Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fact Sheet
Uploaded by
Soraya Al-obinay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesThis document discusses visual impairments and identifying learners with difficulty seeing. It defines various visual impairments like legal blindness, tunnel vision, and functional blindness. Learners with visual impairments may have delays in cognition, language, motor skills and social development. Various conditions that cause visual impairments are described like amblyopia, astigmatism, and strabismus. Teachers should watch for indicators of visual problems like eye appearance, behavior signs, problems with eye movements and refractive errors. The Snellen chart and Vision Services Severity Rating Scale are tools used to evaluate visual acuity.
Original Description:
Original Title
FACT SHEET
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses visual impairments and identifying learners with difficulty seeing. It defines various visual impairments like legal blindness, tunnel vision, and functional blindness. Learners with visual impairments may have delays in cognition, language, motor skills and social development. Various conditions that cause visual impairments are described like amblyopia, astigmatism, and strabismus. Teachers should watch for indicators of visual problems like eye appearance, behavior signs, problems with eye movements and refractive errors. The Snellen chart and Vision Services Severity Rating Scale are tools used to evaluate visual acuity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesFact Sheet
Uploaded by
Soraya Al-obinayThis document discusses visual impairments and identifying learners with difficulty seeing. It defines various visual impairments like legal blindness, tunnel vision, and functional blindness. Learners with visual impairments may have delays in cognition, language, motor skills and social development. Various conditions that cause visual impairments are described like amblyopia, astigmatism, and strabismus. Teachers should watch for indicators of visual problems like eye appearance, behavior signs, problems with eye movements and refractive errors. The Snellen chart and Vision Services Severity Rating Scale are tools used to evaluate visual acuity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Chapter 6 (Part 1): Learners with difficulty Seeing
Reporter: AL-OBINAY, SORAYA D.
Terms that are often associated with having difficulty seeing:
• VISUAL ACUITY- refers to the ability to distinguish forms or discriminate among detail.
• LEGAL BLINDNESS- refers to having a visual acuity of 20/200 or less in the better eye with the use of a corrective lens.
• PARTIALLY SIGHTED- Individuals are those whose visual acuity in the better eye after correction falls between 20/70 and 20/200.
• TUNNEL VISION- condition of having a perception of viewing the world through a narrow tube
.
TOTAL BLINDNESS- refers to receiving no useful information through the sense of vision.
FUNCTIONAL BLINDNESS- means having so little vision that one learns primarily through the tactile and auditory senses.
Characteristics of Learners with Difficulty Seeing:
Cognition and Language Motor Development and Mobility Social Adjustment and Interaction
Learners with difficulty seeing usually perform Blindness may also result to delays and deficits Children with visual impairment may engage
poorly compared to those with normal vision in in motor development. For instance, with in less play, which could affect their social
terms of cognitive task that require babies, purposeful movements involved skills development. Due to their lack of vision,
comprehension or relating various kinds of reading for objects that they could see. it is difficult for them to see and respond.
information.
Visual Impairment
• Is a wide range term of visual problems. It is a concept that includes categories such as total blindness as well as mild or severe cases.
• Visual impairments are prone to develop stereotypic behavior, such as repetitive body movements, including body rocking, eye pressing and
poking, hand flapping, and head weaving.
Types and Causes of Visual Impairment:
CONDITION Definition and Cause Remarks and Implication
AMBLYOPIA Caused by strabismus, unequal refractive Close work mar result in eye fatigue, loss of
errors, or opacity of the lens or cornea place, or poor concentration; seating should
favor the functional eye.
