Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AQA GCSE Separate Science U2 Organisation Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
Gabriel HoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AQA GCSE Separate Science U2 Organisation Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
Gabriel HoCopyright:
Available Formats
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Principles of Organisation
6. Add 2cm3 of starch solution into the test tube, using a different measuring
cylinder to measure, and begin a timer (leave the timer to run continuously).
7. After 10 seconds, use a pipette to extract some of the amylase/starch solution,
and place one drop into the first well of the spotting tile. Squirt the remaining
solution back into the test tube.
8. Continue to place one drop into the next well of the spotting tile, every 10
cell tissue organ organ system organism seconds, until the iodine remains orange.
9. Record the time taken for the starch to be completely digested by the amylase
Cells are the basic A group of cells with An organ is a Organs work together Organ systems work
by counting the wells that were tested positive for starch (indicated by the
building blocks of all a similar structure combination of tissues within an organ together to form whole
blue/black colour change of the iodine). Each well represents 10 seconds of
living things. and function is called carrying out a specific system. living organisms.
time.
a tissue. function.
10. Repeat steps 1 to 8 for pH values 7 and 10.
Food Tests (Required Practical) Effect of pH on the Rate of Reaction of Amylase (Required Practical)
The Digestive System
Iodine is used to test for the presence of starch.
What Which What does a The purpose of the digestive system is to break down large molecules into smaller,
If starch is present, the colour will change to
are you indicator positive result soluble molecules, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream. The rate of these
blue-black.
testing do you look like? reactions is increased by enzymes.
The independent variable in the investigation
for? use?
is the pH of the buffer solution.
sugar Benedict’s Once heated, the The dependent variable in the investigation is the time
reagent solution will change taken for the reaction to complete (how long it takes for all
from blue-green to the starch to be digested by the amylase).
yellow-red. Method:
1. Use the marker pen to label a test tube with the first value of pH buffer
starch iodine Blue-black colour
solution (pH 4) and stand it in the test tube rack.
indicates starch is
present. 2. Into each well of the spotting tiles, place a drop of iodine.
3. Using a measuring cylinder, measure 2cm3 of amylase and pour into the
protein biuret The solution will
test tube.
change from blue to
pink-purple. 4. Using a syringe, measure 1cm3 of the buffer solution and pour into the
test tube.
lipid sudan III The lipids will
5. Leave this to stand for five minutes and then use the thermometer to
separate and the
measure the temperature. Make a note of the temperature.
top layer will turn
bright red.
Page 1 of 6 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Enzymes The Heart and Blood Vessels The Heart as a Double Pump
An enzyme is a biological
catalyst; enzymes speed up The heart is a large muscular organ which pumps blood carrying oxygen The heart works as a double pump for two circulatory
chemical reactions without or waste products around the body. The lungs are the site of gas exchange systems; the pulmonary circulation and the systemic
being changed or used up. where oxygen from the air is exchanged for waste carbon dioxide in the circulation.
This happens because the enzyme lowers the activation blood. Oxygen is used in the respiration reaction to release energy for the The pulmonary circulation serves the
energy required for the reaction to occur. Enzymes are made cells and carbon dioxide is made as a waste product during the reaction. lungs and bring deoxygenated blood to
up of chains of amino acids folded into a globular shape. glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + [energy] exchange waste carbon dioxide gas for
oxygen at the alveoli.
Enzymes have an active site which the substrate (reactants) The systemic circulation serves the rest of the body
fits into. Enzymes are very specific and will only catalyse one and transports oxygen and nutrients from digestion
specific reaction. If the reactants are not the complimentary to the cells of the body, whilst carrying carbon
shape, the enzyme will not work for that reaction. dioxide and other waste away from the cells.
Enzymes also work optimally at specific conditions of pH and The systemic circulation flows through the whole
temperature. In extremes of pH or temperature, the enzyme vein artery capillary body. This means the blood is flowing at a much higher pressure than in the
will denature. This means that the bonds holding together pulmonary circuit.
