Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 1 Part 2 Xmind
Uploaded by
Ahmad AbuelgasimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 1 Part 2 Xmind
Uploaded by
Ahmad AbuelgasimCopyright:
Available Formats
hat Is an
W
Information System?
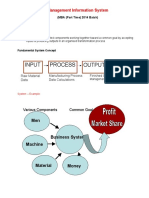
• Set of interrelated components
• Collect, process, store, and distribute
information
1- Information system:
• Support decision making, coordination, and
control
• Data are streams of raw facts.
2- Information vs. data
• Information is data shaped into meaningful
form
aw data from a supermarket checkout
R
counter can be processed and organized
to produce meaningful information, such as
the total unit sales of dish detergent or the
3- Data and Information
total sales revenue from dish detergent for a
specific store or sales territory.
aptures raw data from organization or
C
• Input:
external environment
- Three activities of information
4
systems produce information • Processing: Converts raw data into meaningful form
organizations need :
Transfers processed information to people
• Output:
or activities that use it
• is output returned to appropriate
people or activities in the organization to 5- Feedback:
evaluate and refine the input.
• Computers and software are technical
- Computer/computer program
6
foundation and tools, similar to the
vs. information system: material and tools used to build a house
sing information systems effectively
U
requires an understanding of the
organization, management, and
information technology shaping the systems. - Information Systems Are More
7
An information system creates value for the Than Computers:
firm as an
organizational and management solution to
challenges posed by the environment
• Senior management
• Middle management
• Operational management
• Hierarchy of authority, responsibility:
• Knowledge workers
• Data workers
• Production or service workers
• Sales and marketing
• Human resources
the four business functions are:
• Finance and accounting
• Manufacturing and production
1- Separation of business functions
- Organizational dimension of
8 • Unique business processes
information systems: The separation points: • Unique business culture
• Organizational politics
• Managers set organizational strategy for
responding to business challenges
2- Management dimension of information
systems: • Creation of new products and services
• In addition, managers must act creatively:
• Occasionally re-creating the organization
• Computer hardware and software
• Data management technology
- Technology dimension of information
3
systems • Networking and telecommunications • Networks, the Internet, intranets and
technology extranets, World Wide Web
• IT infrastructure: provides platform that
system is built on
• Information system is instrument for
creating value
• Productivity increases
• Investments in information technology will
• Revenue increases
result in superior returns:
• Superior long-term strategic positioning
• Raw data acquired and transformed through
stages that add value to that information
• Value of information system determined in
part by extent to which it leads to better
• Business information value chain
decisions, greater efficiency, and higher
profits
rom a business perspective, information
F
systems are part of a series of value-adding - Business perspective on
9
activities for acquiring, transforming, and information systems:
distributing information that managers can
use to improve decision making, enhance
organizational performance, and, ultimately,
increase firm profitability
• Calls attention to organizational and
• Business perspective:
managerial nature of information systems
• Investing in information technology does
not guarantee good returns.
• Adopting the right business model
• Assets required to derive value from a
primary investment
• Firms supporting technology investments • There is considerable variation in the
with investment in complementary assets • Complementary assets: • Factors: returns firms receive from systems
receive superior returns investments
• Example: Invest in technology and the
people to make it work properly
• Investing in complementary assets
• Appropriate business model (organizational and management capital)
• Organizational assets, for example:
• Efficient business processes
• Incentives for management innovation
• Managerial assets, for example: • Complementary assets include:
• Teamwork and collaborative work
environment
• The Internet and telecommunications
infrastructure
• Social assets, for example:
• Technology standards
You might also like
- Data Architecture For Statistical Modernization: An Integrated ApproachDocument17 pagesData Architecture For Statistical Modernization: An Integrated ApproachWalter ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Presented byDocument8 pagesDatabase Management System: Presented byFarah FazalNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 - Introduction To Data Managementn Ver 22Document42 pagesModul 1 - Introduction To Data Managementn Ver 22M. FarhanNo ratings yet
- Reference Data Management: Accurate, Responsive, TransformedDocument6 pagesReference Data Management: Accurate, Responsive, TransformedAltisource SLRNo ratings yet
- DataInformationAndKnowledgeManagementFrameworkAndTheDataManagementBookOfKnowledgeDMBOK PDFDocument357 pagesDataInformationAndKnowledgeManagementFrameworkAndTheDataManagementBookOfKnowledgeDMBOK PDFCarly BruynsNo ratings yet
