Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FOM Unit IV
Uploaded by
madhvendra99Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FOM Unit IV
Uploaded by
madhvendra99Copyright:
Available Formats
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
DIRECTING
"Activating deals with the steps a manager takes to get sub-ordinates and others to carry out
plans" - Newman and Warren.
Directing concerns the total manner in which a manager influences the actions of subordinates. It is the
final action of a manager in getting others to act after all preparations have been completed.
Characteristics
• Elements of Management
• Continuing Function
• Pervasive Function
• Creative Function
• Linking function
• Management of Human Factor
Scope of Directing
• Initiates action
• Ensures coordination
• Improves efficiency
• Facilitates change
• Assists stability and growth
Elements of Directing
The three elements of directing are
• Motivation
• Leadership
• Communication
Motivation- According to George R. Terry, "Motivation is the desire within an individual that stimulates
him or her to action."
In the words of Robert Dubin, it is "the complex of forces starting and keeping a person at work in an
organization". Viteles defines motivation as "an unsatisfied need which creates a state of tension or
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 1
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
disequilibrium, causing the individual to move in a goal directed pattern towards restoring a state of
equilibrium, by satisfying the need."
FEATURES OF MOTIVATION
The following are the features of motivation:
It is an internal feeling and forces a person to action.
It is a continuous activity.
It varies from person to person and from time to time.
It may be positive or negative.
IMPORTANCE OF MOTIVATION
Motivated employees make optimum use of available resources for achieving objectives.
Motivation is directly related to the level of efficiency of employees.
Motivated employees make full use of their energy and other abilities to raise the existing level of
efficiency.
Motivated employees make goal-directed efforts. They are more committed and cooperative for
achieving organizational objectives.
Motivated employees are more loyal and sincere to an organization. These factors help reduce
absenteeism and labor turnover.
Motivation is considered as a backbone of good industrial relations.
Theories of Motivation-
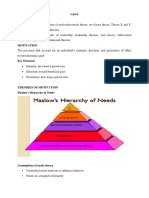
Theory of Hierarchy of Needs
It is recognized by psychologist that needs usually have a hierarchical arrangement among themselves.
Maslow has presented a need priority of five levels. These are:.
1. Basic physiological needs : It includes all needs that have to be satisfied for the well being of the
individual. It is inborn motives. These include hunger, thirst, sex, shelter, etc.
2. Safety and security: Safety needs include a desire for security, stability, freedom from fear and
anxiety protection, dependency and a need for structure, law and order. These include protection
and security from physical and emotional problems. It is acquired motive.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 2
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
3. Belonging and social needs : It include the need for belongingness, love, friendship, affection and
acceptance. In the work place, this need may be satisfied by an ability to interact with one’s
coworkers and perhaps to be able to work collaboratively with these colleagues. In Maslow’s
opinion these are social motives.
4. Esteem and status : This include all needs that give the individual a better self worth. It include the
desire for self-respect, self-esteem, recognition, attention, achievement, autonomy and the
esteem of others. It is called individual motive.
5. Self-actualisation and fulfillment : The highest need in Maslow’s hierarchy is that of self
actualization; the need for self-realization, continuous self-development, and the process of
becoming all that a person is capable of becoming. That is unconscious motive.
Maslow implies that, usually, the needs have a definite sequence of domination. Need number 2 does not
dominate until need number 1 is reasonably satisfied. Need number 3 does not dominate until need
number 1 and 2 have been reasonably achieved and so on. Broadly, it means that until the basic
physiological needs are met, the secondary, social and psychological needs do not come to operate.
Criticism of Maslow’s Theory -Maslow’s model has been criticized on various facts as follows:
1. Maslow’s proposition that one need is satisfied at one time not correct.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 3
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
2. There is no evidence that once a need has been fulfilled, its strength diminishes. It is difficult to
interpret and operationalise its concepts. e.g., what is the time span for the unfolding of hierarchy
etc. What does dominance of a given need mean?
