Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSS Os
Uploaded by
Sean Julius AnceroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CSS Os
Uploaded by
Sean Julius AnceroCopyright:
Available Formats
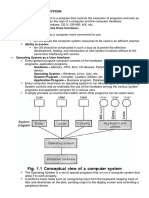
An operating system is software that supports and manages all the
programs and applications used by a computer or mobile device.
An operating system uses a graphic user interface (GUI), a
combination of graphics and text, that allows you to interact with
the computer or device.
Every computer or smart device needs at least one operating
system to run applications and perform tasks.
What are operating systems?
An operating system (OS) is a type of software interface between the user and the
device hardware. This software allows users to communicate with the device and
perform the desired functions. Operating systems use two components to
manage computer programs and applications:
The kernel is the core inner component that processes data at the
hardware level. It handles input-output management, memory and
process management.
The shell is the outer layer that manages the interaction between
the user and the OS. The shell communicates with the operating
system by either taking the input from the user or a shell script. A
shell script is a sequence of system commands that are stored in a
file.
Operating system functions
Basic functions of an operating system include:
Booting: An operating system manages the startup of a device.
Memory management: An operating system coordinates
computer applications and allocates space to different programs
installed in the computer.
Data security: An operating system protects your data from
cyberattacks.
Loading and execution: An operating system starts and executes a
program.
Drive/disk management: An operating system manages computer
drives and divides disks.
Device control: An operating system enables you to allow or block
access to devices.
User interface: This part of an operating system, also known as UI,
allows users to enter and receive information.
Process management: The operating system allocates space to
enable computer processes, such as storing and sharing
information.
Most operating systems come pre-installed on the device. However, users can
change their OS or upgrade to a newer version of the operating system for better
device performance.
Related: Learn About Being a CIO (Chief Information Officer)
Types of operating systems
Here are the different types of operating systems you need to know:
1. Batch OS
The batch operating system does not have a direct link with the computer. A
different system divides and allocates similar tasks into batches for easy
processing and faster response.
The batch operating system is appropriate for lengthy and time-consuming tasks.
To avoid slowing down a device, each user prepares their tasks offline and submits
them to an operator. The advantages and disadvantages of using a batch
operating system include:
2. Time-sharing or multitasking OS
The time-sharing operating system, also known as a multitasking OS, works by
allocating time to a particular task and switching between tasks frequently. Unlike
the batch system, the time-sharing system allows users to complete their work in
the system simultaneously.
It allows many users to be distributed across various terminals to minimize
response time. Potential advantages and disadvantages of time-sharing operating
systems include:
3. Distributed OS
This system is based on autonomous but interconnected computers
communicating with each other via communication lines or a shared network.
Each autonomous system has its own processor that may differ in size and
function.
A distributed operating system serves multiple applications and multiple users in
real time. The data processing function is then distributed across the processors.
Potential advantages and disadvantages of distributed operating systems are:
Distributed operating systems are used for tasks such as
telecommunication networks, airline reservation controls
and peer-to-peer networks.
4. Network OS
Network operating systems are installed on a server providing users with the
capability to manage data, user groups and applications. This operating system
enables users to access and share files and devices such as printers, security
software and other applications, mostly in a local area network. Potential
advantages and disadvantages of network operating systems are: Examples
of
network operating systems include Microsoft Windows, Linux and
macOS X.
5. Real-time OS
Real-time operating systems provide support to real-time systems that require
observance of strict time requirements. The response time between input,
processing and response is tiny, which is beneficial for processes that are highly
sensitive and need high precision.
These processes include operating missile systems, medical systems or air traffic
control systems, where delays may lead to loss of life and property. Real-time
operating systems may either be hard real-time systems or soft real-time systems.
Hard real-time systems are installed in applications with strict time constraints.
The system guarantees the completion of sensitive tasks on time. Hard real-time
does not have virtual memory. Soft real-time systems do not have equally rigid
time requirements. A critical task gets priority over other tasks. Potential
advantages and disadvantages of real-time operating systems include: Real-time
operating systems are used for tasks such as scientific
experiments, medical imaging, robotics and air traffic control
operations.
6. Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems run exclusively on small devices such as smartphones,
tablets and wearables. The system combines the features of a personal computer
with additional features useful for a handheld device.
Mobile operating systems start when a device is powered on to provide access to
installed applications. Mobile operating systems also manage wireless network
connectivity. Potential advantages and disadvantages of mobile operating systems
are:
Examples of mobile operating systems include Android OS, Apple
and Windows mobile OS.
Common operating systems
Here are the most common operating systems in use:
Microsoft Windows
Created by Microsoft, Microsoft Windows is one of the most popular proprietary
operating systems for computers in the world. Most personal computers come
preloaded with a version of Microsoft Windows. One downside of Windows is that
compatibility with mobile phones has been problematic.
Related: 21 Keyboard Shortcuts for Windows and Mac Devices
Apple iOS
Apple iOS from Apple is used on smartphones and tablets manufactured by the
same company. Users of this system have access to hundreds of applications. The
operating system offers strong encryption capabilities to control unauthorized
access to users' private data.
Google Android
Android from Google is the most popular operating system in the world. It's
mainly used on tablets and smartphones. It also runs on devices made by other
manufacturers. Users have access to numerous mobile applications available on
the Google Play Store.
Apple macOS
Developed by Apple, this proprietary operating system runs on the manufacturer's
personal computers and desktops. All Apple and Macintosh computers come
equipped with the latest version of macOS, previously known as OS X systems. The
ability to prevent bugs and fend off hackers make Apple operating systems
popular with their users.
Related: What Is an App? Types of Apps and Examples
Linux
Created by the Finnish programmer Linus Torvalds, Linux is today developed by
programmer collaborators across the world who submit tweaks to the central
kernel software. Linux is popular with programmers and corporate servers. It is
available for free online.
You might also like
- What Is OSDocument6 pagesWhat Is OSaqeelmhar7No ratings yet
- Lec1 Operating SystemDocument33 pagesLec1 Operating SystemMirna AttallahNo ratings yet
- What is an OS? Understanding Operating SystemsDocument5 pagesWhat is an OS? Understanding Operating SystemsSandhya KandikatlaNo ratings yet
- Unit 01-1Document33 pagesUnit 01-1subhankar fcNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows: Types of Operating SystemsDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Windows: Types of Operating SystemsAnonymous VHWPQErC3No ratings yet
- 3 - Software and MobileDocument19 pages3 - Software and Mobileali amjdNo ratings yet
- Pos Notes Unit 1Document13 pagesPos Notes Unit 1Gsp KhadyothNo ratings yet
- What Is An Operating System?: 1. Microsoft WindowsDocument10 pagesWhat Is An Operating System?: 1. Microsoft WindowsNova CadienteNo ratings yet
- Operating System by Ritik ParmarDocument12 pagesOperating System by Ritik Parmarshivam chouhanNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: HistoryDocument9 pagesOperating Systems: HistoryStoryKingNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Operating SystemDocument6 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Operating SystemMc John PobleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Overview: Figure 1-1. A Computer System Consists of Hardware, System Programs, and ApplicationDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Overview: Figure 1-1. A Computer System Consists of Hardware, System Programs, and Applicationyordanos yohannesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Introduction To Operating SystemDocument12 pagesUnit 3 Introduction To Operating SystemAnurag Goel100% (1)
- Operating System 1Document8 pagesOperating System 1mr hexNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemsDocument41 pagesSlide 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemscnajjembaNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Operating SystemDocument3 pagesUnit VI Operating SystemAvisek shresthaNo ratings yet
- OS NOTES COVERS KEY TOPICSDocument5 pagesOS NOTES COVERS KEY TOPICSUrja DhabardeNo ratings yet
- Types of Operating SystemDocument3 pagesTypes of Operating SystemAeafafNo ratings yet
- Essential OS Concepts in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesEssential OS Concepts in 40 CharactersMhiz Oluchukwu CynthiaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Hardware Software ConceptDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 2 Hardware Software ConceptSeema Sehdev100% (1)
- 3 Software and Mobile مختصررDocument6 pages3 Software and Mobile مختصررali amjdNo ratings yet
- Operating System - Complete Notes.Document12 pagesOperating System - Complete Notes.Arjun Bhargava100% (1)
- Operating System ExplainedDocument12 pagesOperating System Explainedking kholiNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Operating System: 1.convenienceDocument6 pagesObjectives of Operating System: 1.conveniencemaryamnasir72001No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument60 pagesOperating SystemAnoppNo ratings yet
- OsDocument18 pagesOsSonaliNo ratings yet
- Rtos Ie 1Document40 pagesRtos Ie 1gamecentre30No ratings yet
- Types of Operating System (OS)Document4 pagesTypes of Operating System (OS)SujataNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Operating SystemsDocument39 pagesLec 6 Operating Systemsomare paulNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument4 pagesOperating Systemfaizaman1461No ratings yet
- Basics of OSDocument22 pagesBasics of OSCherryNo ratings yet
- Operating System and InterfaceDocument8 pagesOperating System and InterfaceAzizNo ratings yet
- CPPC 10 Lecture Notes 1 Overview of Operating Systems PDFDocument13 pagesCPPC 10 Lecture Notes 1 Overview of Operating Systems PDFBlessious Joseph LandoyNo ratings yet
- CSC 321 Operating SystemDocument90 pagesCSC 321 Operating SystemKelly BrownNo ratings yet
- OS Chapter OneDocument5 pagesOS Chapter Onechalie tarekegnNo ratings yet
- The Operating SystemDocument9 pagesThe Operating SystemNorris Nana ChinjongNo ratings yet
- AOS 1-6 CompilationDocument86 pagesAOS 1-6 CompilationALEXANDRA JARANo ratings yet
- Os Guides 1-2Document24 pagesOs Guides 1-2x 4 dNo ratings yet
- 02 Types of Operating SystemDocument8 pages02 Types of Operating SystemZeshan AmirNo ratings yet
- LINUX: AN INTRO TO OPERATING SYSTEMSDocument19 pagesLINUX: AN INTRO TO OPERATING SYSTEMSKanchanaNo ratings yet
- What is computer software? Types of software explainedDocument9 pagesWhat is computer software? Types of software explainedAnuska ThapaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Notes by S DhallDocument124 pagesOperating Systems Notes by S DhallSALMAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Topic One Introduction To Os in GeneralDocument21 pagesTopic One Introduction To Os in Generallilmickey628No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemAlberth Rodillas AbayNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-1Document33 pagesOs Unit-1yoichiisagi09No ratings yet
- Notes On Operating System2013 FormattedDocument212 pagesNotes On Operating System2013 FormattedLaxmiPantNo ratings yet
- Notes of Operating SystemDocument47 pagesNotes of Operating SystemMr. Prempeh N. GuggisbergNo ratings yet
- CSC 112 - LECTURE 1 (OS)Document11 pagesCSC 112 - LECTURE 1 (OS)Abiodun JosephineNo ratings yet
- An Operating System MBADocument15 pagesAn Operating System MBAShwetaNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument12 pagesComputer SoftwareNaomi Nyambaso100% (1)
- Operating System HimanshuDocument12 pagesOperating System Himanshubtech2021.kamranNo ratings yet
- System SoftwareDocument21 pagesSystem SoftwareJessy RajasundarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Operating SystemDocument27 pagesChapter 02 Operating SystemEshan HirushkaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OSDocument17 pagesIntroduction To OSindu kaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Operating SystemDocument21 pagesIntroduction of Operating SystemVaishnavi RajputNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cyber Security 2Document52 pagesFundamentals of Cyber Security 2fayyadmuhammad45No ratings yet
- UNIT 07 - Operating SystemsDocument13 pagesUNIT 07 - Operating Systemsmubanga20000804No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument19 pagesOperating Systemmadalahussein02No ratings yet
- Computer Science Practical BookDocument27 pagesComputer Science Practical BookMuhammad AzamNo ratings yet
- TheNewYorkTimes Tuesday October 23 2012Document60 pagesTheNewYorkTimes Tuesday October 23 2012pardostNo ratings yet
- CRS Manual AndroidDocument47 pagesCRS Manual AndroidForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Campbell Tablet Hardness Tester DHT-150TPDocument2 pagesCampbell Tablet Hardness Tester DHT-150TPHanns65No ratings yet
- Health Care Service Application: Ooad Project ReportDocument21 pagesHealth Care Service Application: Ooad Project ReportSnehit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rugged Android Tablet PC with 10000mAh BatteryDocument2 pagesRugged Android Tablet PC with 10000mAh BatteryAhmar Hayat Khan0% (1)
- Input Output DIVISHADocument25 pagesInput Output DIVISHANifty GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Programming: Engr. Waqar AhmedDocument22 pagesMobile Programming: Engr. Waqar AhmedSajid AliNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Modicon M580Document152 pagesCatalogo Modicon M580Aleks ProañoNo ratings yet
- Comp 2Document2 pagesComp 2Altheae OweNo ratings yet
- ICT Revision PaperDocument3 pagesICT Revision PaperDr Anushka PereraNo ratings yet
- Ict101 Evolution of Media PDFDocument10 pagesIct101 Evolution of Media PDFCatherine Tausa100% (1)
- QuickQ 20 ManualDocument82 pagesQuickQ 20 ManualCryptoNo ratings yet
- Activity Template - Project PlanDocument55 pagesActivity Template - Project PlanTAgore Ravi TejaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Media 2007-2021Document9 pagesEvolution of Media 2007-2021Frenn AceitunaNo ratings yet
- Bookofrandomtables ModernDocument71 pagesBookofrandomtables ModernSir100% (2)
- Creative Pen Displays & Tablets For Drawing - HuionDocument3 pagesCreative Pen Displays & Tablets For Drawing - HuionkrishivNo ratings yet
- Apple Sole Source Draft 24 April 14Document4 pagesApple Sole Source Draft 24 April 14Julian A.No ratings yet
- Lumitester Smart: Instruction ManualDocument23 pagesLumitester Smart: Instruction ManualVerenice TorresNo ratings yet
- Group Fellows Mobile OS History Market SharesDocument12 pagesGroup Fellows Mobile OS History Market SharesDaniyal AliNo ratings yet
- Apple Vs MicrosoftDocument2 pagesApple Vs MicrosoftFlorin-Catalin GrecNo ratings yet
- Project PlanDocument55 pagesProject PlanAlfredo SbNo ratings yet
- Ltwbook 2013 PDFDocument709 pagesLtwbook 2013 PDFMalosisimo MaloNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Textbook Solutions - 19Document31 pagesComputer Science Textbook Solutions - 19acc-expertNo ratings yet
- BlackBerry Desktop Software Version 6.0.2 Release NotesDocument7 pagesBlackBerry Desktop Software Version 6.0.2 Release NotesBlackBerryRocks.comNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Android Based Attendance Management SystemDocument8 pagesDesign and Development of Android Based Attendance Management SystemBITTU RathoreNo ratings yet
- DP L8 Sprint 5.1 Speech Recognition AppDocument46 pagesDP L8 Sprint 5.1 Speech Recognition Appmohamed fathyNo ratings yet
- SAP Fiori On SAP Enterprise PortalDocument12 pagesSAP Fiori On SAP Enterprise Portalkaran.wizardNo ratings yet
- Launch Tablet SystemDocument60 pagesLaunch Tablet SystemNotionNo ratings yet
- GE-EL3 Finals ReviewerDocument90 pagesGE-EL3 Finals ReviewerAshley Villegas RuizNo ratings yet
- Tvl-Ict-Css: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Installing and Configuring Computer System (Iccs)Document27 pagesTvl-Ict-Css: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Installing and Configuring Computer System (Iccs)anderson villalunaNo ratings yet