Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - Solution
Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - Solution
Uploaded by
Ananmay ChauhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - Solution
Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - Solution
Uploaded by
Ananmay ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
Solutions to Advanced Level Problem Solving-2206
JEE 2022 | Chemistry
OCOC-I, Organic Halides & Organic Concepts, p-Block Element-II,
Practical Organic Chemistry & Polymer
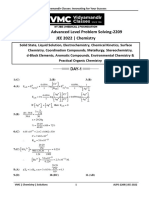
1. [A-q] [B-p] [C-s] [D-r]
(A) MPV reduction of C O (keto) group will take place
(B) With NaBH 4 , both keto and acid-chloride groups will be reduced
(C) With DIBAL-H acid derivatives is reduced
(D) LiAlH 4 reduces the left —COOH group
2.(3) Attack by OMe on Cl(3) would form a carbanion, which can be stabilized by –R effect of NO2 group,
this Cl(3) is substituted by OMe.
3.(B) HCl is most volatile due to weakest inter molecular attractive forces. While HF is least volatile because
of H-bonding.
4.(B) Phenols give violet colour with Fe Cl3 solution while alcohols do not.
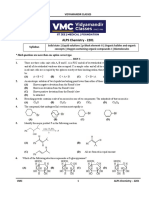
5. [A-p, q, t] [B-r, s] [C-v] [D-u]
(A) All (p), (q), (t) gives this alcohol via Grignard synthesis
(B) Only (r) and (s) can give this alcohol via Grignard synthesis
(C) Only (v) can give this alcohol
(D)
6.(9) Aromatic species : 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14.
7.(C) I I bond is the weakest bond.
RCOOH
RCONH 2
H O
NH3 RCOOH
8.(B) 2
H
n NH3 1 n RCONH2
Mo(amide) 59g Mo(acid) 59 15 16 60g i.e. CH3COOH
9. [A-p, q] [B-p, q] [C-q, r] [D-q]
Other mechanisms can be done similar way.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 1 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
10.(8) The decreasing order of B.P.’s is: (3) > (8) > (2) > (6) > (7) > (1) > (4) > (5)
The sum of numbers pertaining to compounds with lowest & highest B.P. is 5 + 3 = 8.
11.(C) Xe form compounds with fluorine and oxygen and heavier noble gases can be easily liquefied.
38.7
12.(A) %C 38.7 3.225mol
12
16.17
%H 16.17 16.17 mol
1
45.17
% N 45.17 3.225mol
14
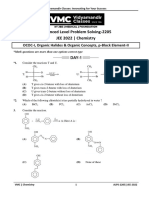
Divide by 3.225
C = 1, H = 5, N = 1
So, empirical formula is CNH5 i.e. CH 3 NH 2 .
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 2 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
13. [A-q] [B-r] [C-p] [D-s]
14.(B) XeF4 is square planar and sp3d2 hybridized.
15.(D) CAN is a test of OH group and not COOH group.
16. [A-q, s] [B-p, r, s] [C-p, s] [D-p, r]
Other mechanisms can be done similar way.
17.(A) Zn 2NaOH
Na 2 ZnO2 H2 ; Zn H2SO4
ZnSO4 H2
y y
18.(D) CX H y x O2 xCO2 H 2O
4 2
20
Moles of organic compound
12x y
10y 10
Moles of H2O 18y 12x y 17y 12x
12x y 18
12x
y 7 1
%H 100 100 5.55%
12x y 1 18
12x 1
17
10
Mass of hydrogen (H 2 ) in the sample 2g
18
( After combustion all the hydrogen in the hydrocarbon will be present in the water formed)
10
2
% of hydrogen 18 100 5.55%
20
19. [A-q] [B-r] [C-s] [D-p]
CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
2 4 CH CH CHCH (cis trans)
H SO
(A) 3 3
(Q)
(B)
(C) SN 2 of I by OH will give overall meso product. (S)
(D)
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 3 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
20.(D) More reactive halogen can displace less reactive halogen from their salts.
0.35 32
0.35
21.(C) Mass of sulphur 32g % sulphur 233.43 100 18.5%
233.43 0.2595
22.(4) A =
Number of alcohol = Number of moles of Ac 2 O consumed = 4
23.(B) Cl2 H2O
HOCl HCl
24.(D) Mass of nitrogen 200 103 14g % of nitrogen
200 1 103 14 100 46.67%
6
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 4 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
25.(2) 2 products are formed during reaction
26.(B) Total electron pairs around central atom are 5 hence its structure is trigonal bipyramidal.
27.(A) Silk is a natural product made from the fibres found in the cocoon of the mulberry silk worm. It is
actually made up of long strands of protein sericin and fibrosin which are polymers of amino acids.
28.(3) Attacking positions are indicated by arrow sign.
29.(D) Na 2S2O3 2HCl
2NaCl SO2 S H2O ;
Br2 SO2 H2O
2HBr SO3
30.(B) Vulcanised rubber contains linear chains having some branches.
31.(3)
Number of alcohol is number of moles of anhydride consumed 3
32.(D) These are polar covalent compounds like ICl, ClF3 etc.
33.(C) CH3 CH 2 NH 2 has only one functional group, have it can’t undergo self-polymerisation.
m m
34.(5) Number of hydroxyl group n
42
Where m Molcular mass of product
M Molcular mass of unknown compound
390 180
n 5
42
35.(D) Oxygen cannot form more than three bonds.
36.(B) Polyethyene, PVC and polycryalonitrie (orlon) are addition polymers.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 5 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
37.(9)
All the above shown nine resonating structures are different.