3. The model is based more on wishes of what man should be rather than what he actually is. It is not
correct to put needs into neat water-right compartments.
4. It is also doubtful whether gratifacations of one automatically activates the next need in the hierarchy.
Also the need hierarchy may not follow the sequence fixed by Maslow.
Herzberg’s Hygiene Theory of Motivation - Fredericks Herzberg provided an interesting extension of
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory and developed the Two Factory Theory. It was also known as
motivational-Hygiene Theory.
Herzberg and his associates conducted extensive interviews with professional persons in the
study and asked them what they liked or disliked about their work. The results indicated that when people
talked about feeling good or satisfied, they mentioned features intrinsic to the job and when people talked
about feeling dissatisfied with the job they talked, about factors extrinsic to the job. Herzberg called these
‘motivation’ and ‘maintenance’ factors respectively.
When motivational factors are not present they prevented satisfaction and motivation. When
these factors are present they increased satisfaction and motivation.
It appeared from the research, that the thing making people happy on the job and those making
them unhappy had two separate themes.
1. Motivation Factors (Satisfaction)
2. Hygienic Factors (Dissatisfaction)
1. Motivation Factors : Motivation Factors are real motivators that are associated with the positive
feelings of employees about the job. If managers wish to increase motivation and performance above the
average level, they must enrich the work and increase a person’s freedom on the job. Their high morale is
evidenced by lack of absenteeism, commitment to goals and late hours working. These factors have a
positive influence on morale satisfaction, efficiency and productivity. Some factors stood out as strong
determiners of job satisfaction:
(i) Achievement
(ii) Recognition
(iii) Advancement
(iv) Work itself
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 4
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
(v) Responsibility
(vi) Possibility of growth
2. Hygiene Factors : Hygiene factors do not help the growth in performance but they prevent
deterioration of performance caused by work restriction. Herzberg believed that hygiene created
little positive motivation but its absence created negative motivation.
All the hygiene factors are environment related factors that must be viewed as preventive
measures that remove job dissatisfaction from the environment. The determinants of job dissatisfaction
were found to be:
(i) Company policy and administration
(ii) Technical Supervision
(iii) Interpersonal relations with peers, supervisor and subordinates
(iv) Status
(v) Working environment
(vi) Salary
(vii) Security
According to Herzberg, the results concluded that replies people gave when they felt bad. Certain
characteristics tend to be consistently related to job satisfaction and others to job dissatisfaction.
'X' AND ‘Y' THEORIES OF MOTIVATION
Douglas McGregor observed two diametrically opposing viewpoints of managers 'about their employees;
one is negative called "Theory of X" and another is positive called "Theory of Y".
Theory of X
Following are the assumptions of managers who believe in the "Theory of X" regarding their employees.
Employees dislike work.
Employees must be coerced, controlled or threatened to do the work.
Employees avoid responsibilities and seek formal direction.
Most employees consider security of job, most important of all other factors in the job and have
very little ambition.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 5
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
Theory of Y
Following are the assumptions of managers who believe in the "Theory of Y" regarding their employees.
Employees love work as play or rest.
Employees are self-directed and self-controlled and committed to the organizational objectives.
Employees accept and seek responsibilities.
Innovative spirit is not confined to managers alone, some employees also possess it.
MC-CLELLAND's NEED THEORY OF MOTIVATION
David C. McClelland and his associate Atkinson have contributed to an understanding of motivation by
identifying three types of basic motivating needs. These needs have been classified as:
1. Need for Power
2. Need for Affiliation
3. Need for Achievement : :
Need for Power- According to this theory the need for power, which might be defined as the desire to be
influential in a group and to control one's environment is an important motivation factor. Research
suggests that people with a strong need for power, are likely to be superior performers and occupy
supervisory positions. Such types of individuals generally look for positions of leadership, they act
effectively, are outspoken, have a stubborn character and exert authority.
Need for Affiliation- The need for affiliation means the desire for human companionship and acceptance.
Those with a high need for affiliation often behave the way they think other people want them to, in an
effort to maintain friendship. They prefer a job that entails a good deal of social interaction and offers
opportunities to make friends. The principal characteristics of such peoples' traits are as follows:
Desire to like and be liked.
Enjoy company and friendship.
Prefer cooperative situation.
Excel in group task.
Star attraction in gathering.
Leadership qualities.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 6
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
Need for Achievement
People with a high need for achievement, always feel ambitious to be successful; are ever prepared to
face challenging situations and set arduous goals .for themselves. They are prone to take calculated
risks; and possess a high sense of personal responsibility in getting jobs done. These people are
concerned with their progress, and feel inclined to put in longer hours of work" Failures never dishearten
them and they are always ready to put in their best efforts for excellent performance.
LEADERSHIP
DEFINITION- Leadership is the art of influencing and inspiring subordinates to perform their duties
willingly, competently and enthusiastically for achievement of groups objectives.
According to Wendell French, "Leadership is the process of influencing the behavior of others in
the direction of a goal or set of goals or, more broadly, toward a vision of the future”,
According to Keith Davis, “Leadership is the process of encouraging and helping others to work
enthusiastically towards objectives”.
FEATURES OF LEADERSHIP- The features of leadership are as follows:
Leadership is the process of influencing behavior of individuals of an organization.
Leadership uses non-coercive methods to direct and coordinate the activities of the
individuals of an organization.
Leadership directs the individuals to attain the tasks assigned to them by following the
instructions of their leaders.
A leader possesses qualities to influence others.
Leadership gives the individuals, a vision for future.
Leadership is a group activity. Leader influences his followers and followers also exercise
influence over his leader.
Leadership is meant for a given situation, given group for a pre-determined period of lime.
Leadership is continuous process of influencing behavior. It encourages liveliness in the group.
Importance of Leadership- The following points can judge the importance of leadership:
A leader should act as a friend of the people whom he is leading.
A leader must have the capacity to recognize the potentials of the individuals and transform them
into realities.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 7
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
A leader should have the confidence of the individuals of the organization.
A leader must be able to unite the people as a team and build up team spirit.
A leader should be able to maintain discipline among his group and develop a sense of
responsibility.
Leadership Styles- The style of leadership is based on the kind of control the leader exercises on a
group and their behaviour.
1. Autocratic or Authoritative Style: It is also known as leader centered style. Under this style of
leadership there is complete centralisation of authority in the leader i.e., authority is centered in the leader
himself He has all the powers to take decisions. He designs the work-load of his employees and exercise
tight control over them. The subordinates are bound to follow his order and directions.
Advantages:
(i) Autocratic leadership style permits quick decision-making.
(ii) It provides strong motivation and satisfaction to the leaders who dictate terms.
(iii) This style may yield better results when great speed is required.
Disadvantages:
(i) It leads to frustration, low moral and conflict among subordinates,
(ii) Subordinates tend to shirk responsibility and initiative.
2. Democratic Style: Under this style, a leader decentralises and delegates high authority to his
subordinates. He makes a final decision only after consultation with the subordinates. Two way
communication channel is used. While delegating a lot of authorities to subordinates, he defines the limits
within which people can function. Democratic leaders have a high concern for both people and work.
Advantages:
(i) Exchange of ideas among subordinates and leader improves job satisfaction and morale of the
subordinates.
(ii) Human values get their due recognition which develops positive attitude and reduces resistance to
change.
(iii) Labour absenteeism and labour turnover are reduced.
(iv) The quality of decision is improved.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 8
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
Disadvantages:
(i) Democratic style of leadership is time consuming and may result in delays in decision-making.
(ii) It is less effective if participation from the subordinates is for name sake.
(iii) Consulting others while making decisions go against the capability of the leader to take decisions.
3. Free Rein or Laissez Fair style: Under this style, a manager gives complete freedom to his
subordinates. The entire decision-making authority is entrusted to them. There is least intervention by the
leader and so the group operates entirely on its own. There is free flow of communication. In this style
manager does not use power but maintains contact with them. Subordinates have to exercise self control.
This style helps subordinates to develop independent personality.
Advantages:
(i) Positive effect on job satisfaction and moral of subordinates.
(ii) It gives chance to take initiative to the subordinates.
(iii) Maximum possible scope for development of subordinates.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 9
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
Disadvantages:
(i) Under this style of leadership, there is no leadership at all.
(ii) Subordinates do not get the guidance and support of the leader.
(iii) Subordinates may move in different directions and may work at cross purpose which may create
problem for the organisation.
Functions of a Leader
1. To take the initiative: A leader initiates all the measures that are necessary for the purpose of
ensuring the health and progress of the organisation in a competitive economy. He should not expect
others to guide or direct him. He should lay down the aims and objectives, commence their
implementation and see that the goals are achieved according to the predetermined targets.
2. He identifies group goals: A leader must always help the group identify and attain their goals. Thus, a
leader is a goal setter.
4. He acts as an arbitrator: When groups experience internal difference, whether based on emotional or
intellectual clashes, a leader can often resolve the differences. He acts as an arbitrator to prevent serious
differences from cropping up within the group.
5. To assign reasons for his action: It is the delicate task of a leader to assign reasons to his every
command. He has to instruct things in such a way that they are intelligible to all concerned and their co-
operation is readily forthcoming.
6. To interpret: He interprets the objectives of the organisation and the means to be followed to achieve
them; he apprises his followers, convinces them, and creates confidence among them.
7. To guide and direct: It is the primary function of the leader to guide and direct the organisation. He
should issue the necessary instructions and see that they are properly communicated.
Theories of Leadership-
The Blake Mouton Managerial Grid is based on two behavioral dimensions:
Concern for People: this is the degree to which a leader considers team members' needs, interests and
areas of personal development when deciding how best to accomplish a task.
Concern for Results: this is the degree to which a leader emphasizes concrete objectives,
organizational efficiency and high productivity when deciding how best to accomplish a task.
Blake and Mouton defined five leadership styles based on these, as illustrated in the diagram below.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 10
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
The Indifferent or Impoverished (1,1)- These leaders have minimal concern for people and production.
Their priority is to fly under the radar while they content to seek solutions that won't bring any negative
focus to themselves or their department. Preserving their employment, position as well as their seniority is
what drives their elusive and evading behaviors. In short, the indifferent leaders are ineffective and are
sorely lacking in any of the traits that can be attributed to successful and effective leaders.
Impact on employees:
Employees have a high degree of dissatisfaction
No harmony within the group
High turn over
Impact on organization:
Inefficient operation
The Country Club or Accommodating (1, 9)
These leaders will go above and beyond to ensure that the needs and desires of his employees are met.
These leaders are making the assumption that their staff will yield maximum results as they are likely to
be self-motivated when they are lead in such environment. These leaders will have behaviours that will
yield and comply with the needs of their staff. The productivity of the group however, can suffer from the
lack of attention on tasks.
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 11
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
Impact on employees:
Employees are Happy
Good team harmony
Impact on organization:
Low productivity
The Status Quo or Middle-of-the-Road (5, 5)
These leaders balance out the needs of their staff with those of the organization, while not adequately
achieving either. These leaders will balance and compromise their decisions, often endorsing the most
popular one. They dedicate minimal efforts towards facilitating the achievements of their staff or the
production results in average or below average levels.
Impact on employees:
Employees are not really discontent nor are they happy
Good harmony within the group
Impact on organization:
Average performance
The Dictatorial or Produce, Perish or Control (9, 1)
These leaders focus all of their attention to production-related matters and very little towards the needs of
their employees. These leaders will direct and dominate while holding the belief that efficiency gains can
only be achieved through rigid disciplines especially those that don't require human interaction.
Employees are considered expendable resources. Productivity is usually short lived as high employee
attrition is unavoidable. The dictatorial style is inspired by the McGregor X theory.
