Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crypto
Uploaded by
ROHAN MAGARCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crypto
Uploaded by
ROHAN MAGARCopyright:
Available Formats
https://www.techtarget.
com/searchsecurity/definition/cryptography
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cryptography-and-its-types/
https://www.encryptionconsulting.com/education-center/what-is-cryptography/
https://www.edureka.co/blog/what-is-cryptography/
https://www.edureka.co/blog/steganography-tutorial
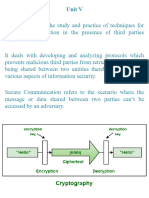
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method of protecting information and communications through the use of codes,
so that only those for whom the information is intended can read and process it.
In computer science, cryptography refers to secure information and
communication techniques derived from mathematical concepts and a set
of rule-based calculations called algorithms, to transform messages in
ways that are hard to decipher. These deterministic algorithms are used for
cryptographic key generation, digital signing, verification to protect data
privacy, web browsing on the internet and confidential communications
such as credit card transactions and email.
Cryptography techniques
Cryptography is closely related to the disciplines of cryptology and cryptanalysis. It includes
techniques such as microdots, merging words with images and other ways to hide information in
storage or transit. However, in today's computer-centric world, cryptography is most often
associated with scrambling plaintext (ordinary text, sometimes referred to as cleartext) into
ciphertext (a process called encryption), then back again (known as decryption). Individuals who
practice this field are known as cryptographers.
Modern cryptography concerns itself with the following four objectives:
1. Confidentiality. The information cannot be understood by anyone for
whom it was unintended.
2. Integrity.The information cannot be altered in storage or transit between
sender and intended receiver without the alteration being detected.
3. Non-repudiation. The creator/sender of the information cannot deny at a
later stage their intentions in the creation or transmission of the
information.
4. Authentication. The sender and receiver can confirm each other's identity
and the origin/destination of the information.
Procedures and protocols that meet some or all of the above criteria are known as
cryptosystems. Cryptosystems are often thought to refer only to mathematical
procedures and computer programs; however, they also include the regulation of
human behavior, such as choosing hard-to-guess passwords, logging off unused
systems and not discussing sensitive procedures with outsiders.
You might also like
- Blockchain: Unlocking the Power of Blockchain: Your Essential Handbook for the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandBlockchain: Unlocking the Power of Blockchain: Your Essential Handbook for the Digital RevolutionNo ratings yet
- What Is Cryptography - Definition FromDocument2 pagesWhat Is Cryptography - Definition FromGirgio Moratti CullenNo ratings yet
- Cryptography1 113832Document17 pagesCryptography1 113832Priyanka NaikNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 - CryptographyDocument12 pagesLESSON 6 - CryptographyKIBENo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its TypesDocument2 pagesCryptography and Its TypesSaloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cryptography (Module 1) NotesDocument21 pagesCryptography (Module 1) NotesColossus GamingNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument8 pagesCryptographySadia Islam ShefaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1SutikshanNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its Types and Stenography and Digital SignDocument8 pagesCryptography and Its Types and Stenography and Digital SignSaloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cryptography TiK KAMISDocument156 pagesCryptography TiK KAMISAnonymous lIxrz9No ratings yet
- A Technique Cryptography PDFDocument4 pagesA Technique Cryptography PDFThet Hmue Hay ThiNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its TypesDocument1 pageCryptography and Its TypesSweta BarnwalNo ratings yet
- A Seminar ReportDocument39 pagesA Seminar ReportDivyaswaroop Srivastav100% (1)
- Topic: Cryptology: History of CryptographyDocument24 pagesTopic: Cryptology: History of CryptographyAziz Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Basics To CryptographyDocument18 pagesBasics To CryptographyEvehn KadusaleNo ratings yet
- Cryptography in ITDocument48 pagesCryptography in ITFego OgwaraNo ratings yet
- CNS Unit 1 NewDocument115 pagesCNS Unit 1 Newinaamulh66No ratings yet
- Unit 307Document25 pagesUnit 307n9166254105No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument5 pagesCryptographyShivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation Cryptography: BY Mothishkumar.S Sharath Abilash Ak Mohamed Ali Jinna A Muralidaran BeeceDocument6 pagesPaper Presentation Cryptography: BY Mothishkumar.S Sharath Abilash Ak Mohamed Ali Jinna A Muralidaran BeeceMohamed jinnaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: A.Irfana Cse-First Year Deepthi Cse-First YearDocument14 pagesSubmitted By: A.Irfana Cse-First Year Deepthi Cse-First YearNiranjan ChandarrajNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument3 pagesCryptographyaran valeroNo ratings yet
- Final RSA DocumentationDocument125 pagesFinal RSA DocumentationKishore PinnintiNo ratings yet
- CNS Notes CS8792 CNS Notes CS8792Document17 pagesCNS Notes CS8792 CNS Notes CS8792KARVENDHAN SNo ratings yet
- Khairunnisa Binti MD ZahirDocument8 pagesKhairunnisa Binti MD ZahirMichałNo ratings yet
- Paper of CryptographyDocument3 pagesPaper of CryptographySuinNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesLovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital Signaturegoyal_No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument19 pagesCryptographyKanimozhiNo ratings yet
- 2021KUCP1001Document5 pages2021KUCP1001Shivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument158 pagesCryptography and Network SecuritySivarajan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- 3630-Article Text-6635-1-10-20180104Document5 pages3630-Article Text-6635-1-10-20180104Anonymous uGow9p7y8No ratings yet
- CRYPTOGRAPHYDocument7 pagesCRYPTOGRAPHYsaeed BarzaghlyNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument99 pagesUnit VYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Gulshan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument14 pagesCryptographyhoneysharmathehackerNo ratings yet
- Assignment Title:: Proposed Cryptographic ProtocolsDocument13 pagesAssignment Title:: Proposed Cryptographic Protocolsco1ossusNo ratings yet
- A Seminar ReportDocument39 pagesA Seminar ReportNutan BhorNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Revamp The Data Security Using Cryptographic TechniquesDocument5 pagesAn Approach To Revamp The Data Security Using Cryptographic TechniquesjyoshnaNo ratings yet
- Atm MINI PROJECT EDITEDDocument32 pagesAtm MINI PROJECT EDITEDshreyashupare.sits.entcNo ratings yet
- Network Security and CryptographyDocument8 pagesNetwork Security and CryptographyKPNo ratings yet
- Cns-Unit I IntroductionDocument39 pagesCns-Unit I IntroductionRamyaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography Full ReportDocument9 pagesCryptography Full ReportSushant SharmaNo ratings yet
- 453 NS Tutorial 1Document5 pages453 NS Tutorial 1SHAMIMUL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Its TypesDocument2 pagesCryptography and Its TypesDev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Criptografia Why We Need ItDocument8 pagesCriptografia Why We Need Itwelington garciaNo ratings yet
- Context of Cryptography: ConfidentialityDocument13 pagesContext of Cryptography: ConfidentialityAnay ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument18 pagesCryptography and Network Securitykarishma vaidyaNo ratings yet
- 27-Chitra G (1) - Desai1, Manisha B. Patil and B. W. GawaliDocument16 pages27-Chitra G (1) - Desai1, Manisha B. Patil and B. W. GawaliPriyanka AbhangNo ratings yet
- Hackers Are Commonly Thought of As The Bad Guys, The People Who Make Your Computer Go As SlowDocument7 pagesHackers Are Commonly Thought of As The Bad Guys, The People Who Make Your Computer Go As Slowutsav_8710No ratings yet
- Network Security & Cryptography: Litam Quest-2K7Document13 pagesNetwork Security & Cryptography: Litam Quest-2K7api-19799369No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument20 pagesCryptographySrilekha RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance and SecurityDocument12 pagesInformation Assurance and SecurityJewel MeniaNo ratings yet
- T. E. Audit Course ReportDocument17 pagesT. E. Audit Course ReportHarshalNo ratings yet
- CrytographyDocument21 pagesCrytographySonia AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Basics of Encryption andDocument4 pagesBasics of Encryption andShruti JainNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Name: T Sampathkumar Name: Sudeep Year: III/IV CSE, Year: III/IV CSE, E-MailDocument9 pagesCryptography: Name: T Sampathkumar Name: Sudeep Year: III/IV CSE, Year: III/IV CSE, E-MailAnimesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Data Security Enhancement Using Number SystemDocument31 pagesData Security Enhancement Using Number Systemmarshal robertNo ratings yet
- Networks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinesDocument6 pagesNetworks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinessufiyanamujawarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and NSDocument68 pagesCryptography and NSWONDYE DESTANo ratings yet
- USER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFDocument20 pagesUSER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFBosi GashiNo ratings yet
- 19 Dark PPT TemplateDocument15 pages19 Dark PPT TemplateKurt W. DelleraNo ratings yet
- Institutional Group Agencies For EducationDocument22 pagesInstitutional Group Agencies For EducationGlory Aroma100% (1)
- Subject OrientationDocument15 pagesSubject OrientationPearl OgayonNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 - Unit 1 Increase and Decrease PatternDocument7 pagesGrade 3 - Unit 1 Increase and Decrease PatternKyo ToeyNo ratings yet
- Coaxial Cable Attenuation ChartDocument6 pagesCoaxial Cable Attenuation ChartNam PhamNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument205 pagesReadingHiền ThuNo ratings yet
- Day6 7Document11 pagesDay6 7Abu Al-FarouqNo ratings yet
- Lightning Arrester Lightningcontroller MC 125-B/Npe: Operation and Fields of ApplicationDocument2 pagesLightning Arrester Lightningcontroller MC 125-B/Npe: Operation and Fields of ApplicationAnas BasarahNo ratings yet
- Registration ListDocument5 pagesRegistration ListGnanesh Shetty BharathipuraNo ratings yet
- (20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataDocument9 pages(20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataSunidhi VermaNo ratings yet
- SP-Chapter 14 PresentationDocument83 pagesSP-Chapter 14 PresentationLoiDa FloresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryDocument17 pagesLesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryNAPHTALI WILLIAMS GONo ratings yet
- Applying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDocument5 pagesApplying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDianitta MaciasNo ratings yet
- Alfa Week 1Document13 pagesAlfa Week 1Cikgu kannaNo ratings yet
- 4.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting A Wired and Wireless LAN InstructionsDocument5 pages4.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting A Wired and Wireless LAN InstructionsAhmadHijaziNo ratings yet
- Very Narrow Aisle MTC Turret TruckDocument6 pagesVery Narrow Aisle MTC Turret Truckfirdaushalam96No ratings yet
- ADocument54 pagesActyvteNo ratings yet
- FMEA Minus The PainDocument7 pagesFMEA Minus The PainMUNISNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EthicsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To EthicsMarielle Guerra04No ratings yet
- Noise and DB Calculations: Smart EDGE ECE Review SpecialistDocument2 pagesNoise and DB Calculations: Smart EDGE ECE Review SpecialistLM BecinaNo ratings yet
- NAV SOLVING PROBLEM 3 (1-20) .PpsDocument37 pagesNAV SOLVING PROBLEM 3 (1-20) .Ppsmsk5in100% (1)
- Hele Grade4Document56 pagesHele Grade4Chard Gonzales100% (3)
- Safety Bulletin 09 - Emergency Escape Breathing Device - Product RecallDocument2 pagesSafety Bulletin 09 - Emergency Escape Breathing Device - Product RecallMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Module 3 Rep in PlantsDocument26 pagesUnit 1 Module 3 Rep in Plantstamesh jodhanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536Document4 pagesSafety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536BanyuNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Metal Properties and Destructive TestingDocument46 pagesModule 6 Metal Properties and Destructive TestingMiki Jaksic100% (6)
- Song Book Inner PagesDocument140 pagesSong Book Inner PagesEliazer PetsonNo ratings yet
- Lacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20Document1 pageLacey Robertson Resume 3-6-20api-410771996No ratings yet
- The Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Co-Op Approach in Improving Visual Motor Integration Skills in Children With Learning DisabilityIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesFrom EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowFrom EverandThe Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowNo ratings yet
- Branding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsFrom EverandBranding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (32)
- Social Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeFrom EverandSocial Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet Scams and Fraud: Credit Card Theft, Work-At-Home Scams and Lottery ScamsFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet Scams and Fraud: Credit Card Theft, Work-At-Home Scams and Lottery ScamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Tor Darknet Bundle (5 in 1): Master the Art of InvisibilityFrom EverandTor Darknet Bundle (5 in 1): Master the Art of InvisibilityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Practical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTFrom EverandPractical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTNo ratings yet
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowFrom EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (388)
- Facing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessFrom EverandFacing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Evaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- More Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingFrom EverandMore Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (24)
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellFrom EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldFrom EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineFrom EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineNo ratings yet
- The Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldFrom EverandThe Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (104)
- React.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)From EverandReact.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueFrom EverandThe YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (33)