Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Climate Variability Web
Uploaded by
PRIYANKA SHIL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesClimate Variability Web
Uploaded by
PRIYANKA SHILCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Climate Variability
Weather can be highly variable on a daily, weekly, or even yearly
basis – one day it might be sunny and the next it’s
snowing. Climate, on the other hand, doesn’t change day-to-day
because it is based on longer time scales and averages. However,
climate is variable as well.
Climate variability is the way aspects of climate (such as
temperature and precipitation) differ from an average. Climate
variability occurs due to natural and sometimes periodic changes in
the circulation of the air and ocean, volcanic eruptions, and other
factors.
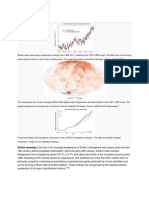
For example, the average daily
maximum temperature in July,
averaged over 30 years from
1988 through 2017, in Boulder,
Colorado was 87.7° F (30.9° C).
However, in some years, the
month of July has been warmer
than the average. In other years,
the month of July is cooler than
the average.
Worldwide, the average global temperature is rarely exactly the
same from year to year. One year might be cooler than the year
before, even though the long-term trend shows increasing
temperature over time due to climate change. There are many
reasons for climate variability, including natural fluctuations like the
ENSO (El Nino Southern Oscillation). Scientists are currently
researching the impact that climate change has on variability.
Climate variability is often natural, however climate change is
causing an increase in the probability of many extreme weather
events, and those events contribute to climate variability.
Extreme events are specific weather events that depart from the
average in some significant. For example, days that exceed 100° F
(37.8° C) are called extreme heat events in many locations. While
it's possible that any given summer day might be over 100° F,
climate warming is causing the frequency of extreme heat days to
increase. In other words, the probability of a summer day with
extreme hear is becoming higher as climate warms.
Climatologists are concerned with more than temperature changes
as climate changes. Extreme precipitation events are also
important. Precipitation patterns that deviate significantly from the
average can result in droughts or floods. The flooding in Texas in
August 2017 caused by Hurricane Harvey is a recent and
devastating example of an extreme precipitation event.
Flooding in Port Arthur, Texas during Hurricane Harvey in August 2017.
Credit: U.S. Air National Guard photo by Staff Sgt. Daniel J. Martinez.
Hurricane Harvey contributed to climate variability in 2017. The
average August precipitation pattern for the thirty-year period from
1981 to 2010 for the United States was very different from the
August precipitation recorded in 2017, as shown on the maps
below. Note that although the color-coding of the maps shows a
maximum value of 8 inches of precipitation, many areas around
Houston received more than 30 inches (76 cm) of rainfall as a result
of Hurricane Harvey... and one weather station recorded more
than 60 inches (1.5 meters) of rain. Hurricane Harvey was definitely
an extreme event!
You might also like
- King Conan - Crown of Iron (P. 14)Document167 pagesKing Conan - Crown of Iron (P. 14)Rafa Eyesman100% (2)
- General Sir Arthur Cotton R E His Life and Work Lady Hope 1000598480Document656 pagesGeneral Sir Arthur Cotton R E His Life and Work Lady Hope 1000598480rajk_onlineNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics Quarter 2 - Module 5 EducationDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics Quarter 2 - Module 5 EducationMhecy Sagandilan100% (4)
- M.V AFFLATUS & WEN YUE Collision Report by China MSADocument23 pagesM.V AFFLATUS & WEN YUE Collision Report by China MSAJasper AngNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument2 pagesWeather and Climateapi-257978541100% (2)
- Interactive Textbook Section One What Is Climate 17 1 1 1Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook Section One What Is Climate 17 1 1 1api-249771030100% (1)
- List of Directors - Indian CompaniesDocument209 pagesList of Directors - Indian CompaniesAditya Sharma100% (1)
- Lesson Plan About Global WarmingDocument4 pagesLesson Plan About Global WarmingToni Gutz50% (4)
- 10 Climate ChangeDocument81 pages10 Climate ChangeJurenz Ibhan BonsolNo ratings yet