38.(D) Sulphur is used for vulcanization of rubber.
39.(C)
(I) gives immediately turbidity by lucas reagent and (II) does not give turbidity appreciably.
40.(4)
2 60
41.(B) 2NaClO3 2NaCl 3O 2 ; w NaClO3 106.5 177.5g
3 24
42.(A) Volume of oxygen produced is equal to area under the curve.
43.(B) BaO 2 2HClO
BaCl2 12 O 2 H 2O
44.(C) The compound gives positive test with Na metal, 2, 4-DNP and it gives single product with
O3 .
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 6 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
45.(3) 2HCHO 3HCOOH CO 2
46.(B) The compound C30 H 60 O has one degree of unsaturation since it gives negative test with Br2 / H 2 O,
2, 4 - DNP and Na metal it must be an epoxide.
47.(6)
48.(ABCD)
Deacon’s process : 4HCl O2
CuCl
723K
2 2Cl2 2H2O
It is also prepared by electrolysis of chloride salt solutions.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 7 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
49.(A) Ziegler-Natta polymerization is an example of addition polymerization.
50.(D) All three (A, B & C) correctly represents addition polymerization process.
51.(A) SO 2 can decolourises characteristic colouration of these solution while CO 2 can’t decolourise.
52.(B) Bleaching action of SO 2 is due to its reducing nature. It reduces colouring matter and reduced colouring
matter will restore its colour by oxidation from air.
53.(D) Na 2SO3 S
Na 2S2O3
54.(13)
55.(AC)
By the condition of the question I & IV both compounds do not give iodoform test and I and II both give
similar test.
56.(60.56%)
75 85 95 100
Overall % yield 60.56
100 100 100 1
57.(C) A = F; B = I; BA 3 IF3 ; KHA y KHF2 ; H x A HF ; H x B HI
2NaF H 2SO 4 Na 2SO 4 2HF
2NaI 2H 2SO 4 Na 2SO 4 SO 2 I 2 2H 2O
58.(C) F2 do not disproportionate in water or alkali. F2 H 2O 2HF O 2
59.(C)
60.(AB)
Methylaniline is the only base in the mixture and benzoic acid is a much stronger acid than phenol.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 8 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
61.(174)
Mass of P increases by 42 unit per OH group, molar mass of P is 90 g/mol.
62.(B)
63.(ABC)
Protein, nylon-6, 6 and nylon-6 are polyamide polymers since all of them have amide linkage.
64.(22) Compound ‘Y’ is n-pantane
Compounds ‘Y’ can form total 28 dichloro products and out of these 22 are optically active.
Compound ‘X’ No reaction at room temperature.
Lucas reagent
C5H8O ppt, X CH 4 ; X n-pentane
Ammoniacal Excess of H 2 /Pt
AgNO 3 CH MgBr
3 HI excess
Above information suggest than X has a terminal triple bond and it contain primary —OH group.
Ag(NH )
H — C C — CH 2 — CH 2 — CH 2OH
3 2
Ag — C C — CH 2CH 2CH 2OH
X
65.(ABC)
Gallium have very low melting point (303K) it exist in liquid form at or near normal room temperature.
Bromine and mercury are two well-known liquid substances.
66.(CD)
Since here two different substances polymerise, copolymerization is said to have occurred. Also since a
water molecule is lost in the process it is condensation polymerisation.
It involves branching by (C1 C6 ) glycosidic linkage.
67.(8)
68.(ABCD)
Species having unpaired electrons are paramagnetic.
O2 , O2 and S2 are paramagnetic on the basis of molecular orbital theory. In ClO 2 there is unpaired
electron in chlorine atom.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 9 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating for Your Success
69.(ACD)
Neoprene is –( CH 2 C CH CH 2 –)n
|
Cl
70.(3) Intermediate is 2, 3-dehydroanisole and H-bonded to benzene ring are vinylic H.
*71.(BD)
Inter halogen compounds are all covalent molecules and are diamagnetic in nature. Their physical
properties are intermediate between those of constituents halogens except that their melting point and
boiling point are little higher than excepted. In general, inter halogen compounds are more reactive than
halogens except fluorine.
*72.(AC)
(A) nHOOC (CH2 )4 COOH nH2 N (CH2 )6 NH2
Nylon 6,6 H2O
(B) Cellulose triacetate is semi synthetic polymer
(C)
(D) Sucrose is disaccharide
73.(7) b, c, e, h, i, j, k
*74.(ABC)
Comproportionation is reverse of disproportionation
75.(ABCD)
Peptide linkage is an amide linkage capable to form H-bond (hydrophilic in nature) and connects
polypeptide chain in protein through H-bond.
VMC | Chemistry | Solutions 10 ALPS-2206| JEE-2022
You might also like
- Dps Diary 21-22apsDocument130 pagesDps Diary 21-22apsAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - SolutionDocument16 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperDocument11 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperDocument9 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-10) - PaperDocument19 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-10) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-8) - SolutionDocument10 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-8) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - PaperDocument14 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-6) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-9) - SolutionDocument10 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-9) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-5) - PaperDocument16 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-5) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperDocument16 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperDocument15 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-2) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-7) - SolutionDocument12 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-7) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-5) - SolutionDocument12 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-5) - SolutionAnanmay Chauhan100% (1)
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - SolutionDocument12 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-4) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - SolutionDocument11 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - SolutionAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric R Atios & Identities: JEE-MathematicsDocument15 pagesTrigonometric R Atios & Identities: JEE-MathematicsAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperDocument15 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)