100% found this document useful (1 vote)
748 views4 pagesAlternating Current Class 12 Notes Chapter 7
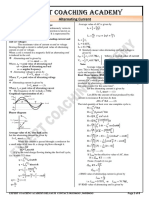
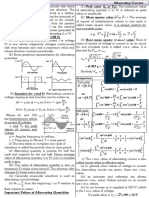
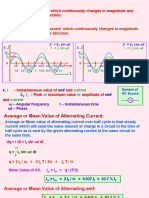
1. Alternating current (AC) varies in both magnitude and direction periodically over time according to mathematical functions like sine or cosine waves.
2. The effective or root mean square (rms) value of AC is defined as the steady current that would generate the same amount of heat in a resistor over a full cycle as the varying AC. It is equal to 70.7% of the peak value.
3. The average or mean value of AC is defined as the current that would send the same total charge through a circuit in half a cycle as a steady current. It is equal to 63.7% of the peak value.
Uploaded by
Sri DharshanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
748 views4 pagesAlternating Current Class 12 Notes Chapter 7
1. Alternating current (AC) varies in both magnitude and direction periodically over time according to mathematical functions like sine or cosine waves.
2. The effective or root mean square (rms) value of AC is defined as the steady current that would generate the same amount of heat in a resistor over a full cycle as the varying AC. It is equal to 70.7% of the peak value.
3. The average or mean value of AC is defined as the current that would send the same total charge through a circuit in half a cycle as a steady current. It is equal to 63.7% of the peak value.
Uploaded by
Sri DharshanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd