Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp - 8
Uploaded by
Md KaziOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp - 8
Uploaded by
Md KaziCopyright:
Available Formats
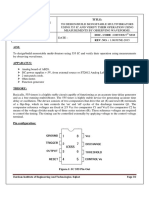
Page No.
: 01
CHITTAGONG UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING,
CHATTOGRAM-4349, BANGLADESH.
COURSE NO.: EEE 112
Experiment No. 8
Study of Transient Behavior of RC Circuit
Instructions:
Revise the lecture notes on the topic DC transient of RC circuit (Course code: EEE
111).
Read this laboratory manual carefully prior to start the laboratory class.
DO NOT copy others.
Submit your lab report before the roll call.
Objective:
(a) Experimental verification of transient behavior of RC circuit
Required Instruments:
1) Function Generator
2) Oscilloscope
3) Resistor
4) Capacitor
5) Bread board
6) Probes / Connecting wires
Transient: The transient response is the temporary response that results from a switching
operation and disappears with time. The steady state response is that which exists after a long
time following any switching operation.
Prepared By: Mohammad Mahmudul Hasan Tareq
Page No.: 02
Let us consider an RC circuit shown in figure.
Figure – 01: Connection diagram of RC circuit
Charging Phase:
When the switch is connected to position 1, applying KVL we can write –
V Ri 1/C idt ------------------------------------ (1)
If the capacitor is initially uncharged, the solution of equation (1) is –
𝑖= 𝑒 -------------------------------------------- (2)
Therefore the voltage across the resistor and capacitor are given by
𝑉 =V𝑒 ------------------------------------------- (3)
𝑉 = 𝑉 − 𝑉 = 𝑉(1 − 𝑒 ) ---------------------- (4)
Where = RC and is called the time constant of the circuit. Equation (2), (3) & (4) are plotted
below:
Figure – 02: Output waveform of voltage and current during charging
It is seen from the curves that the voltage across the capacitor raises from zero to V volts
exponentially and the charging current is maximum at the start i.e. when C is uncharged, then
it decreases exponentially and finally decreases to zero when the capacitor voltage becomes V.
Prepared By: Mohammad Mahmudul Hasan Tareq
Page No.: 03
Discharging Phase:
When the switch is connected to position 2, applying KVL we can write –
0 = 𝑅𝑖 + ∫ 𝑖𝑑𝑡 -------------------------------------- (5)
Therefore the voltage across the resistor and capacitor are given by –
𝑉 = −V 𝑒 ------------------------------------------- (6)
𝑉 =𝑉𝑒 --------------------------------------------- (7)
Equation (6), (7) & (8) are plotted below:
Figure – 03: Output waveform of voltage and current during discharging
It is seen from the curves that the voltage across the capacitor falls from V to zero volts
exponentially. The charging current is maximum at the start i.e. when the switch is just
thrown to position 2, then it decreases exponentially and finally ceases to zero when the
capacitor voltage becomes zero.
Circuit Diagram:
Figure – 04: Connection diagram with oscilloscope to see input voltage and capacitor voltage
Prepared By: Mohammad Mahmudul Hasan Tareq
Page No.: 04
Figure – 05: Connection diagram with oscilloscope to current and capacitor voltage
Steps to Follow:
1. Setup the circuit as shown in Figure – 04.
2. Apply 100Hz square wave from signal generator.
3. Observe the wave shapes at Channel-1 and Channle-2 in DUAL mode and observe
them.
4. Find the time constant from the wave shape of VC.
5. Disconnect Channel-1 and Channle-2 and reconnect them as shown in Figure – 05.
6. Observe the wave shapes at Channel-1 and Channle-2 (INV.) in DUAL mode and
observe them.
Home Task:
Answer the following question –
1. Define capacitor and capacitance. Write the features of a capacitor. What does
capacitance measure?
2. Deduce voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. Why the voltage across a capacitor
cannot change instantaneously.
3. Define time constant for an RC circuit. What is the significance of time constant? How
time constant can be determined?
4. Describe the charging and discharging phase of an RC circuit both qualitatively and
quantitatively.
Prepared By: Mohammad Mahmudul Hasan Tareq
You might also like
- Virtual Lab Report-1 PDFDocument27 pagesVirtual Lab Report-1 PDFCarlton Lobo0% (1)
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDocument24 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Circuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesDocument8 pagesCircuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesCesar Santiago Bolaño SalazarNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Fault Level Calculations For A MVLV Network Using Direct MethodDocument18 pagesA Case Study of Fault Level Calculations For A MVLV Network Using Direct MethodBruno Samos100% (1)
- Surface Vehicle Recommended PracticeDocument29 pagesSurface Vehicle Recommended Practiceidrd8527No ratings yet
- 04 Axes and DrivesDocument68 pages04 Axes and DrivesWanderley Terci Esteves100% (1)
- Transient of R.C. CircuitDocument9 pagesTransient of R.C. CircuitArinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Document11 pagesLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory E-Sources - Second Year B - Tech IV SEM (ECE)Document142 pagesLaboratory E-Sources - Second Year B - Tech IV SEM (ECE)Chen-Wei LiangNo ratings yet
- Em Lab-II ManualDocument45 pagesEm Lab-II Manualrkadiraj701150% (4)
- Ae Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcDocument6 pagesAe Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcPriyanshu KumawatNo ratings yet
- EXP6 Clipper and Clamper CircuitDocument4 pagesEXP6 Clipper and Clamper CircuitMohammed Dyhia Ali100% (2)
- Eeng200-Exp1 3Document7 pagesEeng200-Exp1 3What's new ?No ratings yet
- AP Physc em R L Circuit Lab 2014-06-06Document9 pagesAP Physc em R L Circuit Lab 2014-06-06黃吏維No ratings yet
- Eee Lab Report 07Document11 pagesEee Lab Report 07Sayeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document11 pagesActivity 3Peter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad - Pakistan Electrical EngineeringDocument50 pagesFederal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad - Pakistan Electrical EngineeringMtanveer MunirNo ratings yet
- Resonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperDocument5 pagesResonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperMukesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab 08Document8 pagesLab 08Kashif Mujeeb Abdul MujeebNo ratings yet
- Print Close: Time-Dependent Pulse TrainDocument10 pagesPrint Close: Time-Dependent Pulse TrainLeo_MaxNo ratings yet
- Muscle Stimulator Project ReportDocument9 pagesMuscle Stimulator Project ReportShankarshan GautamNo ratings yet
- ItlogDocument11 pagesItlogkrazyyy chanNo ratings yet
- PSCAD Power System Lab ManualDocument23 pagesPSCAD Power System Lab ManualShiva Kumar100% (2)
- Beee Lab ManualDocument36 pagesBeee Lab ManualChanduVarmaKalidindiNo ratings yet
- Manual Ee IVDocument56 pagesManual Ee IVAkhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics For Utility Applications (EE529) Chapter 2: Static Shunt CompensatorsDocument16 pagesPower Electronics For Utility Applications (EE529) Chapter 2: Static Shunt CompensatorsdebealNo ratings yet
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles CW1Document22 pagesElectrical and Electronic Principles CW1Shaikh FarhaNo ratings yet
- Design of A Under Voltage Lock Out Circuit With Bandgap StructureDocument4 pagesDesign of A Under Voltage Lock Out Circuit With Bandgap Structured_niku100% (1)
- Designing An Astable MultivibratorDocument7 pagesDesigning An Astable Multivibratorjeyaganesh100% (3)
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- Designing A Boost-Switching Regulator With The MCP1650Document0 pagesDesigning A Boost-Switching Regulator With The MCP1650Asad MalikNo ratings yet
- Currents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesDocument14 pagesCurrents Through Inductances, Capacitances and ResistancesZulu LoveNo ratings yet
- A Simple Square Rooting Circuit Based On Operational Amplifiers (Opamps)Document3 pagesA Simple Square Rooting Circuit Based On Operational Amplifiers (Opamps)Harendra Kumar100% (1)
- PEL Lab ManualDocument127 pagesPEL Lab Manualmksamy2021No ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3 PDFDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3 PDFgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- Oc SC PDFDocument5 pagesOc SC PDFVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNo ratings yet
- Core JavaDocument11 pagesCore JavaGangadharNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter For Charging and Discharging Super-Capacitors Used in Electric Hybrid CarsDocument8 pagesDC-DC Converter For Charging and Discharging Super-Capacitors Used in Electric Hybrid CarsTung DaoNo ratings yet
- A New Push Pull Zero Voltage Switching Quasi Resonant Converter-Topology and ExperDocument5 pagesA New Push Pull Zero Voltage Switching Quasi Resonant Converter-Topology and ExperSucheta Chatterjee SethiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument37 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualDawod Shaaban Al-SulifanieNo ratings yet
- SCRDocument19 pagesSCRDavid MartinNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCapacitorsShern Ren TeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Design of Square Wave Generator Using Op-Amp IC 741Document22 pagesExperiment No. 4 Design of Square Wave Generator Using Op-Amp IC 741aditi rajanNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCDocument5 pagesLab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCAbdul QudoosNo ratings yet
- 3330905-Electronic Components and CircuitsDocument8 pages3330905-Electronic Components and CircuitsELENo ratings yet
- Application of Bidirectional Power Converters To Overcome Some Disadvantages of SVC SubstationDocument7 pagesApplication of Bidirectional Power Converters To Overcome Some Disadvantages of SVC SubstationAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Transformer Less DC - DC Converter With High Step Up Voltage Gain MethodDocument6 pagesTransformer Less DC - DC Converter With High Step Up Voltage Gain Methodsurendiran123No ratings yet
- Auto Shut OffDocument5 pagesAuto Shut OffJuan Manuel Han MacNo ratings yet
- Lab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Document11 pagesLab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Ayushman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Machines I SEMESTER II /2023-2024: 1.invertersDocument5 pagesPower Electronics and Machines I SEMESTER II /2023-2024: 1.invertersbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Tests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Document11 pagesTests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Walmy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Dual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.Document3 pagesDual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.sbpatel123No ratings yet
- A Novel Method To Test The Strength of Electrical Equipment Through Impulse Generator and Design of Its Circuit ComponentsDocument5 pagesA Novel Method To Test The Strength of Electrical Equipment Through Impulse Generator and Design of Its Circuit ComponentsIjesat JournalNo ratings yet
- Transient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterDocument5 pagesTransient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterijsretNo ratings yet
- Circuit Meets Challenges of Fast, High-Current NiCd ChargingDocument5 pagesCircuit Meets Challenges of Fast, High-Current NiCd ChargingAlex MarghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Transformer: Circuit ModelDocument10 pagesExperiment 4: Transformer: Circuit ModelManuel AquinoNo ratings yet
- AC Electric Machines Lab ManulDocument98 pagesAC Electric Machines Lab Manulmuhammad_sarwar_27No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Exp 6Document3 pagesExp 6Md KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document3 pagesExp 4Md KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document4 pagesExp 1Md KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document5 pagesExp 5Md KaziNo ratings yet
