Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economics Utility
Uploaded by
fazle rabby MobinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economics Utility
Uploaded by
fazle rabby MobinCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Utility?
Utility is the total satisfaction or benefits derived from consuming a good or service. Economic
theories based on rational choice usually assume that consumers will strive to maximize their
utility.
Ordinal Utility
In economics, an ordinal utility function is a function representing the preferences of an agent on an
ordinal scale. Ordinal utility theory claims that it is only meaningful to ask which option is better than
the other, but it is meaningless to ask how much better it is or how good it is.
Cardinal Utility
The cardinal utility states that the level of satisfaction a consumer acquires after
consuming any goods and services can be measurable and expressed in quantitative
numbers.
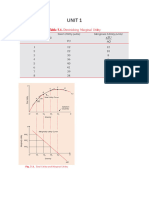
Total Utility
Total utility refers to the amount of satisfaction that a consumer derives from a
specific product or service. It is simply an individual sum of units of all the
marginal utilities.
Marginal Utility
Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit
of a good or service.
Law of diminishing marginal utility.
According to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, marginal utility of a good diminishes as
an individual consumes more units of a good. In other words, as a consumer takes more
units of a good, the extra utility or satisfaction that he derives from an extra unit of the good
goes on falling.
Equi-marginal principle
The equi-marginal principle states that a consumer will be maximizing his total utility when
he allocates his fixed money income in such a way that the utility derived from the last
unit of money spent on each good is equal.
You might also like
- Micro 111 C4 by NayemDocument19 pagesMicro 111 C4 by NayemHasibul Hasan NayemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Reporter: Caballero, DianneDocument14 pagesChapter 6: Reporter: Caballero, Dianne박니치No ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument3 pagesEconomics AssignmentannudusonNo ratings yet
- Um, TuDocument3 pagesUm, TuSebasNo ratings yet
- EconDocument2 pagesEconkedasalandyNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Utility Bhavik 11 TH GDocument10 pagesCardinal Utility Bhavik 11 TH GBhavik gamerNo ratings yet
- Econ 121 Chapter 6Document15 pagesEcon 121 Chapter 6silenthitman775% (4)
- Demand and Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesDemand and Consumer BehaviorBasit KhanNo ratings yet
- INDIAN SCHOOL SOHARDocument29 pagesINDIAN SCHOOL SOHARRitaNo ratings yet
- Basic Micro Reporting5B15DDocument43 pagesBasic Micro Reporting5B15DSheila Mae FajutaganaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 EconomicsDocument9 pagesGrade 10 Economicsdinsaregassa2020No ratings yet
- Eco 7Document30 pagesEco 7Ramish AsifNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Total Utility Dan Marginal UtilityDocument14 pagesPengertian Total Utility Dan Marginal UtilityBella Novitasari100% (4)
- Consumer TheoryDocument12 pagesConsumer TheoryKyla TorcatosNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument5 pagesUtility Analysisp.naliniNo ratings yet
- The Consumer Theory-How They Make The ChoiceDocument42 pagesThe Consumer Theory-How They Make The ChoicePreetham Prinson D'souzaNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Demand Theory Utility ApproachDocument42 pagesConsumer and Demand Theory Utility ApproachrueNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 05Document5 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 05Hasimuddin TafadarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 in CBM 'Document1 pageLecture 3 in CBM 'Kem JennlahNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument15 pagesConsumer BehaviorSaurabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Concept of UtilityDocument20 pagesCH - 3 Concept of UtilityAfzal AhmadNo ratings yet
- UTILITY AnalysisDocument2 pagesUTILITY AnalysisImtiaz RashidNo ratings yet
- M2 L4 Basic MicroeconomicsDocument21 pagesM2 L4 Basic MicroeconomicsBERNARD CALZARNo ratings yet
- The Theoryof Consumer Behavior: Applied Economics 12Document11 pagesThe Theoryof Consumer Behavior: Applied Economics 12Jannah EnrileNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour and Utility MaximizationDocument15 pagesConsumer Behaviour and Utility MaximizationBilalTariq100% (1)
- Assignment - Managerial Economics Riya Singh 19FLICDDNO1106Document4 pagesAssignment - Managerial Economics Riya Singh 19FLICDDNO1106riyaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Consumption and Production Behavior A: The Theory of ConsumptionDocument2 pagesThe Theory of Consumption and Production Behavior A: The Theory of ConsumptionLeslie SearsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Economics 13th Edition Michael ParkinDocument16 pagesSolution Manual For Economics 13th Edition Michael ParkinStevenMurrayxqjny100% (84)
- Me 4Document11 pagesMe 4Jit KhandorNo ratings yet
