Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acryl Is A Name For A Number of Chemical Compounds
Acryl Is A Name For A Number of Chemical Compounds
Uploaded by
Ana Bautista Sánchez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAcryl refers to chemical compounds containing an acrylic group or polymers of these compounds. The acryloyl group, which is derived from acrylic acid, contains a carbon–carbon double bond and a carbon–oxygen double bond separated by a single carbon–carbon bond. Acrylic compounds exhibit properties of both functional groups, including electrophilic addition and substitution reactions at the double bonds.
Original Description:
Original Title
Acryl is a name for a number of chemical compounds
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcryl refers to chemical compounds containing an acrylic group or polymers of these compounds. The acryloyl group, which is derived from acrylic acid, contains a carbon–carbon double bond and a carbon–oxygen double bond separated by a single carbon–carbon bond. Acrylic compounds exhibit properties of both functional groups, including electrophilic addition and substitution reactions at the double bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAcryl Is A Name For A Number of Chemical Compounds
Acryl Is A Name For A Number of Chemical Compounds
Uploaded by
Ana Bautista SánchezAcryl refers to chemical compounds containing an acrylic group or polymers of these compounds. The acryloyl group, which is derived from acrylic acid, contains a carbon–carbon double bond and a carbon–oxygen double bond separated by a single carbon–carbon bond. Acrylic compounds exhibit properties of both functional groups, including electrophilic addition and substitution reactions at the double bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
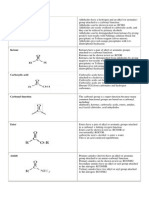
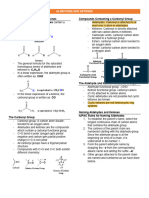
Acryl is a name for a number of chemical compounds that have an acrylic group, or
of polymers of these compounds. Especially esters of acrylic acid are used to help
make certain dyes and paints or as adhesives.
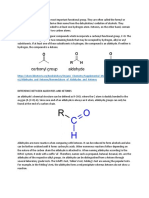
In organic chemistry, the acryloyl group is the functional group with structure
H2C=CH–C(=O)–; it is the acyl group derived from acrylic acid. The preferred IUPAC
name for the group is prop-2-enoyl. It is also (less correctly) known as acrylyl or
simply acryl. Compounds containing an acryloyl group can be referred to as "acrylic
compounds".
An acrylic compound is typically an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound: it contains
a carbon–carbon double bond and a carbon–oxygen double bond, separated by a carbon–
carbon single bond. It has therefore the properties characteristic for both
functional groups :
at the C=C bond: electrophilic addition of acids and halogens, hydrogenation,
hydroxylation and cleavage of the bond
at the C=O bond: nucleophilic substitution (such as in esters) or nucleophilic
addition (such as in ketones). The carboxyl group of acrylic acid can react with
ammonia to form acrylamide, or with an alcohol to form an acrylate ester.
In addition, since both double bonds are separated by a single C–C bond, the double
bonds are conjugated.
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Jack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryLoraNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersDocument133 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids & EstersWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21-25 PDFDocument134 pagesChapter 21-25 PDFHimanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Ncert LessonDocument32 pagesNcert LessonBhagwatNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde PDFDocument32 pagesAldehyde PDFMalti GuptaNo ratings yet
- By: Neneph Oshana Josh Gilbert Mahlon AkhtarDocument7 pagesBy: Neneph Oshana Josh Gilbert Mahlon AkhtarnenephNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument32 pagesAldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AcidAbhishek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Unit Unit Unit Unit UnitDocument32 pagesObjectives: Unit Unit Unit Unit UnitMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Organic CompoundDocument103 pagesLesson 1 - Organic CompoundFreshieeNo ratings yet
- CH - 8 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument32 pagesCH - 8 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidspinkykuku12No ratings yet
- 04 The Carbonyl Group (2313Spr2018) Skeletal NotesDocument56 pages04 The Carbonyl Group (2313Spr2018) Skeletal NotesDiana ToroNo ratings yet
- CHEM 109-Chepter 6Document28 pagesCHEM 109-Chepter 6naifalfarraj3No ratings yet
- Aldehyde Keto. Ncert Book PDFDocument32 pagesAldehyde Keto. Ncert Book PDFAshraf KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 313 PDFDocument29 pagesLesson 27 313 PDFEzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- Class12 Chemistry2 Unit12 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionDocument32 pagesClass12 Chemistry2 Unit12 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionSidharth ThukralNo ratings yet
- CH 21Document48 pagesCH 21Nelly Grace TonacaoNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument78 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidSwapnil MandalNo ratings yet
- AldehydeDocument3 pagesAldehydeSem.Jb TanNo ratings yet
