Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Literary Devices For Xi
Uploaded by
Soham Nag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesThis document defines and provides examples of 18 different literary devices and figures of speech:
1. Simile and metaphor - an explicit or implicit comparison between two unlike objects using "like" or "as" or no connecting word.
2. Personification - investing abstract ideas or objects with human attributes.
3. Apostrophe - addressing an absent or inanimate entity.
4. Hyperbole - exaggerated statements.
5. Euphemism - softening harsh expressions.
It then provides examples and definitions of 13 additional figures of speech including pun, alliteration, anaphora, and asyndeton.
Original Description:
Original Title
LITERARY_DEVICES_FOR_XI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and provides examples of 18 different literary devices and figures of speech:
1. Simile and metaphor - an explicit or implicit comparison between two unlike objects using "like" or "as" or no connecting word.
2. Personification - investing abstract ideas or objects with human attributes.
3. Apostrophe - addressing an absent or inanimate entity.
4. Hyperbole - exaggerated statements.
5. Euphemism - softening harsh expressions.
It then provides examples and definitions of 13 additional figures of speech including pun, alliteration, anaphora, and asyndeton.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesLiterary Devices For Xi
Uploaded by
Soham NagThis document defines and provides examples of 18 different literary devices and figures of speech:
1. Simile and metaphor - an explicit or implicit comparison between two unlike objects using "like" or "as" or no connecting word.
2. Personification - investing abstract ideas or objects with human attributes.
3. Apostrophe - addressing an absent or inanimate entity.
4. Hyperbole - exaggerated statements.
5. Euphemism - softening harsh expressions.
It then provides examples and definitions of 13 additional figures of speech including pun, alliteration, anaphora, and asyndeton.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
LITERARY DEVICES/ FIGURES OF SPEECH
1 Simile : A figure of speech in which one thing is compared to another in such
a way as to clarify and enhance an image.It is an explicit comparison between
two unlike objects, recognizable by the use of the words ‘like’ or ‘as’.
2 A metaphor on the other hand, is an implicit (implied ) comparison between
two unlike objects.
Red as a rose is she. —Simile
A rose is she. – Metaphor
This condensation often makes a metaphor more suggestive and effective than a
simile.
Examples of simile:
Napoleon swept over France like a meteor.
The child shows the man as morning shows the day.
Examples of metaphor:
Variety is the spice of life.
Hope is the brightest when it dawns from fear.
To take up arms against a sea of troubles.
3 Personification: It consists in investing abstract ideas or inanimate objects
with the attributes of a living being.
Examples: The thirsty earth soaks up the rain.
The Pyramids themselves, doting with age, have forgotten the names of their
founders.
4 Apostrophe : By this figure,a speaker or a writer changes the course of his
theme and makes a short impassioned address to a person who is absent or dead
or to an inanimate object or even to an abstract idea.
Examples:
Roll on, thou deep and dark -blue ocean , roll. (Byron)
Hail to thee, blithe spirit!
Bird thou never wert. (Shelley)
O solitude! where are the charms
That sages have seen in thy face?
5 Hyperbole: This is a figure by which things are represented as much greater or
lesser , better or worse, than they really are. A hyperbole is thus just another
name for an exaggerated statement.
Example:
Ten thousand saw I at a glance…… ( The Daffodils by William Wordsworth)
She was by far, the fairest among women.
6 Euphemism: This figure consists in softening down a harsh or disagreeable
expression. It is a way of stating something offensive in an agreeable or
pleasing manner. It is prompted sometimes by courtesy and sometimes by a
sense of decorum.
Examples:
He perished on the scaffold. (was hanged)
Goldsmith was little, pitted with the smallpox and awkward.; and schoolboys
are amazingly frank (ie they unadvisedly blurt out the truth without regard to
the feelings of others.)
7 Pun or paronomasia :
This figure rests on a duplicity of sense under unity of sound. The play of words
found in puns is often interesting:
Examples:
The woman beat her child to make him smart. ( brisk and active/ to feel a sharp
quick pain.)
In cards a good deal depends on good playing and good playing depends on a
good deal. ( The expression ‘a good deal’ first means ‘much’ and then ‘ a good
distribution of cards’.)
8 Alliteration: A figure of speech in which consonants, especially at the
beginning of words , or stressed syllables are repeated. It is common in poetry
as well as in tongue -twisters, nonsense verse and in jingles.
Example:
Five miles meandering with a mazy motion…..
9 Anaphora: This figure consists in the repetition of an expression at the
beginning of successive clauses or sentences:
Example:
Theirs not to make reply,
Theirs not to reason why,
Theirs but to do and die.
10 . Asyndeton: This figure consists in the omission of connecting
conjunctions and is conducive to energy and vividness.
Example:
I slip, I slide, I glance. (Tennyson)
What? not a line, a tear, a sigh
When valour bleeds for liberty? (Scott)
10 Polysyndeton: This figure consists in the excessive use of conjunctive
participles.It serves to impart emphasis to the particulars which are enumerated .
Example:
To- morrow, and to-morrow, and to-morrow
Creeps in this petty pace. ( Macbeth)
11 Antithesis : By this figure contrasted words or ideas are set against each
other in a balanced form for the sake of emphasis.
Examples:
United we stand- divided we fall.
He was not the master but the slave of his speech.
12 Epigram :
The epigram is an apparent contradiction in language which, by causing a
temporary shock, rouses our attention to some important meaning underneath.
Examples:
Our antagonist is our helper.
Beware the fury of a patient man.
Speech was given to man to conceal his thoughts.
13 Metonymy
This figure consists, as its name implies, in substituting the name of one thing
for that of anotherto which it has a certain relation,
Different examples of metonymy:
The symbol or sign for the things symbolized
He ascended the throne. (symbol of sovereignty)
He was raised to the bench. (the office of a judge)
The instrument or organ for the agent
The pen is mightier than the sword.
The press (journalists) wields enormous power.
14 Synecdoche:
By this figure a more comprehensive term is used for a less comprehensive one
or vice versa , but in fact, that less comprehensive term or vice versa is meant.
(a) A part for the whole:
A fleet of twenty sails (ships)
Nearly two thousand hands ( persons) are employed in this office.
(b) A species for the genus/ the genus for a species
Examples: Silver and gold (riches) have I none.
(c ) An individual for the class
Every man is not Solomon.(as wise as king Solomon)
A Daniel ( a wise and impartial judge) comes to judgment.
15 Hypallage or Transferred Epithet:
By this figure an epithet (adjective) is transferred or shifted from the object to
which it properly belongs, to another with which it is associated in the mind of
the writer or speaker.
Examples:
A sleepless pillow was pressed by him, an anxious morning slowly dawned.
They have marched a weary way.
16 Innuendo :
This is a figure by which a thing is insinuated or hinted at instead of being plainly
stated.
Examples:
He was born of rich but honest parents. (It seems to suggest that rich people are
generally dishonest.)
An artist was asked to give his opinion on a portrait and he remarked, “What a
splendid frame!” The insinuation evidently was that the painting itself was bad.
17 Irony:
Irony consists in the use of words, the natural meaning of which is the very
opposite of what is intended to be expressed. By this figure, therefore, we say one
thing when we mean another. We pretend to approve something which we really
want to ridicule.
Examples:
Yet Brutus says he was ambitious,
An Brutus is an honourable man!
18 Onomatopoeia:
This is an artifice of language by which the sound of words is made to reflect
their sense eg:
And Niagara stuns with thundering sound.
Pitter patter falls the rain!
You might also like
- Week1 LS1 Figure of Speech WorksheetsDocument5 pagesWeek1 LS1 Figure of Speech WorksheetsR & Q Food HouseNo ratings yet
- Barbour Deus CatalogDocument28 pagesBarbour Deus CatalogThe State Newspaper100% (1)
- Figures of SpeechDocument28 pagesFigures of SpeechKarl July MamacNo ratings yet
- Figure of Speech and IdiomDocument19 pagesFigure of Speech and IdiomAnthony Rey BayhonNo ratings yet
- W H A T Are The Figures of Speech?Document7 pagesW H A T Are The Figures of Speech?lynne riveraNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument16 pagesFigures of SpeechCharlotte Faye Lacambra100% (2)
- Figures of SpeechDocument8 pagesFigures of SpeechJanelle BatoctoyNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument5 pagesFigure of SpeechA-jay Andong CapusoNo ratings yet
- Figure of Speech QuestionsDocument7 pagesFigure of Speech QuestionsMarjBuccatNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument2 pagesFigures of SpeechCzane Del Rosario BagunuNo ratings yet
- Figures of Speech PDFDocument7 pagesFigures of Speech PDFNitishNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument5 pagesFigures of SpeechHelena MendonçaNo ratings yet
- Rethorical Devices - Examples: You're Acting Like Such A Scrooge!Document4 pagesRethorical Devices - Examples: You're Acting Like Such A Scrooge!Marcel SzymanskiNo ratings yet
- EAPPassignmentDocument12 pagesEAPPassignmentᅴImichiNoMikotoNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument7 pagesFigures of SpeechMaster100% (2)
- Figure of SpeechDocument27 pagesFigure of SpeechPratik PatilNo ratings yet
- What Is A Figure of Speech PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Figure of Speech PDFNorhata Maguid SapalNo ratings yet
- текстологіяDocument8 pagesтекстологіяEmma BlumNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument11 pagesFigure of SpeechReiny Rose AutrizNo ratings yet
- Figures of Speech PDFDocument7 pagesFigures of Speech PDFSadia Tasnin SnehaNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument20 pagesFigures of SpeechSonali RaiNo ratings yet
- L6 - Figures of Speech and Its ExamplesDocument34 pagesL6 - Figures of Speech and Its ExamplesJames Alexander DezaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Creative WritingDocument13 pagesLesson 5 Creative WritingMary Rose MangumpitNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 1 1Document8 pagesActivity Sheet No. 1 1Rea EscotaNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument10 pagesFigures of SpeechCamille Abigail VivoNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument6 pagesFigures of SpeechEsther MirabeteNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument4 pagesFigures of SpeechBala Sai Tulasi Ram MudduNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument9 pagesFigure of SpeechanonymousNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument4 pagesFigures of SpeechWENDY ARNIDONo ratings yet
- Gen - Ed NotesDocument11 pagesGen - Ed Notesbabylyn akilNo ratings yet
- Information Enrichment (IE) Sheet - Figurative LanguageDocument6 pagesInformation Enrichment (IE) Sheet - Figurative LanguageSana MostofaNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechesDocument4 pagesFigure of SpeechesnimranawazNo ratings yet
- FosDocument10 pagesFosYash JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument56 pagesLiterary DevicesKristel EbradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document89 pagesChapter 2Duyên Hoàng Thị MỹNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument6 pagesFigures of SpeechBrylle Caraca100% (1)
- Stylistic DevicesDocument14 pagesStylistic DevicesNatalia LutvunivNo ratings yet
- Figurative LanguagesDocument32 pagesFigurative LanguagesronalynNo ratings yet
- Figures of Speech HandoutDocument4 pagesFigures of Speech HandoutLiz GnvyNo ratings yet
- Exam Review English IIIDocument11 pagesExam Review English IIIFritz Ivan AlonsagayNo ratings yet
