Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motherboard Motherboard Is One of The Main Components of A Computer and Made of The Printed Circuit Board
Uploaded by
Krizia CabangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard Motherboard Is One of The Main Components of A Computer and Made of The Printed Circuit Board
Uploaded by
Krizia CabangCopyright:
Available Formats
MOTHERBOARD
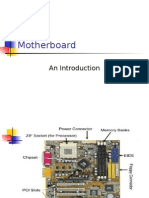
Motherboard is one of the main components of a computer and made of the printed circuit board (PCB). The motherboard is also known as mainboard, system board, logic board or sometimes, shortened as mobo. It serves as the backbone of a system because it provides all the electrical connections by which other components of the system communicate. The parts of the motherboard are shown in the example below:
y y y y y y y y y y y y y
Processor Socket this is where the processor is placed. On the picture above, the processor socket is Socket 478, which means that the compatible processor for this type of socket is Pentium 4. Memory Module Slot this is where the DDR DIMM is placed. Typical motherboards have 4 memory modules that can have a maximum of 1 GB of memory per slot. North Bridge Chipset Chipset located on the north bridge or near the CPU handles communication among CPU, RAM, AGP or PCI-Express and the South Bridge Chipset. South Bridge Chipset Chipset located on the south bridge supports input/output devices. ATX Power Connector this is where the power supply connected. Typical motherboards have 20-pin connectors. But new motherboards are now 24-pin power connector ready. Users can either place a 20-pin or 24-pin ATX connector. HDD IDE Connector this is where the IDE hard disk and CDROM drives are placed. SATA Connector SATA means Serial Advancement Technology Attachment. Its primary function is to transfer data between motherboard and media storage device. It offers faster data transfer rate. Floppy This is where the floppy drive connector is placed. Floppy drives are still important to computer systems especially when a user wants to have an emergency disk of a particular program. AGP slot This is the slot for the video card. Older motherboards still have AGP slots but as technology advances, AGP slots are now considered obsolete on new and modern motherboards. PCI-Express This is also the slot for the video card. It mainly replaces the functions of the AGP slot and it offers faster connection. PCI slots These are the slots where we can place extra network interface cards, modem cards, and other external cards used in computers. Rear panel This is also called the back panel of the computer. This is where the ports of mouse, keyboard, COM, USB, and Audio are located. Front panel This panel consists of connections for power, reset, sound, HDD LED, and power LED. This panel also consists of USB ports, depending on the architecture of the motherboard.
1 - PS/2 mouse port (green). This port is for a PS/2 mouse. 2 - LAN (RJ-45) port. This port allows connection to a Local Area Network (LAN) through a network hub. 3 - Line In port (light blue). This port connects a tape, CD, DVD player, or other audio sources, or it can function as Rear Speakers out. 4 - Line Out port (lime). This port connects to headphones or a speaker, or it can function as Front Speakers Out. 5 - Microphone port (pink). This port connects a microphone, or it can function as Center/Subwoofer Speaker. 6 - USB 2.0 ports 1 and 2. These two 4-pin Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports are available for connecting USB 2.0 devices. 7 - Video Graphics Adapter port. This port is for a VGA monitor or other VGA-compatible devices. 8 - PS/2 keyboard port (purple). This port is for a PS/2 keyboard.
You might also like
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and FunctionsDocument31 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and FunctionsNhil Cabillon QuietaNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi For Beginners: How to get the most out of your raspberry pi, including raspberry pi basics, tips and tricks, raspberry pi projects, and more!From EverandRaspberry Pi For Beginners: How to get the most out of your raspberry pi, including raspberry pi basics, tips and tricks, raspberry pi projects, and more!No ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument13 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard HandoutDocument5 pagesMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Computer Ports - Cases Power Supply - MOBODocument97 pagesComputer Ports - Cases Power Supply - MOBONhoj Bener StreqsNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Parts of a Motherboard and Their FunctionsDocument32 pagesParts of a Motherboard and Their FunctionsgerrygohilNo ratings yet
- A Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataDocument11 pagesA Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataPenchalaiah NarasapuramNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- JammyDocument2 pagesJammyPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- Hardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFDocument8 pagesHardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFKrish NeupaneNo ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts and FunctionsDocument21 pagesMotherboard Parts and FunctionsMelissa Jane MoradoNo ratings yet
- CHS Set2 W4-6Document136 pagesCHS Set2 W4-6Omar Sharif CuyuganNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsDocument70 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsMary MillareNo ratings yet
- M2 Yash AllabadiDocument7 pagesM2 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument3 pagesThe Motherboardbryan ramosNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument78 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsVencent BuellNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument18 pagesParts of MotherboardEviok Anfone ZosaNo ratings yet
- A MotherboardDocument4 pagesA MotherboardOttonniel BenNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts and Functions ExplainedDocument4 pagesMotherboard Parts and Functions ExplainedJaynard Paul ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument98 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Parts of MotherboardDocument63 pagesParts of MotherboardMarivic Omosura ItongNo ratings yet
- Study of Motherboard Components and ConnectorsDocument5 pagesStudy of Motherboard Components and ConnectorsSarang JamwalNo ratings yet
- MOBO Basic PartsDocument17 pagesMOBO Basic PartsJohara Mundas DiocolanoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardWilliam Paras InteNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardIbrahim ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardDocument15 pagesMother BoardSyd SiasonNo ratings yet
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument5 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemIssan VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- Computer Ports and Components GuideDocument5 pagesComputer Ports and Components GuidessssmailnatNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedStar Boy DavieNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputerDocument18 pagesParts of ComputerJazzt D MerencillaNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDocument5 pagesThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of MotherboardJimmySyNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardJohnPaulLlenticNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mother BoardDocument17 pagesParts of Mother BoardJeza Estaura Cuizon100% (1)
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- 21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Document6 pages21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Shreyank PushkarNo ratings yet
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- 27 Main Parts of Motherboard and its Function ExplainedDocument24 pages27 Main Parts of Motherboard and its Function ExplainedVictor M. MorcilloNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardDocument25 pagesMother BoardGershOn LeoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardRodel Romero100% (2)
- Basic Notes 2Document6 pagesBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ConnectorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Connectorsmohitpar128No ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components and portsDocument32 pagesMotherboard components and portsAnanduNo ratings yet
- TESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Document77 pagesTESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Sharalyn P. SiaNo ratings yet
- Essential Motherboard Parts GuideDocument28 pagesEssential Motherboard Parts GuideJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxFrom EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo ratings yet
- Model-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodFrom EverandModel-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodNo ratings yet
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Dancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldFrom EverandDancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionFrom EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- From Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionFrom EverandFrom Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionNo ratings yet
- The No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesFrom EverandThe No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesNo ratings yet
- 2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersFrom Everand2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersNo ratings yet
- Kindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondFrom EverandKindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)