Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Replication
Uploaded by
OG gang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageDNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differs in several key ways. Prokaryotic DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm and can use the theta model, while eukaryotic replication happens in the cell nucleus during S phase. Both processes involve the DNA unwinding and nucleotides pairing with the old strand according to rules. However, prokaryotic replication is much faster at 2000 base pairs per second compared to 100-200 for eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA also contains many origins of replication versus a single origin in prokaryotes.
Original Description:
Original Title
DNA REPLICATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differs in several key ways. Prokaryotic DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm and can use the theta model, while eukaryotic replication happens in the cell nucleus during S phase. Both processes involve the DNA unwinding and nucleotides pairing with the old strand according to rules. However, prokaryotic replication is much faster at 2000 base pairs per second compared to 100-200 for eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA also contains many origins of replication versus a single origin in prokaryotes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageDna Replication
Uploaded by
OG gangDNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differs in several key ways. Prokaryotic DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm and can use the theta model, while eukaryotic replication happens in the cell nucleus during S phase. Both processes involve the DNA unwinding and nucleotides pairing with the old strand according to rules. However, prokaryotic replication is much faster at 2000 base pairs per second compared to 100-200 for eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA also contains many origins of replication versus a single origin in prokaryotes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
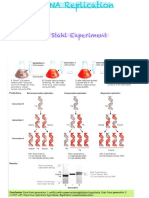
DIFFERENCE B/W PROKARYOTIC & EUKARYOTIC DNA free strands according to pairing rule.
REPLICATION • The pairing rule has 5 postulates
• The circ.DNA molecules of the PK cell undergoes • i) A pairs up with U or T
replication in the cytoplasm itself which can • ii) G pairs up with C
undergo Theta- model of replication • iii) T pairs up with A
• The Lin. DNA molecule of the EK cell undergoes • iv) C pairs up with G
replication inside the nucleoplasm during S-phase of • v) Addition starts from 3' end of Old strand &
Interphase. proceeds towards 5' end always ( In other words it
• During replication the 2 strands of DNA separate & starts from 5' end of new strand & proceeds towards
act as template for construction of a new strand on 3' end)
them, as a result 2 DNA molecules are produced • Step 4: As we consider a Y-shaped replication fork ,
• During replication free nucleotides which are on 1 of the strands construction of new strand
activated by Phosphorylase enzyme into becomes highly difficult bcoz of the 5th rule i.e on “A”
Triphosphate form come to the proximity of the old while on strand “B” construction of new strand is
parent strand according to Pairing rule & get paired very easy
up • On strand A, the new strand is formed in fragments
• The pairing is very fast in PK(2000 bps /sec) but slow after a small distance of unwinding is accomplished
in EK(only 100-200 bps/sec) & these goes on till the unwinding is completed.
• Replication starts from a special sequence called ori • On strand A, for the formation of each Okazaki
(200-250 bps) inside the DNA molecule. fragment , a RNA primer has to be constructed first.
• Prokaryotic DNA has only 1 ori where replication • While on strand B , RNA primer has to be constructed
starts only once.
• Whereas Eukaryotic DNA has many ori where • Step 5: Later on the RNA primers are detached & new
replication starts simultaneously or with small time DNA nucleotides are substituted & the Okazaki
gaps. fragments are joined to form the complete strand
• Later all the DNA fragments get joined by Ligases • Here the new strand formed on A is called
discontinuous strand & that formed on B is called
MECHANISM OF REPLICATION IN GENERAL continuous strand
• Step 1: Phosphorylation of true nucleotides in • Step 6: At the end of replication a process called
cytoplasm into triphosphate proof reading takes place which is conducted in 3' to
• This process is also called as activation /excitation 5' direction of new strand for making it perfect. This
of nucleotides after which they enter the nucleus. is also called as major repair.
• Step 2: From the ori, the 2 strands of DNA starts
unwinding • TABLE OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN DNA REPLICATION:
• Step 3: The activated nucleotide gets arranged on the To be discussed in class
Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/)
You might also like
- Changing the Global Approach to Medicine, Volume 3: Cellular Command and ControlFrom EverandChanging the Global Approach to Medicine, Volume 3: Cellular Command and ControlNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument26 pagesChapter Ten Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellnidsNo ratings yet
- 10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pages10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDayne Ocampo-Soliman100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyDocument34 pagesMolecular BiologyMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationAkhtar MuneerNo ratings yet
- L2 MLB 110 DNA REPLICATION and Protein Synt 1Document9 pagesL2 MLB 110 DNA REPLICATION and Protein Synt 1maxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document67 pagesChapter 5علوم طبية AUG 2020No ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- GROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesGROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Pertemuan 13 - 2022Document101 pagesPertemuan 13 - 2022Fitri AinunNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 9 PDFcarlette11No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- DNA RepilicationDocument57 pagesDNA RepilicationJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication1.Document9 pagesDNA Replication1.9jyqwjpp6sNo ratings yet
- Dna Fin1lDocument12 pagesDna Fin1lDIVYANSH UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument11 pagesDNA Replication and RepairCiroanneNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Cycle, DNADocument78 pages2 Cell Cycle, DNAmphyoyadanarNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplDocument40 pagesDNA ReplnunutsehaynuNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
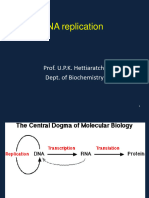
- Central Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument15 pagesCentral Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesLearning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationSphesihle ThekoNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA ReplicationZainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- DNA - The Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument38 pagesDNA - The Molecular Basis of InheritanceEgi JhonoNo ratings yet
- 6 DNA ReplicationDocument13 pages6 DNA ReplicationVenkat RaniNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument45 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyEirla Kneriz Trinidad67% (3)
- Prokaryotic Dna ReplicationDocument53 pagesProkaryotic Dna ReplicationRININo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 10 Cell & Mol Bio DNADocument30 pagesLecture No. 10 Cell & Mol Bio DNAUshna Asif BSCHE-ENo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesDocument30 pagesNucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of ReplicationDocument23 pagesMolecular Mechanism of ReplicationIarrNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Repair #4Document76 pagesDna Replication and Repair #4Len ArellanoNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Dna Replication1Document44 pages1.3. Dna Replication1sabry tapiaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Mod IIDocument61 pagesDNA Replication Mod IIAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication ProcessDocument16 pagesDna Replication ProcessMuhammad MusharafNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument70 pagesDNA ReplicationAnne Gabrielle Marapon AgsunodNo ratings yet
- Presentation on-WPS Office DNADocument16 pagesPresentation on-WPS Office DNANaznin ShahriaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesDNA ReplicationBilal SajidNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document36 pagesSlide 3OdaiNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument36 pagesObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONo ratings yet
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 DNA Replication-3Document69 pagesLecture 4 DNA Replication-3Constance WongNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- 1 23 17 DNA MetabolismDocument49 pages1 23 17 DNA MetabolismShael ZoletaNo ratings yet
- Di truyền cơ sở-Ch7 (9) DNA Replication-IUHDocument21 pagesDi truyền cơ sở-Ch7 (9) DNA Replication-IUHNam NguyenHoangNo ratings yet
- Please Switch Off Your MobilesDocument35 pagesPlease Switch Off Your MobilesSadia MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- DnaDocument68 pagesDnaArif Setiawansyah100% (2)
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument52 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceTech BurnerNo ratings yet
- Dna Assignment 2Document12 pagesDna Assignment 2api-253560385100% (1)
- Assignment General MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment General Microbiology05 Jawad ZahoorNo ratings yet
- 6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefDocument2 pages6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefReeNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationAkss ShauryaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA ReplicationPhilani KheswaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument18 pagesDNA ReplicationAditi PatriyaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- DNA ReplicationDocument83 pagesDNA ReplicationVipin100% (8)
- Jan 06 CCDocument16 pagesJan 06 CCdavid ngNo ratings yet
- Distemper in Canine, ReviewDocument13 pagesDistemper in Canine, ReviewLAURA DANIELA VERA BELTRANNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document13 pagesBio Assignment 1api-491560653No ratings yet
- Medical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyDocument3 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyLaiza JanelleNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 W1 CurieDocument6 pagesGenBio1 W1 CurieJem PagadNo ratings yet
- Faulty Autolysosome Acidification in Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Models Induces Autophagic Build-Up of Abeta in NeuronsDocument39 pagesFaulty Autolysosome Acidification in Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Models Induces Autophagic Build-Up of Abeta in NeuronsShidong XiNo ratings yet
- EEB 162 Final Study GuideDocument13 pagesEEB 162 Final Study GuideSydney ChangNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise Questions: Lab 4 WorksheetDocument6 pagesLaboratory Exercise Questions: Lab 4 WorksheetMadison GreenNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Scie10 Module 3 and 4 Q3Document2 pagesSummative Test in Scie10 Module 3 and 4 Q3Ruth Anne Barrios67% (3)
- Isolation of DNA From Given Sample.Document2 pagesIsolation of DNA From Given Sample.gauravpawar5971252No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cell StructureDocument32 pagesChapter 1: Cell StructureAnneli MarshNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument94 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionHey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Beef Quality and Nutrigenomics of Intramuscular Adipose Tissue DepositionDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting Beef Quality and Nutrigenomics of Intramuscular Adipose Tissue DepositionSofia JimenezNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument11 pagesDna Replication NotesJanine San LuisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument20 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionVinash Shka RaoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 20 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 20 QuestionsHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Steven Johnson SyndromeDocument13 pagesSteven Johnson SyndromeRatu Qurroh AinNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Proteins, and EnzymesDocument17 pagesAmino Acids, Proteins, and EnzymesAna laura FloresNo ratings yet
- Data 2014-2018Document16 pagesData 2014-2018pigWaterNo ratings yet
- List of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsDocument1 pageList of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsJahanzeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- ER/PR+ Her2 - Ve Breast Cancer: Glucose Pathways Supplements / Drugs Source CommentsDocument3 pagesER/PR+ Her2 - Ve Breast Cancer: Glucose Pathways Supplements / Drugs Source CommentsRama KrisnaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ConjugationDocument15 pagesBacterial ConjugationNiveditha ChalukyaNo ratings yet
- General Pathology 1Document39 pagesGeneral Pathology 1Muheto100% (2)
- Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein PositivelyDocument14 pagesRaf Kinase Inhibitor Protein PositivelyGabriel FenteanyNo ratings yet
- 【白细胞数据集】WBCAtt A White Blood Cell Dataset Annotated with Detailed Morphological AttributesDocument23 pages【白细胞数据集】WBCAtt A White Blood Cell Dataset Annotated with Detailed Morphological AttributesJeremy WayinNo ratings yet
- Palmit072012slr PDFDocument22 pagesPalmit072012slr PDFGalina TodorovaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 9th ClassDocument15 pagesCell Structure 9th ClassSri Nagamani ThumuNo ratings yet
- Komplikasi Penyembuhan LukaDocument25 pagesKomplikasi Penyembuhan Lukajmakbar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Biologia A ColorDocument2 pagesBiologia A ColorJorge Andres Vasquez Avila100% (1)