Impact on employees:
Employees experience a high level of dissatisfaction
High level of conflict within the group
Impact on organization:
High employee turnover
Peak performance is short lived
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 12
FUNDAMENTAL OF MANAGEMENT #UNIT-IV
The Sound or Team (9, 9)
According to Dr. Robert R. Blake and Dr. Jane Srygley Mouton (and I agree), the sound leader is the
most effective leadership style. These leaders will contribute and are committed, can motivate and are
motivated while holding the belief that trust, respect, commitment and employee empowerment are
essential for fostering a team environment where team members are motivated, thus resulting in
maximum employee satisfaction as well as the most efficient productivity. This sound leadership style is
also inspired by the McGregor Y theory.
Impact on employees:
Employees are forming a highly cohesive team
Employees are satisfied
Employees are motivated and work as a team
Impact on organization:
Low employee turnover
Attracts highly skills employees
Efficient organization
Situational Theory (Contingency Theory) : Situational leadership approach was applied in 1920 in the
armed forces of Germany to get good generals under different situations. The main attention in
situation theory of leadership (also known as contingency theory) is given to the situation in which
leadership is exercised. The various factors affecting leadership are classified into two major
categories; situational factors and leader’s behaviours.
(i) Situational Factors : Leadership effectiveness is affected by following situational factors:
(a) Leader follower relations
(b) Group situation
(c) Leader’s situation
(d) Organizational factors
(ii) Leader Behavior : It is affected by the following behavioural factors;
(a) Leader’s position
(b) Leader’s characteristics
AIPS (M P SINGH) Page 13
You might also like
- Motivation TheoryDocument12 pagesMotivation TheoryAnurag kumar89% (9)
- 18CS51 - Module-2 - Directing and ControlDocument14 pages18CS51 - Module-2 - Directing and Controlbalaji bonageriNo ratings yet
- HBC 2105 Principles of Management IIDocument23 pagesHBC 2105 Principles of Management IImoza salimNo ratings yet
- Leadership Motivation TheoriesDocument12 pagesLeadership Motivation Theoriesmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Vijay Kumar SodadasiDocument22 pagesVijay Kumar SodadasiVijay Kumar SodadasNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter 4Document33 pagesOB Chapter 4Yabetse DanielNo ratings yet
- Motivational Theories and Current Trends of Motivationg Employees at WorkplaceDocument11 pagesMotivational Theories and Current Trends of Motivationg Employees at WorkplaceVarshish ShahNo ratings yet
- Buddhism and Modern ManagementDocument17 pagesBuddhism and Modern Managementsadawimala33% (3)
- Module - II: MotivationDocument11 pagesModule - II: MotivationRajesh MgNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 MGT PCIUDocument22 pagesChapter-8 MGT PCIUEmuni MarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their ApplicationsDocument11 pagesChapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their ApplicationsAbene Man Wt BreNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel EmpDocument56 pagesTata Steel EmpGULAM GOUSHNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument26 pagesMotivationRahul K PallikkaraNo ratings yet
- Org and Management Chapter 6 LeadingDocument63 pagesOrg and Management Chapter 6 LeadingNhojLaup80% (5)
- Himani Project-3Document64 pagesHimani Project-3sangeeta singhNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Stress ManagementDocument59 pagesMotivation and Stress ManagementGautam BhattaNo ratings yet
- Motivation ConceptDocument17 pagesMotivation ConceptVanshika SoniNo ratings yet
- 1541499143note HerzbergsTheoryofMotivationDocument8 pages1541499143note HerzbergsTheoryofMotivationArti PatelNo ratings yet
- Management Chapter FiveDocument11 pagesManagement Chapter FivechuchuNo ratings yet
- 8.motivation in ClassDocument18 pages8.motivation in ClassADITI PATELNo ratings yet
