Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Related Rates
Uploaded by
DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesRelated rates problems involve calculating the rate of change of two or more quantities that are related and changing with respect to time. The rate of change of one quantity is given, and the goal is to determine the rate of change of the other related quantity. Time is typically the independent variable that the quantities change with respect to. Related rates problems analyze how functions change at instances in time by relating the functions and their derivatives.
Original Description:
ggggggggggg
Original Title
RELATED RATES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRelated rates problems involve calculating the rate of change of two or more quantities that are related and changing with respect to time. The rate of change of one quantity is given, and the goal is to determine the rate of change of the other related quantity. Time is typically the independent variable that the quantities change with respect to. Related rates problems analyze how functions change at instances in time by relating the functions and their derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesRelated Rates
Uploaded by
DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRORelated rates problems involve calculating the rate of change of two or more quantities that are related and changing with respect to time. The rate of change of one quantity is given, and the goal is to determine the rate of change of the other related quantity. Time is typically the independent variable that the quantities change with respect to. Related rates problems analyze how functions change at instances in time by relating the functions and their derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
RELATED RATES
related rates problems
involve finding a rate at which a
quantity changes by relating that
quantity to other quantities whose
rates of change are known. The rate
of change is usually with respect to
time.
WHAT IS MEANT BY RELATED RATES?
Related rates problems involve two
(or more) variables that change at the
same time, possibly at different
rates. If we know how the variables
are related, and how fast one of them
is changing, then we can figure out
how fast the other one is changing.
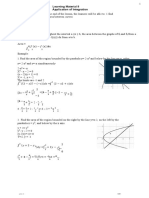
EXAMPLE OF A RELATED RATE?
SUBMITTED BY:
ROSALYN DEOZO
If two related quantities are
changing over time, the rates at SUMITTED TO:
which the quantities change are
related. For example, if a balloon is MATTHEW CAÑEDA
being filled with air, both the radius
of the balloon and the volume of the
balloon are increasing.
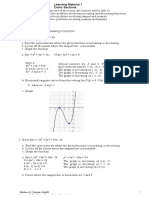
` WHAT IS THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
IN RELATED RATES PROBLEMS?
Note: It's okay to get a
The key phrases that
negative answer in
indicate time to be the
independent variable these problems. A
are "how fast," "how negative answer tells
often," "at what speed," us that that the
"at what rate is this or quantity is decreasing
that changing," and so and positive tells us
on. In rare cases a it's increasing.
WHY ARE RELATED RATES related rate problem
CALLED RELATED RATES? might have something
Related rates problems other than time as its
analyze the rate at which independent variable.
functions change for certain
instances in time. These
problems generally involve
two or more functions where
you relate the functions
themselves and their
derivatives, hence the name
"related rates." A "related
rates'' problem is a problem in
which we know one of the
rates of change at a given
instant—say, ˙x=dx/dt—and
we want to find the other rate
˙y=dy/dt at that instant.
You might also like
- Related Rates Problems: Differential CalculusDocument10 pagesRelated Rates Problems: Differential CalculusFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 Psych AssDocument3 pagesLesson-2 Psych Assalliahc.vergaraNo ratings yet
- Related Rates Problems: Differential CalculusDocument10 pagesRelated Rates Problems: Differential CalculusBianca GuevarraNo ratings yet
- 9 G1 IDAqr WKGDocument23 pages9 G1 IDAqr WKGTheoNo ratings yet
- Related Rates - ProblemsDocument10 pagesRelated Rates - ProblemsLenard MerlinNo ratings yet
- Research AssignmentDocument14 pagesResearch AssignmentRed Christian PalustreNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Model CLRM Assumptions: 1) Linearity Which Means That VariablesDocument3 pagesLinear Regression Model CLRM Assumptions: 1) Linearity Which Means That VariablesBlack PearlNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression in SPSSDocument17 pagesMultiple Regression in SPSSVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledwajeeha tahirNo ratings yet
- Lec 26Document24 pagesLec 26americo molinaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document11 pagesLec 3teyqqgfnyphcyhwnexNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P.K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument18 pagesApplied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P.K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis PDFDocument30 pagesCorrelation Analysis PDFtoy sanghaNo ratings yet
- Independent and Dependent VariablesDocument6 pagesIndependent and Dependent VariablesDawn Lewis100% (2)
- Statistic A 1Document15 pagesStatistic A 1Dana PascuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework and VariablesDocument21 pagesTheoretical Framework and VariablesFawad LatifNo ratings yet
- Independent and Dependent Variables TutorialDocument2 pagesIndependent and Dependent Variables TutorialDead ShotNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Experimental MethodsDocument39 pages3.1 - Experimental MethodsKhae PadiernosNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document22 pagesLec 2udhaya kumarNo ratings yet
- Linear and Volumetric Deformation Perspectives From Mass ConservationDocument10 pagesLinear and Volumetric Deformation Perspectives From Mass ConservationghulamhabibscmeNo ratings yet
- HyDocument31 pagesHyHiba NaseerNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Tools in Research and Data AnalysisDocument5 pagesBasic Statistical Tools in Research and Data AnalysisAira VillarinNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer II Prof. Nishith Verma Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 40Document29 pagesMass Transfer II Prof. Nishith Verma Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 40prthrNo ratings yet
- All About VariablesDocument61 pagesAll About VariablesSasji HasjNo ratings yet
- Logistic RegressionDocument47 pagesLogistic Regressionfatina92100% (2)
- Chapter 15 ANCOVA For Dichotomous Dependent VariablesDocument12 pagesChapter 15 ANCOVA For Dichotomous Dependent Variablesisaac_maykovichNo ratings yet
- Limits of Sequences - Brilliant Math & Science WikiDocument9 pagesLimits of Sequences - Brilliant Math & Science WikiKunal LadhaniNo ratings yet
- OLS Assumptions and TestsDocument5 pagesOLS Assumptions and TestsAakriti JainNo ratings yet
- Independent Vrs Dependent VarriablesDocument1 pageIndependent Vrs Dependent Varriablesapi-241105505No ratings yet
- Business Research Methodology Assignment 1 Submitted By: Sherjeel Zubair 18013005-021 BBA - 13Document6 pagesBusiness Research Methodology Assignment 1 Submitted By: Sherjeel Zubair 18013005-021 BBA - 13Muhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Week 009 The Variables, Hypothesis and Assumptions PPTDocument21 pagesWeek 009 The Variables, Hypothesis and Assumptions PPTdsdsdNo ratings yet
- Me Math 9 q2 0401 PsDocument38 pagesMe Math 9 q2 0401 PsFlor HawthornNo ratings yet
- A Few Words On Time FramesDocument1 pageA Few Words On Time FramesTUAN NGUYỄNNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. S. Vengadesan Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 02Document19 pagesFoundation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. S. Vengadesan Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 02Shahzaib Anwar OffNo ratings yet
- Variables and Quantifiers PDFDocument12 pagesVariables and Quantifiers PDFSebastián SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven Multiple Regression An Introduction To Multiple Regression Performing A Multiple Regression On SpssDocument20 pagesChapter Seven Multiple Regression An Introduction To Multiple Regression Performing A Multiple Regression On SpssAkshit AroraNo ratings yet
- Variables: VariableDocument13 pagesVariables: VariableGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Type of VariableDocument5 pagesType of Variablebayan salahNo ratings yet
- VariableDocument3 pagesVariableJaroushie FlynnNo ratings yet
- Variables in ResearchDocument3 pagesVariables in ResearchJoice Ann PolinarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Pyschology: Experimental MethodsDocument11 pagesExperimental Pyschology: Experimental MethodsShekaina YaniNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-30 at 12.35.43 AMDocument10 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-30 at 12.35.43 AMPriyanka Verma 51No ratings yet
- PPl-7 RL0KoDocument20 pagesPPl-7 RL0KoTheoNo ratings yet
- Unit RootDocument33 pagesUnit RootVaishali SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument21 pagesAdvanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasabimanaNo ratings yet
- Types of VariableDocument9 pagesTypes of VariableGiezel GeurreroNo ratings yet
- Note What Are VariablesDocument3 pagesNote What Are VariablesYahya AzharNo ratings yet
- Self-Regulation of Action and AffectDocument27 pagesSelf-Regulation of Action and AffectClaudia AvendañoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX-RN - Definition of LogitDocument3 pagesNCLEX-RN - Definition of LogitPhilippineNursingDirectory.comNo ratings yet
- What Are Independent and Dependent VariablesDocument13 pagesWhat Are Independent and Dependent VariablesGlendel CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Analysis: Relationships Between Variables and Measures of AssociationDocument22 pagesBivariate Analysis: Relationships Between Variables and Measures of AssociationSri RamNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Fluid QuestionsDocument42 pagesConceptual Fluid QuestionsAmr Faisal RaghebNo ratings yet
- 11 Tense PDFDocument5 pages11 Tense PDFMilosh PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Econometrics 4Document37 pagesEconometrics 4Anunay ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- More Than One Independent Variable Laying Out A Factorial Design A Research Example Choosing A Between-Subjects DesignDocument21 pagesMore Than One Independent Variable Laying Out A Factorial Design A Research Example Choosing A Between-Subjects DesignRain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Multi CollinDocument12 pagesMulti Collingpnm25No ratings yet
- Multi Col LinearityDocument12 pagesMulti Col LinearityTanzin HillaryNo ratings yet
- The Map - 83-100Document10 pagesThe Map - 83-100Anny SpaceNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6From EverandMultivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6No ratings yet