ASTIGMATISM Blurred vision caused by irregularities in the Loss of accommodation when objects are
cornea that produce images on retina not in brought close to the face; avoid long periods of
equal focus (refractive error) reading; child may complain of headaches and
fluctuating vision
CORTICAL VISUAL IMPAIRMENT Caused by damage of the visual cortex or optic Visual functioning may fluctuate depending on
(CVI) nerve; causes include anoxia, head injury and lighting conditions and attention; visual images
infections. should be simple and presented singly
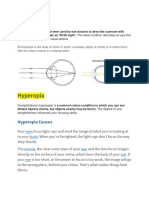
HYPEROPIA (Farsightedness) Caused by a shorter than normal eye that Loss of accommodation when objects are
prevents light rays from converging on the brought close to the face; avoid long periods of
retina. reading,
MUSCULAR DEGENERATION Central are of retina gradually deteriorates, Tasks such as reading, and writing are difficult;
causing loss of clear vision in the center of the prescribed low-vision aid or closed- circuit TV;
visual field; common in older adults but fairly provide good illumination; avoid glare
rare in children
MYOPIA (Nearsightedness) Distant objects are blurred but near objects are Encourage child to wear prescribed glasses or
clear. Caused by an elongated eye that focuses contact lens.
images in front of the retina.
NYSTAGMUS Rapid, involuntary, back- and- forth movement Close tasks for extended period can lead to
of the eyes, which makes it difficult to focus on fatigue; some children turn or tilt head to
objects. obtain the best focus; do not criticize this
STRABISMUS Inability to focus on the same object with both Classroom seating should favor student’s
eyes because of an inward or outward deviation stronger eye.
of one or both eyes; caused by muscle
imbalance
Identifying Learners with Difficulty Seeing
There are a number of indicators of visual impairment that parents and teachers need to be aware of. These indicators may be observed from the
student’s eye appearance and complaints when using eyes during desk work. There are also behavioral signs such as deficits in eye teaming abilities,
eye- hand coordination, visual form perception, as well as refractive status (e.g., nearsightedness, farsightedness, and focus problems) indicating
visual impairment (Bhargava, n.d; Elmwood Visual Resource Centre, n.d.).
In terms of eye appearance: In terms of behavioral signs: Other behavioral indicators: Problems with refractive
status:
Turning of one eye in or • Turning of head as one reads Deficits in eye- hand Diminished
out at any time. across the page. coordination abilities comprehension
Reddening of eyes or lids. • Frequently losing place during Inability to keep Mispronouncing similar
Excessive tearing of eyes. reading. alignment. words
Having encrusted eyelids. • Having short attention span in Using the other hand Excessive blinking when
reading or copying. as “spacer” and the doing desk work
Students complain about. • Frequent omission of words. other to keep place on Closing one eye
Headache Behavior signs that could indicate the page. Making errors when
Itching of eyes dysfunction in eye binocularity includes: Repeatedly getting copying notes
Feeling dizzy Having double vision confused with left- Requesting to move
Blurring vision Repeating/Omitting of letters right direction. closer
Frequent squinting
Extreme tilting of head Failure to recognize Constant rubbing of eyes
Consistent gross postural same words Easily being fatigued
deviations Whispering to oneself when doing visual
for reinforcement activities
while reading silently.
“Drawing with
fingers” in order to
decide likes and
differences.
The Snellen Chart
-Used to test visual acuity. It was developed by a Dutch ophthalmologist in 1962. It consists of rows of letter, with each row
corresponding to the distance that a normally sighted person could discriminate letter (Heward, 2017).
The Vision Services Severity Rating Scale (VSSRS)
-It was developed by the Michigan Department of Education (2013) in order to assist the Teacher Consultant for the visually Impaired (TCVI) in
making recommendations for services to students who are blind.
You might also like
- Group 3Document25 pagesGroup 3Kimberly DuitesNo ratings yet
- Chapter.6 - Bea&dhel Report.Document69 pagesChapter.6 - Bea&dhel Report.CUDAL, APRIL JOY G.No ratings yet
- Educ6 - Chapter 6,7 & 8 FactsheetDocument13 pagesEduc6 - Chapter 6,7 & 8 FactsheetNiña Edrienne JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Types and Identification of Visual Impairments in LearnersDocument13 pagesTypes and Identification of Visual Impairments in LearnersLaleth Mendoza OjalesNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Sir RobertDocument17 pagesMODULE 6 Sir RobertManilyn DominguezNo ratings yet
- SPED PresentationDocument132 pagesSPED PresentationZariyah IslaNo ratings yet
- Educ-3 Chapter-3.1 TypesCharacteristicsIdentificationDocument34 pagesEduc-3 Chapter-3.1 TypesCharacteristicsIdentificationMYLE MANAYONNo ratings yet
- Educ Chapter 6 Lesson - CompressDocument19 pagesEduc Chapter 6 Lesson - CompressMhay Pale BongtayonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5Document10 pagesLecture Notes 5Christine Joy DelaCruz CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument5 pagesVisual ImpairmentRowly Pearl Iradiel NedicNo ratings yet
- Blue and Grey Modern Simple SchoNotable Guestsol Trifold Brochure PDFDocument36 pagesBlue and Grey Modern Simple SchoNotable Guestsol Trifold Brochure PDFAshley Jade DomalantaNo ratings yet
- Refractive Errors ExplainedDocument2 pagesRefractive Errors ExplainedIdesarie SilladorNo ratings yet
- FIXXXXXXDocument35 pagesFIXXXXXXRani Dwi HapsariNo ratings yet
- Presbyopia: What Is Presbyopia? What Is Refraction?Document2 pagesPresbyopia: What Is Presbyopia? What Is Refraction?UlfNo ratings yet
- Vision CardsDocument1 pageVision CardssghdgudfshjcsNo ratings yet
- FarsightednessDocument2 pagesFarsightednesst_tvoNo ratings yet
- Vision and Hearing Disorders FinalsDocument7 pagesVision and Hearing Disorders FinalsMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- Notes50 - PEDIATRIC VISION OR HEARING DISORDERSDocument9 pagesNotes50 - PEDIATRIC VISION OR HEARING DISORDERSTJ ZamarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 50 Vision and HearingDocument7 pagesChapter 50 Vision and HearingAlmer OstreaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Vision ExamDocument5 pagesComprehensive Vision Exameva.bensonNo ratings yet
- Module 37 Nur 145Document38 pagesModule 37 Nur 145Marga WreatheNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorder in Children and AdolescentsDocument13 pagesEye Disorder in Children and AdolescentsChandrasekhar MotipalleNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 7 Difficulties in SeeingDocument4 pagesProf Ed 7 Difficulties in Seeingyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Sore EyesDocument2 pagesSore EyesYobiraiton RedNo ratings yet
- VisionDocument8 pagesVisionapi-367611011No ratings yet
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeDocument4 pagesCarlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeDemo TeachingNo ratings yet
- Eye Symptoms GuideDocument10 pagesEye Symptoms Guidemelannie napisaNo ratings yet
- Visual Impairments,: Including BlindnessDocument17 pagesVisual Impairments,: Including BlindnessJoahna Bulaong SacdalanNo ratings yet
- SPED Lesson Plan GuideDocument7 pagesSPED Lesson Plan GuideAngelica Dongque AgunodNo ratings yet
- Amblyopia, Astigmatism & HyperopiaDocument1 pageAmblyopia, Astigmatism & HyperopiaBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Learners With Additional Needs: ModuleDocument10 pagesLearners With Additional Needs: ModuleMeldhin Aspera Billones - CoEdNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument15 pagesRefractive ErrorsMubasher 783No ratings yet
- Learners With Difficulty SeeingDocument35 pagesLearners With Difficulty SeeingORTILANO, Lyka Mae F.No ratings yet
- Different Vision ProblemsDocument2 pagesDifferent Vision ProblemsKissy Neri Mae EscabusaNo ratings yet
- VISUAL PERCEPTION DISORDER HandoutsDocument3 pagesVISUAL PERCEPTION DISORDER HandoutsJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Refractiveerror 200625072525Document18 pagesRefractiveerror 200625072525Akshay BadoreNo ratings yet
- Visual Deficits In Children: Causes and TreatmentsDocument27 pagesVisual Deficits In Children: Causes and TreatmentsSue ZhangNo ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument47 pagesVisual Impairmentcj romagosa67% (3)
- Visual Impairments Fact SheetDocument4 pagesVisual Impairments Fact SheetNational Dissemination Center for Children with DisabilitiesNo ratings yet
- Eye Variations - Docx 5.2Document15 pagesEye Variations - Docx 5.2cryptojanus25No ratings yet
- Errors of RefractionDocument25 pagesErrors of RefractionCharlene Ann San AndresNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY - Docx2.oDocument27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY - Docx2.oK GhatageNo ratings yet
- Visually Impaired With Blindness (Modified)Document18 pagesVisually Impaired With Blindness (Modified)Edmaly Abonacion GaldoNo ratings yet
- Eye DisorderDocument8 pagesEye DisorderNURSETOPNOTCHERNo ratings yet
- Visual screening in childrenDocument5 pagesVisual screening in childrenSafitriNo ratings yet
- NCLEX SimpleNursing PediatricsDocument120 pagesNCLEX SimpleNursing PediatricsOlrac Agairdam100% (4)
- Topic 5 Lecture 3 - Visual & Hearing ImpairmentDocument87 pagesTopic 5 Lecture 3 - Visual & Hearing ImpairmentLogavani ThamilmaranNo ratings yet
- What are refractive errorsDocument20 pagesWhat are refractive errorsEduardo Niepes Jr.No ratings yet
- Children With Visual ImpairmentDocument35 pagesChildren With Visual Impairmentkobby klausNo ratings yet
- Impairement NeedsDocument1 pageImpairement NeedsChrisNo ratings yet
- Visual Impairment and Autism GuideDocument1 pageVisual Impairment and Autism GuideChrisNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Eye Disorders: 2.4.1 Refractive Errors (Myopia, Hyperopia, Presbyopia, Astigmatism)Document2 pages2.4 Eye Disorders: 2.4.1 Refractive Errors (Myopia, Hyperopia, Presbyopia, Astigmatism)Amry Irsyada YusufNo ratings yet
- Visual ImpairmentDocument29 pagesVisual ImpairmentHazel BayerNo ratings yet
- Mental Health ConditionDocument2 pagesMental Health ConditionChrisNo ratings yet
- Eye DefectsDocument3 pagesEye DefectsAbdul HannanNo ratings yet
- D.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesD.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjecthashimNo ratings yet
- Name Module No: - 8 - Module Title: Learners With Difficulty Seeing Course and Section: BSED-3A - Major: Social ScienceDocument6 pagesName Module No: - 8 - Module Title: Learners With Difficulty Seeing Course and Section: BSED-3A - Major: Social ScienceChristine Joy MarcelNo ratings yet
- Reffractive ErrorsDocument13 pagesReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuNo ratings yet
- Student Handbook Orthoptics.Document13 pagesStudent Handbook Orthoptics.Nur AminNo ratings yet
- Far-Sightedness, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFar-Sightedness, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- C4 ProteinsDocument34 pagesC4 ProteinsSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- C6 Nucleic AcidsDocument57 pagesC6 Nucleic AcidsSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Structure Determines Optical PropertiesDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates: Structure Determines Optical PropertiesSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- AL-OBINAY - DecodingDocument1 pageAL-OBINAY - DecodingSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- BIO 007 (Cell Mol For Educ) Syllabus 2022Document3 pagesBIO 007 (Cell Mol For Educ) Syllabus 2022Soraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Michigan For TVIDocument14 pagesMichigan For TVISoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- 5 Midterm 1 Nucleus and Cell CycleDocument119 pages5 Midterm 1 Nucleus and Cell CycleSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Assessment: Prepared By: Fernando R. Sequete JR., LPT, MsciedDocument38 pagesBasic Concepts in Assessment: Prepared By: Fernando R. Sequete JR., LPT, MsciedAsmeenah Casanguan MohammadNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction Lab ResultsDocument3 pagesDNA Extraction Lab ResultsSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Shan - Consumer Evaluations of Processed Meat Products Reformulated To Be HealthierDocument8 pagesShan - Consumer Evaluations of Processed Meat Products Reformulated To Be HealthierMarcos RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Working at Height PolicyDocument7 pagesWorking at Height PolicyAniekan AkpaidiokNo ratings yet
- Manual de Reparacion TXV75Document16 pagesManual de Reparacion TXV75Ovh MaquinariasNo ratings yet
- Why encouraging entrepreneurship to boost economies is flawedDocument9 pagesWhy encouraging entrepreneurship to boost economies is flawedLaureanoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDenis Martinez100% (1)
- Thermal Mass Flow Meter PrincipleDocument2 pagesThermal Mass Flow Meter Principleyousaf_zai_khan81995No ratings yet
- WHO Guidelines For Drinking Water: Parameters Standard Limits As Per WHO Guidelines (MG/L)Document3 pagesWHO Guidelines For Drinking Water: Parameters Standard Limits As Per WHO Guidelines (MG/L)114912No ratings yet
- Survitec Mooring Ropes BrochureDocument20 pagesSurvitec Mooring Ropes Brochurearifsarwo_wNo ratings yet
- End Time ProphecyDocument16 pagesEnd Time ProphecyMarven JabianNo ratings yet
- Brachytherapy GYN Applicator CatalogDocument64 pagesBrachytherapy GYN Applicator CatalogJuan Lombardero100% (1)
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocument5 pagesCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- Worksheet#3Document3 pagesWorksheet#3Richard GrayNo ratings yet
- Vegetarianism A Salvation Issue?Document7 pagesVegetarianism A Salvation Issue?ChetiweKapilaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Isolation Work PermitDocument2 pagesElectrical Isolation Work PermitGreg GenoveNo ratings yet
- Practical 5.17 Protein MaterialsDocument2 pagesPractical 5.17 Protein MaterialsdeeyamullaNo ratings yet
- Laser LightDocument27 pagesLaser Lightdcool3784No ratings yet
- Devsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops BasicsDocument3 pagesDevsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops Basicshelo nameNo ratings yet
- SG Salary Guide 2021-22Document66 pagesSG Salary Guide 2021-22Gilbert ChiaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Aso Security TrainingDocument60 pages2017 Aso Security TrainingTanzila SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Problems of Elder AbuseDocument13 pagesProblems of Elder AbuseNeha Jayaraman100% (3)
- ResiboDocument1 pageResiboAlex RespicioNo ratings yet
- Pds - Sunshades Instrument CoverDocument2 pagesPds - Sunshades Instrument CoverAntonio LantiguaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Nurse - Patient Communication in Saudi Arabia: An Integrative ReviewDocument10 pagesBarriers To Nurse - Patient Communication in Saudi Arabia: An Integrative Reviewmark3dasaNo ratings yet
- SGLGB Form 1 Barangay ProfileDocument3 pagesSGLGB Form 1 Barangay ProfileHELEN CASIANONo ratings yet
- Amidoxime Vanadium U Da Çekiyor SıkıntısıDocument7 pagesAmidoxime Vanadium U Da Çekiyor SıkıntısıMelike AltayNo ratings yet
- Altivar 71 - ATV71H037M3Document13 pagesAltivar 71 - ATV71H037M3Mite TodorovNo ratings yet
- Klubermatic Lubricant DispensersDocument13 pagesKlubermatic Lubricant Dispenserstatankise100% (1)
- Nurs478 Healthcaredelivery Audrey GohDocument12 pagesNurs478 Healthcaredelivery Audrey Gohapi-316372858No ratings yet
- MWRC Policies & Procedures Manual 2020Document10 pagesMWRC Policies & Procedures Manual 2020Emma RyersonNo ratings yet
- Letter From Springfield Mayor Sarno To License Commission Re: Late Night Hours.Document12 pagesLetter From Springfield Mayor Sarno To License Commission Re: Late Night Hours.Patrick JohnsonNo ratings yet