- A Study On Employees MotivationDocument89 pagesA Study On Employees MotivationT S Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- LITERATURE REVIEW On Emlpoye MotivationDocument9 pagesLITERATURE REVIEW On Emlpoye MotivationAbhi JainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document7 pagesLesson 6Nishani wickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Motivation I: Basic ConceptsDocument16 pagesChapter 5: Motivation I: Basic ConceptsSadiqSagheerNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Theories of MotivationDocument46 pagesUnit-3 Theories of MotivationRachit GoyalNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument71 pagesMotivationratanNo ratings yet
- Basic Motivation Concepts: Chapter 6 OutlineDocument12 pagesBasic Motivation Concepts: Chapter 6 OutlinePragash KaliyanNo ratings yet
- Motivation ObDocument19 pagesMotivation ObAnkita MahajanNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Its SignificanceDocument22 pagesMotivation and Its SignificanceAgam ShatodarNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1-MotivationDocument21 pagesModule 2.1-MotivationBenjamin Codilla Gerez, Jr.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Project: The Concept of MotivationDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Project: The Concept of MotivationSmiti WaliaNo ratings yet
- Otb Notes2016Document44 pagesOtb Notes2016brian ochiengNo ratings yet
- CC C ! ! C"#$%#"Document6 pagesCC C ! ! C"#$%#"Rajesh MgNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document15 pagesUnit 6Manjunath ShivannaNo ratings yet
- MGT 251Document9 pagesMGT 251GolamRabbaneNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATION THEORIESDocument11 pagesMOTIVATION THEORIESPoonam SachdevNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motivation ExplainedDocument28 pagesTheories of Motivation Explaineds_87045489No ratings yet
- Employee Motivation On Tata SteelsDocument56 pagesEmployee Motivation On Tata SteelsVarsha Singh91% (11)
- MotivationDocument24 pagesMotivationruchikunalNo ratings yet
- Motivating Change and Others EffectivelyDocument58 pagesMotivating Change and Others Effectivelyyatin rajputNo ratings yet
- CH6 MOTIVATION in Extension OrganizationDocument70 pagesCH6 MOTIVATION in Extension OrganizationTokkummaa GalatuuNo ratings yet
- Basic Motivation ConceptsDocument11 pagesBasic Motivation ConceptsLeena DeepuNo ratings yet
- Erg 43 Redsvt 4 EtvsdvsDocument24 pagesErg 43 Redsvt 4 EtvsdvsJimmyorajayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motivation TheoriesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Motivation TheoriesJonavie TorresNo ratings yet
- PawanDocument19 pagesPawanRubina LalotraNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Types, TheoriesDocument35 pagesMeaning, Types, TheoriesmaninderNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoriesDocument6 pagesMotivation TheoriesDal.giNo ratings yet
- UCC - Intro To Psy - Ppoint Unit 9Document19 pagesUCC - Intro To Psy - Ppoint Unit 9Demeico DavisNo ratings yet
- OBE Unit 5 (Motivation)Document7 pagesOBE Unit 5 (Motivation)Prateek DaveNo ratings yet
- Motivation Notes (Organizational Behavior)Document11 pagesMotivation Notes (Organizational Behavior)MD Salahuddin Kader MonnaNo ratings yet
- A Project On Employee MotivationDocument18 pagesA Project On Employee MotivationPiyush Chothe100% (1)
- The Four Functions of ManagementDocument5 pagesThe Four Functions of ManagementWaqas IqbalNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 Leadership and MotivationDocument13 pagesModule - 4 Leadership and MotivationUllas GowdaNo ratings yet
- Directing & MotivationDocument16 pagesDirecting & Motivationarijit75% (4)
- UNIT 4 - (A) MOTIVATIONDocument8 pagesUNIT 4 - (A) MOTIVATIONLikkle MikeNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motivation: Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor and OuchiDocument5 pagesTheories of Motivation: Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor and OuchijithuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceFrom EverandUnderstanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- OB Chapter 7Document13 pagesOB Chapter 7Naiha AbidNo ratings yet
- KNIPSS Management Institute BBA Sessional Test FundamentalsDocument1 pageKNIPSS Management Institute BBA Sessional Test Fundamentalsmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- DemandDocument38 pagesDemandrohan_jangid8No ratings yet
- E-Vehicle adoption factors and UTAUT2 modelDocument1 pageE-Vehicle adoption factors and UTAUT2 modelmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Design Thinking QuestionDocument1 pageDesign Thinking Questionmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Behavioural Issues in Strategy ImplementationDocument5 pagesBehavioural Issues in Strategy Implementationmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Fundamental of ManagementDocument1 pageFundamental of Managementmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- BBA#Business Organization PaperDocument2 pagesBBA#Business Organization Papermadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Ad Mad ShowDocument4 pagesAd Mad Showmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Digital Marketing CourseDocument1 pageDigital Marketing Coursemadhvendra99No ratings yet
- List of English Words With Meaning and SentencesDocument10 pagesList of English Words With Meaning and Sentencesmadhvendra9967% (9)
- Syllabus en 21 04 09Document61 pagesSyllabus en 21 04 09Soumil SarkarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Socilogy - Question BankDocument2 pagesIndustrial Socilogy - Question Bankmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Economics Question Paper (UPTU)Document2 pagesEconomics Question Paper (UPTU)madhvendra99No ratings yet
- Sessional Test - I (Ece-Ii Year) : 40 KM Stone, NH-24, Delhi - Hapur Road, Pilkhuwa, GhaziabadDocument2 pagesSessional Test - I (Ece-Ii Year) : 40 KM Stone, NH-24, Delhi - Hapur Road, Pilkhuwa, Ghaziabadmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Economics Question BankDocument5 pagesEconomics Question Bankmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Business OrganisationLecture Notes - Unit - 2Document8 pagesBusiness OrganisationLecture Notes - Unit - 2madhvendra99No ratings yet
- Logistics ManagementDocument8 pagesLogistics Managementmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Production & Operation ManagementDocument13 pagesProduction & Operation Managementmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument22 pagesBusiness Communicationmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- QBDocument3 pagesQBmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Media Planning BasicsDocument9 pagesMedia Planning Basicsmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- No ITR for salary, interest up to Rs 5LDocument1 pageNo ITR for salary, interest up to Rs 5Lmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Business Organization (Question Bank)Document2 pagesBusiness Organization (Question Bank)madhvendra99No ratings yet
- Guardian Antivirus Manual2012Document62 pagesGuardian Antivirus Manual2012Amit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Professionalism Unit - 4Document3 pagesProfessionalism Unit - 4madhvendra99No ratings yet
- Define Organizational BevaiourDocument1 pageDefine Organizational Bevaiourmadhvendra99No ratings yet
- Business Organization (Question Bank)Document2 pagesBusiness Organization (Question Bank)madhvendra99No ratings yet
- Assignment - 2: Aryabhatt College of Management & TechnologyDocument1 pageAssignment - 2: Aryabhatt College of Management & Technologymadhvendra99No ratings yet
- CH 3: Forecasting: Techniques and RoutesDocument19 pagesCH 3: Forecasting: Techniques and RoutesZaeem Uddin AliNo ratings yet
- 6.6.2 Updated Local Shelter Planning Manual by Housing - Urban Development Coordinating Council and United Nations Resettlement ProgrDocument12 pages6.6.2 Updated Local Shelter Planning Manual by Housing - Urban Development Coordinating Council and United Nations Resettlement ProgrPrincess VistalNo ratings yet
- Q3 JHS Pre TestDocument6 pagesQ3 JHS Pre Test-09876543123456789No ratings yet