- Day 03 - MECHADocument11 pagesDay 03 - MECHAMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Tragedy of CommonsDocument5 pagesTragedy of CommonsMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp - 4. Determination of Series & Shunt Motor Characteristic CurveDocument5 pagesExp - 4. Determination of Series & Shunt Motor Characteristic CurveMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorDocument3 pagesExp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp - 3. Study of Load Characteristics of D.C. GeneratorDocument3 pagesExp - 3. Study of Load Characteristics of D.C. GeneratorMd KaziNo ratings yet
- Exp - 1. Familiarization of Electrical Machines LabDocument1 pageExp - 1. Familiarization of Electrical Machines LabMd KaziNo ratings yet
- f2164 Gprs Rtu Technical SpecificationDocument4 pagesf2164 Gprs Rtu Technical SpecificationCocofourfaithNo ratings yet
- Vishnu Internship ReportDocument24 pagesVishnu Internship ReportShivaiah G ENo ratings yet
- Egate Utility ManagerDocument8 pagesEgate Utility ManagerKaleem ShaikNo ratings yet
- CSC 101 - Operating System-Week1Document10 pagesCSC 101 - Operating System-Week1shadowbee 47No ratings yet
- Programming LanguagesDocument2 pagesProgramming LanguagesMA. CLARA AIRYN CIPRESNo ratings yet
- Cla 76 Compressor LimiterDocument11 pagesCla 76 Compressor LimiterWR100% (1)
- Emr DGDocument662 pagesEmr DGgeorgiNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 041035Document10 pagesLab Assignment 041035123fakehaNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures Week 1 Css 11Document6 pagesStandard Operating Procedures Week 1 Css 11JerryNo ratings yet
- USB Forensics and PentestingDocument24 pagesUSB Forensics and PentestingRaviraj DarisiNo ratings yet
- 3rd - Python - L 1Document9 pages3rd - Python - L 1zainab alhussainyNo ratings yet
- How To Stop Automatic Updates On Windows 10Document8 pagesHow To Stop Automatic Updates On Windows 10ghisuddinNo ratings yet
- Dji Terra: User ManualDocument57 pagesDji Terra: User ManualRazvan Julian PetrescuNo ratings yet
- ManDocument574 pagesManPham Van DungNo ratings yet
- Geethanjali College of Engineering and Technology: Unit - I: Introduction To IC TechnologyDocument19 pagesGeethanjali College of Engineering and Technology: Unit - I: Introduction To IC TechnologyECE A5No ratings yet
- EE-211 Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument28 pagesEE-211 Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherHadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- CSE2006 - Java Qs Bank - All ModulesDocument3 pagesCSE2006 - Java Qs Bank - All ModulesShaswat kumarNo ratings yet
- Presentasi 1Document9 pagesPresentasi 1RAHMAT AZUARDINo ratings yet
- DIL-32 Communication-IC With Modbus Host Interface: Slave Solution For Simple Field DevicesDocument3 pagesDIL-32 Communication-IC With Modbus Host Interface: Slave Solution For Simple Field DevicesJuan Carlos MoscosoNo ratings yet
- BSC Sem4 Software Engineering Assignment 1 AnsDocument4 pagesBSC Sem4 Software Engineering Assignment 1 AnsMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CAN, LIN & Flex Ray Protocols in Automotive Vehicles: Aryan SinghDocument4 pagesCAN, LIN & Flex Ray Protocols in Automotive Vehicles: Aryan SinghAryan.Singh Btech2019No ratings yet
- Uvm MethodologyDocument2 pagesUvm MethodologyFeroz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Screencast 7Document15 pagesScreencast 7ardanmorisNo ratings yet
- Sensors 18 00366 PDFDocument21 pagesSensors 18 00366 PDFAgoeng NoegrossNo ratings yet
- Sqlite As An Application File Format: Executive SummaryDocument7 pagesSqlite As An Application File Format: Executive Summarysrirama raoNo ratings yet
- Yozo LogDocument3 pagesYozo LogSirajuddin CalmNo ratings yet
- p5kpl Am Se Manual PDFDocument40 pagesp5kpl Am Se Manual PDFTaruna FandanuNo ratings yet
- Release Notes Nfnic 5.0.0.43-1OEMDocument2 pagesRelease Notes Nfnic 5.0.0.43-1OEMNilesh AjgaonkarNo ratings yet