Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 13
Uploaded by
jane garcia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pages1. Earned value management (EVM) directly links the three primary project success metrics of cost, schedule, and performance by considering their joint impact on project status.
2. EVM establishes project baselines by defining the work breakdown structure and time-phased project budget.
3. EVM offers top management an excellent view of a firm's ability to efficiently run projects through portfolio tracking and control using earned value.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Earned value management (EVM) directly links the three primary project success metrics of cost, schedule, and performance by considering their joint impact on project status.
2. EVM establishes project baselines by defining the work breakdown structure and time-phased project budget.
3. EVM offers top management an excellent view of a firm's ability to efficiently run projects through portfolio tracking and control using earned value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesChapter 13
Uploaded by
jane garcia1. Earned value management (EVM) directly links the three primary project success metrics of cost, schedule, and performance by considering their joint impact on project status.
2. EVM establishes project baselines by defining the work breakdown structure and time-phased project budget.
3. EVM offers top management an excellent view of a firm's ability to efficiently run projects through portfolio tracking and control using earned value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
CHAPTER 13- PROJECT EVALUATION AND CONTROL o The S-curve also provides real-time tracking information Milestone in one
formation Milestone in one form or another, are probably the
in that budget expenditures can be constantly updated simplest and most widely used pf all project control
Elements of Control Cycles
and the new values plotted on the graph devices
1. Setting a goal The problem with them is that, like S-curves, they are
S-Curve Drawbacks
- Project goal setting goes beyond overall scope reactive control system
development to include setting the project baseline 1. S-curve can identify positive or negative variance The problem is compounded
plan (budget expenditure above or below projections) but
2. Measuring Progress Tracking Gantt Chart
they do not allow us to make reasonable interpretation as
- Effective control systems require accurate project to the cause of variance Is useful for evaluating project performance at specific
measurement mechanisms 2. They are providing “reactive” data; that is we plot the point in time
3. Comparing Actual with Planned Performance result of expenditures after the money has already been The tracking Gantt chart allows the project team to
- Comparing actual with planned performance. When spent constantly update the project’s status by linking task
we have some sense of the original baseline (plan) completion to the schedule baseline
and a method for accurately measuring progress, the Milestone Analysis
It is also possible to measure both positive and negative
next step is to compare the two pieces of information - A milestone is an event or stage of the project that deviations from the schedule base line with the tracking
4. Taking Action represents a significant accomplishment on the read Gantt chart
- One we detect significant deviations from the project to the project’s completion
plan, it become necessary to engage in some form of Benefits & Drawbacks of Tracking Gantt Charts
corrective action minimize or remove the deviation Several Benefits to using milestone as form of Project
Control: A key benefit of tracking Gantt chart is that they are
Monitoring Project Performance quite easy to understand
1. Milestone signal the completion of important project This type of control chart can be updated very quickly,
steps providing a sense of real-time project control
2. Milestone can motivate the project team It is difficult to accurately estimate the time to
3. Milestone offer points at which to reevaluate client needs completion for project, particularly in the case of
and any potential change request significant positive or negative variation from the
4. Milestone help coordinate schedule with vendors and baseline
suppliers
5. Milestone identify key project review gates Earned Value Management
6. Milestones tell other team members when their
An increasingly popular method used in project
participation is expected to begin
monitoring and control consists of a mechanism
The Project S-Curve: A basic tool 7. Milestone can delineate the various deliverables
developed in the work Breakdown Structure thereby EVM has been practiced in multiple settings by agencies
o To determine project performance and status, a enable the project team to develop a better overall view from governments as diverse as Australia, Canada, and
straightforward time/cost analysis is often our first of the project Sweden, as well as by a host of project-based firms in
choice numerous industries
o Monitoring the status of a project using S-curve become Problems with Milestone EVM recognizes that it is necessary to jointly consider
a simple tracking problem the impact of time, cost, and project performance on any
o Simplicity is the key benefit of S-curve analysis analysis of current project status.
We can illustrate the advance in the project control 3. The use of earned value management for portfolio
process that Earned Value Management represents by tracking and control offers top management an excellent
comparing it to the other project tracking mechanisms. window in the firm’s ability to efficiently run projects
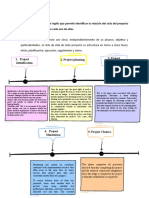
Earned value (EV), on the other hand, directly links all Creating Project Baselines
Flow of Earned Value System
three primary project success metrics (cost, schedule,
and performance). Baseline information is critical regardless of the control - Earned value begins early at North Grumman
process we employ, but baselines are elemental when project. In fact, there is a “flow” to the EVM system
performing EVM. o Proposal Stage – the specifics of the
The actual steps in establishing the project baseline are program are determined at this stage
fairly straightforward and require two pieces of data: o Contract award – when North Grumman is
o Work Breakdown Structure – identified the
selected as the successful contractor, all
individual work packages and tasks necessary to critical elements and requirements of the
accomplish the project project are defined
o Time-Phased Project Budget – takes the WBS o Baseline stage – once the preliminary scope
one step further: It allows us to identify the and deliverables have been agreed to
correct sequencing of tasks, but more between the contractor and the client, the
importantly it enables the project team to detailed planning, project schedule, and
determine the points in the project when budget formal work authorization is developed
money is likely to be spent in pursuit of those o Maintenance phase – once the project
Terminologies for Earned Value tasks.
baseline is established and formally signed
Steps in Earned Value Management off by key parties, the project passes top\ the
monitoring and control stage, where the key
1. Clearly define each activity or task that will be advantage of EVM are clearly realized
performed on the project, including its resource needs as
well as detailed budget Issues in the Effective use of EVM
2. Create the activity and resource usage schedules
0/100 – the simplest and perhaps least effective method
3. Develop a ‘time-phase” budget that shows expenditures
requires that a project activity be assigned a value of
across the project’s life
zero until the point activity is finished, at which time
4. Total the actual costs of doing each task to arrive at the
value switches to 100%
actual cost of work performed
50/50 rule – under this decision rule, an activity that has
5. Calculate both a project’s budget variance and schedule
been started automatically receives a valuation of 50%
variance while it is still in process
completed
Using Earned Value to Manage a Portfolio of Projects Percentage complete rule – the project manager and team
members mutually agree on a set of completion
1. Earned value management can work at the portfolio level
milestones, whether they are based on quarters, thirds, or
as well as with individual projects
some other values
2. Portfolio earned value management table includes the
total positive variances for both budget and schedule Human Factors in Project Evaluation & Control
Another recurring problem with establishing accurate or The 10 critical success factors represent an important,
meaningful EVM results has to do with the need to supplemental source of information on the project’ s
recognize the human factor in all project activity status.
completion projections.
Critical Success Factor Definitions
The common feature of control approaches is their
reliance on measurable data based on project outcomes; 1. Project mission – relates to the underlying purpose for
A key component of any process evaluation of project the project
performance must include an assessment of its people, 2. Top management support – has ling been considered of
their technical skills, management, teamwork, great importance in distinguishing between ultimate
communication processes, motivation, leadership, and so success and failure
forth. 3. Project plans and schedules – refers to the importance of
Past research examining the impact of human factors on developing a detailed plan of the required stages of the
project success bears out the importance of considering implementation process
the wider management challenge inherent in managing 4. Client consultation – the “client” is anyone who
projects. Included in their list were issues such as: ultimately will be using the product of the project, either
o Project coordination and relations among as a customer outside the company or as a department
stakeholders within the organization
o Adequacy of project structure and control 5. Personnel – includes recruitment, selection, and training
o Project uniqueness, importance, and public of project team members
exposure 6. Technical task – refers to the necessity of having not
o Success criteria salience and consensus only required numbers of personnel for the
o Lack of budgetary pressure implementation team but also ensuring that they passes
o Avoidance of initial overoptimism and the technical skills and the technology and technical
support needed to perform their task
conceptual difficulties
7. Client acceptance – refers to the final stage in the project
Their findings bear out the importance of having a clear
development process, at which time the overall efficacy
knowledge of the managerial challenges involved when
of the project is to be determined
implementing projects
8. Monitoring & feedback – refers to the project control
The findings of such research are intriguing because of
process by which key personnel receive feedback at each
the importance they place on the managerial and human
stage of the project implementation on how the project is
behavioral aspects of project management for project
progressing compared to initial projections
success.
9. Communication – is not only essential within the
One of the key recurring problems, however, with projects team itself, but also vital between the team and
making wider use of nontechnical information as a the rest of the organization as well as with clients
method for controlling projects and assessing their 10. Troubleshooting – problem areas exist in almost every
ongoing status lies in the question of measurement project development. The measure of a successful
The work of Pinto and Slevin13 addresses the project is not the avoidance of problems, but taking the
shortcomings with behavioral assessments of project correct steps once problems develop
management processes.
You might also like
- Guitar Movable ChordsDocument7 pagesGuitar Movable ChordsgernNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non ProfitsDocument58 pagesPerformance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non ProfitsadhikaNo ratings yet
- Additional Character OptionsDocument30 pagesAdditional Character Optionsdreaming geckoNo ratings yet
- Value Investors Club - Treasure ASA (TRE ASA)Document9 pagesValue Investors Club - Treasure ASA (TRE ASA)Lukas Savickas100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non-ProfitsDocument58 pagesPerformance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non-ProfitsAnjali Angel Thakur93% (14)
- Campaign Planning and Project Management 123Document21 pagesCampaign Planning and Project Management 123magoNo ratings yet
- Estimating CategoriesDocument4 pagesEstimating CategoriesCPittmanNo ratings yet
- CH 5 - Project Management and Resource AllocationDocument86 pagesCH 5 - Project Management and Resource AllocationFikiru DubaNo ratings yet
- Minggu Ke 10 - Keadah-Keadah Pengurusan ProjekDocument43 pagesMinggu Ke 10 - Keadah-Keadah Pengurusan ProjekNur'Aina Farhana NorzelanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project Schedule Management PDFDocument96 pagesChapter 6 Project Schedule Management PDFPravinPrabhakarWakodeNo ratings yet
- Prog Copywriting Exercise 10Document3 pagesProg Copywriting Exercise 10azertyNo ratings yet
- 2015-13 Schedule Golden Rules v0Document2 pages2015-13 Schedule Golden Rules v0Mario MendezNo ratings yet
- Brief PMPDocument11 pagesBrief PMPAliNo ratings yet
- WWII Europe Organization ChartsDocument56 pagesWWII Europe Organization ChartsCAP History Library100% (1)
- Project Management (Project Managment Processes)Document4 pagesProject Management (Project Managment Processes)sophiaNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management For Design and Construction ProjectDocument21 pagesEarned Value Management For Design and Construction ProjectEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Lifecycle of A Project ManagementDocument35 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Lifecycle of A Project ManagementhalinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookFrom EverandIntroduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter-5Document18 pagesPM Chapter-5GolamSarwar100% (1)
- TCR22-2 Operating Manual - SkutevikenDocument266 pagesTCR22-2 Operating Manual - SkutevikenFlo Marine100% (2)
- Script 123Document11 pagesScript 123Miles HizonNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Cost To Complete On Mega Construction Projects: 1 AbstractDocument14 pagesForecasting Cost To Complete On Mega Construction Projects: 1 AbstractOzanNo ratings yet
- Managing ProjectDocument119 pagesManaging ProjectCharisa SamsonNo ratings yet
- Project Cost ControlDocument3 pagesProject Cost ControlJulius Yao SossahNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter-5Document18 pagesPM Chapter-5GolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- Project Management Lesson 6Document15 pagesProject Management Lesson 6Saneliso MartinNo ratings yet
- Role of Project Auditor: Line of BalanceDocument3 pagesRole of Project Auditor: Line of BalanceMadhusudan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Comparing Waterfall and Agile Approaches PDFDocument2 pagesComparing Waterfall and Agile Approaches PDFLourenço PimentaNo ratings yet
- Sen Unit 5 5 2Document11 pagesSen Unit 5 5 2Sarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Comparing Waterfall and Agile ApproachesDocument2 pagesComparing Waterfall and Agile Approachesd7qj7856g7No ratings yet
- Project Control Process Unit 5Document6 pagesProject Control Process Unit 5gkvimal nathanNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Jahid Hasan Assistant Professor, Dept. of IPE, SUSTDocument30 pagesProject Management: Jahid Hasan Assistant Professor, Dept. of IPE, SUSTRaihan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- DDDM Assignment - PRNs-11,24,53,58,59Document10 pagesDDDM Assignment - PRNs-11,24,53,58,59Shivnath KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Waterfall and Agile ComparisonDocument2 pagesWaterfall and Agile ComparisonASRAR ALAYLINo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PMDocument61 pagesAssignment 2 PMInfant RajNo ratings yet
- Computers & Industrial Engineering: Forough Vaseghi, Mario VanhouckeDocument17 pagesComputers & Industrial Engineering: Forough Vaseghi, Mario Vanhoucketractorclub286No ratings yet
- Fase 1 - ConceptualizaciónDocument3 pagesFase 1 - ConceptualizaciónANGIE VANESSA RIVERA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Seting Tolerance Limits For Statistical Project Control Using Earned Value ManagementDocument16 pagesSeting Tolerance Limits For Statistical Project Control Using Earned Value ManagementRinno Iqsyam PriyanantaNo ratings yet
- Project Auditing or Evaluation: Chapter # 5Document20 pagesProject Auditing or Evaluation: Chapter # 5Mohammad RafiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document13 pagesChapter 5mylove6947No ratings yet
- Ramping Up at Warp SpeedDocument7 pagesRamping Up at Warp SpeedLarryNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT - Fundamentals and FunctionsDocument10 pagesCONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT - Fundamentals and FunctionsAris AmbosNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Project Control and MonitoringDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 5 Project Control and MonitoringIqasya AhmadNo ratings yet
- MNGT 3108 - M3-Project ManagementDocument13 pagesMNGT 3108 - M3-Project ManagementArjay GuillandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project Planning - Bus Stop Case StudyDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Project Planning - Bus Stop Case StudyAndres Cedeno TutivenNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument30 pagesChapter ThreeAlfiya DemozeNo ratings yet
- Bsbpmg512 Manage Project Time: Assessment Part B Short Answer QuestionsDocument2 pagesBsbpmg512 Manage Project Time: Assessment Part B Short Answer QuestionsAllana WardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project AuditingDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Project AuditingLeelybai SambolawanNo ratings yet
- Management of Computer System Performance: Evaluation and Project ManagementDocument39 pagesManagement of Computer System Performance: Evaluation and Project ManagementDinesh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoringand Control PMCDocument6 pagesProject Monitoringand Control PMCAhmedAliKhaskayaNo ratings yet
- Project Control in ConstructionDocument2 pagesProject Control in Constructionagung dwi nugrohoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 SPMDocument49 pagesLec 4 SPMabubakarqasim080No ratings yet
- Benefits of Project ControlDocument3 pagesBenefits of Project ControlPadma PatilNo ratings yet
- Project Recovery It Can Be DoneDocument4 pagesProject Recovery It Can Be DoneSean Lee PaulNo ratings yet
- Unit - VDocument14 pagesUnit - V153-B RAKSHITHANo ratings yet
- Define The Term ProjectDocument4 pagesDefine The Term ProjectKasili MasilikaniNo ratings yet
- List The Role of Project ManagerDocument10 pagesList The Role of Project ManagerSilent girlNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Monitoring and ControlDocument12 pagesCH 9 Monitoring and Controlkarunya vNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Construction Project Management & Construction OrganizationDocument22 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Construction Project Management & Construction OrganizationPavan BharadwajNo ratings yet
- The Project MethodologyDocument6 pagesThe Project MethodologyTrọng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Project ManagementDocument7 pagesObjectives of Project Managementkareem gamelNo ratings yet
- Guideline 3 Implementation and Monitoring Plan Preparation and AssessmentDocument60 pagesGuideline 3 Implementation and Monitoring Plan Preparation and AssessmentEthiopian Citizen100% (1)
- Acumen FuseDocument4 pagesAcumen FuseLam Thanh HoangNo ratings yet
- 04 Project CycleDocument7 pages04 Project CycleAnikNo ratings yet
- Project Managemt Process GroupsDocument6 pagesProject Managemt Process GroupsAlex MartinezNo ratings yet
- CAPM NotesDocument15 pagesCAPM NotesRitvik kNo ratings yet
- ForexDocument2 pagesForexjane garciaNo ratings yet
- The Stock MarketDocument4 pagesThe Stock Marketjane garciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Corporate Performance-Governance-Business EthicsDocument3 pagesChapter 11 - Corporate Performance-Governance-Business Ethicsjane garciaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 11 Mortgage MarketsDocument3 pagesTOPIC 11 Mortgage Marketsjane garciaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-02-14 at 11.35.01 PMDocument32 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-14 at 11.35.01 PMemaantejani10No ratings yet
- Junior 3 Future-Passive VoiceDocument1 pageJunior 3 Future-Passive VoiceJonathan QNo ratings yet
- Islam in The Middle Ages - WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesIslam in The Middle Ages - WORKSHEETcrabbydreamerNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Education: Dr. Ghanshyam Singh P.G. College, Soyepur, Lalpur, VaranasiDocument4 pagesFaculty of Education: Dr. Ghanshyam Singh P.G. College, Soyepur, Lalpur, VaranasiRajeshKumarJainNo ratings yet
- Loan Modifications - Workout Plans and ModificationDocument43 pagesLoan Modifications - Workout Plans and ModificationSudershan ThaibaNo ratings yet
- 850 SQ MM AAC Conductor PDFDocument1 page850 SQ MM AAC Conductor PDFSamyak DeoraNo ratings yet
- SSLD Stairways LowresDocument44 pagesSSLD Stairways LowresboyNo ratings yet
- Levy - Chapter 4Document48 pagesLevy - Chapter 4ANUPAMA RAMACHANDRANNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TestDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect TestMárta FábiánNo ratings yet
- Friday HeatsDocument29 pagesFriday HeatsTGrasley6273No ratings yet
- Yr 10 2016 You Are What You Eat ProgDocument10 pagesYr 10 2016 You Are What You Eat Progapi-322152156No ratings yet
- Vibration Control Technology Industry (Freudenberg Schwab)Document111 pagesVibration Control Technology Industry (Freudenberg Schwab)ismailNo ratings yet
- Job Offer Electrical EngineerDocument3 pagesJob Offer Electrical EngineerAbner ZaldivarNo ratings yet
- ICICI - Manufacture in India Fund - Investor One PagerDocument4 pagesICICI - Manufacture in India Fund - Investor One PagerInimitable IdeasNo ratings yet
- Task Performance EuthenicsDocument3 pagesTask Performance EuthenicsKimberly MarquezNo ratings yet
- Communityhealth 141122094330 Conversion Gate02Document22 pagesCommunityhealth 141122094330 Conversion Gate02Titser JoNo ratings yet
- 3.6-6kva Battery Cabinet: 1600Xp/1600Xpi SeriesDocument22 pages3.6-6kva Battery Cabinet: 1600Xp/1600Xpi SeriesIsraelNo ratings yet
- Attention and Effort. (1973)Document253 pagesAttention and Effort. (1973)Robert C. CasasNo ratings yet
- 2019 Admax CataDocument30 pages2019 Admax CataEVENTIA AFRICANo ratings yet
- Ece 250 Project PortfolioDocument7 pagesEce 250 Project Portfolioapi-511924847No ratings yet
- CDBFRDDocument88 pagesCDBFRDmarcol99No ratings yet
- HS-193070003 Exxon Oil Mobilgrease 28 CertificatesDocument3 pagesHS-193070003 Exxon Oil Mobilgrease 28 Certificatesflacuchento2013No ratings yet
- How Does Texting Worsens Our Vocabulary & Writing Skills ?Document10 pagesHow Does Texting Worsens Our Vocabulary & Writing Skills ?Manvi GoelNo ratings yet
- Wall Panels Thesis PDFDocument161 pagesWall Panels Thesis PDFSanjay EvaneNo ratings yet