- The Weather of the Future: Heat Waves, Extreme Storms, and Other Scenes from a Climate-Changed PlanetFrom EverandThe Weather of the Future: Heat Waves, Extreme Storms, and Other Scenes from a Climate-Changed PlanetNo ratings yet
- Impact of Climate Change's in PakistanDocument12 pagesImpact of Climate Change's in Pakistanhary1186% (7)
- Climate Change (Reviewer)Document12 pagesClimate Change (Reviewer)Keziah PepitoNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Extreme WeatherDocument20 pagesClimate Change and Extreme WeatherKelas Empat DuaaarNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument8 pagesClimate Change: Frequently Asked QuestionsAdriano Racho MelendresNo ratings yet
- Climate Variability and Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate Variability and Climate ChangeIvan AvramovNo ratings yet
- Meteorology-Chapter 17-Climate DynamicsDocument6 pagesMeteorology-Chapter 17-Climate DynamicsMorales, Jerome R.No ratings yet
- Kuliah 11Document20 pagesKuliah 11Kelas Empat DuaaarNo ratings yet
- Weather and ClimateDocument1 pageWeather and ClimateInmNmNo ratings yet
- Educ 207Document7 pagesEduc 207Donnalyn DomdomNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate ChangeJeramie Sarita SumaotNo ratings yet
- 2 ND NumberDocument6 pages2 ND NumberManish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming SummaryDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming SummaryWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- The Climate and The Weather - El Niño y La NiñaDocument4 pagesThe Climate and The Weather - El Niño y La NiñajorgebwongNo ratings yet
- English Lesson 1 Model TextDocument2 pagesEnglish Lesson 1 Model TextnoormustafaibupotoNo ratings yet
- Angl ADocument5 pagesAngl Akirikuja23No ratings yet
- Publications: Geophysical Research LettersDocument9 pagesPublications: Geophysical Research LettersCRISTIAN RIOS VANEGASNo ratings yet
- Climate Is The Usual Weather of A PlaceDocument2 pagesClimate Is The Usual Weather of A Placeteddy tavaresNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Presentation On Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesMultimedia Presentation On Climate ChangeJulia ToewsNo ratings yet
- Climatology AssignmentDocument6 pagesClimatology AssignmentPrince SiawNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate Changefgabor251No ratings yet
- NASA - What's The Difference Between Weather and Climate?Document3 pagesNASA - What's The Difference Between Weather and Climate?Jane Krisha LadricaNo ratings yet
- Climate Vs WeatherDocument2 pagesClimate Vs Weathermio maoNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Climate in The PhilippinesDocument3 pages4 Types of Climate in The PhilippinesDA CVRCNo ratings yet
- The Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesThe Climate Changexanza alexandraNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of Climate ChangeDocument7 pagesCauses and Effects of Climate ChangeYisrael LopezNo ratings yet
- Climate (Students)Document17 pagesClimate (Students)Wamm MadlaNo ratings yet
- 10.3 - The Effect of Ice On Water SystemsDocument3 pages10.3 - The Effect of Ice On Water Systemsapi-251806635No ratings yet
- Overview: Weather, Global Warming, and Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesOverview: Weather, Global Warming, and Climate ChangeAkira EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Weather & Climate: 7TH GradeDocument37 pagesWeather & Climate: 7TH Gradejem100% (1)
- What Is Climate Change?Document2 pagesWhat Is Climate Change?Aiswarya ViswanathNo ratings yet
- Environmental RegionsDocument63 pagesEnvironmental RegionsChalise SupremeNo ratings yet
- Environment ManagementDocument11 pagesEnvironment ManagementbillatonyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesEffects of Climate ChangeJan100% (1)
- Final NatscieclimateDocument3 pagesFinal NatscieclimateFebe NievaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument1 pageClimate Changekylecars123456789No ratings yet
- Climate and WeatherDocument10 pagesClimate and WeatherLKP GhNo ratings yet
- Climate Change-LPDocument3 pagesClimate Change-LPErica O. PagurayanNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate Changesrushti hulyaladNo ratings yet
- Definition of Climate ChangeDocument14 pagesDefinition of Climate ChangeMari GovinNo ratings yet
- Name: Dewi Anggraeni NIM: 161411007 Class: 1A - D3 Teknik KimiaDocument3 pagesName: Dewi Anggraeni NIM: 161411007 Class: 1A - D3 Teknik KimiaFebrian Rifkhi FahrizalNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Final Draft ScienceDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Final Draft Scienceapi-679545134No ratings yet
- Climate Change: BluralphaxDocument7 pagesClimate Change: BluralphaxJulia ToewsNo ratings yet
- The World Climate Refers To The LongDocument2 pagesThe World Climate Refers To The LongTg GhabhyNo ratings yet
- CLIMATE FinalDocument35 pagesCLIMATE FinalDaisy MagalonaNo ratings yet
- Natural Climate and Interior DesignDocument7 pagesNatural Climate and Interior DesignDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - A Silent Threat To HumanityDocument8 pagesClimate Change - A Silent Threat To HumanityVignesh AukNo ratings yet
- ROVANTE KIRLEW - EDPM - Climate Change ArticleDocument2 pagesROVANTE KIRLEW - EDPM - Climate Change Articlerovante.kirlewNo ratings yet
- A Difference: Climate-WeatherDocument18 pagesA Difference: Climate-WeatherAwadhraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesClimate ChangeNevaeh SuarezNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument11 pagesClimate ChangeHayate TsukadaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Climate Change - Canada - CaDocument4 pagesCauses of Climate Change - Canada - CaChristine Jane Hansol ObutaNo ratings yet
- Lord Lawson Letter AttachmentDocument9 pagesLord Lawson Letter AttachmentAndyRowellNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal Warmingsam_m4bNo ratings yet
- Market Conduct Guidelines Philippine Life Insurance Association June 2009Document28 pagesMarket Conduct Guidelines Philippine Life Insurance Association June 2009Roselle Perez-BariuanNo ratings yet
- Cement SegmentDocument18 pagesCement Segmentmanish1895No ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and Conventions MCQs Financial Accounting MCQs Part 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesAccounting Concepts and Conventions MCQs Financial Accounting MCQs Part 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsKanika BajajNo ratings yet
- International Scientific Journal "Interpretation and Researches"Document5 pagesInternational Scientific Journal "Interpretation and Researches"wowedi333No ratings yet
- Case Study Little Enough or Too MuchDocument2 pagesCase Study Little Enough or Too MuchMalik GhunaibNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Information and Communication Technology 0417/12Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Information and Communication Technology 0417/12Ibrahim Abdi ChirwaNo ratings yet
- Ryterna Modul Architectural Challenge 2021Document11 pagesRyterna Modul Architectural Challenge 2021Pham QuangdieuNo ratings yet
- MilenaPopovaThesisWithCorrectionsAsSubmitted PDFDocument233 pagesMilenaPopovaThesisWithCorrectionsAsSubmitted PDFkakka kikkareNo ratings yet
- Professionals and Practitioners in Counselling: 1. Roles, Functions, and Competencies of CounselorsDocument70 pagesProfessionals and Practitioners in Counselling: 1. Roles, Functions, and Competencies of CounselorsShyra PapaNo ratings yet
- Oscar Cornelius Goodman v. Thomas F. Keohane, 663 F.2d 1044, 11th Cir. (1981)Document5 pagesOscar Cornelius Goodman v. Thomas F. Keohane, 663 F.2d 1044, 11th Cir. (1981)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 1702758529Document3 pages1702758529Szymon SłomskiNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: Irb04-43Document27 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: Irb04-43IRSNo ratings yet
- Greece and Britain Since 1945Document1 pageGreece and Britain Since 1945Νότης ΤουφεξήςNo ratings yet
- DMDocument12 pagesDMDelfin Mundala JrNo ratings yet
- Compiled LR PDFDocument13 pagesCompiled LR PDFFrh RzmnNo ratings yet
- People or PenguinsDocument6 pagesPeople or Penguinskblitz83No ratings yet
- Journal Jul Dec14 Art4Document16 pagesJournal Jul Dec14 Art4paromita bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument8 pagesResearch ProposalZahida AfzalNo ratings yet
- AcadinfoDocument10 pagesAcadinfoYumi LingNo ratings yet
- Athet Pyan Shinthaw PauluDocument6 pagesAthet Pyan Shinthaw PaulupurifysoulNo ratings yet
- CM - Mapeh 8 MusicDocument5 pagesCM - Mapeh 8 MusicAmirah HannahNo ratings yet
- CCP Motivation Letter 2022Document3 pagesCCP Motivation Letter 2022mohammed ahmed0% (1)
- Part II. Market Power: Chapter 4. Dynamic Aspects of Imperfect CompetitionDocument9 pagesPart II. Market Power: Chapter 4. Dynamic Aspects of Imperfect Competitionmoha dahmaniNo ratings yet
- Notes: 1 Yorùbá Riddles in Performance: Content and ContextDocument25 pagesNotes: 1 Yorùbá Riddles in Performance: Content and ContextDofono ty NísèwèNo ratings yet
- HSE RMO and Deliverables - Asset Life Cycle - Rev0Document4 pagesHSE RMO and Deliverables - Asset Life Cycle - Rev0Medical Service MPINo ratings yet