0% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views4 pagesGrade 8 Lesson Plan
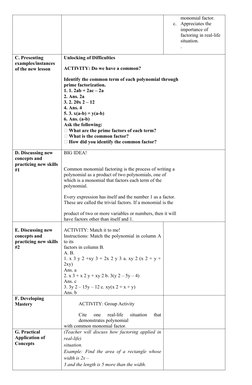
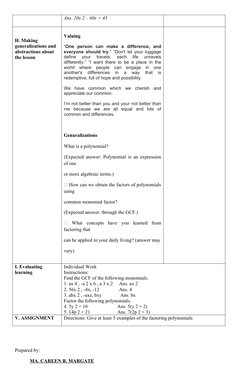
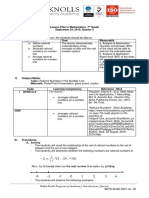
The document provides a detailed lesson plan for teaching systems of linear equations in two variables using graphing in Grade 8 math. It includes objectives, content, learning resources, procedures, and activities. The lesson plan aims to teach students to (1) identify whether a system has a solution or not, (2) solve systems by graphing, and (3) collaborate with peers. Sample activities include identifying common monomial factors in polynomials, matching polynomials to their factors, citing real-life examples, and discussing how factoring can be applied.
Uploaded by
Armand LicandaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views4 pagesGrade 8 Lesson Plan
The document provides a detailed lesson plan for teaching systems of linear equations in two variables using graphing in Grade 8 math. It includes objectives, content, learning resources, procedures, and activities. The lesson plan aims to teach students to (1) identify whether a system has a solution or not, (2) solve systems by graphing, and (3) collaborate with peers. Sample activities include identifying common monomial factors in polynomials, matching polynomials to their factors, citing real-life examples, and discussing how factoring can be applied.
Uploaded by
Armand LicandaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd