Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atoll 312 General Features Radio
Uploaded by
Mohamed EmadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atoll 312 General Features Radio
Uploaded by
Mohamed EmadCopyright:
Available Formats
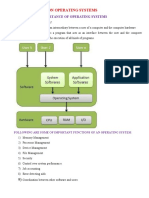
ATOLL GENERAL RADIO FEATURES
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 2 of 95
Atoll General Concepts (1/2)
Multi-Technology Tool
Several technologies modelled:
• 2G (GSM/GPRS/EDGE),
• 3G (UMTS/HSPA, CDMA2000 1xRTT 1xEV-DO, TD-SCDMA),
• 4G (LTE),
• Wi-Fi (802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac),
• WiMAX (802.16e),
• Microwave radio links
3GPP Multi-RAT document available
• Possibility to model GSM, UMTS and LTE in the same Atoll document
Open, Scalable and Flexible Architecture
Core structure + Technology modules (32-bit and 64-bit editions)
API available (Application Programming Interface)
• Allows to create Add-ins and Macros
• Allows third-parties to develop tools that will be compatible with Atoll (such as ACPs, AFPs,
Propagation models, etc.)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 3 of 95
Atoll General Concepts (2/2)
Ergonomic and User-friendly GUI
Windows-based tool
• Easy copy-paste and import-export of data from-into standard applications
Flexibility in Data Management
Possibility to choose what to display, what to filter, etc.
Possibility to add user-defined columns in the tables
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 4 of 95
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 5 of 95
2. Atoll Working Environment
How to Create a New Atoll Document
Atoll General GUI
Tabs of the Menu Bar
Toolbars and Explorer
Workspace
Open and Save an Atoll Document
Archive and Refresh in Multi-User Mode
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 6 of 95
How to Create a New Atoll Document (1/2)
“File → New”
2 Ways of Creating a New Atoll Document
From a document Template
From an existing Database Available Templates
Supported formats
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 7 of 95
How to Create a New Atoll Document (2/2)
Atoll documents / ATL Files
Data are saved in an Atoll document , which is a file with an ATL extension
ATL files can contain one or several technologies
ATL files can be duplicated, opened under any workstation and can only be read by Atoll
Working Modes
Database
.atl User 1
2 working modes with Atoll:
Archive
.atl User 2
Stand-alone: .atl or Multi-user:
Refresh
.atl User i
Document created from a template => Stand-alone document
Document created from an existing database => Multi-user document
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 8 of 95
Atoll General GUI
Document’s technologies Document’s name
Menu bar
Toolbars
Event viewer
Explorer
(Network / Geo Workspace
/ Parameters) (Maps / Tables
/ Reports)
Other windows
(Legend /
Panoramic)
Site
Configuration
Window
Status bar Point Analysis
Tools
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 9 of 95
Tabs of the Menu Bar (1/4)
“File” and “Edit” tabs
Create a new document
Open an existing / recent document
Close the active document Undo / Redo last actions
Save the active document
Cut / Copy / Paste data
Save an area of the map as a into / from the tables
graphic image
Import data in the active
document
Printing functionalities
Quit Atoll
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 10 of 95
Tabs of the Menu Bar (2/4)
“View” and “Document” tabs
Reload map and folders
Select elements on the map
Move the map
Zoom functionalities Calculate predictions
Show the workspace on full Database functionalities
screen
for the multi-user
Explorer documents
(Network/Geo/Parameters)
Audit tools
Event viewer
Other windows XML import / export
(Panoramic/Legend/Site
Configuration) Co-planning
functionalities for Single-
List of toolbars RAT documents
Display or hide the status bar
Properties of the active
Measure distances on the map document
Information about elements on
the map
Display or hide the coordinates
rulers/scale on the map
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 11 of 95
Tabs of the Menu Bar (3/4)
“Tools” tab
Locate an element on the map
Interactive Frequency Planning tool
Site Configuration tool
Profile between two points on the map
CW Measurement analysis tool
Drive tests analysis tool
GSM Interference tool
Point Analysis tool
Microwave link analysis tool
Tool for 360° view (MW only)
Load / Save user configuration files
Configure distributed calculations
List of available Add-ins and Macros
Configure backups of active document
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 12 of 95
Tabs of the Menu Bar (4/4)
“Window” and “Help” tabs
Open a new map window for
the active document
Atoll Help topics
Rest default layout Atoll information
and version
number
Switch between all windows
opened in the workspace
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 13 of 95
Toolbars and Explorer
Toolbars
Radio Planning toolbar Standard toolbar Map toolbar Addins toolbar
Microwave Link Planning toolbar Windows toolbar Vector Editor toolbar
Network / Geo / Parameters Explorer
Made of Folders and Visibility boxes
Order between folders can be changed
Context menus available on each folder
• Properties
• Tables
• Additional functionalities
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 14 of 95
Workspace (1/3)
Possibility to create different tab groups
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 15 of 95
Workspace (2/3)
Possibility to place your active window anywhere in the workspace
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 16 of 95
Workspace (3/3)
Auto-Hide functionality on the Tools
Auto-Hide
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 17 of 95
Open and Save an Atoll Document
Open an existing Atoll document Save the active Atoll document
Possibility to open several ATL files in
the same Atoll platform
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 18 of 95
Archive and Refresh in Multi-User Mode (1/2)
The Atoll document is not connected all the time to the database
Modifications made in the document are not saved in real time in the database
Need to Archive your modifications to the database
Need to Refresh your Atoll document to get the database’s latest modifications
Archive command
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 19 of 95
Archive and Refresh in Multi-User Mode (2/2)
Refresh command
Options if you refresh
while still having some
pending changes not
archived
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 20 of 95
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 21 of 95
3. Geographic Data
Coordinate Systems and Units
Geographic Data Types
Import a Raster-format Geographic Data File
Import a Vector-format Geographic Data File
Resolution Management
Geographic Data Properties
User Configuration File
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 22 of 95
Coordinate Systems and Units
“Document→ Properties...”
Access to
Coordinate
The Projection System Systems
You need to define in Atoll which Map catalogue
Projection System has been used to
obtain your geographic maps
The Display System
You also need to define which
Coordinate System you prefer to use
for the Display in Atoll (used for the
Sites coordinates, position of a point
on the map (in status bar), rulers, etc.)
The Units System
You then need to define which Units will
be used for the Distances (m, km,
miles), the Heights and the Offsets (m,
feet) in Atoll
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 23 of 95
Geographic Data Types
Several Different Geographic Data types are used in an Atoll Document
Example of Geographic Data
Digital Terrain Model
Clutter Classes Used in Propagation calculation
Clutter Heights
Traffic Maps Used in Dimensioning
Population Maps Used in Statistics
Scanned Maps
Used for Display
Contours, lines and points representing Roads, Railways or Regions purposes
Etc.
Atoll supports Geographic Data files of 2 formats
Raster format
• Clutter classes and heights, DTM, images, some traffic and population maps
Vector format
• Polygons, lines and points for display, filtering + some traffic and population maps
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 24 of 95
Import a Raster-format Geographic Data File
The Raster-format Geographic Data files you want to import must be represented in
the same Projection Coordinate System as the one defined in your Atoll document
“File → Import”
Choose
“Altitudes” for a DTM file
“Clutter Classes” for a Clutter Classes file
“Clutter Heights” for a Clutter Heights file
“Image or Scan” for a scanned Image
Etc.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 25 of 95
Import a Vector-format Geographic Data File
When you import a Vector-format Geographic Data file, its coordinate system can be
converted to the one used in your Atoll document
“File → Import”
Coordinate
System
conversion
You need to specify what you will use
Used when
importing a
your Vector file for:
Population a simple layer in the Geo tab
vector file
a Computation Zone
a Focus Zone
a Population map
Etc.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 26 of 95
Resolution Management
Multi-Layer Management
Each Geographic Data file becomes one layer in the Geo tab
Display order of each layer can be changed
If for a specific map type (Clutter Classes, DTM, etc.) you have several files with different
resolutions, you will need to put the one with the highest resolution on top for Atoll to take it
into account in the calculations
Properties of each Geographic Data is accessible from its context menu
(“Right-click → Properties”)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 27 of 95
Geographic Data Properties (1/5)
Tables of Vector maps
Possibility to edit your vector directly from Atoll through its table
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 28 of 95
Geographic Data Properties (2/5)
Properties of Vector maps 3 types of display
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 29 of 95
Geographic Data Properties (3/5)
Properties of DTM Maps
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 30 of 95
Geographic Data Properties (4/5)
Properties of Clutter Classes Maps
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 31 of 95
Geographic Data Properties (5/5)
Properties of Clutter Heights Maps
Clutter Height information provided in the
status bar
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 32 of 95
User Configuration File
User Configuration
Possibility to Import/Export the complete Geographic Data Set from/into a User Configuration
file (.geo)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 33 of 95
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 34 of 95
4. Radio Data
Radio Data Overview
How to Create a Station (Drag and Drop / Duplicate / Import)
Create Repeaters and Remote Antennas
Sites’ Properties
Transmitters’ Properties
Radio Network Equipment
Geographic Profile
Filtering and Grouping Data
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 35 of 95
Radio Data Overview
For Any Technology
Site
• Geographical location where Transmitters are installed
Transmitter
• Radio interface built on a Site and using antennas and equipment such as TMA and feeder cables
Station
• One or several Transmitters sharing the same Site
Repeater
• Device which receives, amplifies and re-transmit the signal from a donor Transmitter
Remote Antenna