- Examples of Figures of Speech: Using AlliterationDocument14 pagesExamples of Figures of Speech: Using AlliterationNica Jane MacapinigNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument5 pagesFigures of SpeechSaanviNo ratings yet
- Stylistic Devices - Alliteration: Repetition of Initial Consonant SoundDocument13 pagesStylistic Devices - Alliteration: Repetition of Initial Consonant SoundRACHID AIT EL MAATINo ratings yet
- Types of Figures of SpeechDocument4 pagesTypes of Figures of Speechastrid asseuNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument18 pagesFigures of SpeechMaccassNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument2 pagesFigure of SpeechJoserie Barioga HernaneNo ratings yet
- Language of Creative WritingDocument23 pagesLanguage of Creative Writingcecille v. loristoNo ratings yet
- Poetry Terms-1Document2 pagesPoetry Terms-1israelshafaNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century Lit. Lesson 4Document34 pages21ST Century Lit. Lesson 4Mellyjolly AbadNo ratings yet
- Stylistics Ex 3Document5 pagesStylistics Ex 3Irina ParkhomenkoNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument30 pagesFigures of Speechernest macalaladNo ratings yet
- CNF Lesson 7Document29 pagesCNF Lesson 7nicatanekuNo ratings yet
- Syed Israr Ali Naqvi Bs English Linguistics 3 Year. Institute of English Language & Literature University of Sindh JamshoroDocument29 pagesSyed Israr Ali Naqvi Bs English Linguistics 3 Year. Institute of English Language & Literature University of Sindh JamshoroSyed Israr AliNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument5 pagesFigures of SpeechLovely FloresNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument27 pagesLiterary DevicesNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument55 pagesFigures of SpeechJohn Paul HabladoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CNFDocument18 pagesModule 3 CNFMary Grace Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature Assingment 1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Literature Assingment 1honeykhanNo ratings yet
- Safari - 26 Jan 2023 5:35 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 26 Jan 2023 5:35 PMoh.yes.this.is.an.emailNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument4 pagesFigures of SpeechSoul- HarryNo ratings yet
- CW Handouts 3Document2 pagesCW Handouts 3Lerramie Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesHydrocarbonSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Assign-110 MOCK TEST SYLLABUS FOR CLASS 12 SCIENCE - 2023-24Document4 pagesAssign-110 MOCK TEST SYLLABUS FOR CLASS 12 SCIENCE - 2023-24Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, BT-2, SET-IDocument6 pagesChemistry, BT-2, SET-ISoham NagNo ratings yet
- Class 12: DPS RPK: 2023-24/254/012 NoticeDocument1 pageClass 12: DPS RPK: 2023-24/254/012 NoticeSoham NagNo ratings yet
- 16 Solutions Revision Notes Getmarks AppDocument34 pages16 Solutions Revision Notes Getmarks AppSoham NagNo ratings yet
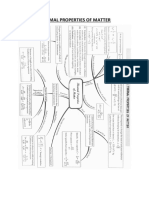
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesThermal Properties of MatterSoham NagNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesThermodynamicsSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Waves Study MAterialDocument16 pagesWaves Study MAterialSoham NagNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument6 pagesGravitationSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Block Test-I Chemistry Class Xi 2021-22Document10 pagesBlock Test-I Chemistry Class Xi 2021-22Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of Gas: Concept MapDocument7 pagesKinetic Theory of Gas: Concept MapSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 2 Class 11 2022 23Document1 pageUnit Test 2 Class 11 2022 23Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Online Examination Schedule 2022-23 - Class 11 November - December 2022Document1 pageOnline Examination Schedule 2022-23 - Class 11 November - December 2022Soham NagNo ratings yet