- Utility PrintDocument17 pagesUtility Printtahsim laptopNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ Module 1 Unit 2Document7 pagesApplied Econ Module 1 Unit 2CES DOROTHY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- Marginal UtilityDocument37 pagesMarginal UtilityBipasha NiyogiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and MaximizationDocument24 pagesConsumer Behavior and MaximizationZJ CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Elmer Juares Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Topic - Consumer Theory: Rajagiri Business School Kakkanad ERNAKULAM - 682039Document6 pagesTopic - Consumer Theory: Rajagiri Business School Kakkanad ERNAKULAM - 682039Tijo ThomasNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument52 pagesEconomicssredha mathewNo ratings yet
- Economics For Managers: Unit - 2Document68 pagesEconomics For Managers: Unit - 2srinivasa_rcNo ratings yet
- Economics ProjectDocument8 pagesEconomics ProjectAshvika JMNo ratings yet
- Economics: Submitted To DR. Adeel SaleemDocument31 pagesEconomics: Submitted To DR. Adeel SaleemMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Consumer'S Behavior Theory: Rhyan Mike R. BacaroDocument12 pagesConsumer'S Behavior Theory: Rhyan Mike R. BacaroLovelyn Ramirez100% (1)
- Introduction To Economics Bs-It 5 Semester: Teacher Name: Fizza ShaukatDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Economics Bs-It 5 Semester: Teacher Name: Fizza Shaukatwarda abbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Theory of Consumer Behavior or Choice: Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Theory of Consumer Behavior or Choice: Introduction To MicroeconomicsElijah Reign RodrigoNo ratings yet
- ECONDocument16 pagesECONDon Michaelangelo BesabellaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics For Today 9th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual DownloadDocument11 pagesMicroeconomics For Today 9th Edition Tucker Solutions Manual DownloadPeggy Lopez100% (22)
- Lecture 5Document58 pagesLecture 5Nikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer DemandDocument28 pagesTheory of Consumer DemandTimothy StanislausNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics-I Chapter - One AndThreeDocument41 pagesMicro Economics-I Chapter - One AndThreeYonatanNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics: Consumer Behavior and Utility MaximizationDocument13 pagesMicro Economics: Consumer Behavior and Utility MaximizationsamitunioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10-Theory of Consumer's BehaviorDocument75 pagesLesson 10-Theory of Consumer's BehaviorGracielle Espiritu80% (5)
- Consumer BehaviourDocument9 pagesConsumer BehaviourAlex HongoNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Chapter-Two: Theory of DemandDocument37 pagesManagerial Economics Chapter-Two: Theory of Demandabey.mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument4 pagesConsumer BehaviorGrace G. ServanoNo ratings yet
- Utility AnalysisDocument14 pagesUtility AnalysisJigar PethaniNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Presentation ON Utility: Presented By: Vishnu S1 MbaDocument11 pagesWelcome To The Presentation ON Utility: Presented By: Vishnu S1 MbariyasacademicNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Utility AnalysisDocument9 pagesCardinal Utility AnalysisVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- WWW Investopedia Com Terms C Consumer - Surplus Asp - Text A 20consumer 20surplus 20happens 20when They 20were 20willing 20to 20payDocument4 pagesWWW Investopedia Com Terms C Consumer - Surplus Asp - Text A 20consumer 20surplus 20happens 20when They 20were 20willing 20to 20payᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument15 pagesConsumer BehaviorEunice Laarnie SimonNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection in India: A brief Guide on the Subject along with the Specimen form of a ComplaintFrom EverandConsumer Protection in India: A brief Guide on the Subject along with the Specimen form of a ComplaintNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Triple Revenue Growth: Mastering Value-Added StrategiesFrom EverandUnlocking Triple Revenue Growth: Mastering Value-Added StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Summary, Analysis & Review of Robbie Kellman Baxter's The Membership Economy by InstareadFrom EverandSummary, Analysis & Review of Robbie Kellman Baxter's The Membership Economy by InstareadNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument3 pagesSurveyfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- System TaskDocument1 pageSystem Taskfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Routine of Clas 6Document1 pageRoutine of Clas 6fazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment FormDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Formfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Research Topic SubmissionDocument3 pagesResearch Topic Submissionfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Eco 104 Quiz 2Document3 pagesEco 104 Quiz 2fazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Title: Good Show, Great Teaching: 1 Body ParagraphDocument1 pageTitle: Good Show, Great Teaching: 1 Body Paragraphfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet
- Eco104 MidtermDocument5 pagesEco104 Midtermfazle rabby MobinNo ratings yet