• Shifted antenna using the resources of a donor Transmitter
For GSM Documents
Subcell
• Set of TRXs of a same type (BCCH, TCH, TCH inner, TCH GPRS) in a Transmitter
For UMTS, CDMA, LTE, WiMAX and TD-SCDMA Documents
Cell
• Specifications of a Carrier in a Transmitter
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 36 of 95
How to Create a Station
A Station is a Site which has one to several Transmitters
Mains Ways of Creating a Station
Drag and Drop a station template
Duplicate an existing station
Import your lists of Sites / Transmitters / Cells in the corresponding tables
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 37 of 95
Create a Station by Drag and Drop (1/2)
Station Templates Properties
Available in the Parameters Explorer
Templates for each technology
Station Templates in a MultiRAT GSM/UMTS/LTE document Station Templates in a document containing only one technology
In a CDMA2000 document
In a WiMAX document
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 38 of 95
Create a Station by Drag and Drop (2/2)
Drag and Drop a Station Template
1. Choose a Station
Template from the list
2. Click on the icon “New Transmitter or Station”
3. Drag and Drop on the Map
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 39 of 95
Create a Station by Duplicate
Possibility to Create a new Station by Duplicating an Existing one on the Map
Duplicate of Site BRU070
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 40 of 95
Create a Station by Import
Import your Lists of Sites / Transmitters / Cells in the corresponding Tables
Sites’ list in the Sites’ table
Transmitters’ list in the Transmitters’ table
Cells’ list in the Cells’ table
Right-click inside of the table Import
Will add new records and update existing ones
Requirements
Can import *.TXT and *.CSV files
Need to respect the following order
• 2G : sites transmitters
• 3G, 4G and WiMAX : sites transmitters cells
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 41 of 95
Create Repeaters and Remote Antennas
Create a Repeater or a Remote Antenna
1. Click on the Transmitter that will be the Donor Transmitter for the Repeater / Remote
Antenna
2. Click on the right part of the icon “New Repeater or Remote Antenna” to choose what you
want to create
3. Click on the left part of the icon “New Repeater or Remote Antenna” and then Drag and
Drop on the Map
Repeater Remote
Antenna
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 42 of 95
Sites’ Properties (1/4)
Sites’ Properties
The properties dialogue of each Site contain several tabs
User-defined fields (all technologies)
MW-specific fields
UMTS-specific fields
Name of the site
Position and
Altitude of the site
You can enter
comments in
this field
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 43 of 95
Sites’ Properties (2/4)
Sites’ Table
Access all the parameters of all the Sites through the Table
Properties of the Columns Sorting Fill down/up
selected Site functionalities functionalities and Select all
Centre on the
Filtering Align left/centre/right,
Import/Export map the Statistics
functionalities Bold and Italic
selected Site
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 44 of 95
Sites’ Properties (3/4)
Sites’ Display options
Can be set for all the Sites or on a per Site basis
Three display types available:
• Unique - the same symbol will be used for all the Sites
• Discrete values - the display of each Site will be according to the value of a selected field
• Value intervals - the display of each Site will be according to set ranges of the value of a selected field
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 45 of 95
Sites’ Properties (4/4)
Sites’ Display options
Example of the “Unique” and “Discrete values” display types
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 46 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (1/8)
Transmitters’ Properties
In the “General” tab you can setup the name of your transmitter, the site it belongs to, a
possible shift in its antenna position, a comment, etc.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 47 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (2/8)
Transmitters’ Properties
Example: “General” tab of a GSM Transmitter
Name of the transmitter This flag is used to identify the
transmitters of different
technologies, located at the
You can enter an ID for the same site, that share antennas
transmitter
Site on which the transmitter
is located
You can modify the
position of the antenna.
