Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CA Governance Lecture
Uploaded by
Muhammad AijazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CA Governance Lecture
Uploaded by
Muhammad AijazCopyright:
Available Formats
Current Affairs - Understanding Governance Structure Uzair Khan
Governance
Etymology:
The word “governance” came from the Latin verb “gubernare,” or more originally from the
Greek word “kubernaein,” which means “to steer.” Based on its etymology governance refers to
the manner of steering or governing a group of people or a state.
Definition:
“In simpler terms, Governance is defined as the action or manner of governing a state or an
organization”
“The manner in which power is exercised in the management of a country's economic and social
resources for development” --World Bank
“Governance can be seen as the exercise of economic, political and administrative authority to
manage a country’s affairs at all levels” -- UNDP
What is State?
According to Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of State, a state should possess
A defined territory
A permanent population
A government
Capacity to enter into relations with other states
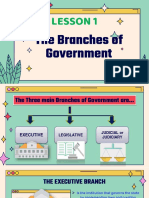
Governance Structure
Legislature
Executive
Judiciary
Makes
enforces
thethe
Laws
laws
Interprets the laws
Legislature Executive Judiciary Informal Instits
o Parliament o Prime Minister o Supreme Court o Media 4th
o NA lower house o President o High Court pillar
o Senate Upper House o Cabinet/ o Lower Court o Civil
o Standing Committees Ministries o Specialized Society
o Specialized o Bureaucracy Courts o NGO’s
Committees o Civil Secretariat o Ombudsman o Community
o Provincial/Local Govts o Policy Boards
Implementing
institutions
Current Affairs - Understanding Governance Structure Uzair Khan
Policy Making in Pakistan:
Approach 1 (proactive): State Legislatures formulate a policy, executive implements it.
Approach 2: Informal institutions (media, civil society) highlight a problem and push
government machinery to formulate a policy to curtail that problem.
Role of Governance in a Nation’s success:
An effective governance structure must be in place as a foundation for the effective
implementation of policies.
Effective Coordination of governance institutions is a benchmark for success.
Robust governance mechanism creates a bulwark against abuse of power and social ills.
Acemoglu and Robinson’s central argument in book Why Nations Fail
Problems in Governance Structure of Pakistan:
Lack of ‘trias politica’ (Montesquieu’s Separation of Powers)
No system of Checks and Balances (US system of Checks and Balances)
Blame the other games
Overstepping of institutions
Absence of policy Coordination among institutions
Lack of Policy Cohesion
Fragile institutions of Jinnah’s nation
Absence of institutional approach
Absence of Community based Governance approach
Lessons from the Successful nations:
Singaporean Governance model
Malaysian Governance framework
Madisonian Governance Model
Global Agencies and the Idea of Good Governance
Participation
Accountability
Rule of Law
Transparency
Consensus
Efficiency
Equity
Responsiveness
Strategic Vision
Recommended Readings: Why Nations Fail Acemoglu and Robinson
Governing the Ungovernable Ishrat Husain
Ishrat Hussain’s Chapter Retooling Institutions in Beyond the Crisis State (Maleeha Lodhi)
You might also like
- Topic 4. Significance of Different Branches of Power in A Public Administration ProcessDocument6 pagesTopic 4. Significance of Different Branches of Power in A Public Administration ProcessEliz SemenkoNo ratings yet
- LESSON-1-BRANCHES-OF-GOVERNMENT Part 5Document17 pagesLESSON-1-BRANCHES-OF-GOVERNMENT Part 5Dee Cyree RusiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vietnamese Legal System: Week 1 - State & LawDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Vietnamese Legal System: Week 1 - State & Lawvivi AnNo ratings yet
- General Studies-II: (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)Document14 pagesGeneral Studies-II: (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)Aakash LawaNo ratings yet
- Drishti IAS Coaching in Delhi, Online IAS Test Series & Study Material General Studies-IIDocument9 pagesDrishti IAS Coaching in Delhi, Online IAS Test Series & Study Material General Studies-IISneha KantNo ratings yet
- Government Structures Help Us Live Together CivicsDocument4 pagesGovernment Structures Help Us Live Together CivicsGunazdeep SidhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Law in MalaysiaDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Law in MalaysiaAhmad Aizzat SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Business Law CBE NEWDocument63 pagesBusiness Law CBE NEWBenjamin EliasNo ratings yet
- Assessing Political and Social InstitutionsDocument12 pagesAssessing Political and Social InstitutionsJanaeirah Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- First, Second, Third ClassDocument29 pagesFirst, Second, Third ClassAditya SubbaNo ratings yet
- Judiciary and Good GovernanceDocument4 pagesJudiciary and Good GovernanceAliHussnainBhalliNo ratings yet
- MP Jain - Indian Constitutional LawDocument1,963 pagesMP Jain - Indian Constitutional LawAuxEn87% (75)
- Introduction To Administrative LawDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Administrative Lawwajidali454No ratings yet
- En Wikipedia Org Wiki Administrative Law# Text Administrative20is20division, Or20enforcement20lawsDocument11 pagesEn Wikipedia Org Wiki Administrative Law# Text Administrative20is20division, Or20enforcement20lawslorenca bejkoNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Business & Corporate LawDocument14 pagesTopic1 Business & Corporate LawLearnmore ChikukwaNo ratings yet
- Organs of Govt. ProjectDocument16 pagesOrgans of Govt. ProjectAnkur Bhatt88% (8)
- General Studies IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Studies IIshrekNo ratings yet
- Unitary and Federal GovernmentDocument5 pagesUnitary and Federal Governmentariah janeNo ratings yet
- Definition of JudiciaryDocument8 pagesDefinition of JudiciaryshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Admin Law NotesDocument62 pagesAdmin Law NotesMay SandeNo ratings yet
- EXAM Constitutional LAW 1Document6 pagesEXAM Constitutional LAW 1Dann JOCKERNo ratings yet
- Federalism: Emergence of Multiple Legal and Judicial Systems Within The CountryDocument3 pagesFederalism: Emergence of Multiple Legal and Judicial Systems Within The CountryFina SchuckNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Admin LawDocument17 pagesLecture of Admin LawAyanNo ratings yet
- GS2 Mains SyllabusDocument9 pagesGS2 Mains SyllabusGarvNo ratings yet
- What Is PoliticsDocument7 pagesWhat Is PoliticsJayson ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nataliemoore Political and Legal SystemsDocument2 pagesNataliemoore Political and Legal Systemsjairuz matthew bernardoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Administrative LawDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Administrative LawAtif Rehman100% (1)
- Stakeholder DLL 2Document25 pagesStakeholder DLL 2kingNo ratings yet
- Planning Legislation: Unit 1 LawDocument14 pagesPlanning Legislation: Unit 1 LawReeshmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ConstitutionsDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - ConstitutionsSokun Thearos VisalNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Topic Part 1Document7 pagesPreliminary Topic Part 1The Monitor CatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 MPM 5024 1Document142 pagesLesson 2 MPM 5024 1Hayleye Kinfe100% (1)
- MAN Introduction To Law HandoutDocument3 pagesMAN Introduction To Law HandoutstjosephtheworkercorcueraNo ratings yet
- Adminstrative Notes by Professor DawitDocument18 pagesAdminstrative Notes by Professor Dawitrekik tegeneNo ratings yet
- Gs 2Document5 pagesGs 2Narendra KumawatNo ratings yet
- PRLS LRD PN 001 2022Document12 pagesPRLS LRD PN 001 2022MOH'D. AL-KHALEEL BOGABONGNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument3 pagesSeparation of PowersShamaal KhattakNo ratings yet
- General Studies IIDocument15 pagesGeneral Studies IIKeerrthi VasanNo ratings yet
- Preamble, Article 6-8 Section IDocument4 pagesPreamble, Article 6-8 Section ILendrei QuerimitNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Reviewer-General Info by NequintoDocument10 pagesCivil Service Reviewer-General Info by NequintoAnonymous iMFmFjmfhNo ratings yet
- UPSC GS II SyllabusDocument10 pagesUPSC GS II SyllabusGhouse cyber cafeNo ratings yet
- States, Political Regimes, and Government InstitutionsDocument3 pagesStates, Political Regimes, and Government InstitutionsBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Legal Methods and JurisprudenceDocument68 pagesLegal Methods and Jurisprudenceජෛන සොහ්රාබ්100% (1)
- 1 PB PDFDocument9 pages1 PB PDFElujekwute BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Politics, Government & Laws: Chatper 3Document25 pagesPolitics, Government & Laws: Chatper 3Saufi AnasNo ratings yet
- Admin LawDocument49 pagesAdmin LawKumar KishlayNo ratings yet
- Legal Research Mikee Louise Q. Mirasol JD 1E-BDocument5 pagesLegal Research Mikee Louise Q. Mirasol JD 1E-BMikee BornforThis MirasolNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Definitions, Concept and Nature of Administrative LawDocument32 pagesMeaning, Definitions, Concept and Nature of Administrative LawSARIKANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Law: Ass Prof. Dr. Vesna TrajanovskaDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Law: Ass Prof. Dr. Vesna TrajanovskaBube AndreskaNo ratings yet
- Legislation As A Source of Law in Lawmaking Process - IpleadersDocument1 pageLegislation As A Source of Law in Lawmaking Process - IpleadersLaxmi KantNo ratings yet
- ECELAW1 DocuDocument163 pagesECELAW1 DocuJay AlmerolNo ratings yet
- LAW 253 Slide 1Document129 pagesLAW 253 Slide 1tetojogoldenboyNo ratings yet
- Political InstitutionsDocument59 pagesPolitical Institutionsandrea monaresNo ratings yet
- Adminstrative Note by DevaDocument27 pagesAdminstrative Note by Devarekik tegeneNo ratings yet
- The Role of Law: Power-That Is, Establishing and Distributing AuthorityDocument19 pagesThe Role of Law: Power-That Is, Establishing and Distributing AuthorityMicha EllahNo ratings yet
- Business Law Edited For BetyDocument93 pagesBusiness Law Edited For Betygach getasewNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Law and The Legal SystemDocument28 pagesSession 5 Law and The Legal SystemNeil Bryan N. MoninioNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law PPT-1Document45 pagesAdministrative Law PPT-1Niraj Pandey100% (1)
- Lesson 2 MPM 5024Document27 pagesLesson 2 MPM 5024Hayleye Kinfe100% (1)
- DynamicsDocument11 pagesDynamicsMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Data Science CareerDocument1 pageData Science CareerMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- ASM Mohsin PresentationDocument8 pagesASM Mohsin PresentationMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Maritime AwarenessDocument5 pagesMaritime AwarenessMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Sofia Naveed Final ThesisDocument400 pagesSofia Naveed Final ThesisMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Is Media Globalization A Form of Cultural..Document7 pagesIs Media Globalization A Form of Cultural..Muhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Globalization LinksDocument1 pageGlobalization LinksMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Polarized PoliticsDocument1 pagePolarized PoliticsMuhammad AijazNo ratings yet
- Drap ActDocument35 pagesDrap Actaqeel1970No ratings yet
- Writ Petition Filed (11290) With The Lahore High Court On GMODocument22 pagesWrit Petition Filed (11290) With The Lahore High Court On GMOIjaz Ahmad Rao100% (1)
- Parliament of PakistanDocument20 pagesParliament of PakistanNasir AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Provincial Autonomy and 18th AmendmentDocument17 pagesProvincial Autonomy and 18th AmendmentAdeel Ahmed SindhuNo ratings yet
- Civil Service ManualDocument171 pagesCivil Service Manualasghar_rana78No ratings yet
- Law and Med - 2Document9 pagesLaw and Med - 2Anirudh RanaNo ratings yet
- Election Officer Jobs 2017 All Solved Mcqs Tests Model Papers PDF Book Free Download Election Officers (Bs-17) Course Outline Written Syllabus PaperDocument7 pagesElection Officer Jobs 2017 All Solved Mcqs Tests Model Papers PDF Book Free Download Election Officers (Bs-17) Course Outline Written Syllabus PaperTalha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights PDFDocument128 pagesFundamental Rights PDFMehar UsmanNo ratings yet
- Cheif Justice Decision Pakistan Steel Mills CaseDocument79 pagesCheif Justice Decision Pakistan Steel Mills CaseAsim Bashir KhanNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Studies and Global PerspectiveDocument6 pagesPakistan Studies and Global PerspectiveMinahil NasserNo ratings yet
- Dr. Fahmida Mirza Dr. Fahmida Mirza Was Born On DecemberDocument67 pagesDr. Fahmida Mirza Dr. Fahmida Mirza Was Born On DecemberNainaJamesNo ratings yet
- V - 62 Caroni, Trinidad, Thursday 2nd March, 2023-Price $1.00 N - 34Document17 pagesV - 62 Caroni, Trinidad, Thursday 2nd March, 2023-Price $1.00 N - 34ERSKINE LONEYNo ratings yet
- Electoral System of PakistanDocument26 pagesElectoral System of PakistanJaveria ZafarNo ratings yet
- Law - EnvironmentDocument12 pagesLaw - EnvironmentNavid GodilNo ratings yet
- Pak StudiesDocument28 pagesPak StudiesAmeer MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Elections in Pakistan-1Document6 pagesElections in Pakistan-1Sania ShahNo ratings yet
- Constitution of PakistanDocument10 pagesConstitution of PakistanAamir HussainNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Part 2Document10 pagesConstitutional Law Part 2Muhammad Imran Ahmad Kamboh0% (1)
- Constitutional History of Pakistan#01Document18 pagesConstitutional History of Pakistan#01Nargis ShamimNo ratings yet
- State - Politics and Economy of Rajasthan Volume-7Document23 pagesState - Politics and Economy of Rajasthan Volume-7abhilasha raoNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY DEBATES Eng Vol 05Document1,024 pagesCONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY DEBATES Eng Vol 05CKNo ratings yet
- Delegated Legislation NotesDocument102 pagesDelegated Legislation NotesAfham Zaffar100% (1)
- Interview PreparationDocument34 pagesInterview Preparationjawadseo1214No ratings yet
- Rules of Business 1973Document85 pagesRules of Business 1973fahimkhan1986No ratings yet
- Ordinance Making Power of The PresidentDocument11 pagesOrdinance Making Power of The PresidentAayushi TomerNo ratings yet
- 2013 S C M R 1337Document35 pages2013 S C M R 1337Shehzad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Case BookDocument275 pagesConstitutional Law Case BookKwaku Adom OseiNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Labour LawsDocument25 pagesPakistan Labour Lawshelperforeu100% (1)
- National Assembly of PakistanDocument77 pagesNational Assembly of PakistanHasan AliNo ratings yet
- Final PTB Pakistan Studies 10 EM Prepress 08-02-2020 - 0Document128 pagesFinal PTB Pakistan Studies 10 EM Prepress 08-02-2020 - 0SAQIB ALINo ratings yet