- Organic Functional GroupsDocument8 pagesOrganic Functional GroupsScientology1No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Module - 7Document29 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Module - 7TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesAmahNo ratings yet
- Ald. Ket and Carboxylic AcidDocument12 pagesAld. Ket and Carboxylic AcidBenoniNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Is An Organic Compound: Carbonyl Group Is ADocument2 pagesAlcohol Is An Organic Compound: Carbonyl Group Is AajlouiseibanezNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups ContainingDocument8 pagesFunctional Groups ContainingViku GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesAlehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidYoNo ratings yet
- Title of ExperimentDocument5 pagesTitle of ExperimentAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Organic Chemistry EssentialsDocument8 pagesFunctional Groups: Organic Chemistry EssentialsJeremiah Paul Gotia HumiwatNo ratings yet
- Fuctional GroupsDocument12 pagesFuctional GroupsNina HamadaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupDocument45 pagesFunctional Groupmonasteriomatthew7No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Alkanes: 10.5 Functional GroupsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Alkanes: 10.5 Functional GroupsDotaKINGNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument34 pages9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesgoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument2 pagesAldehydes and KetonesKhamron BridgewaterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11Document8 pagesCHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11sjjsjsNo ratings yet
- Aldehye KetoneDocument21 pagesAldehye KetoneMirNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds PDFDocument15 pagesLab 5 Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds PDFThyrraNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ether by AarkumarDocument0 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ether by AarkumarNikhil Surya MukhiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and KetonesViaBNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Subtitusi Asil Nukleofilik Pada Turunan Asam KarboksilatDocument24 pagesReaksi Subtitusi Asil Nukleofilik Pada Turunan Asam KarboksilatSri DewiNo ratings yet
- M6 TransesDocument6 pagesM6 TransesDaniela SchenleyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesChemistry Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: 3.1.1 Hydrocarbons & AlkanesDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry: 3.1.1 Hydrocarbons & AlkanesFarhan SadiqueNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds: Jalil Ur Rehman Roll No. 19782 Muhammad Mustafa Roll No. 18960 Chemistry DepartmentDocument11 pagesReactions of Carbonyl Compounds: Jalil Ur Rehman Roll No. 19782 Muhammad Mustafa Roll No. 18960 Chemistry DepartmentJalil bschemNo ratings yet
- AlkyneDocument30 pagesAlkyneKiela ArizobalNo ratings yet
- ALCOHOLSDocument12 pagesALCOHOLSAmon RicoNo ratings yet
- 13 Full ChaptDocument33 pages13 Full ChaptHasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument25 pagesChemistryMa. Angelica Claire LuayonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistryauni ramizahNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-01 - TheoryDocument45 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Minimalist Black and White Report PresentationDocument72 pagesModern Minimalist Black and White Report PresentationPRINCESS NOELLEE TRAYVILLANo ratings yet
- Cac Bo EngliDocument4 pagesCac Bo EngliLinh ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- Assembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsFrom EverandAssembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsNo ratings yet
- The Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesFrom EverandThe Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Fused HeterocyclesFrom EverandSynthesis of Fused HeterocyclesGwynn P. EllisNo ratings yet
- The Term Alternation of Generations Is Used To DescribeDocument3 pagesThe Term Alternation of Generations Is Used To DescribeAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Plants Are One of Five Big GroupsDocument4 pagesPlants Are One of Five Big GroupsAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Is How Most Animals and Plants ReproduceDocument2 pagesSexual Reproduction Is How Most Animals and Plants ReproduceAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Spores Are The Way Fungi and Some Non-Seed PlantsDocument1 pageSpores Are The Way Fungi and Some Non-Seed PlantsAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Painting Is Using Colors To Make Visual ArtDocument1 pagePainting Is Using Colors To Make Visual ArtAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- GNU Free Documentation LicenseDocument2 pagesGNU Free Documentation LicenseAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Means The Stages A Living Thing Goes Through During Its LifeDocument1 pageLife Cycle Means The Stages A Living Thing Goes Through During Its LifeAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- Gesso Is A Primer or Foundation For Art PaintingDocument1 pageGesso Is A Primer or Foundation For Art PaintingAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet
- A Chemical Compound Is A Chemical FormedDocument1 pageA Chemical Compound Is A Chemical FormedAna Bautista SánchezNo ratings yet