Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
Uploaded by
Dharan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageOriginal Title
DOC_2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page2
Uploaded by
DharanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
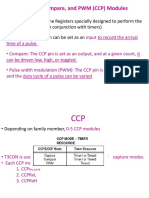
Figure
8.10. Circuit diagram of the project. In this project, the 40
kHz PW1 signal is output from pin OC1 (or RD0, pin 72) of the
microcontroller. If you are using the LV-32MX V6 development board,
then the following jumper must be set as follows: DIP switch SW20,
jumper 8, set to ON 8.2.3 Project PDL Before developing the PDL for
this project, it is important to understand how the project works.
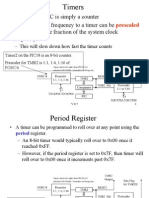
The PWM module inside the PIC32 microcontroller uses a timer to
control the signal frequency and duty cycle. The period of the
generated PWM signal is given by the following: PWM Period = [(PR +
1) × TPB × (Timer prescaler value)] where PR is the value loaded
into the period register, and TPB is the clock period of the
peripheral clock. Assuming a peripheral clock frequency of 80 MHz,
the peripheral clock period is given by the following: TPB = 1/(80 ×
10−6) = 0.0125 × 10−6 s We are normally interested in finding the
value to be loaded into the period register. Assuming that we are
using Timer 2 (Timer 1 cannot be used in PWM mode), the value loaded
into this register is calculated as follows: Also, PWM frequency =
1/[PWM Period] The PWM duty cycle is specified by writing to the
OCxRS register. The maximum PWM duty cycle resolution is calculated
using the following formula: where, FPB is the peripheral clock
frequency, and FPWM is the clock frequency of the PWM signal to be
generated. The specifications of this project are summarized below: •
Frequency of the PWM signal = 40 MHz (or, period = 0.025 × 10−3 s) •
Peripheral bus clock frequency = 80 MHz (or 0.0125 × 10−6 s) • Timer
to be used = Timer 2 • Timer 2 prescaler value = 1 • Duty cycle =
50%. The value to be loaded into period register PR2 is calculated as
follows: The maximum PWM resolution is calculated as follows: The
steps for configuring the PWM module for the above specifications are
given below (notice that since we are using output pin OC1, the
register OCxCON is the register OC1CON): • Calculate the PWM period
(0.025 × 10−3) • Calculate the PWM duty cycle (50%) • Use Timer 2 in
16-bit mode • Clear register OC1CON, bit 5 (OC32) for 16-bit
operation • Load PR2 with decimal 1999 • Load OC1RS low 16-bits with
duty cycle (50% duty cycle corresponds to 1999/2 = decimal 1000) • No
interrupts required • Set OCM bits of OC1CON to six to enable PWM
mode of operation • Select Timer 2 as the timer source • Clear TCKPS
bits of T2CON to set Timer 2 prescal
You might also like
- Supply Voltage: Download Full-Size ImageDocument7 pagesSupply Voltage: Download Full-Size ImageDharanNo ratings yet
- Generate 40kHz PWM Waveform with 50% Duty CycleDocument8 pagesGenerate 40kHz PWM Waveform with 50% Duty CycleDharanNo ratings yet
- 211Document1 page211DharanNo ratings yet
- CCP PWMDocument19 pagesCCP PWMalaa_saq100% (1)
- 5.2 PWM 7 Mac 2017Document34 pages5.2 PWM 7 Mac 2017Elawarasi Nadarajan100% (1)
- MICRO Servo Motor Control using PIC16F877ADocument12 pagesMICRO Servo Motor Control using PIC16F877Aeeindustrial100% (1)
- PIC (PWM PGM Steps)Document20 pagesPIC (PWM PGM Steps)Elena Gilbert100% (2)
- PIC18F4550 PWM - PIC ControllersDocument7 pagesPIC18F4550 PWM - PIC ControllersKrishanu Modak100% (2)
- Defense MechanismDocument27 pagesDefense MechanismgkkishorekumarNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5 - Part 2 PWMDocument30 pagesTOPIC 5 - Part 2 PWMSharifah SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- PWMDocument17 pagesPWMmaintboardNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed ControlDocument5 pagesDC Motor Speed ControlAnita WulansariNo ratings yet
- HBridgeMotorControl With PICDocument11 pagesHBridgeMotorControl With PICcoceicr100% (3)
- Osmeoisis 2022-09-06 15-33-19PIC - Enh - A - 18Document50 pagesOsmeoisis 2022-09-06 15-33-19PIC - Enh - A - 18Tomás BurónNo ratings yet
- The University of Texas at Arlington Timers, Capture/Compare/PWMDocument22 pagesThe University of Texas at Arlington Timers, Capture/Compare/PWMadamwaiz100% (1)
- Tata 1Document20 pagesTata 1vamsidhar999No ratings yet
- AVR_Timers0Document32 pagesAVR_Timers0Muhammad ejaz RamzanNo ratings yet
- Timers and PWM on PIC MicrocontrollersDocument38 pagesTimers and PWM on PIC MicrocontrollersThanh LeNo ratings yet
- PIC PWM LabDocument9 pagesPIC PWM LabGhulam E Muhammad Usman100% (1)
- ES Exp 10Document13 pagesES Exp 10Maryam TariqNo ratings yet
- PWM Speed & Direction Control of DC Motor: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesPWM Speed & Direction Control of DC Motor: Objectivevipulkondekar100% (1)
- UG - EC303 DSP Part-6 On-Chip Peripherals-Print PDFDocument20 pagesUG - EC303 DSP Part-6 On-Chip Peripherals-Print PDFapuurvaNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave Generation and Implementation Using DsPIC33FJDocument27 pagesSine Wave Generation and Implementation Using DsPIC33FJpaaraib100% (1)
- Sesion - 11 - Timer 2 y PWMDocument22 pagesSesion - 11 - Timer 2 y PWMMafa GuillénNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave GeneratorDocument12 pagesSine Wave GeneratorkjfensNo ratings yet
- LPC214x Architecture - Peripherals and ProgrammingDocument44 pagesLPC214x Architecture - Peripherals and ProgrammingAbhijeet ShekharNo ratings yet
- Sine Wave Generation and Implementation Using dsPIC33FJDocument27 pagesSine Wave Generation and Implementation Using dsPIC33FJTahmid100% (10)
- Micro Lab 6Document10 pagesMicro Lab 6Hacker YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- AN594 - Using The CCP Module(s)Document25 pagesAN594 - Using The CCP Module(s)Guillermo Hernandez100% (3)
- Microcontrollers LabDocument19 pagesMicrocontrollers LabAMARNATHNAIDU77No ratings yet
- Timer Counter Modes 8051 Microprocessor DesignDocument30 pagesTimer Counter Modes 8051 Microprocessor Designcleopatra2121No ratings yet
- Control DC Motor Speed using STM32 PWMDocument4 pagesControl DC Motor Speed using STM32 PWMJohn FarandisNo ratings yet
- Controlling Interrupt Frequencies - LectureDocument16 pagesControlling Interrupt Frequencies - Lectureraajeshn18No ratings yet
- Timers of ATmega328PDocument26 pagesTimers of ATmega328PZaryab Khalil SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Osmeoisis 2022-09-06 15-33-19PIC - Mid - C - 12Document42 pagesOsmeoisis 2022-09-06 15-33-19PIC - Mid - C - 12Tomás BurónNo ratings yet
- CCP ModuleDocument11 pagesCCP ModuleAltaaf Mulani100% (1)
- LPC2148 PWM Programming GuideDocument14 pagesLPC2148 PWM Programming GuideVinothkumar UrumanNo ratings yet
- ECPE18 DSP Part-6 On-Chip PeripheralsDocument20 pagesECPE18 DSP Part-6 On-Chip PeripheralseyantranccaflightNo ratings yet
- Subject: Student: Practice Name: Digital Systems 2Document2 pagesSubject: Student: Practice Name: Digital Systems 2Yamil López PérezNo ratings yet
- EET203 Tutorial TimerDocument2 pagesEET203 Tutorial Timerkay_rolNo ratings yet
- Timer 1Document6 pagesTimer 1joxenoNo ratings yet
- Time Division Multiplexing & DemultiplexingDocument11 pagesTime Division Multiplexing & Demultiplexingaeganajith9No ratings yet
- CHP 3 - Pic Timer Programming in CDocument12 pagesCHP 3 - Pic Timer Programming in CTajuddin Razali100% (1)
- ATMPWMDocument6 pagesATMPWMOkiPetrus Hutauruk LumbanBaringinNo ratings yet
- PWM With Microcontroller 8051 For SCR or Triac Power ControlDocument3 pagesPWM With Microcontroller 8051 For SCR or Triac Power ControlDirek BoonturmNo ratings yet
- Pic18f4550 PWM Example Using Ccs Pic CDocument2 pagesPic18f4550 PWM Example Using Ccs Pic CJonathan Lazo100% (1)
- TOPIC 5 - PWMDocument23 pagesTOPIC 5 - PWMMuhammad WaqiuddinNo ratings yet
- AVR Timer/Counter: Prof Prabhat Ranjan DA-IICT, GandhinagarDocument40 pagesAVR Timer/Counter: Prof Prabhat Ranjan DA-IICT, GandhinagardangkhuyenmaiNo ratings yet
- Bai13 PWMDocument20 pagesBai13 PWMDương ThịnhNo ratings yet
- Dong, Roy - Application NoteDocument7 pagesDong, Roy - Application Notepritam kalaimaniNo ratings yet
- 16-B PWM U O - C T Relevant Devices: IT Sing AN N HIP ImerDocument12 pages16-B PWM U O - C T Relevant Devices: IT Sing AN N HIP ImerLauderi MartinsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MSP430 MicrocontrollersDocument32 pagesIntroduction To MSP430 MicrocontrollersAlejandro OrtizNo ratings yet
- PAMTDMGen RecDocument6 pagesPAMTDMGen RecSarika KumariNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Sinusoidal PWM Inverter For Photovoltaic ApplicationDocument4 pagesMicrocontroller Based Sinusoidal PWM Inverter For Photovoltaic ApplicationDumitrescu Camil SorinNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4From EverandDigital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Edge Learning InfographicDocument1 pageEdge Learning InfographicDharanNo ratings yet
- PWM TechniquesDocument39 pagesPWM TechniquesDharanNo ratings yet
- DX 200Document116 pagesDX 200DharanNo ratings yet
- PWM TechniquesDocument39 pagesPWM TechniquesDharanNo ratings yet
- 7Document1 page7DharanNo ratings yet
- 7Document1 page7DharanNo ratings yet
- GX SimulatorDocument1 pageGX SimulatorDharanNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Plant and FACTS Controllers: Download Full-Size ImageDocument1 pageReactive Power Plant and FACTS Controllers: Download Full-Size ImageDharanNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1DharanNo ratings yet
- SQRT, TAN, TANH, ROUND functionsDocument1 pageSQRT, TAN, TANH, ROUND functionsDharanNo ratings yet
- Operators and Math Trig Functions TableDocument1 pageOperators and Math Trig Functions TableDharanNo ratings yet
- Ev Power CalculationsDocument2 pagesEv Power CalculationsDharanNo ratings yet
- FANUC Robotics VariablesDocument488 pagesFANUC Robotics VariablesAndres Romero83% (12)
- Impact of PWM Schemes on Coupled Inductor Core LossesDocument2 pagesImpact of PWM Schemes on Coupled Inductor Core LossesDharanNo ratings yet
- The New RDF SecretDocument1 pageThe New RDF SecretDharanNo ratings yet
- The RDF SecretDocument24 pagesThe RDF SecretDharanNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2DharanNo ratings yet
- 1MRK511415 UEN Communication Protocol Manual Iec 61850 Edition 2 650 Series 2 2 PrintedDocument1 page1MRK511415 UEN Communication Protocol Manual Iec 61850 Edition 2 650 Series 2 2 PrintedDharanNo ratings yet
- Anabond 666 RTV Silicone SealantDocument1 pageAnabond 666 RTV Silicone SealantDharanNo ratings yet
- ProfinetConfigurator PDFDocument5 pagesProfinetConfigurator PDFJose María CastroNo ratings yet
- Technical Reference Manual: RAPID Instructions, Functions and Data TypesDocument1,760 pagesTechnical Reference Manual: RAPID Instructions, Functions and Data TypesDharanNo ratings yet
- ZOHO Expense User Manual R1Document100 pagesZOHO Expense User Manual R1DharanNo ratings yet
- Anabond 666 RTV Silicone Sealant Product InfoDocument1 pageAnabond 666 RTV Silicone Sealant Product InfoDharan100% (1)
- Problems Faced in SS Welding ProjectDocument2 pagesProblems Faced in SS Welding ProjectDharanNo ratings yet
- Motion Functions and Events: Application ManualDocument56 pagesMotion Functions and Events: Application ManualJakkam GirishNo ratings yet