• Relative to Site: select
this option if you want to
enter the antenna
position as an offset with
You can enter comments in respect to the site
this field location
• Coordinates: select this
option if you want to
enter the exact
coordinates of the
antenna
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 48 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (3/8)
Transmitters’ Properties
In the “Transmitter” tab you can setup the activity flag of your transmitter, its type, the power
and losses, the settings of the main and secondary antennas, etc.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 49 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (4/8)
Transmitters’ Properties
Example: “Transmitter” tab of a GSM Transmitter
• Intra-Network (Server and
Activity flag (only active Interferer) = Atoll will consider
transmitters are taken the transmitter as a potential
into consideration during server as well as an interferer
calculations)
• Extra-Network (Interferer
Only) = Atoll will consider the
transmitter as an interferer
only
Power and Losses definition
(Losses can be either user-
defined or calculated by
Atoll according to the
equipment specified in the
“Equipment…” box)
Settings for the main antenna
and the optional secondary
antennas
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 50 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (5/8)
Transmitters’ Table
Access all the parameters of all the Transmitters through the Table
Properties of the Columns Sorting Fill down/up
selected Transmitter functionalities functionalities and Select all
Centre on the
Filtering Align left/centre/right,
Import/Export map the selected Statistics
functionalities Bold and Italic
Transmitter
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 51 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (6/8)
Transmitters’ Display options
Can be set for all the Transmitters or on a per Transmitter basis
Four display types available:
• Unique - the same symbol will be used for all the Transmitters
• Discrete values - the display of each Transmitter will be according to the value of a selected field
• Value intervals - the display of each Transmitter will be according to set ranges of the value of a
selected field
• Automatic - Atoll will automatically assign a colour to each Transmitter, ensuring that each Transmitter
has a different colour than the Transmitters surrounding it.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 52 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (7/8)
Transmitters’ Display options
Example of the “Unique” display type
Change the colour, type and
size of your symbols
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 53 of 95
Transmitters’ Properties (8/8)
Transmitters’ Display options
Example of the “Automatic” display type
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 54 of 95
Radio Network Equipment
In the Parameters Explorer
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 55 of 95
Geographic Profile
Display the Geographic profile from a selected transmitter
You need to select “Profile” and “Geographic” in the Point Analysis tool
“Profile” and
“Geographic”
selected
Selected Transmitter
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 56 of 95
Filtering and Grouping Data (1/4)
Filtering
Anything outside a Filter will not be taken into account during the Calculations
Filtering applies to
Data in tables
• Records filtered out are hidden from the tables
Map
• Records filtered out are hidden from the display
Explorer window
• Records filtered out are hidden from the Explorer display
• Specific “filter” symbol on folders on which a filter is applied
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 57 of 95
Filtering and Grouping Data (2/4)
Types of Filters
Graphical filter (Filtering Zone)
Filter according to Object Attributes (from the Properties or the Tables)
Filter according to Object Filter according to Object
Graphical Filter (Filtering Zone)
Attributes (from the Properties) Attributes (from the Tables)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 58 of 95
Filtering and Grouping Data (3/4)
Grouping
No effect on computations
Applies to Explorer window
• Generate subfolders for each grouping field
o Creation of a manageable table per subfolder
• Specific commands for each subfolder
o Calculations of predictions, neighbours, transmitter activation, frequency planning, etc.
Subfolders
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 59 of 95
Filtering and Grouping Data (4/4)
Types of Groups
Possibility to group data according to a field
• First level grouping from the folder context menu
• Advanced grouping in the general tab of the folder properties dialogue
Possibility to group folder according to the Focus or Computation zones
Grouping according to a zone
First level grouping according to any field in this list
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 60 of 95
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 61 of 95
5. Predictions
How to Create a Prediction
Standard Predictions
Predictions Settings
Computation Zone
Transmitters Propagation Parameters
Path Loss Matrices Storage
Standard Predictions Properties
Calculation Process
Prediction Lists and Templates
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 62 of 95
How to Create a Prediction (1/2)
“Prediction -> New...”
Predictions grouped
by technology
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 63 of 95
How to Create a Prediction (2/2)
Definition of a Prediction
To group, sort and filter the
results of the prediction
To calculate the prediction
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 64 of 95
Standard Predictions (1/2)
Coverage by Transmitter
Need to choose the “Automatic” display type for the Transmitters
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 65 of 95
Standard Predictions (2/2)
Coverage by Signal Level
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 66 of 95
Predictions Settings
Workflow:
(1) Create a Computation Zone
(2) Define the Transmitters’ propagation settings
(3) Define the Path Loss matrices storage directories
(4) Define the parameters in the “Conditions” tab of the prediction’s properties
(5) Define the parameters in the “Display” tab of the prediction’s properties
(6) Calculate the prediction
(7) Display the prediction
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 67 of 95
Computation Zone (1/2)
Use of the Computation Zone
Define which Transmitters have to be taken into account in the calculation
Define in which area the prediction plot will be displayed
Create a Computation Zone
Draw it on the map
Import specific coordinates in the Computation Zone’s properties
Use an existing polygon as the Computation Zone
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 68 of 95
Computation Zone (2/2)
Create a Computation Zone
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 69 of 95
Transmitters Propagation Parameters (1/2)
Powers / Antennas / Activity parameters
Example for a GSM Transmitter:
If not active, the
transmitter will not be
taken into account in
the prediction
Power definition
Antennas definition
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 70 of 95
Transmitters Propagation Parameters (2/2)
Propagation Model / Calculation Radius / Grid Resolution
Example for a GSM Transmitter:
Extended path loss
matrix if you want to use
different propagation
models/calculation
radius and grid
resolutions close and far
from the transmitter
List of propagation models
available in your document
Calculation radius of the
transmitter’s path loss
matrix
Grid resolution of the
transmitter’s path loss
matrix
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 71 of 95
Path Loss Matrices Storage
Path Loss Matrices Storage Directories
Directory where will
be stored the path
loss matrices you
generate
If you are loading
path loss matrices
from the shared
directory, any path
loss matrix that
needs to be
recalculated will be
saved in the Private
Used in Multi-user mode. Directory
directory
where the common path loss matrices
are stored and accessible to all users.