- An Ecosystem Is A Region Where A Bubble of Life Is Created by PlantsDocument4 pagesAn Ecosystem Is A Region Where A Bubble of Life Is Created by PlantsDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Published Article Math13Document4 pagesPublished Article Math13DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Ge3Document3 pagesLesson 11 Ge3DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Ge3Document2 pagesLesson 10 Ge3DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Ge3Document2 pagesLesson 7 Ge3DHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities Written ReportDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Identities Written ReportDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 Mathematics RobertDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 Mathematics RobertDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- 3 LM1 Conics CirclesDocument5 pages3 LM1 Conics CirclesDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- 16 LM9 Integral Calculus Area Between CurvesDocument2 pages16 LM9 Integral Calculus Area Between CurvesDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Gagne's Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGagne's Lesson PlanDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Activity in RING AND FIELDSDocument3 pagesActivity in RING AND FIELDSDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocument7 pagesPlane and Solid GeometryDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- 8 LM3 Implicit DifferentiationDocument7 pages8 LM3 Implicit DifferentiationDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- 11 LM1 Application of DerivativesDocument6 pages11 LM1 Application of DerivativesDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- PCK6 COMPILATION Rosalyn Deozo BSED MATHEMATICS 2ADocument9 pagesPCK6 COMPILATION Rosalyn Deozo BSED MATHEMATICS 2ADHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- StatDocument24 pagesStatDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- FS - Detailed LPDocument16 pagesFS - Detailed LPDHAPNY GRACE ESCORRONo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Vertical Geometric Irregular Building Considering Soil Structure InteractionDocument11 pagesSeismic Analysis of Vertical Geometric Irregular Building Considering Soil Structure InteractionStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- ISO 1940-2 1997 - Mechanical Vibration - Balance Quality Requirements For Rotors Part 2Document20 pagesISO 1940-2 1997 - Mechanical Vibration - Balance Quality Requirements For Rotors Part 2Chaiana ScabeloNo ratings yet
- Testing & Commissioning Manual SECDocument125 pagesTesting & Commissioning Manual SECmissle2007100% (6)
- Sikadur-330 EpoxyDocument6 pagesSikadur-330 EpoxySarfraz MunirNo ratings yet
- Performing Mensuration and Calculation: Amperage (Amps) - A Unit of Measurement of Electrical Current FlowDocument28 pagesPerforming Mensuration and Calculation: Amperage (Amps) - A Unit of Measurement of Electrical Current FlowAries Gonzales CaraganNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Strut and Tie ModelDocument5 pagesAssignment 1-Strut and Tie ModelYUK LAM WONGNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing: Ajit Panesar, Meisam Abdi, Duncan Hickman, Ian AshcroftDocument14 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: Ajit Panesar, Meisam Abdi, Duncan Hickman, Ian AshcroftrahulNo ratings yet
- Appbrief Porcine TracheaDocument2 pagesAppbrief Porcine TracheamgimohNo ratings yet
- SPCNDocument30 pagesSPCNElias ChavezNo ratings yet
- 3 Oil and Gas Separation Design Manual by C Richard SivallsDocument63 pages3 Oil and Gas Separation Design Manual by C Richard SivallsSemih Özsağıroğlu100% (1)
- Building Two Prototypes in OpenraveDocument3 pagesBuilding Two Prototypes in OpenraveAlex Aguirre ParedesNo ratings yet
- ProgramDocument52 pagesProgramSantanu SenNo ratings yet
- Medina (193253920) Problemset7 V1Document6 pagesMedina (193253920) Problemset7 V1shaunmedina0006No ratings yet
- SG Rule of Thumb For RC DesignDocument13 pagesSG Rule of Thumb For RC DesignRsjBugtongNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Preparation BooksDocument2 pagesIIT JEE Preparation BooksAkshit Jain83% (6)
- Laboratory Manual For Air Permeability MeasurementDocument4 pagesLaboratory Manual For Air Permeability Measurementadeelsn0% (2)
- Operator's ManualDocument226 pagesOperator's ManualHernan PerezNo ratings yet
- The Three-Body ProblemDocument69 pagesThe Three-Body ProblemCamila LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Transicion de Un Ambiente Epitemal A Un PorfidoDocument50 pagesTransicion de Un Ambiente Epitemal A Un PorfidoAngel SincheNo ratings yet
- Hamilton's PrincipleDocument8 pagesHamilton's Principleletter_ashish4444No ratings yet
- Rocas EjerciciosDocument2 pagesRocas EjerciciosStiwarth Cuba Asillo0% (1)
- Practical No: 08 Title: Explanation of Mass Balance by Algebraic Equations Objective: To Acquaint Food Processing Operation by Mass Balance. TheoryDocument4 pagesPractical No: 08 Title: Explanation of Mass Balance by Algebraic Equations Objective: To Acquaint Food Processing Operation by Mass Balance. TheoryMuhammad Faisal AdreesNo ratings yet
- 2815 FullDocument13 pages2815 Fullazam ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bocker Giant Construction HoistDocument8 pagesBocker Giant Construction HoistRajanbabuNo ratings yet
- GERDES, Paulus. The Philosophical-Mathematical Manuscripts of Karl Marx On Differential CalculusDocument120 pagesGERDES, Paulus. The Philosophical-Mathematical Manuscripts of Karl Marx On Differential CalculusjosuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Gas Dynamics PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 1 Gas Dynamics PDFKarim MagdyNo ratings yet
- CHEM123: Lab 11Document3 pagesCHEM123: Lab 11Kamil KrawczykNo ratings yet
- Birla PresentationDocument16 pagesBirla Presentationluis fazendaNo ratings yet