Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Draft Planner
Uploaded by
Đỗ Minh HuyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1st Draft Planner
Uploaded by
Đỗ Minh HuyCopyright:
Available Formats
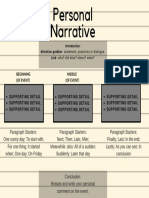
Paragraph 1: Orientation
Sets the scene, mood and introduces the characters. Try to include ‘When’, ‘Where’, ‘Who’ and ‘What’ in this section to explain to the
reader what the story is going to be about.
Paragraph 2: Complication
Often in the form of a dilemma or challenge that needs to be overcome, creates tension or excitement for the reader and usually needs
a response from the main character.
Paragraph 3: Sequence of events
When a struggle disrupts the normal life or comfort of the characters and sets off a sequence of interesting events. These might be the
overcoming steps in the story progression.
Paragraph 4: Resolution
Includes a description of the final outcome or ending. It could also underline how the character has changed and what they learnt as a
result of the experience they went through.
Menu of cohesive devices that will become useful in your story organization.
Time references Dramatic effect Concluding stories
It all began Later that day Suddenly Quite unexpectedly When it was all over
Shortly afterwards A little later All of a sudden As if from nowhere Looking back now
Meanwhile Finally Without warning Just at that moment In retrospect
Not long afterwards In the end Out of the blue In the end
Some time later Eventually After all that had happened
You might also like
- Essay PlannerDocument3 pagesEssay PlannerMeni GeorgopoulouNo ratings yet
- Telling A StoryDocument1 pageTelling A StoryVad FanniNo ratings yet
- Tips For Monologue 1Document2 pagesTips For Monologue 1Almudena T.GNo ratings yet
- How To Write A StoryDocument1 pageHow To Write A StoryJavier Padilla MartínNo ratings yet
- Plot GuideDocument3 pagesPlot Guidefindmonk75% (4)
- Personal NarrativesDocument1 pagePersonal Narrativesapi-392257524No ratings yet
- Narrative Writing: How To Write A Short StoryDocument23 pagesNarrative Writing: How To Write A Short StoryPatricia MoggioNo ratings yet
- RWS W1finalDocument9 pagesRWS W1finalKaren RoyoNo ratings yet
- What Is Plot? Conflict Plot Structure Timing and Pacing Flashback Flash-Forward Foreshadowing PracticeDocument20 pagesWhat Is Plot? Conflict Plot Structure Timing and Pacing Flashback Flash-Forward Foreshadowing PracticeOlga SmochinNo ratings yet
- NARRATIVESDocument10 pagesNARRATIVESTheHectox85No ratings yet
- Foreshadowing and Flashback Foreshadowing and Flashback Sentence Starters Sentence StartersDocument12 pagesForeshadowing and Flashback Foreshadowing and Flashback Sentence Starters Sentence StartersWhitney cremonaNo ratings yet
- Suspense StrategiesDocument1 pageSuspense StrategiesMadhu SahooNo ratings yet
- Narrative Paragraph: Md. Shahrear Faruq Johan Sabiha Nour Hurain JannatDocument12 pagesNarrative Paragraph: Md. Shahrear Faruq Johan Sabiha Nour Hurain JannatShahrear Faruq JohanNo ratings yet
- Event PlotDocument4 pagesEvent PlotNurulfidya Haryautama19No ratings yet
- PLOT DIAGRAM Most Dangerous GameDocument21 pagesPLOT DIAGRAM Most Dangerous Gamemissgillis119No ratings yet
- JauntDocument38 pagesJauntÖzgür GüvenNo ratings yet
- Literary Elements NewDocument25 pagesLiterary Elements NewLamia ZayedNo ratings yet
- Narrative-A Short Story: Scenes and Dialogue Lubna ImranDocument16 pagesNarrative-A Short Story: Scenes and Dialogue Lubna ImranLubna ImranNo ratings yet
- Big X Narrative Send 17.1.2023Document23 pagesBig X Narrative Send 17.1.2023SMK ADITAPANo ratings yet
- Narratives FCE 1Document3 pagesNarratives FCE 1iXerxommNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document80 pagesUnit 4Darling MesaNo ratings yet
- Writing Workshop 4: How To Write A StoryDocument5 pagesWriting Workshop 4: How To Write A StoryCristhian ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Taking The Mystery Out of Writing A MysteryDocument10 pagesTaking The Mystery Out of Writing A MysteryTriviana RemonNo ratings yet
- Drama TechniquesDocument12 pagesDrama TechniquesRosalinda AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Story B1Document1 pageStory B1Aptis Instituto EurospeoNo ratings yet
- Writting A Story (b1)Document12 pagesWritting A Story (b1)MarinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 AdverbsDocument20 pagesLesson 2 AdverbsJaja LacsonNo ratings yet
- The Adventures of Grim Willard, A Grim Beginning, A Grimmer END!From EverandThe Adventures of Grim Willard, A Grim Beginning, A Grimmer END!No ratings yet
- Narrative Essay: Academic and Scientific WritingDocument12 pagesNarrative Essay: Academic and Scientific WritingEVELYN GUISELLE CASTILLO ZHAMUNGUINo ratings yet
- Adverbs in NarrationDocument7 pagesAdverbs in NarrationAubrae Frances Engngeg Bannawi100% (1)
- Basic 3 Act StructureDocument5 pagesBasic 3 Act StructurepradeepNo ratings yet
- Sequence Defination: Beginning Middle EndingDocument2 pagesSequence Defination: Beginning Middle EndingSage SultanNo ratings yet
- Show Vs Tell MinilessonsDocument5 pagesShow Vs Tell MinilessonsIman MounirNo ratings yet
- Narrative ParagraphDocument15 pagesNarrative Paragraphhibaek072No ratings yet
- Story Elements 2Document102 pagesStory Elements 2Irene Milcah CastroNo ratings yet
- Black and White Transition Words Word MatDocument1 pageBlack and White Transition Words Word MatWu CarolNo ratings yet
- LSD Trip ReportDocument6 pagesLSD Trip ReportVasudev JojiNo ratings yet
- (English) Inside The Mind of A Master Procrastinator - Tim Urban (DownSub - Com)Document13 pages(English) Inside The Mind of A Master Procrastinator - Tim Urban (DownSub - Com)Danys Daniela Alvarez ToroNo ratings yet
- The Fellowship PlaybooksDocument40 pagesThe Fellowship PlaybooksWilliam100% (4)
- Narrative-Layout Unit 1: TitleDocument6 pagesNarrative-Layout Unit 1: TitlejudithNo ratings yet
- The Fellowship PlaybooksDocument40 pagesThe Fellowship PlaybooksMarcus100% (1)
- Rough Day PDFDocument9 pagesRough Day PDFVhjdfkkmNo ratings yet
- IDIOMSDocument11 pagesIDIOMSPapa Madiop NdiayeNo ratings yet
- The Quest: Filling in The BlanksDocument4 pagesThe Quest: Filling in The BlankszansheenNo ratings yet
- 11-Creating Suspense, Part 1Document4 pages11-Creating Suspense, Part 1Molina Fel TimoNo ratings yet
- Tether SpreadsDocument9 pagesTether SpreadsKelly M.No ratings yet
- Tell A Story or Personal Anecdote - Exercise 1Document1 pageTell A Story or Personal Anecdote - Exercise 1Fatima AliyevaNo ratings yet
- FIve Images For Mental ChatterDocument11 pagesFIve Images For Mental ChatterArun AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Reading and Writing DramaDocument17 pagesLesson 5-Reading and Writing DramaRyan Estonio100% (1)
- Cuts in EditingppDocument29 pagesCuts in Editingppapi-531127383No ratings yet
- Scary Movie Project Belousov GlebDocument3 pagesScary Movie Project Belousov GlebgleminerNo ratings yet