- Data Governance Keystone of Information Management InitiativesDocument102 pagesData Governance Keystone of Information Management InitiativesAlan McSweeney100% (2)
- Modul 1 - Introduction To Data ManagementDocument42 pagesModul 1 - Introduction To Data Managementmitc.khoiriNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument4 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument3 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Data, Information and Knowledge Management Framework and The Data Management Book of Knowledge (DMBOK)Document356 pagesData, Information and Knowledge Management Framework and The Data Management Book of Knowledge (DMBOK)Alan McSweeney100% (9)
- IS ModelDocument17 pagesIS Modelsoumys19No ratings yet
- Data Mining 1680334251765 PDFDocument57 pagesData Mining 1680334251765 PDFtest testNo ratings yet
- Chapter One MisDocument7 pagesChapter One MisMETANOIANo ratings yet
- IGNOU MCA AssignmentDocument12 pagesIGNOU MCA AssignmentafifaNo ratings yet
- G. Data Leakage: Domain 2. Asset SecurityDocument1 pageG. Data Leakage: Domain 2. Asset SecurityMddlp DdlpNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Data Warehouse and Big DataDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Data Warehouse and Big DataMo EmadNo ratings yet
- MindMap - Waste ManagementDocument1 pageMindMap - Waste ManagementRafidah RashidNo ratings yet
- Data and InformationDocument8 pagesData and Informationoureducation.inNo ratings yet
- Turning Data Into Business Outcome With A 360 Data HubDocument2 pagesTurning Data Into Business Outcome With A 360 Data HubJordi Morato LluviàNo ratings yet
- Cab Unit 1Document11 pagesCab Unit 1Sabitha PadmajNo ratings yet
- Mis Mod 1Document47 pagesMis Mod 1mukleshtiwariNo ratings yet
- MGT705 PDFDocument167 pagesMGT705 PDFn_a852726No ratings yet
- Accessibility EffectivenessDocument31 pagesAccessibility EffectivenessRoselle AquinoNo ratings yet
- 1.chapter 1 - Overview Information System FinalDocument131 pages1.chapter 1 - Overview Information System FinalMikiyas AbateNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 2 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Data Science: Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesData Science: Chapter TwoEzas MobNo ratings yet
- Presentation Intel TeradataDocument13 pagesPresentation Intel TeradataSubash ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Information Protection For Office 365Document1 pageInformation Protection For Office 365javiyahooNo ratings yet
- For The Data Economy: A Trustworthy ArchitectureDocument1 pageFor The Data Economy: A Trustworthy ArchitectureMorteza DianatfarNo ratings yet
- SAP Agile Data Preparation: Road MapDocument16 pagesSAP Agile Data Preparation: Road MapAnonymous s1zWy06ZDNo ratings yet
- Solving Business Problems: Systems Approach: CSC230, Spring'03 CSC230, Spring'03Document54 pagesSolving Business Problems: Systems Approach: CSC230, Spring'03 CSC230, Spring'03Kasim MergaNo ratings yet
- AIS 205 Chapter 1Document2 pagesAIS 205 Chapter 1pcrwzhwqmdNo ratings yet
- Ruben A. Parazo Department of Computer StudiesDocument7 pagesRuben A. Parazo Department of Computer StudiesPaula Rodalyn MateoNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument64 pages1 Introductionpatil_555No ratings yet
- Copy of DFD Diagram - Blank ERD & Data Flow PDFDocument1 pageCopy of DFD Diagram - Blank ERD & Data Flow PDFAnish YadavNo ratings yet
- Business Information Systems - Week 1 - IntroductionDocument5 pagesBusiness Information Systems - Week 1 - IntroductionlucyNo ratings yet
- Output Process Input: Management Information SystemDocument23 pagesOutput Process Input: Management Information SystemMohamed ArifNo ratings yet
- Data Quality Issues For Accounting Information Systems' Implementation: Systems, Stakeholders, and Organizational FactorsDocument13 pagesData Quality Issues For Accounting Information Systems' Implementation: Systems, Stakeholders, and Organizational FactorssandyjbsNo ratings yet
- Data StorytellingDocument12 pagesData StorytellingMudrit SoodNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument48 pagesData WarehousingPravah ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Oromia State University: Course Title: Fundamentals of Information SystemsDocument27 pagesOromia State University: Course Title: Fundamentals of Information SystemsAbdi kasimNo ratings yet
- Information Systems:: FundamentalsDocument14 pagesInformation Systems:: FundamentalsEsma EkmekciNo ratings yet
- FILS ExamDocument15 pagesFILS Examapi-3738338No ratings yet
- Datawarehousing&Datamining: R.Kartheek B.Tech-Iii RD I.T V.R.S College, ChiralaDocument18 pagesDatawarehousing&Datamining: R.Kartheek B.Tech-Iii RD I.T V.R.S College, ChiralaRavula KartheekNo ratings yet
- Information Produced by The DBMS Are Classified Into Thre1Document9 pagesInformation Produced by The DBMS Are Classified Into Thre1RicHArdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MISDocument12 pagesIntroduction To MISAMITY BHMNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 1 - Module 1 - Obj 6Document20 pagesCape Unit 1 - Module 1 - Obj 6Aggrie OsbourneNo ratings yet
- Information Related Specialistsv 8Document1 pageInformation Related Specialistsv 8Bob WigginsNo ratings yet
- Logistics-Discussion-Questions (1) - 1Document1 pageLogistics-Discussion-Questions (1) - 1Lidia GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Data and DatabasesDocument14 pages5.1 Data and DatabasesBLADE LEMONNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of MISDocument46 pagesFundamental Concepts of MISaromal josephNo ratings yet
- Data Governance Cheat SheetDocument1 pageData Governance Cheat SheetFernando HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 Basics of Information Organization and Content ManagementDocument35 pagesLecture - 1 Basics of Information Organization and Content ManagementtimNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Healthcare CommunicationsDocument1 pageThe Periodic Table of Healthcare Communicationscoolarun86No ratings yet
- Class 2 DPDocument17 pagesClass 2 DPrajeshmanamNo ratings yet
- Information Science 1Document22 pagesInformation Science 1yukoo2034No ratings yet
- Data Mining AbhasDocument24 pagesData Mining AbhasMohit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ch7 - Data Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesCh7 - Data Resource ManagementMirza NayeemNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 2 XmindDocument1 pageLec 2 Part 2 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Part 3 XmindDocument1 pageLec 1 Part 3 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 1 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 2 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- DOMINO Pizza Case StudyDocument2 pagesDOMINO Pizza Case StudyAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- E-Mail Spam Detection Using Machine Lear PDFDocument7 pagesE-Mail Spam Detection Using Machine Lear PDFTrending this yearNo ratings yet
- Valaris Exl I: Capacities Primary Rig CharacteristicsDocument1 pageValaris Exl I: Capacities Primary Rig Characteristicsmelody04223No ratings yet
- Topic04 - Recovering Graphics FileDocument44 pagesTopic04 - Recovering Graphics FileHappy Plants BDNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingDocument1 pageEyepiece Objective Lenses Head Nosepiece: Proper Care and HandlingRafael SaldivarNo ratings yet
- VAGT Catalog EnglishDocument24 pagesVAGT Catalog EnglishAlexandru AndreiNo ratings yet
- Test Plan and DocumentsDocument4 pagesTest Plan and DocumentsvimudhiNo ratings yet
- PSP VintageMeter Operation ManualDocument11 pagesPSP VintageMeter Operation Manualmunderwood1No ratings yet
- (Re - Work) Sample Interview RubricDocument1 page(Re - Work) Sample Interview Rubricyasamin shajiratiNo ratings yet
- Boyd's Harrisburg-Steelton City Directory 1904 (Pennsylvania) OCRDocument795 pagesBoyd's Harrisburg-Steelton City Directory 1904 (Pennsylvania) OCRKAW100% (1)
- 02 NetNumen U31 Software Installation - 54PDocument54 pages02 NetNumen U31 Software Installation - 54PAppolenaire Alexis86% (7)
- IOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM - DakshDocument17 pagesIOT BASED HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM - DakshMohit MehraNo ratings yet
- Description: Packag eDocument4 pagesDescription: Packag eVicenteAlvarezNo ratings yet
- 1 ABE 111 FinalDocument94 pages1 ABE 111 FinalMarooning ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Systems Security and Internal ControlsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Systems Security and Internal ControlsKEL ASMRNo ratings yet
- 8865 - Test CarDocument13 pages8865 - Test CarabigarxesNo ratings yet
- DevOps ProjectDocument160 pagesDevOps ProjectAkhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- SHEHERAZADE - 1001 Stories For Adult LearningDocument4 pagesSHEHERAZADE - 1001 Stories For Adult LearningAntonella MariniNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Candidacy For Member, Sangguniang Bayan: Commission On ElectionsDocument2 pagesCertificate of Candidacy For Member, Sangguniang Bayan: Commission On ElectionsPiagapo Lanao del SurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction: Online Shopping (Sometimes Known As E-Tail From "Electronic Retail" or E-Shopping) Is A FormDocument32 pagesChapter 1-Introduction: Online Shopping (Sometimes Known As E-Tail From "Electronic Retail" or E-Shopping) Is A FormdevilsharmaNo ratings yet
- FRP 1543494499564 - Grating Brochure - 2018Document6 pagesFRP 1543494499564 - Grating Brochure - 2018Ganesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Iso Iec 18013 2 2020Document74 pagesIso Iec 18013 2 2020Mykola AstratonovNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Optimization With GradientsDocument17 pagesBayesian Optimization With Gradients刘明浩No ratings yet
- READ ME - InfoDocument2 pagesREAD ME - InfoSalih AktaşNo ratings yet
- The Disadvantages of An NTFS File SystemDocument3 pagesThe Disadvantages of An NTFS File Systemwip789No ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering Exam Reference ManualDocument144 pagesControl Systems Engineering Exam Reference ManualArmand Muteb100% (2)
- PM PPM OHT 777E CaterpillarDocument75 pagesPM PPM OHT 777E CaterpillarDiki Abu Meshal67% (6)
- Digital ForensicsDocument23 pagesDigital ForensicsMunagala Sai SumanthNo ratings yet
- 3 Program Flowchart LectureDocument37 pages3 Program Flowchart LectureRyan Moises De MesaNo ratings yet
- Verilog HDL: Special ClassesDocument11 pagesVerilog HDL: Special ClassesUnique ProNo ratings yet
- Brosur L-Gutter TJMDocument4 pagesBrosur L-Gutter TJMPandu HarisurawanNo ratings yet