Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Protein Poster 2
Biology Protein Poster 2
Uploaded by
BuffReynaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Protein Poster 2
Biology Protein Poster 2
Uploaded by
BuffReynaCopyright:
Available Formats
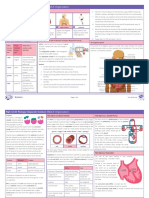
Albumin How do different methods of denaturation, including temperature changes of 30ºC and 60ºC, as well as 5g of Sodium Chloride
(NaCl), 5g of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate (NaHCO3), 5 ml of Citric Acid (C₆H₈O) in Lemon juice, and 5 ml of Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
Protein affect albumin in 40 ml of Gallus gallus domesticus (chicken) egg white after a xed duration of 5 minutes, and hence which
Lab method is the most effective at denaturing albumin?
Scienti c Background Research: Environmental/Ethical Considerations and Safety Issues:
Proteins are large molecules made up of amino acids, and are held in a natural shape from interaction
(Hydrogen or disul de bonds) of side groups on the amino acids between different areas of molecules.
Disruption of H-bonds causes the protein to change shape and denature, altering properties such as
solubility, gel formation, and enzyme activity. The globular protein albumin found in egg whites change
from a yellow tinted color to a white color when denatured.
Temperature: Albumin is hypothesized to denature over an optimum temperature of 62ºC when at a pH
of 7.4 (Baler et al., 2014). A temperature above will change the tertiary structure and shape (Clark, 1943)
Sodium Chloride Salt: High salt concentrations creates competition between the protein and salt ions to
hydrate. The salt will remove water molecules from protein surfaces which eventually denatures the
protein (Sinha & Khare, 2014).
Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate (aka. Sodium Bicarbonate) and Citric acid: Changes in pH alter electrostatic
changes and positions of hydrophobic and hydrophobic regions of the protein (Baler et al., 2014),
leading to a change in solubility which denatures the protein. Albumin has an average pH of around or Methodology of the Experiment
just above 7. Overall set up of the experiment:
Silver Nitrate (heavy metal): Silver Nitrate has a pH of just above 3. Heavy metals can form a complex 1. Crack ope n10 eggs (Fig 1F). pour the egg white into a 600 ml
with functional side chain groups of proteins, which interfere with the proteins’ physiological activities, beaker (Fig 1B), and the egg yolk into another beaker.
therefore changing their functionality (Tamás et al., 2014). 2. Prepare 6 test tubes (Fig 1D) each with 40 ml of egg white
using a syringe (Fig 1A). Label each of the test tubes (should
look similar to gure 2). Prepare a timer set to 5 minutes.
Variable 1: Temperature
Independent and Dependent Variables: 3. Prepare and 2 sous vide water baths at ideally 30ºC and 60ºC.
Place a 600 ml beaker into each water bath and place a test
tube in each. Start the timer. When the timer ends, use the
tongs to place the test tubes in from of a black background.
Make any observations.
Variable 2: Sodium Chloride Salt (NaCl)
4. Prepare 5 grams of Sodium Chloride by adding the salt to a
weighing boat (Fig 1C) on top of a weight scale (Fig 1G). Add
the Sodium Chloride into one test tube, and start the timer.
Figure 1: An image of the apparatus used in this experiment
5. Stir the solution using a glass stirring rod. Start the timer and
write down observations. When the timer ends, place the test
tube in front of a black background, and make any nal
observations.
Variable 3: Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
6. Prepare 5 grams of Sodium Bicarbonate using a weighing boat on top of a weight scale (as done for Sodium Chloride).
Controlled Variables: Add the Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate into one test tube, and immediately start to timer. Repeat step 5.
Variable 4: Citric Acid (C₆H₈O)
7. Prepare 3 lemons (Fig 1E), and extract lemon juice by squeezing them with a lemon squeezer.
Pour the solution into a 100 ml beaker. Dispose of the leftover lemons. Use a pipette to
transfer 5 ml of the juice into one test tube, and immediately start the timer. Repeat step 5.
Variable 5: Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
8. Measure 5 ml of Silver Nitrate using a pipette and a graduated cylinder. Pour the Silver
nitrate from the graduated cylinder into one test tube, and immediately start the
timer. Repeat step 5.
9. After all the experiments are complete, wash and clean any apparatus including glassware,
and safely dispose of any left over solutions. Return any apparatus to their original locations.
Raw Data: Qualitative observations of the egg whites containing albumin after being denatured through varying
methods of denaturation. These observations are seen in Figure 3, and explanations are referenced back to the
background research.
Uncontrolled Variables:
Apparatus and Materials:
Evaluation:
Conclusion and Analysis of Collected Data:
Strengths of the experiment:
The data collected in this investigation shows the effectiveness of 5 This investigation reveals the overall effect of
different protein denaturation methods on albumin proteins found in temperature, salt, pH, and heavy metals on the
egg white. The temperature was adjusted using sous vide water baths, denaturation of albumin. The methodology and
and solutions and compounds were simply added to the egg whites. results are not limited to Sodium Chloride salt,
The data collected is purely observational qualitative data. Using the or Silver Nitrate as the heavy metal variable.
Figure 2: Initial appearance of albumin egg observation and
white in test tubes. theorized explanations, Limitations of the experiment:
the followed conclusion
can be made:
References:
1. AGC Chemicals. (n.d.). Sodium bicarbonate. Sodium
Bicarbonate. Retrieved December 6, 2022, from:
https://www.agc-chemicals.com/jp/en/products/detail/
index.html?pCode=JP-
ENC010#:~:text=Sodium%20bicarbonate%20is%20a
Although the
%20white,substances%20with%20the%20lowest%20
alkalinity Hydrogen bicarbonate
2. Baler, K., Martin, O. A., Carignano, M. A., Ameer, G.
A., Vila, J. A., & Szleifer, I. (2014, January 30). seems to have a
Electrostatic unfolding and interactions of albumin
driven by ph changes: A molecular dynamics study.
The journal of physical chemistry. B. Retrieved signi cant effect on
December 6, 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
pmc/articles/PMC3983335/ the albumin based
3. Clark, J. H. (1943, November 20). Denaturation
changes in egg albumin with urea, radiation, and heat.
The Journal of general physiology. Retrieved
only on observations,
December 6, 2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
pmc/articles/PMC2142588/ the explanation behind
4. Marengo, K. (Ed.). (2019, May 21). Citric acid:
Structure, uses, intolerance, and more. Medical News the reaction suggests
Today. Retrieved December 6, 2022, from https://
www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/citric-acid that the foam was Further Investigations:
5. Sinha, R., & Khare, S. K. (2014, April 9). Protective
role of salt in catalysis and maintaining structure of
halophilic proteins against denaturation. Frontiers in unlikely to be purely • Expand the investigation to use a more varied range of temperatures and pH to
microbiology. Retrieved December 6, 2022, from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/ the denaturation of albumin. However, the other reactions do not make additional observations.
PMC3988381/
6. Tamás, M. J., Sharma, S. K., Ibstedt, S., Jacobson, T.,
& Christen, P. (2014, February 25). Heavy metals and
have notable chemical reactions that would interfere with results, • Investigate the effect of the denaturation methods on other proteins such as
metalloids as a cause for protein misfolding and
which therefore determines the reactivity as shown in the diagram. meat based proteins, or gelatin as examples.
aggregation. Biomolecules. Retrieved December 6,
2022, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
Figure 3: Final image of results
PMC4030994/
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
You might also like
- (Bio 024) Biochemistry Lab Activity 8 Factors Influencing Enzyme ActionDocument3 pages(Bio 024) Biochemistry Lab Activity 8 Factors Influencing Enzyme ActionAnandu RajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment 7 ReportDocument12 pagesChemistry Experiment 7 ReportFN6012021 RAVICHANDRAN GOKULNo ratings yet
- Criterion B CHEM REPORT TERM 3 PDFDocument9 pagesCriterion B CHEM REPORT TERM 3 PDFsayema sadimaNo ratings yet
- Title: Aim:: Arushi Sinha Coordinated Sciences BDocument5 pagesTitle: Aim:: Arushi Sinha Coordinated Sciences BSIDDHANo ratings yet
- Water Bubbles Testing Lab ReportDocument11 pagesWater Bubbles Testing Lab Reportapi-302340711No ratings yet
- (DONE) Le Chat's Principle - Iron Thiocyanate Ion EquilibriumDocument3 pages(DONE) Le Chat's Principle - Iron Thiocyanate Ion EquilibriumAngelo PascoaNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration 2nd Hour Nurayda Aleena Joanna ChristeenaDocument10 pagesCell Respiration 2nd Hour Nurayda Aleena Joanna Christeenaapi-616433899No ratings yet
- Scribd Download - Com Experiment 7Document7 pagesScribd Download - Com Experiment 7Kevin Brylle SantosNo ratings yet
- BFC 32501Document24 pagesBFC 32501Nadhirah LilyNo ratings yet
- Notes Alternative To Practical BiologyDocument6 pagesNotes Alternative To Practical BiologyOmar TahaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Amylase Lab With DataDocument2 pagesEffect of Temperature On Amylase Lab With DataKateNo ratings yet
- Elliot Prest - Criterion B - NeutralizationDocument7 pagesElliot Prest - Criterion B - NeutralizationElliot PrestNo ratings yet
- Lab: Reaction Rate LabDocument9 pagesLab: Reaction Rate LabfionaNo ratings yet
- Heat of Solutions - Exp 2Document6 pagesHeat of Solutions - Exp 2owl lawletNo ratings yet
- LR - KineticsDocument9 pagesLR - Kineticsapi-357715756No ratings yet
- Strand1: SA1, SA2, SA3Document6 pagesStrand1: SA1, SA2, SA3Mico Angelo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Water of Crystalisation of CuSO4 Lab ReportDocument4 pagesWater of Crystalisation of CuSO4 Lab ReportSaransh JainNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Effects of BlanchingDocument3 pagesLaboratory Effects of Blanchingdiwata444No ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme LabDocument7 pagesCatalase Enzyme LabJunhyoung ParkNo ratings yet
- Kertas 3Document13 pagesKertas 3cekminNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 1: Measurement of Acceleration Due To Gravity (G) by Using A Simple PendulumDocument12 pagesPhysics Lab Report 1: Measurement of Acceleration Due To Gravity (G) by Using A Simple PendulumWill LeiNo ratings yet
- Kertas 3Document19 pagesKertas 3Ct CalifaNo ratings yet
- Amylase Quantification - StarchDocument4 pagesAmylase Quantification - StarchMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Practical QDocument8 pagesPractical QS Ms.No ratings yet
- Vernier Act9 Evaporation of AlcoholsDocument8 pagesVernier Act9 Evaporation of AlcoholsBerra SirmaliNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity Experiment With Liver CellsDocument12 pagesEnzyme Activity Experiment With Liver CellsCami Yañez0% (1)
- LAB Determination of Uric AcidDocument2 pagesLAB Determination of Uric Acidmusembijosef2011No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ManualDocument8 pagesChemistry Lab ManualKritin ReddyNo ratings yet
- ICP User's Guide (English) 112.08.24Document18 pagesICP User's Guide (English) 112.08.24Nur Novilina ArifianingsihNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 4&5Document12 pagesLaboratory Activity 4&5Pearl CartasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Jar Test G7Document12 pagesExperiment 4 Jar Test G7khaito K5No ratings yet
- LAB#7 - Enthalpy Change of A ReactionDocument3 pagesLAB#7 - Enthalpy Change of A ReactionNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- 08.53 Calcimeter: Operating InstructionsDocument6 pages08.53 Calcimeter: Operating InstructionsBogdanNo ratings yet
- Percent Compositionofa Hydrate LabDocument3 pagesPercent Compositionofa Hydrate LabTanisha MarieNo ratings yet
- H8 Operation Flow ChartDocument1 pageH8 Operation Flow Chartgerente soportecNo ratings yet
- Le ChatelierDocument6 pagesLe ChatelierCeline Diantha CunaNo ratings yet
- Cromo TotalDocument6 pagesCromo TotalWendy Anaís Carrera MerloNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Laboratory Section 2: SEM 2 2006/2017 Prepared by HJH Roslinda SeswoyaDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Laboratory Section 2: SEM 2 2006/2017 Prepared by HJH Roslinda SeswoyaKerol Kerol KerolNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymesboxz2258No ratings yet
- 261 Labs - U1 - Osmolarity - Lab ReportDocument12 pages261 Labs - U1 - Osmolarity - Lab ReportSummerNo ratings yet
- 09 Testing Catalysts PDFDocument1 page09 Testing Catalysts PDFkNo ratings yet
- Biologi Form 4 Pat k3Document8 pagesBiologi Form 4 Pat k3Mohd Shafiq Husin TutorNo ratings yet
- 116 Astorga-Bronzal-Araniador Report #4Document21 pages116 Astorga-Bronzal-Araniador Report #4Lucile BronzalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Bio560Document31 pagesLab Report Bio560Alis SyamimiNo ratings yet
- Animalbehaviorlabreport CharitywhiteDocument10 pagesAnimalbehaviorlabreport Charitywhiteapi-347561171No ratings yet
- Lab Report (Physics)Document10 pagesLab Report (Physics)Jessie Jae CruzNo ratings yet
- Aniline Point Test Aparatus (By U-Tube Method)Document48 pagesAniline Point Test Aparatus (By U-Tube Method)Violett ParrNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Jar TestDocument10 pagesLab Report Jar TestnainaNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document16 pagesLab 5Amine DehaneNo ratings yet
- Hierro Total Method 8008Document8 pagesHierro Total Method 8008angelo saldarriagaNo ratings yet
- Operation and Calibration of UV-VIS SpectrophotometerDocument8 pagesOperation and Calibration of UV-VIS SpectrophotometerMaruthi K100% (1)
- Alut The Pogi Legend Fud Anal 2 Lab Exercise Number2Document3 pagesAlut The Pogi Legend Fud Anal 2 Lab Exercise Number2albertshaluz gatdulaNo ratings yet
- Cheese LabDocument4 pagesCheese Labapi-339328458No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Lab ReportDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Lab ReportCecilia LindbergNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 7 and 8Document5 pagesEXPERIMENT 7 and 8Ttalgis CartNo ratings yet
- Fair Test, Variables (P4)Document14 pagesFair Test, Variables (P4)Jegendren TanapalNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Separate Science U2 Organisation Knowledge OrganiserDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Separate Science U2 Organisation Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Experiment A1: Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument4 pagesExperiment A1: Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor: Department of Chemical EngineeringChuchayLucasNo ratings yet
- LAJU REAKSI English pdf2Document9 pagesLAJU REAKSI English pdf2aqilla sadine warangganiNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualNo ratings yet
- Effect of Micro-Spray On Plant Growth and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameter of Tomato Under High Temperature Condition in A GreenhouseDocument11 pagesEffect of Micro-Spray On Plant Growth and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameter of Tomato Under High Temperature Condition in A GreenhouseDerly Alejandra Garzon CasallasNo ratings yet
- CS 301 - Lecture 5 Regular Grammars, Regular Languages, and Properties of Regular Languages ReviewDocument16 pagesCS 301 - Lecture 5 Regular Grammars, Regular Languages, and Properties of Regular Languages ReviewFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems LabDocument15 pagesOperating Systems LabkajalNo ratings yet
- KEF KHT 9000 ACE Speaker ManualDocument2 pagesKEF KHT 9000 ACE Speaker ManualSimon SparksNo ratings yet
- Pampered by Maddie TheDocument8 pagesPampered by Maddie TheLuke GlassmanNo ratings yet
- Act 202 Midterm Fall 2020 MathsDocument2 pagesAct 202 Midterm Fall 2020 MathsMahiNo ratings yet
- Why Polyphase Induction Never Attains Synchronous SpeedDocument2 pagesWhy Polyphase Induction Never Attains Synchronous SpeedKaruppu SamyNo ratings yet
- Test Lamp TL8Document1 pageTest Lamp TL8Vincent GabrielNo ratings yet
- Principles of TQM and Strategies and Customer SatiDocument5 pagesPrinciples of TQM and Strategies and Customer SatiSheila Mae L. BordomeoNo ratings yet
- BEME Guide No. 3: Systematic Searching For Evidence in Medical Education-Part 2: Constructing SearchesDocument22 pagesBEME Guide No. 3: Systematic Searching For Evidence in Medical Education-Part 2: Constructing Searchesarum cahyaning kartikaNo ratings yet
- FSE ProjectDocument19 pagesFSE ProjectDibora TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Training Plan Template and InstructionsDocument2 pagesTraining Plan Template and InstructionsMahmoud Hatem IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Department: Computerized Payment Receipt (CPR - It)Document2 pagesIncome Tax Department: Computerized Payment Receipt (CPR - It)Mian EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - Reliance Trends Internship ProjectDocument94 pagesDocuments - Pub - Reliance Trends Internship ProjectAgney KudekarNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting SolubilityDocument1 pageFactor Affecting SolubilityBeatrice ShokryNo ratings yet
- 11.davydenko NadiiaDocument9 pages11.davydenko NadiianataliaNo ratings yet
- Medical Device Materials - Stainless SteelDocument5 pagesMedical Device Materials - Stainless Steelmaran.suguNo ratings yet
- 20 - M - DATA Bajaj High MastDocument2 pages20 - M - DATA Bajaj High Mastrohit1980No ratings yet
- Mytchenok 160 Trillons Agreement and Pay Order Latonya FullerDocument14 pagesMytchenok 160 Trillons Agreement and Pay Order Latonya FullerEsteban Enrique Posan BalcazarNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument842 pagesCatalogMAURO PALOMINO LASCARRONo ratings yet
- Go Getter 2 (Unit 1-2)Document5 pagesGo Getter 2 (Unit 1-2)Julia BaghdasaryanNo ratings yet
- Ba Eng LCS-XXXDDDocument3 pagesBa Eng LCS-XXXDDpecf VOLTESTNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills LE Week 1Document10 pagesReading and Writing Skills LE Week 1Glen Welle SuarezNo ratings yet
- Powerlifting - USA - 2 - 2010 PDFDocument59 pagesPowerlifting - USA - 2 - 2010 PDF健身老扈100% (1)
- Intze Type Tank DetailingDocument1 pageIntze Type Tank DetailingRagib Nur Alam ShuvoNo ratings yet
- CA - LYSOL Disinfecting Wipes (All Sizes, All Scents) - English (Feb 2012) PDFDocument6 pagesCA - LYSOL Disinfecting Wipes (All Sizes, All Scents) - English (Feb 2012) PDFMartiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Economics - NotesDocument10 pagesClass 9 Economics - NotesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraDocument41 pagesIV Fluid Management: Islam Awni Abu SamraIslam AwniNo ratings yet
- Sach Ielts Speaking 3 Parts Thang 5678 by NgocbachDocument186 pagesSach Ielts Speaking 3 Parts Thang 5678 by NgocbachHang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cryptographic Storage Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesCryptographic Storage Cheat SheetRyuNo ratings yet