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 72 of 95
Standard Predictions Properties (1/4)
Conditions Tab
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 73 of 95
Standard Predictions Properties (2/4)
Conditions Tab
Can choose upper and lower thresholds for the Signal level (or Path Loss/Total Losses)
• for GSM, the lower threshold can either be user-defined (Global C threshold) or taken from the values
in the Subcell table (Subcell C threshold)
Different options to be considered as a Serving transmitter
• possibility to add a margin to the Server condition (handover margin)
GSM-related
options
Handover margin
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 74 of 95
Standard Predictions Properties (3/4)
Conditions Tab
Possibility to model Shadowing and Indoor coverage
• Shadowing modelled by adding to the link budget an additional loss according to the cell-edge
coverage probability
• Indoor coverage modelled by adding to the link budget an additional loss according to the clutter class
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 75 of 95
Standard Predictions Properties (4/4)
Display tab
Default display type for the Default display type for the
“Coverage by Transmitter” prediction “Coverage by Signal Level” prediction
Three display types available: Possibility to use the “Shading” option to create
• Unique automatically a shading of colours from a “Start colour”
• Discrete values to an “End colour”
• Value intervals
You can also use the “Shading” option to create the
different thresholds automatically with a regular interval
between them (First Break, Last Break and Interval)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 76 of 95
Calculation Process
Requirements for a Transmitter to be taken into account in the calculation
Active
Filtered (Transmitter or Site folder)
Calculation area intersecting the rectangle including the Computation Zone
Calculation process
1) Calculate the Path Loss matrices
• Atoll will calculate the Path Loss matrices missing
• Atoll will recalculate an existing Path Loss matrix if one parameter related to the propagation has been
changed (parameters such as the antenna type / azimuth / height, the propagation model, the matrix
calculation radius, the computation zone, etc.)
2) Create the plot
3) Lock the plot
• After a prediction has been calculated, a “lock” symbol will appear on it
• This lock symbol will prevent Atoll from recalculating the prediction if you press on the “Calculate” icon
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 77 of 95
Prediction Management (1/3)
User Configuration File
Possibility to save the definition of your predictions in a User Configuration file
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 78 of 95
Prediction Management (2/3)
Customised Predictions
Possibility to save a prediction as a Template (=Customised Prediction)
The list of templates will appear under the “Customised Predictions” folder
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 79 of 95
Prediction Management (3/3)
Predictions Folder
Possibility to group predictions in subfolders
Predictions can be moved to folders using drag and drop
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 80 of 95
Training Programme
1. Atoll General Concepts
2. Atoll Working Environment
3. Geographic Data
4. Radio Data
5. Predictions
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 81 of 95
6. Prediction Analysis, Reports and Exports
Point Analysis
Prediction Plot
Reports
Histogram
Exports
Printing Functionality
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 82 of 95
Point Analysis (1/2)
Profile Tab
In the “Profile” tab you have access to real-time calculations (Path Loss matrices not needed)
Real-time calculation
(“Signal Level” or
“Path Loss” or “Total
Losses” based on the
Result type chosen in
the Options dialogue)
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 83 of 95
Point Analysis (2/2)
Reception Tab
In the “Reception” tab you can see the signal levels received (Path Loss matrices needed)
Links between the
location and the
Transmitters received
Signal levels received
at that location from
various Transmitters
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 84 of 95
Prediction Plot
Tip Text and Legend
The Tip text and the Legend allow the visual analysis of the plot
Tip text
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 85 of 95
Reports (1/2)
Hierarchy between Zones
Without any zone Filtering Zone Computation Zone Focus Zone
Reporting Priorities between Focus and Computation Zones
If a Focus Zone exists, the report will be based on the Focus Zone
If there is no Focus Zone, but there is a Computation Zone, the report will be based on the
Computation Zone
If there is no Focus or Computation Zone, the report will be based on the covered area
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 86 of 95
Reports (2/2)
Reporting Priorities between Focus and Computation Zones
Focus Zone (green)
Report based on the Focus Zone and Computation
Zone (red) defined
Only Computation
Report based on the Computation Zone Zone (red) defined
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 87 of 95
Histogram
Histogram
The Histogram follows the same rule than the Report when it comes to the priorities between
the Focus and the Computation Zones
You can also display the CDF and the Inverse CDF
You can select and zoom on a specific histogram part
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 88 of 95
Exports (1/4)
Image Export
Copy-Pasting into another application a selected zone (Focus Zone, Computation Zone...)
Copy the selected zone
Paste the
selected area
into another
application
Selected zone pasted into a Word document
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 89 of 95
Exports (2/4)
Image Export
Saving as an Image a selected zone from the map or the Geo tab
Available formats
Selected zone saved as a BMP file
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 90 of 95
Exports (3/4)
Prediction Export
You can export one single prediction or several predictions simultaneously (from Predictions
folder or any Predictions subfolder)
Export of several
predictions simultaneously
Export of one
single prediction
Available formats : or If raster export not supported
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 91 of 95
Exports (4/4)
Geographic Export Zone
You can define a zone that will be used to export a part of the map or a prediction in a raster-
format
Save the area of the map which is
inside of the Geographic Export
Zone as an image
Export a prediction in a raster-format
and choose to only export the area
inside of the Geographic Export Zone
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 92 of 95
Printing Functionality (1/2)
Define the Printing Zone
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 93 of 95
Printing Functionality (2/2)
Print Setup and Preview
© Forsk 2012 Confidential – Do not share without prior permission Slide 94 of 95
THANK YOU!
You might also like
- Better - Homes.&.gardens Secrets - Of.getting - Organized.early - Spring.2020 P2PDocument100 pagesBetter - Homes.&.gardens Secrets - Of.getting - Organized.early - Spring.2020 P2PPaul Mitriș88% (8)
- Snowflake Snowpro Certification Exam Cheat Sheet by Jeno YammaDocument7 pagesSnowflake Snowpro Certification Exam Cheat Sheet by Jeno YammaRavi Chandra100% (1)
- Zdlra 2020 V2Document53 pagesZdlra 2020 V2Tran Quoc DungNo ratings yet
- TN045 Atoll Scripting Tutorial 3.0Document8 pagesTN045 Atoll Scripting Tutorial 3.0Optimización RFNo ratings yet
- Issues DatastageDocument4 pagesIssues DatastagerkpoluNo ratings yet
- Oracle Data Guard 12c PDFDocument53 pagesOracle Data Guard 12c PDFSrinivas EllendulaNo ratings yet
- Testing PentestDocument53 pagesTesting Pentesttapion_solNo ratings yet
- Atoll 3.4.1 General Features Radio 5G NRDocument114 pagesAtoll 3.4.1 General Features Radio 5G NRmdanishaminNo ratings yet
- Insar Tutorial With NESTDocument100 pagesInsar Tutorial With NESTAdito MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Atoll GSM Training SlidesDocument128 pagesAtoll GSM Training SlidesClaudio Ramón López MezaNo ratings yet
- GTTC ReportDocument27 pagesGTTC ReportDhavan Y Kumar100% (2)
- CW Test and Propagation Model Tuning FILEminimizerDocument59 pagesCW Test and Propagation Model Tuning FILEminimizerMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Cadence Fpga Board Design FSP Intro PRESENTATIONDocument18 pagesCadence Fpga Board Design FSP Intro PRESENTATIONsamarra250% (1)
- Dimetra IP System OverviewDocument201 pagesDimetra IP System OverviewMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- CafeTele Guest Expert - Gaurav Goyal - ATOLLDocument61 pagesCafeTele Guest Expert - Gaurav Goyal - ATOLLLeonardo CalleNo ratings yet
- System Architecture (Old) : Team Project Name ManifestDocument6 pagesSystem Architecture (Old) : Team Project Name ManifestTobias SjögrenNo ratings yet
- CAT Gr11 Theory MEMO Nov2018 StudyOppDocument12 pagesCAT Gr11 Theory MEMO Nov2018 StudyOppvuyimakamu2No ratings yet
- CS 351 Database Management Systems 1 Prelims Notes 1Document10 pagesCS 351 Database Management Systems 1 Prelims Notes 1Leighyvy HehdgeNo ratings yet
- Intro To Petrel 2009Document30 pagesIntro To Petrel 2009alicNo ratings yet
- UPR PATSI Training: Introduction To Oracle DiscovererDocument32 pagesUPR PATSI Training: Introduction To Oracle DiscovereralejandromoraNo ratings yet
- The Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) Version 5: December 2011Document4 pagesThe Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) Version 5: December 2011Okfis KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Database: Suchindran Kannan Sathishkumar RangarajDocument29 pagesAutonomous Database: Suchindran Kannan Sathishkumar Rangarajgreenland1212No ratings yet
- Middleware SystemsDocument5 pagesMiddleware Systemsdameantd0310No ratings yet
- Basic Radar Altimetry Toolbox Practical: V. Rosmorduc (CLS)Document32 pagesBasic Radar Altimetry Toolbox Practical: V. Rosmorduc (CLS)MAnohar KumarNo ratings yet
- Os QBDocument39 pagesOs QBBenitaarunNo ratings yet
- File Matadata Tool Use CaseDocument11 pagesFile Matadata Tool Use CaseSantosh kumar beheraNo ratings yet
- A Study of Open-Source Data Mining Tools For Forecasting: Nurdatillah Hasim Norhaidah Abu HarisDocument4 pagesA Study of Open-Source Data Mining Tools For Forecasting: Nurdatillah Hasim Norhaidah Abu HarisPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Paper2018 MsDocument16 pagesComputer Science Paper2018 MsTaksh PathakNo ratings yet
- Atoll Vs Planet PDF FreeDocument4 pagesAtoll Vs Planet PDF FreeAmjad MsoukerNo ratings yet
- Arelle Users ManualDocument27 pagesArelle Users Manualjuanp1256No ratings yet
- Lesson 4, 5: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLesson 4, 5: ObjectivesAzan KhanNo ratings yet
- ABB Remote Support ServiceDocument13 pagesABB Remote Support Servicemostafagoly1358No ratings yet
- Esmvaltool V2.0: Technical OverviewDocument16 pagesEsmvaltool V2.0: Technical Overviewsuraj.atmos458No ratings yet
- C 2 O S O: Hapter Perating Ystem VerviewDocument3 pagesC 2 O S O: Hapter Perating Ystem VerviewFaizan RahimNo ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument6 pagesOperating System NotesRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Architecture: 1. 1. Layers and ComponentsDocument4 pagesArchitecture: 1. 1. Layers and Componentseling.laura3382No ratings yet
- Cat Gr11 Theory Memo Jun2013 StudyoppDocument8 pagesCat Gr11 Theory Memo Jun2013 StudyoppKatie ArendseNo ratings yet
- OPERATING SYSTEM in KenyaDocument61 pagesOPERATING SYSTEM in KenyaNickNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document137 pagesDay 1tonystark8052No ratings yet
- LLT Release NoteDocument14 pagesLLT Release Notesiddharth bandekarNo ratings yet
- Monitoring-Management-Tools - ReqmntsDocument7 pagesMonitoring-Management-Tools - ReqmntsairaceNo ratings yet
- ADB HOL # 3-2 - Connect With SQL - Plus - Oracle CommunityDocument4 pagesADB HOL # 3-2 - Connect With SQL - Plus - Oracle CommunityDang Huu AnhNo ratings yet
- CS3451 Operating SystemDocument96 pagesCS3451 Operating Systempassion jobNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To OsDocument15 pages1.introduction To OsEddy AyattaNo ratings yet
- Selector Web - DefinitionsDocument8 pagesSelector Web - Definitionsa_kumkumaNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Data Engineering Full NotesDocument39 pagesFoundation in Data Engineering Full NotesMoNo ratings yet
- ECDL / ICDL Computer Essentials: Syllabus Version 1.0Document9 pagesECDL / ICDL Computer Essentials: Syllabus Version 1.0Ismail Isko HasanovićNo ratings yet
- BD & CCDocument3 pagesBD & CCpratuaroskarNo ratings yet
- 62 Cbse Main Ict Curriculum Class Ix XDocument4 pages62 Cbse Main Ict Curriculum Class Ix XprasadNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Paper 1 HL MarkschemeDocument16 pagesComputer Science Paper 1 HL Markschemedonn dadaNo ratings yet
- Stop Global WarmingDocument10 pagesStop Global Warmingspsuman05No ratings yet
- Unit - 4-CloudDocument122 pagesUnit - 4-CloudsujayNo ratings yet
- Getting Started SCILAB PDFDocument56 pagesGetting Started SCILAB PDFmajutakgentarNo ratings yet
- CSE312 Sınav Öncesi TekrarDocument27 pagesCSE312 Sınav Öncesi TekraraktarmamailimNo ratings yet
- Rstudio Allows The User To Run R in A More User-Friendly Environment. It Is Open-Source (I.E. Free) and Available atDocument15 pagesRstudio Allows The User To Run R in A More User-Friendly Environment. It Is Open-Source (I.E. Free) and Available atRasel AhamedNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts About RACDocument40 pagesInteresting Facts About RACBlack SwanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Big Data Ecosystem - 06.05.18Document21 pagesUnit 5 - Big Data Ecosystem - 06.05.18Asmita GolawtiyaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Discoverer: An OverviewDocument9 pagesOracle Discoverer: An OverviewRamesh SingNo ratings yet
- Complete Endpoint Management: System RequirementsDocument2 pagesComplete Endpoint Management: System Requirementsyehtetlay42No ratings yet
- Introduc) On To BigdataDocument103 pagesIntroduc) On To BigdataSivaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Delphi ORM: Object Relational Mapping Using TMS AureliusFrom EverandIntroducing Delphi ORM: Object Relational Mapping Using TMS AureliusNo ratings yet
- Best Free Open Source Data Recovery Apps for Mac OS English EditionFrom EverandBest Free Open Source Data Recovery Apps for Mac OS English EditionNo ratings yet
- Ra'ed AL-Omari: Telecommunication and Radio Networking Engineer With 15+ Years of Industry ExperienceDocument4 pagesRa'ed AL-Omari: Telecommunication and Radio Networking Engineer With 15+ Years of Industry ExperienceMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Adel Adel Abd El-Maged Mergawy (Updated CV) PDFDocument3 pagesAdel Adel Abd El-Maged Mergawy (Updated CV) PDFMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Emad C.VDocument3 pagesMohamed Emad C.VMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- NSN Lte ImplementationDocument52 pagesNSN Lte ImplementationMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Link Budget Lte UplinkDocument3 pagesDokumen - Tips - Link Budget Lte UplinkMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Atoll Measurement CalibrationDocument55 pagesAtoll Measurement CalibrationMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- FE20 P032 ReportDocument90 pagesFE20 P032 ReportMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Atoll Test Report CompleteDocument121 pagesAtoll Test Report CompleteMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Omar Younis Salama CVDocument2 pagesOmar Younis Salama CVMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Solutions 3rd Int WB Keys by Victoria - IssuuDocument1 pageSolutions 3rd Int WB Keys by Victoria - Issuumatergaming110No ratings yet
- Monthly Test Syllabus Date SheetDocument5 pagesMonthly Test Syllabus Date SheetIbrahim BilalNo ratings yet
- Mobile: 0755/0715 912 366: Rashid AbdalahmanDocument44 pagesMobile: 0755/0715 912 366: Rashid Abdalahmanpaco kazunguNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Media On Creativity and Innovation in The Modern Business WorldDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Social Media On Creativity and Innovation in The Modern Business WorldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Neural CryptographyDocument13 pagesNeural CryptographyManoj SinghNo ratings yet
- Metodos Estaticos: FECHA: 18/04/2023Document4 pagesMetodos Estaticos: FECHA: 18/04/2023Lucio MercadoNo ratings yet
- Manish Kumar KaushalDocument2 pagesManish Kumar KaushalManish KaushalNo ratings yet
- UssdDocument5 pagesUssdcalboresNo ratings yet
- 1GIS ScienceDocument537 pages1GIS ScienceANa FilipovicNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesNova Tenorio Peret-FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Banner Form DescDocument62 pagesBanner Form DesckvukonicNo ratings yet
- Yamaha mw8cx 8 CH MixerDocument37 pagesYamaha mw8cx 8 CH MixerLachlanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For e Marketing 7 e Judy Strauss Raymond FrostDocument11 pagesSolution Manual For e Marketing 7 e Judy Strauss Raymond FrostMaynard Mcdaniel100% (30)
- Game Design WorkshopDocument80 pagesGame Design WorkshopAccióDigital FtpNo ratings yet
- Turn Off Windows File ProtectionDocument3 pagesTurn Off Windows File ProtectionCitra ArumiaNo ratings yet
- Resume Biyuni ChalukaDocument2 pagesResume Biyuni ChalukaJenniferNo ratings yet
- How To Add Arduino Gas Sensor Library in To Proteus ISIS 7 & 8 - Electronics Lovers Technology We LoveDocument10 pagesHow To Add Arduino Gas Sensor Library in To Proteus ISIS 7 & 8 - Electronics Lovers Technology We LoveindoramaNo ratings yet
- IBM System I5 HandbookDocument442 pagesIBM System I5 Handbookdzope2002100% (2)
- A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToDocument2 pagesA Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToPaulo Taganas MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument44 pagesGraph TheoryAkash AkmNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Gaming AppsDocument12 pagesA Case Study On Gaming AppsRehan ShahNo ratings yet
- SUZO Hopper: August 99 6501 0760Document6 pagesSUZO Hopper: August 99 6501 0760willian eduardo santiago cardenasNo ratings yet
- Din 824-1981Document4 pagesDin 824-1981juan caNo ratings yet
- Error For FilesDocument23 pagesError For FilesGaurav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)Document10 pagesAnatomy of Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)Ecuaman EcuamanNo ratings yet
- Alarm Annunciators With Plastic EnclosureDocument14 pagesAlarm Annunciators With Plastic EnclosureswarupkumarnayakNo ratings yet