Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Governance Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Fernando HernandezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Governance Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Fernando HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
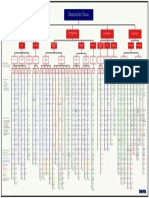
Data Governance Data Use & Availability > Data Governance Roles
Fundamentals Cheat Sheet Data use and availability refers to users being able to consistently access the data when they need it.
Can legitimate users get access to the data assets they need
Are the data assets consistently available when they are needed
Role
Executive Sponsor
Description
A senior employee acting as a conduit between the
C-suite and the data governance lead or council.
Governance responsibilities
Coordinate
teams
data governance activities across
Ensure alignment between corporate goals and
Are the data assets in a state that they can be used? the data governance program.
Learn online at www.DataCamp.com
Data Governance Lead Usuallythe CIO, CTO, or CDAO. Oversees the data Develop and implement a data governance
Data Management governance program. framework
Communicate with stakeholders.
Data Governance Group of individuals setting the strategic direction for Define what the data governance program needs
Are the processes and technologies in place to ensure other aspects of data governance? Council the data governance program. to accomplish by what date
Prioritize data governance initiatives.
Are the data assets stored securely Data Owner/Admin Someone with authority to make decisions about a Define standards for data use, including who has
Are the data assets kept up to date dataset. access
Define data quality properties such as accuracy,
>
Are the data assets protected from problems? completeness, reliability, relevance, and
Definitions Data Steward Provides enforcement of the rules set by the data
timeliness.
Implement the data use and data quality rules set
>
owner. by the data owner
Data governance: is a set of principles and processes for data collection, management, and use. Data Governance Framework Components Understand how the data is used by the
organization.
The goal is to ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and available for use, while protecting Data Custodian Manages and protects the data assets. Usually from
an IT team.
Manage and monitor data access and
Provide backup and recovery of data
usage
Respond to data breaches.
data privacy and security.
Data Stakeholder Anyone affected by data governance decisions. Provide feedback to the Data Governance Lead
A data governance framework: Is a set of policies, procedures, and standards that implements Policies &
Processes &
or Council
Strategy
standards technology
data governance for an organization. That is, where data governance describes what the Data User Someone who makes use of the data assets. Can Generate insights or value from the data
include employees or external users.
organization needs to do, the data governance framework describes how to do it.
Progress
Coordination &
Data literacy &
> The pillars of data governance
collaboration
monitoring &
communication
culture
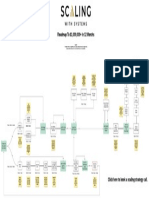
> Common Regulatory Frameworks
Regulation Region Description Who this applies to Key highlights
Strategy: Strategy defines how data should be used, treated, and managed safely, efficiently, and effectively to solve
business problems and meet business goals to ensure that data is consistently recognized and leveraged as a valuable GDPR European Union Designed to provide greater Businesses with customers
Need to obtain explicit
control over personal data for in EU consent from individuals
asset EU residents. before collecting and
processing their personal
Data driven decisions
data
actionable insights
Policies and Standards: Policies are documents of data management principles that outline decision-making rights, Data breaches must be
measurable outcomes reported within 72 hours.
goals, expectations, and responsibilities. Standards are guidelines of best practices to comply with the policies
CCPA California state Designed to provide greater Businesses with customers in Consumers have the right to
control over personal data for California that have gross know what information is
Processes and Technology: Processes involving data should describe procedures for monitoring data quality, handling California residents. collected about them, the
revenues over US$25M
Data governance
Data governance
issues, permissions for sharing data, managing metadata, and master data management. The technology needed to right to have that
information deleted, and the
implement, monitor, and maintain these processes also needs to be described right to opt out of the sale
of their personal data.
Coordination and Collaboration: Data governance is a cross-team effort, and the responsibilities of each role must be NY SHIELD New York state Designed to provide greater Businesses with customers
Provides broader definitions
Ownership &
Data Quality Data protection
Data use &
Data
documented, as well as the processes for how each role interacts with the others control over personal data for in NY of "private information" and
accountability & safety availability management New York residents. "breach" than federal law
Businesses must implement
a data security program
Progress Monitoring and Communication: The progress of data governance at the organization must be monitored including employee training,
vendor contracts, risk
using metrics for data quality, risk exposure, policy compliance, and return on investment assessments, and timely
data disposal.
People, processes & technology
Data Literacy and Culture: Workforces should be able to understand the importance of data governance, as well as PIPL China Designed to provide greater Businesses with customers
R
Similar to GDP , but for
how to get value from data assets. Good data governance requires a culture in which data governance is respected control over personal data for in China China
China residents. Has stricter rules around
and encouraged. data storage and
international transfer.
Ownership and Accountability Sarbanes
United States Designed to protect investors Publicly traded companies Financial statements must
–Oxley
> Data Governance Framework Principles
by improving the accuracy and in USA be checked by independent
reliability of disclosures by auditors
publicly traded companies Controls and procedures
In order to ensure that there are no gaps in data governance, and that work is not duplicated, a clear must be in place to ensure
financial statements are in
structure of accountability needs to be defined. line with Generally
Accepted Accounting
Every data asset should have an owner Principles (GAAP).
Integrity
For each data governance task, the person or role responsible for working on that task should be CCAR United States Designed to ensure resiliency Banks and bank holding Banks must submit a capital
clear Ownership and accountability of large banks against severe
economic situations
companies with US$50B plan to regulators
Capital reserve data and
assets forecasts under economic
For each data governance task, the people or roles accountable for the completion of the task scenarios are reviewed by
should be clear. Standardization and consistency regulators.
Change management HIPAA United States Designed to protect individuals Organizations dealing with Sensitive information cannot
personal health information health data be shared without patient
Data quality Risk management and compliance
knowledge of consen
Patients must be educated
on their data privacy rights,
and given access to their
medical records
Data quality means whether or not data is fit for purpose. There are several factors that affect data Strategy and alignment
quality.
Accuracy: Is the data free from errors? Does the data capture the thing it is meant to represent Integrity:
Data stakeholders should be honest and transparent with each other to ensure the success of the data
Completeness: Is all the data that is needed present? Have missing values been dealt with governance program, as well as promoting a culture of trust, teamwork, and collaboration
appropriately
Ownership and Accountability: The responsibilities of each data governance role must be clearly defined in order to
Timeliness: Is the data available when it is needed
prevent gaps in ownership or duplication of work
Consistency: Is the data the same, regardless of where it is accessed from
Integrity: Can you guarantee that the data has not been corrupted or tampered with? Standardization and Consistency: Data definitions need to be standardized to make it easier to use data across
multiple teams and projects. Consistency ensures that processes are repeatable throughout the organization and over
time
Learn Online at
Data Protection & Safety www.DataCamp.com
Change Management: The impact of new data governance policies or processes against existing projects should be
considered, and the framework needs to be robust against changing business needs and new employees
Data protection and safety refers to measures to prevent misuse of data. There are several aspects to it.
Risk Management and Compliance: The data governance framework should comply with any relevant laws and
Preventing unauthorized access of data through access management
regulatory frameworks. This includes having auditable processes, and controls to ensure compliance
Preventing personal or commercially sensitive data being leaked publicly through data masking and
encryption Strategy Alignment: In order to ensure the continued existence of a data governance framework, it needs to be clear
Preventing data being deleted or corrupted through disaster recovery. how that framework supports business goals and drives value.
You might also like
- Value-Map TM DeloitteDocument1 pageValue-Map TM DeloitteHugo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Base Enterprise Value Map PDFDocument1 pageBase Enterprise Value Map PDFjvr001100% (1)
- Power Pivot Client Server ArchitectureDocument2 pagesPower Pivot Client Server ArchitectureBalakrishna SappaNo ratings yet
- Responsibility Matrix PDFDocument1 pageResponsibility Matrix PDFNour MerjaniNo ratings yet
- Cobit 2019 - IsO20K MappingDocument1 pageCobit 2019 - IsO20K MappingAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Itil, CobitDocument1 pageItil, CobitParvez2zNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingDocument18 pagesStress and Strain - Axial LoadingClackfuik12No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics and Statistics: Fundamentals ofDocument468 pagesBusiness Mathematics and Statistics: Fundamentals ofSamirNo ratings yet
- Delloite Operator Value MapDocument1 pageDelloite Operator Value MapDiogo Pimenta Barreiros0% (1)
- MP 2.1.3 Matrix of Tasks AssignmentDocument4 pagesMP 2.1.3 Matrix of Tasks AssignmentenfrspitNo ratings yet
- Using BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldDocument6 pagesUsing BPM For Agility in A Globalized WorldWonderware Skelta BPM100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis Microtel by WyndhamDocument10 pagesSWOT Analysis Microtel by WyndhamAllyza Krizchelle Rosales BukidNo ratings yet
- Operations Projects Service Performance: Financial Snapshot Project Resource Hours Service OfferingsDocument1 pageOperations Projects Service Performance: Financial Snapshot Project Resource Hours Service OfferingsEdd AguaNo ratings yet
- TrakCare Overview 09012015Document5 pagesTrakCare Overview 09012015keziajessNo ratings yet
- BP Azspu Driver Fatigue & Tiredness Management ProcedureDocument11 pagesBP Azspu Driver Fatigue & Tiredness Management ProcedureEl Khan100% (1)
- 0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and SecurityDocument1 page0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and SecurityJorge Enrique Rico MarulandaNo ratings yet
- Digital Product Value Stream Management Architecture Blueprint v1 RC1Document1 pageDigital Product Value Stream Management Architecture Blueprint v1 RC1ofd86174No ratings yet
- Autoclave 2Document52 pagesAutoclave 2SILVANA ELIZABETH ROMO ALBUJANo ratings yet
- Data 11052022Document1 pageData 11052022aljarrahcs2431No ratings yet
- Digest of Ganila Vs CADocument1 pageDigest of Ganila Vs CAJohn Lester LantinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- API Pentesting Mindmap ATTACKDocument1 pageAPI Pentesting Mindmap ATTACKBondNo ratings yet
- Itil V3 Cobit V4.1 Mapping OverviewDocument8 pagesItil V3 Cobit V4.1 Mapping OverviewDwdroo DiwokNo ratings yet
- Finman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsDocument2 pagesFinman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsNorie De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card4Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card4GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- Mindmap For Operational Transparency in SAP: Supply Chain MindmappingDocument1 pageMindmap For Operational Transparency in SAP: Supply Chain MindmappingobNo ratings yet
- Operations and Maintenance Responsibility MatrixDocument22 pagesOperations and Maintenance Responsibility MatrixmelieneideaNo ratings yet
- Embedded Project WorksheetDocument4 pagesEmbedded Project WorksheetcammanderNo ratings yet
- BPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business AnalystsDocument1 pageBPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business AnalystsinigomNo ratings yet
- BPMN-Poster2019 FINAL en PDFDocument1 pageBPMN-Poster2019 FINAL en PDFsimdowNo ratings yet
- 0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and SecurityDocument1 page0202 Microsoft Team System Roles and Securitypradeepku.bNo ratings yet
- Central Finance 1709Document38 pagesCentral Finance 1709Romain DepNo ratings yet
- ITIL Edition 2011 - COBIT 5 - Mapping-22Document1 pageITIL Edition 2011 - COBIT 5 - Mapping-22Jeovanny MeraNo ratings yet
- Performance Manage MenDocument1 pagePerformance Manage MenmariaaltammamNo ratings yet
- SWS - Roadmap To $1,000,000+Document1 pageSWS - Roadmap To $1,000,000+crazymichNo ratings yet
- AWS Cloud PracticionerDocument1 pageAWS Cloud PracticionerwejsiNo ratings yet
- Raci Matrix: Yasm RslesDocument1 pageRaci Matrix: Yasm RslesxfireloveNo ratings yet
- HR Analytics Project (Responses)Document39 pagesHR Analytics Project (Responses)Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ashok Kumar Prasad - 190918Document4 pagesAshok Kumar Prasad - 190918DonNo ratings yet
- Culture and GuardrailsDocument1 pageCulture and Guardrailsdgloyn_coxNo ratings yet
- Reklamobil-Mobile Ad Industry 2009 by MobileraDocument1 pageReklamobil-Mobile Ad Industry 2009 by Mobileraasliguel_aktasNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Map ITIL4Document2 pagesValue Chain Map ITIL4Belem PianaNo ratings yet
- Metrics That Impact Bank Business Results: Introducing Human Capital Financial StatementsDocument31 pagesMetrics That Impact Bank Business Results: Introducing Human Capital Financial StatementsAlexander RuizNo ratings yet
- Exchange PosterDocument1 pageExchange Postergururajmvs100% (2)
- Presentation 2Document1 pagePresentation 2Oladayo AyodejiNo ratings yet
- In Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VDocument5 pagesIn Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VJulian HortaNo ratings yet
- AWS Periodic TableDocument1 pageAWS Periodic Tabledouglas.dvferreiraNo ratings yet
- Agile Hybrid TeamDocument1 pageAgile Hybrid Teamsalma ben salmaNo ratings yet
- Contracts Core 11510 ERDDocument1 pageContracts Core 11510 ERDtracejmNo ratings yet
- API Pentesting Mindmap While Trying To AttackDocument1 pageAPI Pentesting Mindmap While Trying To Attackvifiga9745No ratings yet
- DBMSDocument4 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument3 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- PRS Overview Poster PDFDocument1 pagePRS Overview Poster PDFOlivier KNNo ratings yet
- ITD Re-Org As of 17feb2017 2 PDFDocument1 pageITD Re-Org As of 17feb2017 2 PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- Masterpact NT RETURN Masterpact NW RETURN NS630b... 1600 33170Document1 pageMasterpact NT RETURN Masterpact NW RETURN NS630b... 1600 33170Anas BasarahNo ratings yet
- Chap 8Document1 pageChap 8Phu Nguyen NhutNo ratings yet
- Intervention Name: Word - Problem MnemonicsDocument3 pagesIntervention Name: Word - Problem MnemonicsJamuna Pandiyan MuthatiyarNo ratings yet
- Operations and Maintenance Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesOperations and Maintenance Plan Templatehieunt2489No ratings yet
- PM One Page FlowchartDocument1 pagePM One Page FlowchartbenNo ratings yet
- Vendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioDocument1 pageVendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioLIGAYA SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- Brochure SP Option Plus UK HDDocument2 pagesBrochure SP Option Plus UK HDkentNo ratings yet
- (PREVIEW - ONLY) SH SCCCI Flyer - 20160815 - 4Document2 pages(PREVIEW - ONLY) SH SCCCI Flyer - 20160815 - 4me2 monkNo ratings yet
- Good IrmodelingDocument263 pagesGood IrmodelingBhavy SinghNo ratings yet
- Materials Poster 18x24Document1 pageMaterials Poster 18x24nikima.netNo ratings yet
- TIP - IPBT M - E For MentorsDocument3 pagesTIP - IPBT M - E For Mentorsallan galdianoNo ratings yet
- ASTM A586-04aDocument6 pagesASTM A586-04aNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Instructions For The Safe Use Of: Web LashingsDocument2 pagesInstructions For The Safe Use Of: Web LashingsVij Vaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewDocument14 pagesEvaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewJaber AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Indian Consumer - Goldman Sachs ReportDocument22 pagesIndian Consumer - Goldman Sachs Reporthvsboua100% (1)
- Application Form New - Erik WitiandikaDocument6 pagesApplication Form New - Erik Witiandikatimmy lauNo ratings yet
- Organization of Brigada Eskwela Steering and Working CommitteesDocument2 pagesOrganization of Brigada Eskwela Steering and Working CommitteesCherry Lou RiofrirNo ratings yet
- Hyflow: Submersible PumpsDocument28 pagesHyflow: Submersible PumpsmanoNo ratings yet
- 14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFDocument10 pages14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFsabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- IMO Special Areas Under MARPOLDocument2 pagesIMO Special Areas Under MARPOLRavi Viknesh100% (1)
- Blockchain Technology in The Banking SectorDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology in The Banking Sectorvaralakshmi aNo ratings yet
- CH 2 How LAN and WAN Communications WorkDocument60 pagesCH 2 How LAN and WAN Communications WorkBeans GaldsNo ratings yet
- Aug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyDocument48 pagesAug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyBuildersLineMonthlyNo ratings yet
- Energia Eolica Nordex N90 2500 enDocument20 pagesEnergia Eolica Nordex N90 2500 enNardo Antonio Llanos MatusNo ratings yet
- INSURANCE BROKER POLICIES Erna SuryawatiDocument7 pagesINSURANCE BROKER POLICIES Erna SuryawatiKehidupan DuniawiNo ratings yet
- Case Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicDocument3 pagesCase Title: G.R. No.: Date: Venue: Ponente: Subject: TopicninaNo ratings yet
- About UPSC Civil Service Examination Schedule and Subject ListDocument4 pagesAbout UPSC Civil Service Examination Schedule and Subject Listjaythakar8887No ratings yet
- User Manual OptiPoint 500 For HiPath 1220Document104 pagesUser Manual OptiPoint 500 For HiPath 1220Luis LongoNo ratings yet
- Scout Activities On The Indian Railways - Original Order: MC No. SubjectDocument4 pagesScout Activities On The Indian Railways - Original Order: MC No. SubjectVikasvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNoteRSViewME 5 10 02Document12 pagesReleaseNoteRSViewME 5 10 02Jose Luis Chavez LunaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Foundation of ROB at LC-9 Between Naroda and Dabhoda Station On Ahmedabad-Himmatnagar RoadDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Design of Foundation of ROB at LC-9 Between Naroda and Dabhoda Station On Ahmedabad-Himmatnagar RoadmahakNo ratings yet
- Reterta V MoresDocument13 pagesReterta V MoresRam Migue SaintNo ratings yet
- Defination of ValuesDocument11 pagesDefination of ValuesDipannita GhoshNo ratings yet