- New Yashoda Public School: Split Up SyllabusDocument6 pagesNew Yashoda Public School: Split Up Syllabusamandeep khasaNo ratings yet
- Regional Context SuratDocument13 pagesRegional Context SuratSonali HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- Call of The Void - The Attraction of Ultimate AbsurdityDocument3 pagesCall of The Void - The Attraction of Ultimate AbsurdityMạnh Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1 Malaysia ConceptDocument12 pages1 Malaysia ConceptIskandar IskandarNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Protagonist A Good Person Can Vary Depending On The StoryDocument3 pagesWhat Makes A Protagonist A Good Person Can Vary Depending On The StorySANTOS SHENA MAY D.No ratings yet
- PreviewDocument73 pagesPreviewDmitri PopaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Persuasive Speech Acts Used in SomeDocument25 pagesA Study of Persuasive Speech Acts Used in SomealhelawyhNo ratings yet
- College Mathematics For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 12th Edition Barnett Test BankDocument26 pagesCollege Mathematics For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 12th Edition Barnett Test Bankrussellarnoldmbgzcoqiyd100% (26)
- Definitions of EconomicsDocument5 pagesDefinitions of EconomicsMinakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Maffie - 'We Eat of The Earth Then The Earth Eats Us'. The Concept of Nature in Pre-Hispanic Nahua ThoughtDocument15 pagesMaffie - 'We Eat of The Earth Then The Earth Eats Us'. The Concept of Nature in Pre-Hispanic Nahua ThoughtFabio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Uploads EJournalDetail 32 1052 64Document24 pagesUploads EJournalDetail 32 1052 64olga orbaseNo ratings yet
- Ben & Jerry's Dream Team Creates SEO-Optimized Ad CampaignDocument14 pagesBen & Jerry's Dream Team Creates SEO-Optimized Ad CampaignamitmaharNo ratings yet
- HDQJHJHRJQ 2Document5 pagesHDQJHJHRJQ 2hhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument42 pagesPractical ResearchMilly RuizNo ratings yet
- Leslie Bethell - The Cambridge History of Latin America (Vol XI)Document1,002 pagesLeslie Bethell - The Cambridge History of Latin America (Vol XI)caiofelix_rj100% (3)
- Chapter Nine: Intra-Personal and Interpersonal Skills Self-Concept and Self-AwarenessDocument11 pagesChapter Nine: Intra-Personal and Interpersonal Skills Self-Concept and Self-Awarenesshalewat AbebeNo ratings yet
- SELF AND PERSONALITY Chapter 2 12th STDDocument14 pagesSELF AND PERSONALITY Chapter 2 12th STDdency1saji1No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Filipino Character and ValueDocument10 pagesModule 3 - Filipino Character and ValueJomel Kennedy Manuel100% (2)
- Arriaga, E. y K. Davis (1969), "The Pattern of Mortality Change in Latin America", Demography, Vol. 6, #3Document21 pagesArriaga, E. y K. Davis (1969), "The Pattern of Mortality Change in Latin America", Demography, Vol. 6, #3Jose Alberto Cubillos EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii: Managing and Caring For The Self B. Setting Goals For SuccessDocument9 pagesChapter Iii: Managing and Caring For The Self B. Setting Goals For Successzed cozNo ratings yet
- Glaserian CodingDocument3 pagesGlaserian CodingJane VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Billy Elliot's Journey into the World of DanceDocument2 pagesBilly Elliot's Journey into the World of DanceAn Kim Nguyen100% (3)
- The Nature of Securitisation TheoryDocument34 pagesThe Nature of Securitisation TheoryBelén WildnerNo ratings yet
- KuhnDocument8 pagesKuhncandelariaNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No. 120 Series of 2020 Proposed Implementation Arrangement Proposed Next StepsDocument14 pagesExecutive Order No. 120 Series of 2020 Proposed Implementation Arrangement Proposed Next StepsPDRRMO LagunaNo ratings yet
- Globalization in ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGlobalization in ArchitectureShipra AnandNo ratings yet
- Trust Vs MistrustDocument6 pagesTrust Vs MistrustMehdi AdileeNo ratings yet
- Personality DevelopmentDocument67 pagesPersonality Developmentlen lenNo ratings yet