allergic to mornings? How your genes affect being a morning or night personaeryll1305100% (1)
- Lipid Metabolism: Stoker Chapter 25 Lippincott Chapter 16Document21 pagesLipid Metabolism: Stoker Chapter 25 Lippincott Chapter 16Shane G.No ratings yet
- Physio Ex 3-01Document8 pagesPhysio Ex 3-01edie tyler100% (4)
- AQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B10Document3 pagesAQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B10Mahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionDocument21 pagesCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionKvaleramNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document7 pagesTest 2Rahmat RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument35 pagesHomeostasis and ExcretionronaldwepukhuluNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Body Fluids and Circulation Test 01 Answer Ki8gDocument2 pages11 Biology Body Fluids and Circulation Test 01 Answer Ki8gJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Dela Peña NCP 3Document2 pagesDela Peña NCP 3Mark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Questions For ApmcDocument15 pagesQuestions For ApmcAde AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Pain ManagementDocument36 pagesUnit 9 - Pain ManagementPetrinaNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Lab ActivityDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Lab ActivityMARY GLORY IGNACIONo ratings yet
- Regulation of Tissue Oxygenation: Second EditionDocument114 pagesRegulation of Tissue Oxygenation: Second EditionrezqNo ratings yet
- Phyp211 - Week 2Document2 pagesPhyp211 - Week 2KHRIZZA PAULETTE ANTIFORDA VEGANo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 UrinaryDocument22 pagesChapter 19 UrinaryAnişoara FrunzeNo ratings yet
- Science 3Document66 pagesScience 3Neon True BeldiaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Quick and Easy Medical Terminology 8th Edition by LeonardDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Quick and Easy Medical Terminology 8th Edition by Leonardamyrileyixgnaoqjmt100% (21)
- Cardiovascular System (Seeley)Document110 pagesCardiovascular System (Seeley)Reniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- HA-RLE-WS # 5 Assessing General Status and Vital SignsDocument5 pagesHA-RLE-WS # 5 Assessing General Status and Vital SignsAshley Blaise JoreNo ratings yet
- Initial Management of Moderate To Severe Hemorrhage in The Adult Trauma Patient - UpToDateDocument38 pagesInitial Management of Moderate To Severe Hemorrhage in The Adult Trauma Patient - UpToDateiustin loghinNo ratings yet