- Notice 204 - Joy of GivingDocument1 pageNotice 204 - Joy of GivingSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument11 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Document16 pagesHydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Soham NagNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING AssignmentSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Bhawanipur College Merit ListDocument15 pagesBhawanipur College Merit ListSoham NagNo ratings yet
- PRMO Registration Form 2019Document1 pagePRMO Registration Form 2019paras jainNo ratings yet
- COM154 Task 2 Poetic DevicesDocument7 pagesCOM154 Task 2 Poetic DevicesMarifel Corpuz LopezNo ratings yet
- Poetic Conventions - Sound Devices WorksheetDocument6 pagesPoetic Conventions - Sound Devices WorksheetCHRISTIAN CANASNo ratings yet
- Onomatopoeia Words: A C E K Q RDocument3 pagesOnomatopoeia Words: A C E K Q RLjbica Ilic100% (1)
- Figures of Speech QuizDocument2 pagesFigures of Speech QuizRio OrpianoNo ratings yet
- Finken-SLAM Poetry AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinken-SLAM Poetry AnalysisNicholas FinkenNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language - Hyperbole and Idioms (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and WorksheetsDocument2 pagesFigurative Language - Hyperbole and Idioms (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and WorksheetsLouise Yongco100% (1)
- Figures of Speech - QUIZDocument15 pagesFigures of Speech - QUIZTitserynah Iugalac100% (1)
- FIGURES OF SPEECH Grade 11Document51 pagesFIGURES OF SPEECH Grade 11Jacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument27 pagesFigure of SpeechSabel Ross CaliliwNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5SDocument17 pagesLecture 5SsahrizodakodirovaNo ratings yet
- ROMION - Asynchronous-Midterm-Activity-4-Poetic-TechniquesDocument4 pagesROMION - Asynchronous-Midterm-Activity-4-Poetic-TechniquesChristine Erika RomionNo ratings yet
- Poetic Devices: Special Poetry TechniquesDocument17 pagesPoetic Devices: Special Poetry TechniquesRamil F. AdubalNo ratings yet
- Figures of Speech 12thDocument4 pagesFigures of Speech 12thVikram TelangNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st Summative Test Grade 7Document2 pagesQ2 1st Summative Test Grade 7Reyan BallasoNo ratings yet
- SR No Roll No Student NameDocument13 pagesSR No Roll No Student NameJAY SolankiNo ratings yet
- Alliteration Onomatopoeia Metaphor Simile Hyperbole Personification I D I O MDocument11 pagesAlliteration Onomatopoeia Metaphor Simile Hyperbole Personification I D I O MJochelleNo ratings yet
- CS 2023 T 3 (Key)Document3 pagesCS 2023 T 3 (Key)Мартиненко Вероніка, ЯЕ-32No ratings yet
- Definition of Nature of LiteratureDocument6 pagesDefinition of Nature of LiteratureJambres DelacruzNo ratings yet
- What Is A Figure of Speech PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Figure of Speech PDFNorhata Maguid SapalNo ratings yet
- La FontaineDocument5 pagesLa FontaineRadoi MirceaNo ratings yet
- Class X English Poem Test Term 1Document6 pagesClass X English Poem Test Term 1Jai MadaanNo ratings yet
- Questions - My Family and Other AnimalsDocument1 pageQuestions - My Family and Other AnimalsHHDGDSFREWT SDFDSFDSFEWTREWNo ratings yet
- Poetic DevicesDocument21 pagesPoetic DevicesNyesha GrahamNo ratings yet
- Inervention Materials in Figurative LanguageDocument7 pagesInervention Materials in Figurative LanguageFrancis Alyana Bustante MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Poe Tic Dev Ices Poe Tic Dev Ices: Simile Rhyme SimileDocument29 pagesPoe Tic Dev Ices Poe Tic Dev Ices: Simile Rhyme SimileAnastasia DestiningrumNo ratings yet
- Evaluation in Literary DevicesDocument3 pagesEvaluation in Literary DevicesHyra GonoNo ratings yet
- Stylistic Semasiology - Figures of Co-OccurrenceDocument43 pagesStylistic Semasiology - Figures of Co-OccurrenceqamaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Poetic DevicesDocument6 pagesClass 12 Poetic DevicesManav Ji Manav100% (8)