The three types of blood vessels, shown above, are each adapted to carry
the 3D shape of the active site will break and the active out their specific function.
shape will deform. The substrate will not be able to fit into The Heart as Pacemaker
Capillaries are narrow vessels which form networks to closely supply cells
the active site anymore and the enzyme cannot function.
and organs between the veins and arteries. The walls of the capillaries are The rate of the heart beating is very carefully,
only one cell thick, which provides a short diffusion pathway to increase and automatically, controlled within
Enzyme Reactant Product the heart itself.
the rate at which substances are transferred.
amylase starch sugars (glucose) Located in the muscular walls of
The table below compares the structure and function of arteries and veins:
the heart are small groups of
protease protein amino acids cells which act as pacemakers.
Artery Vein
lipase lipid glycerol and fatty acids They produce electrical impulses
direction of blood flow away from the heart towards the heart
which stimulate the surrounding
The products of digestion are used to build new oxygenated or oxygenated (except deoxygenated muscle to contract, squeezing the
deoxygenated blood? the pulmonary (except the chambers of the heart and pumping
carbohydrates and proteins and some of the glucose is used
artery) pulmonary vein) the blood.
for respiration.
pressure high low (negative)
Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. The sino-atrial node (SAN) is located near the
It is an alkaline substance which neutralises the wall structure thick, elastic, thin, less right atrium and it stimulates the atria to contract.
hydrochloric acid in the stomach. It also works to emulsify muscular, connective muscular, less
The atrio-ventricular node (AVN) is located in between the ventricles and
fats into small droplets. The fat droplets have a higher tissue for strength connective tissue
stimulates them to contract.
surface area and so the rate of their digestion by lipase is lumen (channel inside narrow wide (with valves)
increased. the vessel)
Page 2 of 6 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Artificial pacemakers can be surgically implanted into a person if their Drugs – illegal drugs (e.g. ecstasy and cannabis) can lead to increased heart rate
heart nodes are not functioning correctly. and blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Alcohol – regularly exceeding unit guidelines for alcohol can lead to increased
blood pressure and risk of heart disease.
Coronary Heart Disease
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood via the vena
Coronary heart disease is a condition resulting from blockages in the cava. It is then pumped down through the valves
coronary arteries. These are the main arteries which supply blood to the into the right ventricle. From here, it is forced up
heart itself and they can become blocked by build-up of fatty deposits. through the pulmonary artery towards the lungs
where it exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen.
In the UK and around the world, coronary heart disease is a major cause
The oxygenated blood then enters the left atrium via the
of many deaths. Blood pulmonary vein and down into the left ventricle. The
The main symptoms can include chest pain, heart attack or heart failure. Blood is composed of red blood cells muscular wall of the left ventricle is much thicker so it can
Yet, not all people suffer the same symptoms, if any at all. (erythrocytes), white blood cells and platelets, all pump the blood more forcefully out of the heart and around
Lifestyle factors can increase the risk of a person developing coronary suspended within a plasma (a tissue). the entire body, via the aorta.
heart disease. The plasma transports the different blood cells The blood only flows in one direction. This is because there
around the body as well as carbon dioxide, are valves in the heart which close under pressure and
Diet – a high-fat diet (containing lots of saturated fat) can lead to higher
nutrients, urea and hormones. It also distributes prevent the backward flow of blood.
cholesterol levels and this cholesterol forms the fatty deposits which
the heat throughout the body.
damage and block the arteries.
Red blood cells transport oxygen attached to the
Smoking – chemicals in cigarette smoke, including nicotine and carbon
monoxide, increase the risk of heart disease. Carbon monoxide reduces haem group in their structure. It has a biconcave shape to increase surface area
the amount of oxygen which can be transported by the red blood cells and does not contain a nucleus so it can bind with more oxygen molecules.
and nicotine causes an increased heart rate. The lack of oxygen to the White blood cells form part of the immune system and ingest pathogens
heart and increased pressure can lead to heart attacks. and produce antibodies. Platelets are important blood clotting factors.
Stress – prolonged exposure to stress or stressful situations (such as high at the lungs
pressure jobs) can lead to high blood pressure and an increased risk of haemoglobin + oxygen oxyhaemoglobin
heart disease. at the cells
Page 3 of 6 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Rate Calculations for Blood Flow Plant Tissues, Organs and Systems Root Hair Cells
The number of beats the heart performs each minute is called the Leaves are plant organs and their main function is to absorb sunlight Plants absorb water by osmosis through
pulse (or heart rate). energy for use in photosynthesis. Within the cells are small organelles called the root hair cells of the roots. Dissolved
It is easily measured by counting the number of beats in a given time, chloroplasts which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. This is the in the water are important minerals for
e.g. 15s, and finding the total beats per minute. part of the plant which absorbs the sunlight and where photosynthesis occurs. the plant’s growth and development,
sunlight which are absorbed by active transport.
Typically, a lower resting pulse rate indicates a greater level of
physical fitness. During exercise, and for some time after, the pulse carbon dioxide + water oxygen + glucose The root hair cells are adapted to their
rate increases while the heart is working to provide more oxygen to function with the following features:
Leaves are adapted to carry out their function. Leaves are typically flat and
the muscles. • Finger-like projection in the membrane increases the surface
thin with a large surface area. This means they have a maximum area to
absorb the sunlight and carbon dioxide. The thin shape reduces the distance area available for water and minerals to be absorbed across.
Cardiac output is a measure of the volume of blood pumped by the
heart each minute. Stroke volume is a measure of the volume of for diffusion of water and gases. • The narrow shape of the projection can squeeze into small
blood pumped from the heart each contraction (heart beat). spaces between soil particles, bringing it closer and reducing
Leaves contain vessels called xylem and phloem. The xylem transport water
the distance of the diffusion pathway.
Cardiac output (cm³/min) = heart rate (bpm) × stroke volume (cm³/beat) and dissolved minerals toward the leaves. The phloem transport glucose and
• The cell has many mitochondria, which release energy required
other products from photosynthesis around the plant.
Cancer for the active transport of some substances.
The large air spaces between the cells of the spongy mesophyll layer allow
Cancer is the result of uncontrolled cell growth and division.
for the diffusion of gases. Carbon dioxide enters the leaves and oxygen exits
The uncontrolled growth of cells is called a tumour. Xylem and Phloem
the leaves.
Benign Tumour Malignant Tumour Xylem vessels transport water through
waxy cuticle palisade layer
• Usually grows slowly. • cancerous the plant, from roots to leaves.
They are made up of dead, lignified
• Usually grows within • Usually grows rapidly.
a membrane and can cells, which are joined end to end
• Can spread around upper epidermis
be easily removed. xylem with no walls between them, forming
the body, via the
a long central tube down the middle.
bloodstream.
• Does not normally grow back. The movement of the water, and
• Cells can break away and
spongy mesophyll lower epidermis dissolved minerals, along the xylem is
• Does not spread around the body. cause secondary tumours
to grow in other areas of in a transpiration stream.
• Can cause damage to organs
the body (metastasis). Xylem vessels also provide support and strength to the plant
and be life-threatening.
guard cells stomata structure. They are found in the middle of roots so they
aren’t crushed within the soil. They are found in the middle
The guard cells are specially adapted cells located on the underside of the leaf. of the stem to provide strength and prevent bending. In the
They are positioned in pairs, surrounding the stomata (a small opening in the leaves, they are found in vascular bundles alongside the
epidermis layer). The guard cells change shape to open and close the stomata, phloem and can be seen as the veins which network across
controlling the rate of gas exchange in the leaf. the leaf.
Page 4 of 6 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Phloem vessels transport food such as
Disease Interactions Health and Disease
dissolved sugars and glucose from
photosynthesis. The food is transported Having one type of illness can often make a person more susceptible to Health is the state of being free from illness or disease. It
around the plant to where growth is occurring another type of illness: refers to physical and mental wellbeing.
(root and shoot tips), as well as to the organs Disease and lifestyle factors, such as diet, stress, smoking,
• immune disorders increased risk of infectious disease
which store the food. The transport occurs alcohol consumption and the use of illegal drugs, can all
in all directions throughout the plant. • viral infection of cells increased risk of cancer impact the health of a person.
The cells making up the phloem tube are Some conditions are associated with certain lifestyle choices:
• immune reactions can trigger allergies
living, with small holes in the walls where the
• Liver conditions are associated with poor diet and prolonged
cells are joined. • very poor physical health increased risk of depression or other mental excessive alcohol consumption.
illness
Transpiration and Translocation • Lung cancer is associated with smoking.
• Memory loss, poor physical health and hygiene are
Transpiration is the loss of water, by evaporation and diffusion,
associated with the use of illegal or recreational drugs.
from the leaves of the plant. Water is a cohesive molecule and as it evaporates,
• Obesity and diabetes are associated with poor diet.
there is less water in the leaf, so water from further back moves up to take
its place. This, in turn, draws more water with it. This is the transpiration • Anxiety and depression are associated with stress and
stream. prolonged excessive alcohol consumption.
Transpiration occurs naturally as there is a tendency for water to diffuse
There can often be correlations between some factors
from the leaves (where the concentration is relatively high) to the air around and types of illness or specific diseases.
the plants (where the concentration is relatively low), via the stomata.
For example, in the graph shown to the right, there is a
Environmental factors can change the rate at which transpiration occurs:
positive correlation between the number of cigarettes
• Increased light intensity will increase the rate of transpiration because light
smoked and the number of lung cancer deaths.
stimulates the stomata to open. The leaf will also be warmed by the sunlight.
• Increased temperature will cause the water to evaporate more quickly and However, there are other factors which can contribute
so increase the rate of transpiration. to the development of lung cancer e.g. working with
asbestos, genetic predisposition.
• Increased humidity (moisture in the air) will reduce the rate of
transpiration. Whereas if the air becomes drier, the rate increases. This means that although the evidence in the graph
A greater concentration gradient will increase the rate of diffusion. gives a strong indication that smoking is a cause of
• If the wind speed increases, then the rate of transpiration also increases. lung cancer, it cannot be stated that ‘smoking will
This is because as the water surrounding the leaves is moved away more cause lung cancer’. Not every person who smokes
quickly, the concentration gradient is increased. will develop lung cancer and not every person who
• If the water content in the soil is decreased, then the rate of absorption in develops lung cancer will be a smoker.
the roots decreases. This causes the stomata to become flaccid and close, Therefore, it can be stated that smoking increases the
reducing transpiration. If the loss of turgor affects the whole plant, then it risk of lung cancer.
will wilt.
Page 5 of 6 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Biology (Separate Science) Unit 2: Organisation
Heart Disease (Treatments)
There are a range of medical treatments for heart disease.
Treatment Description Advantages Disadvantages
statins Drugs used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood, • Can be used to prevent heart disease developing. • Long-term treatment.
by reducing the amount produced in the liver. • Possible negative side-effects.
• Improved quality of life.
stents Mechanical device which is used to stretch narrow or • Used for patients where drugs are less effective. • Requires surgery under general anaesthetic, which
blocked arteries, restoring blood flow. carries risk of infection.
• Offers long-term benefits.
• Made from metal alloys so will not be rejected by the
patients body.
• Improved quality of life.
heart transplant The entire organ is replaced with one from an organ • Can treat complete heart failure in a person. • Requires major surgery under general anaesthetic,
donor (a person who has died and previously expressed which carries risks.
• extended life
a wish for their organs to be used in this way).
• Lack of donors available.
• Improved quality of life.
• Risk of infection or transplant rejection.
• Artificial plastic hearts can be used temporarily until
a donor is found. • Long recovery times.
Page 6 of 6 visit twinkl.com
You might also like
- Scribd Download - Com Experiment 7Document7 pagesScribd Download - Com Experiment 7Kevin Brylle SantosNo ratings yet
- Test Name Principal Apparatus/ Requirement Procedure Observation Result/ Concluison PrecautionsDocument4 pagesTest Name Principal Apparatus/ Requirement Procedure Observation Result/ Concluison PrecautionsHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio462 Exp 3Document12 pagesBio462 Exp 32023491958No ratings yet
- 4 Isolation and Identification of Subcellular ComponentsDocument6 pages4 Isolation and Identification of Subcellular ComponentsMagnus Jordan100% (2)
- Formal Report - Subcellular ComponentsDocument12 pagesFormal Report - Subcellular ComponentsJoanna Faye SimsuangcoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 3 Wbi13Document7 pagesEdexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 3 Wbi13Bara' Hammadeh100% (1)
- Biology IADocument16 pagesBiology IAAngelina TomacNo ratings yet
- Osmolarity ExperimentDocument5 pagesOsmolarity Experimentanthoniaronald7No ratings yet
- Expt 6 ActivityDocument3 pagesExpt 6 ActivityAlthea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Column Chromatography of LipidsDocument4 pagesExtraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Column Chromatography of LipidsJoseph SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Instruments: No Name & Picture FunctionDocument5 pagesLaboratory Instruments: No Name & Picture FunctionAisha AyuNo ratings yet
- Biology 10 LabreportDocument7 pagesBiology 10 Labreportapi-276985927No ratings yet
- Deffusion and Osmosis (Pre-Lab) : Activity 4 Gbsg3Document19 pagesDeffusion and Osmosis (Pre-Lab) : Activity 4 Gbsg3CHIOU MORALESNo ratings yet
- Deffusion and Osmosis (Pre-Lab) : Activity 4 Gbsg3Document19 pagesDeffusion and Osmosis (Pre-Lab) : Activity 4 Gbsg3CHIOU MORALESNo ratings yet
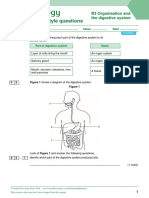
- Exam-Style Questions: B3 Organisation and The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesExam-Style Questions: B3 Organisation and The Digestive Systemchemphycomb100% (1)
- Biology Digestion Higher TierDocument6 pagesBiology Digestion Higher Tierchemphycomb100% (1)
- Isolation and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Group 3BDocument8 pagesIsolation and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Group 3BArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- CP 4Document6 pagesCP 4Yaping ZhangNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Rate of Oxygen UptakeDocument2 pagesMeasuring The Rate of Oxygen UptakeSachitra WijethungaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design OsmosisDocument3 pagesExperimental Design OsmosisAnka QiuNo ratings yet
- Chem 132.2 Experiment 7Document6 pagesChem 132.2 Experiment 7Genry TanNo ratings yet
- Practical Biochem Notes MIDTERMDocument6 pagesPractical Biochem Notes MIDTERMKAREN RODASNo ratings yet
- GCSE Combined RP Methodology + Video LinksDocument6 pagesGCSE Combined RP Methodology + Video Linkszhinia HossainNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Examination of Urine: (Pick The Date) (Edition 1, Volume 1)Document11 pagesThe Chemical Examination of Urine: (Pick The Date) (Edition 1, Volume 1)Francis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity 04Document5 pagesEnzyme Activity 04Dhandapani PerumalNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM - Enzyme ActivityDocument6 pagesBIOCHEM - Enzyme ActivityHanz Albrech AbellaNo ratings yet
- Analyucal PH M Ple: 4) Flaume Photomelo Jpwe 4) Flxtleves 3) StcwdingDocument25 pagesAnalyucal PH M Ple: 4) Flaume Photomelo Jpwe 4) Flxtleves 3) Stcwdingharshal sayareNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Yuwen SunDocument14 pagesLab Report Yuwen SunFran cNo ratings yet
- Practical Booklet Current SyllabusDocument29 pagesPractical Booklet Current SyllabusMufaddal KaderbhaiNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument15 pagesEnzyme Lab ReportJessa Marie UseroNo ratings yet
- Fractionation of Cells Via Differential CentrifugationDocument5 pagesFractionation of Cells Via Differential CentrifugationEthanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyMeet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- BP 2 - PH and Enzyme ActivityDocument3 pagesBP 2 - PH and Enzyme ActivityEshaal KhanNo ratings yet
- Mineral Trioxide Aggregate But Not Light-Cure MineralDocument4 pagesMineral Trioxide Aggregate But Not Light-Cure MineralMihaela TuculinaNo ratings yet
- SA2 Criterion B and C-taskid16036TSK1120230412085553611Document10 pagesSA2 Criterion B and C-taskid16036TSK1120230412085553611Ashneel ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Exp. 2 Scientific PaperDocument8 pagesExp. 2 Scientific PaperMeara Lalaine AbiogNo ratings yet
- NATS 103 - The Biological World EnzymesDocument3 pagesNATS 103 - The Biological World EnzymesVera MillerNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cellular Components Through Cell Fractionation: Exercise 1Document4 pagesAnalysis of Cellular Components Through Cell Fractionation: Exercise 1Honneh ConsadNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseDocument6 pagesLAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseBasem AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument2 pagesFood TestsLaraineNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and PH Practical ResearchDocument2 pagesEnzyme and PH Practical ResearchjonNo ratings yet
- Bed Bug Behavior in Response To OdorsDocument1 pageBed Bug Behavior in Response To OdorsChandu LandaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis LabDocument12 pagesOsmosis LabMarcelle LamarcheNo ratings yet
- Research Question: Does The Increasing Concentration of Natural Food Color Crocin (In Saffron)Document15 pagesResearch Question: Does The Increasing Concentration of Natural Food Color Crocin (In Saffron)RitikaFandaNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2Document35 pagesBiology Unit 2thisismashael07No ratings yet
- Picture Name DescriptionDocument3 pagesPicture Name DescriptionElga RahayuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1A The CellDocument3 pagesExperiment 1A The CellLeah SunioNo ratings yet
- Aswika Project ContentDocument7 pagesAswika Project ContentRoshini SNo ratings yet
- Biuret Protein Assay f18Document6 pagesBiuret Protein Assay f18new worldNo ratings yet
- Biology - Form 2 Scheme of Work - Term 1: Week Topic Syllabus Objectives Number OF Sessions Activities/LabsDocument2 pagesBiology - Form 2 Scheme of Work - Term 1: Week Topic Syllabus Objectives Number OF Sessions Activities/LabsramjdNo ratings yet
- ACT. 1 Laboratory ReportDocument27 pagesACT. 1 Laboratory ReportRAYMOND REGALADONo ratings yet
- 7ae Quick CheckDocument2 pages7ae Quick CheckMajdoline SadeddineNo ratings yet
- 173 Food Tests and ChromatographyDocument3 pages173 Food Tests and Chromatographykpb6261No ratings yet
- b1 Required PracticalsDocument5 pagesb1 Required Practicalsapi-372082105No ratings yet
- Jurnal Penelitian HematologiDocument8 pagesJurnal Penelitian HematologiSri SucitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Abubakar Siddiq RaminNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- Problems of Cell Permeability: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological Sciences, Vol. 26From EverandProblems of Cell Permeability: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological Sciences, Vol. 26No ratings yet
- Section Check in Mechanics Newton S Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesSection Check in Mechanics Newton S Laws of MotionGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 3 Particle Model of Matter Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Unit 3 Particle Model of Matter Student Progress SheetDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Unit 3 Particle Model of Matter Student Progress SheetGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Unit 1 Energy Student Progress SheetDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Unit 1 Energy Student Progress SheetGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Unit 6 Waves Student Progress SheetDocument7 pagesAQA Physics Unit 6 Waves Student Progress SheetGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Islam Quotes For GcseDocument4 pagesIslam Quotes For GcseGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- 4 5 Energy ChangesDocument3 pages4 5 Energy ChangesAmmaarNo ratings yet
- L22 - Revision Lesson On HazardsDocument24 pagesL22 - Revision Lesson On HazardsGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassDocument9 pagesRevision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Orallichenplanus 170929075918Document40 pagesOrallichenplanus 170929075918Aymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis and Simulation of Linear Model of A STATCOM For Reactive Power Compensation With Variation of DC-link VoltageDocument7 pagesDesign, Analysis and Simulation of Linear Model of A STATCOM For Reactive Power Compensation With Variation of DC-link VoltageAtiqMarwatNo ratings yet
- Bright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukDocument100 pagesBright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukЕкатерина Матушинец100% (2)
- Inheritance: Compiled By: Brandon Freel Stolen and Edited From: IMS and Dr. Kyle Stutts (SHSU)Document25 pagesInheritance: Compiled By: Brandon Freel Stolen and Edited From: IMS and Dr. Kyle Stutts (SHSU)Mary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- BS 5655-14Document16 pagesBS 5655-14Arun Jacob Cherian100% (1)
- Vo 1263 AaDocument8 pagesVo 1263 Aa801400No ratings yet
- Identifing Legends and CultureDocument2 pagesIdentifing Legends and CultureHezekaiah AstraeaNo ratings yet
- Affiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennai Regulations - 2009 Curriculum Ii To Iv Semesters (Full Time) M.E. Applied ElectronicsDocument21 pagesAffiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennai Regulations - 2009 Curriculum Ii To Iv Semesters (Full Time) M.E. Applied ElectronicsRamya VNo ratings yet
- The Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit PlantDocument7 pagesThe Design of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan For Biscuit Plantttk_maniNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpDocument20 pagesSpare Parts: LKH Centrifugal PumpService CTANo ratings yet
- Analisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaDocument6 pagesAnalisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaTommy ChandraNo ratings yet
- Psychosomatic DisordersDocument79 pagesPsychosomatic DisordersMONIKANo ratings yet
- Radiator - Kts-Sec-Bsdg-Arc-103Document1 pageRadiator - Kts-Sec-Bsdg-Arc-103Mohammed BasheeruddinNo ratings yet
- Lanier Half ManifiestoDocument47 pagesLanier Half ManifiestoSeba CopanNo ratings yet
- Natal Chart ReportDocument23 pagesNatal Chart ReportEvelyn WilsonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Today PDFDocument112 pagesNuclear Energy Today PDFDaniel Bogdan DincaNo ratings yet
- Previews 2502414 PreDocument9 pagesPreviews 2502414 PreAlex Andre RojasNo ratings yet
- Rieter k42 Brochure 2539 v3 - 89691 en PDFDocument28 pagesRieter k42 Brochure 2539 v3 - 89691 en PDFAjay Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Sample Theory With Ques. - Organometallic Compounds (NET CH UNIT-3) PDFDocument26 pagesSample Theory With Ques. - Organometallic Compounds (NET CH UNIT-3) PDFPriyanshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Radio MobileDocument11 pagesTutoria Radio MobileGanti Nama Aja LahNo ratings yet
- Diy AquariumsDocument108 pagesDiy Aquariumshalo_bing100% (2)
- 20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1Document1 page20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1newattelectricNo ratings yet
- BS en 480-6-2005Document5 pagesBS en 480-6-2005Abey Vettoor0% (1)
- Relative Clauses - Revisión Del IntentoDocument4 pagesRelative Clauses - Revisión Del IntentoYordy Rodolfo Delgado RosarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-5 EEEN323 March2022Document139 pagesLecture 1-5 EEEN323 March2022Lekono KagoNo ratings yet
- Just Walk Across The RoomDocument8 pagesJust Walk Across The Roomstuutterrs100% (1)
- The Hidden Word Is: The CluesDocument2 pagesThe Hidden Word Is: The CluesИра НикулочкинаNo ratings yet
- EarlyDocument59 pagesEarlyjrtlimNo ratings yet
- Manual Sony HCD-SH2000 (88 Páginas)Document2 pagesManual Sony HCD-SH2000 (88 Páginas)Alberto CaseroNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Exam 3 - This SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Exam 3 - This Semesterapi-3723612100% (1)