0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views36 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions Overview
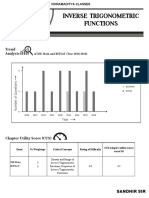
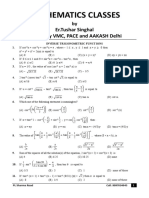
The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions. It defines inverse trigonometric functions as obtaining the angle given a trigonometric ratio. Some restrictions are imposed on the angles based on the principle values of the angles to satisfy the definition of a function. The document then lists definitions of inverse trigonometric functions with their domains and ranges. It provides some useful formulas for inverse trigonometric functions. Finally, it includes examples of solving problems involving inverse trigonometric functions.
Uploaded by
2007naxayan2007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views36 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions Overview
The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions. It defines inverse trigonometric functions as obtaining the angle given a trigonometric ratio. Some restrictions are imposed on the angles based on the principle values of the angles to satisfy the definition of a function. The document then lists definitions of inverse trigonometric functions with their domains and ranges. It provides some useful formulas for inverse trigonometric functions. Finally, it includes examples of solving problems involving inverse trigonometric functions.
Uploaded by
2007naxayan2007Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd