Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Global Delay Development
Uploaded by
Riani DwiastutiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Global Delay Development
Uploaded by
Riani DwiastutiCopyright:
Available Formats
GLOBAL DELAY DEVELOPMENT
Saat anak dewasa, refleks primitif yang awalnya dikembangkan untuk membantu kelangsungan
hidup, menjadi terintegrasi ke dalam gerakan yang lebih halus. Anak-anak cenderung
memperoleh keterampilan ini secara teratur dan dalam kelompok usia tertentu. Pola perolehan
keterampilan ini, sering disebut sebagai "Typical Development", digunakan untuk memantau
kemajuan perkembangan anak. Dalam beberapa kasus, keterlambatan perolehan ‘milestones’ ini
dapat mengindikasikan keterlambatan perkembangan. Namun, harus diingat bahwa rentang
waktu di mana perolehan keterampilan ini masih dianggap 'khas', luas, dan beberapa anak
mungkin melewatkan satu pencapaian sama sekali (contoh merangkak).
Principles of Typical Development
Cranial to Caudal
Proximal to Distal
Flexion to Extension
Asymmetry - Symmetry – Asymmetry
Gross to Fine; Simple to Complex
Global Patterns in 3 Planes (Frontal, Sagittal, Transverse)
Asymmetry and Flexion Period.
[4]
Physiological Flexion. 2 Month Milestone:
Mass Movements. Makes Smoother Movements with
Slight intentioned movements of the head in Arms and Legs.
prone and supine.
In supine there are large movements of the
upper limbs.
In prone activities are limited to the lifting and
turning of the head to breathe.
Slight increase of extensor muscles control
head / neck.
The baby is more alert, begins to respond to the
environment.
MORO Primitive Reflex Active.
ATNR Present.
Gesture - Communication: Smile (6-12
weeks) [3] [2]
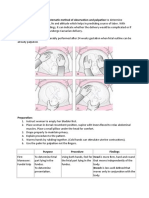
SUPINE PRONE
Functional Achievement: Functional Achievement:
Slight movements in rotation of the head + Raises head less than 45°, pushes
lateral flexion of the trunk when trying to move the floor with the fists trying to lift
the head, gesture, stare at the mother. head against gravity and against
Posture: the resistance of spinal and hip
Head Position: that remain in flexion.
Weightbearing:
Hyperextended and rotated. (Asymmetry) On cheek, hands, forearms and
Trunk Position: upper chest.
Posture:
Very active in frontal plane. Head Position:
Upper Limbs:
Baby uses the extension of
Remain in Abduction and External upper trunk from an
Rotation. (Absorbed by Gravity) asymmetrical position to raise
Hands in Ulnar Deviation although in 2 the head, uses upward gaze (eye
months. Thumb is not included any more in extension) to assist the spinal
the hand. extension. Eyes play a
Pelvic Girdle: significant role in postural
control.
Pelvis in Anteversion. Upper Limbs:
Lower Limbs:
Shoulders in protraction, arms
Remain more asymmetric and extension close to the body, elbows behind
lying in the plain, not very active. shoulders and in flexion.
Trunk Position:
Lumbar flexion and asymmetric
in the frontal plane. (concave or
convex)
Pelvic Girdle:
Pelvis in Anteversion.
Lower Limbs:
Hip Joints in Flexion,
Abduction and External
Rotation.
You might also like
- Typical Development: Global Milestones for Infants 0-5 MonthsDocument4 pagesTypical Development: Global Milestones for Infants 0-5 MonthsRiani DwiastutiNo ratings yet
- AniMotion, Energy of the four animals: Fitness & Power WorkoutFrom EverandAniMotion, Energy of the four animals: Fitness & Power WorkoutNo ratings yet
- Motor Development (1year)-1Document31 pagesMotor Development (1year)-1Ashwini BajajNo ratings yet
- Radio Taiso Routine 2: More Exercises for Health & Vitality: Radio Taiso, #2From EverandRadio Taiso Routine 2: More Exercises for Health & Vitality: Radio Taiso, #2No ratings yet
- Tahapan Perkembangan Motor Skill (0-12 BLN) Fisiopedi Ums: Ridho Budi Rahmad, S.FisDocument46 pagesTahapan Perkembangan Motor Skill (0-12 BLN) Fisiopedi Ums: Ridho Budi Rahmad, S.FisAtikah HanunNo ratings yet
- Ontogenesis Postural Claudia LorcaDocument12 pagesOntogenesis Postural Claudia LorcaDiego Alejandro100% (2)
- Lab Module 4 - ReflexesDocument3 pagesLab Module 4 - Reflexeskxb22bNo ratings yet
- CP HemiplegiaDocument3 pagesCP HemiplegiaNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pilates Stretch Class FormatDocument3 pagesPilates Stretch Class FormatDieu Thu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument3 pagesNeurology Notesdlynne23No ratings yet
- Facilitation Techniques in Prone PositionDocument37 pagesFacilitation Techniques in Prone PositionMartha FrankNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument49 pagesPARTOGRAPHMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool ChildrenDocument7 pagesManual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool Childrendeasy100% (1)
- Leopold's Maneuvers: Identifying Fetal PositionDocument11 pagesLeopold's Maneuvers: Identifying Fetal PositionErcel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Rolling & Crawling/CreepingDocument17 pagesRolling & Crawling/CreepingChris EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Neonate Motor DevelopmentDocument12 pagesNeonate Motor DevelopmentFatenNo ratings yet
- normaldevelopmentnew-140904124938-phpapp02Document104 pagesnormaldevelopmentnew-140904124938-phpapp02Hello VintunnaraNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver StudentsDocument40 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver StudentsCarlo GacadNo ratings yet
- Primitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesDocument5 pagesPrimitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesAmirul Zakri IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cervical Scapula ProgramDocument6 pagesCervical Scapula Programmansigupta88No ratings yet
- Reflex Testing (Week 11) ReviewerDocument8 pagesReflex Testing (Week 11) ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- LeopoldDocument2 pagesLeopoldiura echinNo ratings yet
- TRX Mobility WorkoutDocument4 pagesTRX Mobility WorkoutShaoYenNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 PT 201 - Upright Motor Control, Infant, Toddler and ChildrenDocument50 pagesTopic 14 PT 201 - Upright Motor Control, Infant, Toddler and ChildrenEJ GejonNo ratings yet
- Final FW ProjectDocument11 pagesFinal FW Projectapi-412489828No ratings yet
- Name: Mary Chielo Dorondon BSN2ADocument3 pagesName: Mary Chielo Dorondon BSN2AMARY CHIELO DORONDONNo ratings yet
- 12 Minute Run Fitness AssessmentDocument32 pages12 Minute Run Fitness AssessmentMaricrisNo ratings yet
- Thera Neuromotor Approaches NirDocument10 pagesThera Neuromotor Approaches NirCeline Kyla MalloNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Labour: DR - Wasan Nori MBCHB FicogDocument18 pagesMechanism of Labour: DR - Wasan Nori MBCHB FicogROY ALPHYNo ratings yet
- Motordelays EnglishDocument23 pagesMotordelays Englishicevie00No ratings yet
- ReflexDocument6 pagesReflexsiti syafiqahNo ratings yet
- How To Perform LeopoldDocument5 pagesHow To Perform LeopoldChared Lumba100% (3)
- NCM 107 Rle 2Document2 pagesNCM 107 Rle 2Patricia RamosNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Stabilization Hip StrengtheningDocument8 pagesPelvic Stabilization Hip StrengtheningEva Nurjannah100% (1)
- Pelvic Stabilization Hip StrengtheningDocument8 pagesPelvic Stabilization Hip StrengtheningKarlosNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LaborDocument7 pagesMechanism of LaborAjay DNo ratings yet
- LeopoldsDocument2 pagesLeopoldsMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Tasnim Albarakati 1 CP Spastic Diplegia-Impaired BalanceDocument6 pagesTasnim Albarakati 1 CP Spastic Diplegia-Impaired BalanceTasneem AlshareefNo ratings yet
- Dry Land Workout PlanDocument2 pagesDry Land Workout PlanMaryvan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Developmental Clinical ObservationsDocument2 pagesNeuro-Developmental Clinical ObservationsAmitesh NarayanNo ratings yet
- Diisfunção Sensorial Na BocaDocument4 pagesDiisfunção Sensorial Na BocaGislaine Barbosa BezerraNo ratings yet
- Biokare Posture PresentationDocument30 pagesBiokare Posture PresentationMarius Andre VisserNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reflex TestingDocument4 pagesDevelopmental Reflex TestingJica GulaNo ratings yet
- Yoga AsanasDocument174 pagesYoga AsanasMax NovaxNo ratings yet
- Primitive Reflexes 240130 213501Document11 pagesPrimitive Reflexes 240130 213501Atharva PawarNo ratings yet
- Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist TablesDocument4 pagesPrimitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist TablesAmy EmylaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Reflexes in BabiesDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord Reflexes in BabiesLouis ImperatoNo ratings yet
- Flores Juliane Average Newborn ActivityDocument4 pagesFlores Juliane Average Newborn ActivityJuliane FloresNo ratings yet
- Warm Up SessionDocument7 pagesWarm Up SessionDIABLA FFNo ratings yet
- Hot Topics 2 MonthsDocument2 pagesHot Topics 2 MonthsPathways AwarenessNo ratings yet
- GMB FF Bap PDFDocument1 pageGMB FF Bap PDFcavaleramaxNo ratings yet
- Movement ScreeningDocument12 pagesMovement ScreeningCláudio Milane De Oliveira100% (1)
- Leopolds and FetalDocument7 pagesLeopolds and Fetaltyche100% (1)
- Green Light ReflexDocument4 pagesGreen Light ReflexEmilia LarraondoNo ratings yet
- pathfit-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagespathfit-WPS OfficeEphrem MedallaNo ratings yet
- Weighted Hoop Guide Eng PDFDocument10 pagesWeighted Hoop Guide Eng PDFEli LazarevskaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Children and Women in SportsDocument9 pagesChapter-2 Children and Women in SportsLakshaya YadavNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Milestones-1Document1 pagePediatrics Milestones-1Lana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Movement Features GuideDocument10 pagesPhysical Education Movement Features GuideJelly BeanNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDocument7 pagesLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22Document4 pagesNeuroanatomy 2nd Year Topical Past Papers 2005-22HussnainNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument118 pagesHeart FailureAli Murtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- What Is General Adaptation SyndromeDocument3 pagesWhat Is General Adaptation SyndromeCARLOS, Ryan CholoNo ratings yet
- UNIT VI Neurobiology of BehaviourDocument18 pagesUNIT VI Neurobiology of BehaviourShatakshi MishraNo ratings yet
- Richard McCarty - Stress, Health, and Behavior-The Guilford Press (2023)Document355 pagesRichard McCarty - Stress, Health, and Behavior-The Guilford Press (2023)Mustafa ŞEKERNo ratings yet
- 3 Principles of Cell MetabolismDocument53 pages3 Principles of Cell MetabolismKristine Claire TarucNo ratings yet
- ZOOL 322 Lecture 1 2019-2020Document10 pagesZOOL 322 Lecture 1 2019-2020Timothy MutaiNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Worksheet On TranspirationDocument15 pagesYear 12 Worksheet On TranspirationlilianNo ratings yet
- Inh NetworkDocument12 pagesInh Networkalbercarpio89No ratings yet
- Diagnostics: Rare Causes of Arterial Hypertension and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms-A Case-Based ReviewDocument16 pagesDiagnostics: Rare Causes of Arterial Hypertension and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms-A Case-Based ReviewBreeze ChloeNo ratings yet
- Inscopix NVista Product BrochureDocument8 pagesInscopix NVista Product BrochureSEO NeuroscienceNo ratings yet
- 7.07mitosis QuizDocument1 page7.07mitosis QuizYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Electrofisiologia Cardiaca Guia Viasual 2 PDFDocument82 pagesElectrofisiologia Cardiaca Guia Viasual 2 PDFMiguel LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Bio150-80 Syllabus-Instructor Addendum-2016 Fall PDFDocument5 pagesBio150-80 Syllabus-Instructor Addendum-2016 Fall PDFFatmata BanguraNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care Planjohncarlo ramosNo ratings yet
- BioPsy 5 - SensationsDocument13 pagesBioPsy 5 - SensationsTim AroscoNo ratings yet
- Els (Characteristics of Life)Document4 pagesEls (Characteristics of Life)cdcheijdnekjdNo ratings yet
- Walker - Argulus: Ecology of A Fish PestDocument192 pagesWalker - Argulus: Ecology of A Fish Pestsadida anindyaNo ratings yet
- Body Type AyurvedaDocument4 pagesBody Type AyurvedaE. G. PrimusNo ratings yet
- Anemia of Abnormal Iron MetabolismDocument17 pagesAnemia of Abnormal Iron MetabolismJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- BAPNE Method and Neurorehabilitation in Patients with Severe Brain InjuryDocument15 pagesBAPNE Method and Neurorehabilitation in Patients with Severe Brain InjuryTCaller trueNo ratings yet
- MS4013: Introduction to BiomaterialsDocument33 pagesMS4013: Introduction to BiomaterialsMichael KerenzaNo ratings yet
- Tehnologija Vitamina I Hormona: 1. Što Su Vitamini?Document11 pagesTehnologija Vitamina I Hormona: 1. Što Su Vitamini?J.No ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Type III and Type IV HypersensitivityDocument36 pagesHypersensitivity Reactions: Type III and Type IV HypersensitivityDil NavabNo ratings yet
- Glenoid Fossa RemodellingDocument59 pagesGlenoid Fossa RemodellingArnabNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder. NatureDocument20 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder. NatureMANUEL ALCIDES PUERTA BARRETO100% (1)
- Clinical Osteopathic Approaches To Emotions: - Kenneth Lossing DO - AAO Convocation 2016Document57 pagesClinical Osteopathic Approaches To Emotions: - Kenneth Lossing DO - AAO Convocation 2016Diana SchlittlerNo ratings yet
- Monólogo Lady MacbethDocument3 pagesMonólogo Lady MacbethJessica OcampoNo ratings yet
- Effect of stimulation site on superficial peroneal nerve conduction studiesDocument7 pagesEffect of stimulation site on superficial peroneal nerve conduction studiesfulgencio garciaNo ratings yet