0% found this document useful (0 votes)
162 views8 pagesUnderstanding Cardiac Arrest Causes and Management
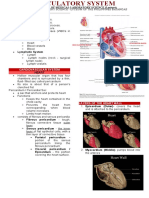
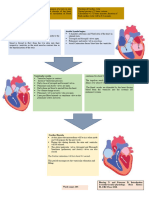
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to problems with its electrical system. It can be caused by ventricular diseases, coronary artery disease, severe stress, or structural heart issues. Diagnosis involves assessing vital signs, EKG, echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, and blood tests. Treatment focuses on restoring blood flow through CPR, defibrillation, and managing the underlying cause through medications, surgery, or lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and managing stress. The goals are to prevent further dysrhythmias, improve tissue perfusion, and restore healthy cardiac function and output.
Uploaded by
MICHELLE JOY GAYOSOCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
162 views8 pagesUnderstanding Cardiac Arrest Causes and Management
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to problems with its electrical system. It can be caused by ventricular diseases, coronary artery disease, severe stress, or structural heart issues. Diagnosis involves assessing vital signs, EKG, echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, and blood tests. Treatment focuses on restoring blood flow through CPR, defibrillation, and managing the underlying cause through medications, surgery, or lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and managing stress. The goals are to prevent further dysrhythmias, improve tissue perfusion, and restore healthy cardiac function and output.
Uploaded by
MICHELLE JOY GAYOSOCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd