Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edgcse Aap Sb9k 0430 W
Uploaded by
Said ErcanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edgcse Aap Sb9k 0430 W
Uploaded by
Said ErcanCopyright:
Available Formats
Decomposition and carbon
SB9k.1 dioxide
Your teacher may watch to see if you can:
● use appropriate apparatus to measure temperature and carbon dioxide concentration accurately.
Introduction
Bacteria are decomposers of dead plant and animal material. Respiration by bacteria releases the energy
needed for decay processes. This investigation compares the release of carbon dioxide from untreated dead
plant material and plant material that has been sterilised to kill all microorganisms.
Aim
To investigate the release of carbon dioxide from decaying plant material.
Prediction
1 Predict how the temperature and release of carbon dioxide from the untreated and sterilised plant material
will differ after the plant material has been left for a period of time. Give a reason for your prediction.
Method
Apparatus Safety
● carbon dioxide sensor Wear eye protection.
● untreated grass cuttings in
plastic bag with clip ● thermometer Handle the grass cuttings as little as
● sterilised grass cuttings in ● paper towel possible.
plastic bag with clip Wash hands thoroughly after touching
grass cuttings.
A Remove the clip from one bag of cuttings. Open the bag as little as possible to insert the carbon dioxide
sensor. Record the carbon dioxide concentration in the bag.
B Measure the temperature of the bag of cuttings by placing the bulb of the thermometer into the middle of
the cuttings. Record the value then remove the thermometer and close the bag with the clip.
C Wipe the thermometer with the paper towel then repeat steps A and B with the other bag of cuttings.
D After 30 minutes repeats steps A to C.
E If there is time, repeat steps A to C after 1 hour.
Recording your results
2 Record your results in a suitable table.
3 Calculate the change in temperature and carbon dioxide concentration in both bags over the time of the
experiment.
Considering your results/conclusions
4 Compare the change in temperature and carbon dioxide concentration in the two bags of cuttings.
5 Explain any differences in change in temperature and carbon dioxide concentration in the two bags.
Evaluation
6 Suggest one way in which the method could be improved to give better results. Give a reason for your
answer.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
1
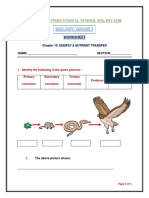
SB9k.2 Carbon dioxide jigsaw
Cut out the boxes below. Arrange the six pictures and link them with the arrows so that they
show the carbon cycle. Then place the text boxes next to the appropriate arrows to show the
processes in the carbon cycle. Some blank text boxes have been included for any processes that
need to be used more than once.
Compare your carbon cycle with a partner to check that you have everything in the right place. Discuss any
differences and try to agree the best arrangement. Then stick the boxes onto blank paper to make a poster.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
2
The carbon cycle
SB9k.3 Strengthen
Name Class Date
7 Choose the correct words from the box below to complete the boxes on the diagram of the carbon cycle.
You can use each word once, more than once or not at all.
animals consumers decomposers plants
8 Colour the arrows in the carbon cycle to show which process they represent. Use a different colour for each
process. Complete the key below with the colours you use on the diagram.
respiration
combustion
photosynthesis
feeding
death
9 Pilobolus is a type of fungus. Like many fungi, Pilobolus is a decomposer.
a Name the process that decomposers use to release energy for getting food.
___________________________________________________________________________________
b Name the gaseous product of the process that you named in part a.
___________________________________________________________________________________
c Explain why the bodies of dead organisms and animal waste ‘disappear’ over time.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
S1 Explain why Pilobolus is important in the carbon cycle.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
3
Carbon cycle questions
SB9k.4 Homework 1
Name Class Date
10 Draw lines to link each process to its role in the carbon cycle.
photosynthesis releases carbon dioxide into the air from complex
carbon compounds in fossil fuels
respiration transfers complex carbon compounds from one
organism to another in biomass
combustion takes carbon dioxide from the air to build carbon
compounds in plants and algae
feeding releases carbon dioxide into the air from complex
carbon compounds in living organisms
11 Explain why fossil fuels contain large amounts of carbon compounds.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
12 a Name two groups of microorganisms that are decomposers.
___________________________________________________________________________________
b Describe the role of decomposers in ecosystems.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
13 Students place some fresh peas in a plastic bag and some sterilised peas in another plastic bag. They
measure the temperature of the peas and the carbon dioxide concentration in both bags. They then place
the bags inside separate insulated boxes. A few hours later they repeat the measurements. The table
shows their results.
Fresh peas Sterilised peas
Temperature (°C) Carbon dioxide Temperature (°C) Carbon dioxide
concentration concentration
(ppm) (ppm)
at start 19 400 19 400
2 hours 24 800 19 400
later
a Describe the differences in results for the fresh peas and the sterilised peas.
___________________________________________________________________________________
b Explain the differences in results.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
c Explain why the bags were placed in insulated boxes during the experiment.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
4
Global carbon cycle
SB9k.5 Homework 2
The table shows the amount of carbon transferred to and from the atmosphere globally by different processes
in the carbon cycle.
Process Mass of carbon transferred
(billion tonnes/year)
terrestrial (on land) photosynthesis 123
respiration (plant and animal) 60
respiration (decomposition) 60
aquatic (in water) photosynthesis by microscopic sea plants 92
respiration (plants, animals, decomposition) 90
human activity 9
14 a Sketch a carbon cycle to display the transfers of carbon between the atmosphere and terrestrial and
aquatic organisms.
b Use the data in the table to label your cycle so that it shows the masses of carbon transferred.
15 a Name the form of carbon in the atmosphere.
b Name two forms of carbon in the biotic part of the cycle.
16 Explain how respiration is related to decomposition.
17 a Calculate the net transfer of carbon between soil and the atmosphere in the terrestrial part of the cycle.
b Calculate the net transfer of carbon between the atmosphere and ocean sediments in the aquatic part
of the cycle.
18 Explain how the combustion of fossil fuels contributes to the value for human activity shown in the table.
19 Use all the information in the table to calculate the net transfer of carbon to the atmosphere in one year.
Extra challenge
20 When predicting the effects of future atmospheric carbon transfers, scientists need to consider the effect of
carbon dioxide concentration on living organisms. Suggest how the values for photosynthesis shown in the
table might change, giving a reason for your answer.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
5
SB9k Progression check
Name Class Date
Progression questions
Answer these questions.
1 What is a decomposer?
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
2 How is carbon cycled through an ecosystem?
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
3 What is the role of decomposers in the carbon cycle?
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Now circle the faces in the ‘Start’ row in the table showing how confident you are of your answers.
Question 1 2 3
Start
Assessment
Using a different colour, correct or add to your answers above. You may need to use the back of this sheet or
another piece of paper. Then circle the faces in the ‘Check’ row in the table.
Question 1 2 3
Check
Feedback
What will you do next? Tick one box.
strengthen my learning strengthen then extend extend
Note down any specific areas you need to improve.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Action
You may now be given another activity. After this, note down any remaining areas you need to improve and
how you will try to improve in these areas.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
© Pearson Education Ltd 2017. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
6
You might also like
- Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarFrom EverandCarbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarNo ratings yet
- S2 Is 1st WorkbookDocument84 pagesS2 Is 1st WorkbookWinnie ChanNo ratings yet
- Abstract PDFDocument10 pagesAbstract PDFjayden.patel10No ratings yet
- Kami Export - PlantsSnailsSEDocument4 pagesKami Export - PlantsSnailsSESammy DejliNo ratings yet
- Evr LabsDocument70 pagesEvr LabsJulishiamor HarperNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument33 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPNirashaNo ratings yet
- Version TwoDocument30 pagesVersion Twoerick kanyiNo ratings yet
- Bio RevisionsheetDocument4 pagesBio RevisionsheetKhushbu DaveyNo ratings yet
- Shigemoto 2006Document6 pagesShigemoto 2006Serwin Elias Suazo BajañaNo ratings yet
- Background of The Study: Catalino, Gayaso, Pacsay, Palsiyeng, Alagon, Dacquias, and PanitDocument29 pagesBackground of The Study: Catalino, Gayaso, Pacsay, Palsiyeng, Alagon, Dacquias, and PanitAriNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of High-Specific-Surface-Area Activated Carbons From K CO - Treated Waste PolyurethaneDocument7 pagesPreparation and Characterization of High-Specific-Surface-Area Activated Carbons From K CO - Treated Waste PolyurethaneNIVEDHA TNo ratings yet
- Pollution Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesPollution Exam QuestionsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Novel Treatment and Value-Added Utilization of Oily Sludge Using Ionic Liquid and PyrolysisDocument244 pagesNovel Treatment and Value-Added Utilization of Oily Sludge Using Ionic Liquid and PyrolysisLaiadhi DjemouiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 (Stoichiometry)Document18 pagesExperiment No. 5 (Stoichiometry)gudoybenedictlNo ratings yet
- Edp ContentDocument22 pagesEdp ContentJohn Kenneth SenatoNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Copper From Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbons Obtained by Pyrolisis of Cassava PeelDocument6 pagesAdsorption of Copper From Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbons Obtained by Pyrolisis of Cassava PeelevinNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon UllmanDocument27 pagesActivated Carbon UllmanMelumzi NontanganaNo ratings yet
- Alexa Kirsten Marundan - Photosynthesis Exploration Lab - Understanding The Movement of CarbonDocument3 pagesAlexa Kirsten Marundan - Photosynthesis Exploration Lab - Understanding The Movement of CarbonAlexa Kirsten MarundanNo ratings yet
- The Comparison of Two Activation Techniques To Prepare Activated Carbon From Corn CobDocument7 pagesThe Comparison of Two Activation Techniques To Prepare Activated Carbon From Corn CobRafaelaMarinhoFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Mass-Ssam Relationships in Reactions: Pre-Lab DiscussionDocument2 pagesMass-Ssam Relationships in Reactions: Pre-Lab DiscussionKeifer BellNo ratings yet
- 0654 w18 QP 41Document28 pages0654 w18 QP 41EYE RIZNo ratings yet
- Aresta 2016Document44 pagesAresta 2016sigit cahyonoNo ratings yet
- Biocarbon From Different Biomass PrecursDocument4 pagesBiocarbon From Different Biomass PrecursboikoNo ratings yet
- Carboncyclemodel 1Document3 pagesCarboncyclemodel 1api-267068877No ratings yet
- 2 2 Carbon Cycle WorksheetDocument4 pages2 2 Carbon Cycle WorksheetVince HernándezNo ratings yet
- Nurhilal 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1080 012024Document7 pagesNurhilal 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1080 012024Emmanuel MatutuNo ratings yet
- A Level OCR Chemistry A - Paper 1 June 2023Document27 pagesA Level OCR Chemistry A - Paper 1 June 2023kapedispurs50% (2)
- Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon From Waste Sawdust From Saw MillDocument7 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon From Waste Sawdust From Saw MillDiana CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon PHD ThesisDocument6 pagesActivated Carbon PHD Thesisbk32hdq7100% (2)
- Stoichiometry Review PacketDocument5 pagesStoichiometry Review PacketMario CalderonNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: R. Ben-Mansour, M.A. Habib, O.E. Bamidele, M. Basha, N.A.A. Qasem, A. Peedikakkal, T. Laoui, M. AliDocument31 pagesApplied Energy: R. Ben-Mansour, M.A. Habib, O.E. Bamidele, M. Basha, N.A.A. Qasem, A. Peedikakkal, T. Laoui, M. AliMoaz KhursheedNo ratings yet
- SS 22 Ex6Document6 pagesSS 22 Ex6Jean Gabrelle DoradoNo ratings yet
- 433-437 PreparationofhighsurfaceDocument5 pages433-437 PreparationofhighsurfaceRohan ChauguleNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- Coconut Shell Versus Bituminous Coal Activated CarbonDocument6 pagesCoconut Shell Versus Bituminous Coal Activated Carbonnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Cycling of MaterialsDocument5 pagesThe Cycling of Materialstamuno7No ratings yet
- E.Sci9 - Q2 - Week 5Document7 pagesE.Sci9 - Q2 - Week 5HersheyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Worksheet - Chapter 19 (270123) - 1Document5 pagesGrade 7 Worksheet - Chapter 19 (270123) - 1TalhaNo ratings yet
- Improvemet of Carbon Dioside Biofixation in A Photobioreactor Using Anabaena SPDocument7 pagesImprovemet of Carbon Dioside Biofixation in A Photobioreactor Using Anabaena SPNancy TPNo ratings yet
- IB Style Test - Topic 2: Molecular Biology: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesIB Style Test - Topic 2: Molecular Biology: Multiple Choice QuestionsHilary YuNo ratings yet
- A Study Into The Cultivation of Algae - 2008Document71 pagesA Study Into The Cultivation of Algae - 2008PatchworkFishNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of Ibuprofen From Aqueous Solution On Chemically Surface-Modified Activated Carbon ClothsDocument11 pagesAdsorption of Ibuprofen From Aqueous Solution On Chemically Surface-Modified Activated Carbon ClothsSeptian Perwira YudhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Substances: Reading TextDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Substances: Reading TextGreselNo ratings yet
- Pyrolisis 8 OkDocument7 pagesPyrolisis 8 OkegofientsNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Trae Student - PlantsSnailsSEDocument4 pagesKami Export - Trae Student - PlantsSnailsSETrae CalderonNo ratings yet
- KKU Engineering JournalDocument5 pagesKKU Engineering JournalBello yusufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (The Air Around Us) : Symbol Percentage (%) A B C D EDocument3 pagesChapter 5 (The Air Around Us) : Symbol Percentage (%) A B C D EMaharani LawakNo ratings yet
- Cantillo 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1386 012038Document7 pagesCantillo 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1386 012038David MoralesNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting Microwave Assisted Preparation ofDocument11 pagesFactor Affecting Microwave Assisted Preparation ofeva reysitaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Mass Balance Model For Biological Sequencing Batch Reactors Used For Carbon and Nitrogen Removal D.Mazouni, M. Ignatova, J. HarmandDocument6 pagesA Simple Mass Balance Model For Biological Sequencing Batch Reactors Used For Carbon and Nitrogen Removal D.Mazouni, M. Ignatova, J. Harmandsharan kommiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Analytical and Applied PyrolysisDocument4 pagesJournal of Analytical and Applied PyrolysisMathilda Jowito PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Article Chemical Engineering July 2017 Activated Carbon Fundamentals and New ApplicationsDocument10 pagesArticle Chemical Engineering July 2017 Activated Carbon Fundamentals and New ApplicationsHonguito WebNo ratings yet
- KS3 Revision 6th July 2020Document25 pagesKS3 Revision 6th July 2020Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- C. Guizani, F.J. Escudero Sanz, S. Salvador: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesC. Guizani, F.J. Escudero Sanz, S. Salvador: SciencedirectTrường TùngNo ratings yet
- Benzene Is An Important Starting Material in The Production of Dyes, Detergents and Medicines. (A)Document9 pagesBenzene Is An Important Starting Material in The Production of Dyes, Detergents and Medicines. (A)Rayyan BariNo ratings yet
- Amines 2 QPDocument9 pagesAmines 2 QPdanyNo ratings yet
- Xperiments With Arbon Ioxide: HapterDocument12 pagesXperiments With Arbon Ioxide: HapterBashar Al ZoobaidiNo ratings yet
- PNNL Coal Gasification ResearchDocument30 pagesPNNL Coal Gasification ResearchAlberto Rivera CantilloNo ratings yet
- Is Anything Really Moving in Your Biospheres?Document18 pagesIs Anything Really Moving in Your Biospheres?api-486349248No ratings yet
- Online Classwork - Simultaneous Linear EquationsDocument1 pageOnline Classwork - Simultaneous Linear EquationsSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Year10 Homework - Practice QuestionsDocument12 pagesYear10 Homework - Practice QuestionsSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 - Homework - Simultaneous Linear and Quadratic EquationsDocument1 pageYear 10 - Homework - Simultaneous Linear and Quadratic EquationsSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Homework - Solving Equations Involving IndicesDocument2 pagesHomework - Solving Equations Involving IndicesSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Homework Similar Shapes Area and VolumeDocument11 pagesHomework Similar Shapes Area and VolumeSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap Sb9 Ws 0430 WDocument5 pagesEdgcse Aap Sb9 Ws 0430 WSaid ErcanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Apostolou Wang 2020Document11 pagesApostolou Wang 2020Riotgryph LepitorusNo ratings yet
- Bifurcation Analysis of An Ecological Food-Chain Model With Switching PredatorDocument12 pagesBifurcation Analysis of An Ecological Food-Chain Model With Switching PredatorAnindita BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFDocument8 pagesOrigin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFaco_golarNo ratings yet
- NANDA Nursing Diagnosis List 2018-2020: Domain 1: Health PromotionDocument6 pagesNANDA Nursing Diagnosis List 2018-2020: Domain 1: Health PromotionAngelaNo ratings yet
- PROTOCHORDATESDocument4 pagesPROTOCHORDATESapi-26570979100% (1)
- Jurnal Ilmiah Platax Vol. 6: (1), Januari 2018: Tongkaina and Bintauna Coastal Areas)Document12 pagesJurnal Ilmiah Platax Vol. 6: (1), Januari 2018: Tongkaina and Bintauna Coastal Areas)Shalltear BloodFallenNo ratings yet
- PDEV2111 Lesson 6 Coping With Stress in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument4 pagesPDEV2111 Lesson 6 Coping With Stress in Middle and Late AdolescenceJohn RoasaNo ratings yet
- Chelex 100-Instruction ManualDocument14 pagesChelex 100-Instruction Manualu77No ratings yet
- Eggs Fase 1Document3 pagesEggs Fase 1Gustav MolMedNo ratings yet
- Activity Book 2Document14 pagesActivity Book 2Josune Arévalo75% (4)
- Pener1991, Locust Phase Polymorphism and Its EndocrineDocument79 pagesPener1991, Locust Phase Polymorphism and Its EndocrineAdriano Medeiros de SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- RHS Masterclass On Rose Pruning PDFDocument3 pagesRHS Masterclass On Rose Pruning PDFCebotari Tatiana50% (2)
- 2794-Article Text-8720-1-10-20191103Document9 pages2794-Article Text-8720-1-10-20191103blowyour mindNo ratings yet
- Murder MysteryDocument12 pagesMurder Mysteryapi-272999528No ratings yet
- Parts of TheEyesDocument4 pagesParts of TheEyesAden Keith Paus ValdezNo ratings yet
- Report On The New Zealand Connemara Pony Population.Document14 pagesReport On The New Zealand Connemara Pony Population.Sheila RamsayNo ratings yet
- 1.wall of ThoraxDocument14 pages1.wall of ThoraxChandru ANo ratings yet
- Filogenia de Briofitos SensulatoDocument1 pageFilogenia de Briofitos SensulatoYuyitoS2714No ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDocument130 pagesThe Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesTricia Mae CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument23 pagesNursing Processjulesubayubay5428100% (6)
- Pronunciation Stress Language ExchangesDocument5 pagesPronunciation Stress Language ExchangesHàNhậtNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument15 pagesVital SignsSelene HmpNo ratings yet
- MCB 101 Lecture NoteDocument29 pagesMCB 101 Lecture Noteemeka.nn.ceNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: Garrison O'Level Campus Cantt, QuettaDocument6 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: Garrison O'Level Campus Cantt, QuettagulminaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Meets Conversation Do Does Did Are Is Was Fun Activities Games - 2965Document3 pagesGrammar Meets Conversation Do Does Did Are Is Was Fun Activities Games - 2965Yendy GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Fascia of The Head & NeckDocument8 pagesFascia of The Head & NeckMahesh Jung KhadkaNo ratings yet
- 9780702072987-Book ChapterDocument2 pages9780702072987-Book ChaptervisiniNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest Tobacco Infestation ControlDocument160 pagesPost Harvest Tobacco Infestation ControlKhosiKuneneNo ratings yet
- Lec16 Human PedigreeDocument33 pagesLec16 Human PedigreeSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet