Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medication Potential Use in COVID19 Delirium
Medication Potential Use in COVID19 Delirium
Uploaded by
Abdualaziz AlmalkiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medication Potential Use in COVID19 Delirium
Medication Potential Use in COVID19 Delirium
Uploaded by
Abdualaziz AlmalkiCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacological Recommendations for Delirium with COVID-19
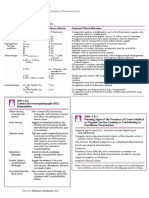
TABLE 1. Pharmacologic Agents With Potential Utility in Treating Delirium in COVID-19
Medication Mechanism Advantages Disadvantages
Melatonin Circadian rhythm regulation; Minimal side effects PO formulation only; caution in the
anti-inflammatory immunosuppressed
Alpha-2 agonists
Dexmedetomidine Decreases NE release both Available in IV; can be rapidly Use restricted to ICU setting;
centrally and peripherally titrated; no respiratory sedation; expensive; occasional shortages;
analgesic properties hypotension, bradycardia
Clonidine Decreases NE release both PO and patch formulation; short Hypotension and bradycardia acutely,
centrally and peripherally time to peak concentration and rebound tachycardia and
short half-life hypertension if not tapered
Guanfacine Decreases NE release Less systemic effects than clonidine Only PO formulation; longer to peak
centrally . peripherally effect
Antipsychotic agents
Aripiprazole D2 partial agonist Shortens QTc; less likely to cause PO only; akathisia; long half-life
EPS requires extensive washout period
Chlorpromazine H1, a1, muscarinic antagonist. PO, IM, IV formulations, very Hypotension; anticholinergic side
5HT2A antagonism . D2 sedating, wide dose range, less effects; greater QT prolongation
antagonism EPS
Haloperidol D2 antagonist PO, IV, IM formulations; most High risk of EPS with PO, reports of
evidence in hospital delirium TdP with IV formulation
literature
Olanzapine D2, H1, a1, and muscarinic PO (tab and dissolvable) and IM IM formulation cannot be combined
antagonist formulations; sedating; fast- with benzodiazepines; anticholinergic
acting side effects
Quetiapine H1, a1, a2, 5HT2A, D1, and D2 Wide dose range; different PO only; onset of action up to 1 h;
antagonist. 5HT1A partial receptors targeted at different hypotension at doses . 100 mg
agonist. doses; minimal EPS
Risperidone D2 and 5HT2A antagonist Tab and dissolvable available; High risk of EPS
minimally anticholinergic
Ziprasidone D2, 5HT2A, H1 antagonist, 5HT1A IM formulation available Greater QT prolongation
partial agonist
Trazodone 5HT2A antagonist, a1antagonist Preferred hypnotic for geriatric PO formulation only; onset of action
patients; low EPS and QTc risk up to 1 h
Valproic acid Unclear; regulated GABA/ PO and IV formulations; weight- CYP450 inhibitor; contraindicated in
glutamate, D, NE, and 5HT. based loading possible; useful in patients with pancreatic or hepatic
sodium channel blocker comorbid seizure d/o, TBI, and failure
ETOH withdrawal
Dopamine agonists
Amantadine Indirect D agonist and NMDA- Useful for abulia, akinetic mutism, PO formulation only in United States;
receptor antagonist and catatonia when lorazepam/ contraindicated in end-stage renal
ECT contraindicated disease; lowers seizure threshold; can
worsen delirium and psychosis
Methylphenidate D and NE reuptake inhibition PO (IR and ER) and patch Increases heart rate and blood
formulations; short-half life for pressure; may worsen appetite; can
ease of titration; useful for abulia worsen delirium and psychosis
Lorazepam Enhances the activity of GABA at PO, IV and IM formulations; rapid Respiratory suppression, especially
the GABA-A receptor onset; very sedating; can decrease when combined with opioids; can
neuroleptic requirement worsen delirium
We review and summarize medications commonly used in the treatment of delirium. Attention is given to the advantages and disadvantages
of medications specific to their use in patients with COVID-19.
5HT = 5-hyrdoxytryptamine; D = dopamine; ECT = electroconvulsive therapy; EPS = extrapyramidal symptoms; ER = extended release; ETOH =
ethanol; GABA = gamma aminobutyric acid; H = histamine; ICU = intensive care unit; IM = intramuscular; IR = immediate release; IV = intravenous;
NE = norepinephrine; NMDA = N-methyl-D-aspartate; PO = per oral; QTc = corrected QT interval; TBI = traumatic brain injury; TdP = torsades de pointes.
Melatonin
More recent data also suggest specific utility in COVID-
There is significant interest in using melatonin and 19, perhaps due to its sleep-regulating, immunomodula-
melatonin-receptor agonists in delirium management.20,21 tory, and neuroprotective factors.20–22 In theory, the
588 www.psychosomaticsjournal.org Psychosomatics 61:6, November/December 2020
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Memory Loss FullDocument252 pagesMemory Loss FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- FULLTEXT01Document134 pagesFULLTEXT01Abdualaziz Almalki100% (1)
- Role Play 5Document5 pagesRole Play 5Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 4Document5 pagesRole Play 4Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument3 pagesAntipsychoticsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 6Document5 pagesRole Play 6Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Addiction SummeryDocument2 pagesAddiction SummeryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Dudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Document9 pagesDudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalDocument22 pagesKnowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- E300630 FullDocument8 pagesE300630 FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteDocument9 pagesPsychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsDocument4 pagesFact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Neurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Document12 pagesNeurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryDocument13 pages4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- CYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsDocument6 pagesCYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamDocument2 pagesAbnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 9-12 Qs Test PreparationDocument1 page9-12 Qs Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4-8 Answer Test PreparationDocument1 page4-8 Answer Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- DrugofchoiceDocument16 pagesDrugofchoiceAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Document2 pagesPsychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Llr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsDocument2 pagesLlr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- ACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Document5 pagesACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- PrognosisDocument7 pagesPrognosisAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Child Development 2020-2021Document40 pagesChild Development 2020-2021Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Important TablesDocument22 pagesKaplan Important TablesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Validation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestDocument10 pagesValidation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Lesions Location in Brain and AffectsDocument1 pageLesions Location in Brain and AffectsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Red FlagsDocument1 pageDevelopmental Red FlagsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Piaget's Developmental StagesDocument1 pageSummary of Piaget's Developmental StagesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Missed Doses of Long Acting InjectionsDocument5 pagesMissed Doses of Long Acting InjectionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet