Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 1 - '22.11.25
Uploaded by
Preeti NarvekarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 1 - '22.11.25
Uploaded by
Preeti NarvekarCopyright:
Available Formats
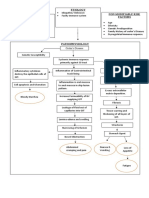
TABLE 1
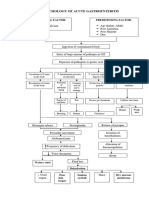
Mechanism and etiology of chronic diarrhea
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Mechanisms Results of stool collection Etiologies
Osmotic Fecal osmotic gap > 50 mosmol/kg Lactase deficiency
Artificial sugars (mannitol, sorbitol,
etc.)
Magnesium
Malabsorption
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Bacterial overgrowth
Secretory Fecal osmotic gap < 50 mosmol/kg Diarrhea caused by enterotoxins (for
example, V. cholerae, E. coli)
Hormones (serotonin, VIP, gastrin)
Malabsorption of bile acids
Collagenous colitis
Lymphocytic colitis
Inflammatory Neutrophils in stools IBD
Elevated fecal calprotectin Radiation colitis
Entero-invasive infections
(e.g., Shigellosis, Y. enterocolitica,
Entamoeba histolytica)
Motor Normal fecal calprotectin Irritable bowel syndrome
Diabetes
Scleroderma
Bacterial overgrowth
You might also like
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentFrom EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNo ratings yet
- The Large IntestineDocument33 pagesThe Large IntestineElena ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CholeClyde AleczandreNo ratings yet
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part II. Healing Foods in the Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersFrom EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part II. Healing Foods in the Digestive (Pancreatic) DisordersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Report On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Document3 pagesReport On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Adnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of GastroenteritisNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of CholelithiasisNicol John CeballosNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology Gastroenteritisjeneva029No ratings yet
- Campylobacteriosis-An Infection by The Campylobacterium Most Commonly Known As C. JejuniDocument2 pagesCampylobacteriosis-An Infection by The Campylobacterium Most Commonly Known As C. JejuniEspiridionNo ratings yet
- Chart - GI InfectionsDocument3 pagesChart - GI InfectionsRedNo ratings yet
- Toxic Responses of The LiverDocument36 pagesToxic Responses of The LiverPeejay OllabracNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Case StudyDocument30 pagesNutrition Case StudyCher BautistaNo ratings yet
- Dirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningDocument17 pagesDirrhoea Dysentery & Food PoisoningAbcdefg HijklNo ratings yet
- Smallintestinalbacterial Overgrowth: Daniel Bushyhead,, Eamonn M. QuigleyDocument12 pagesSmallintestinalbacterial Overgrowth: Daniel Bushyhead,, Eamonn M. QuigleyHugo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Management of Chronic Diarrhea: Joe Harkins, PA-C Gastroenterology Center of Maine EMMC Bangor, MEDocument74 pagesEvaluation and Management of Chronic Diarrhea: Joe Harkins, PA-C Gastroenterology Center of Maine EMMC Bangor, MErehan hayderNo ratings yet
- Regurgitation, The Result of Gastroesophageal Reflux, Occurs Commonly in The 1st Year of LifeDocument7 pagesRegurgitation, The Result of Gastroesophageal Reflux, Occurs Commonly in The 1st Year of LifeImam AlifurqonNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Infections Due To Enterobacteriaceae: Diarrheogenic E. Coli, Shigellosis, Nontyphoidal Salmonellosis, YersiniosisDocument39 pagesGastrointestinal Infections Due To Enterobacteriaceae: Diarrheogenic E. Coli, Shigellosis, Nontyphoidal Salmonellosis, YersiniosisHyny P'gallaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption SyndromesDocument14 pagesMalabsorption SyndromesRAFI ABRAR PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 pagesPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalNo ratings yet
- Diarreia AgudaDocument5 pagesDiarreia Agudacatia cristinaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholelithiasis Cholecystitissamliebareng77No ratings yet
- Diarrhoea: More Than Just A Splash in The PanDocument16 pagesDiarrhoea: More Than Just A Splash in The PanIgor DemićNo ratings yet
- E M C D: Valuation and Anagement of Hronic IarrheaDocument74 pagesE M C D: Valuation and Anagement of Hronic IarrheaRevila AuliaNo ratings yet
- Not Activity No. 7Document12 pagesNot Activity No. 7Patricia Marie Laman YadaoNo ratings yet
- DR Kiki Lukman Patofisiologi Acute CholangitisDocument36 pagesDR Kiki Lukman Patofisiologi Acute CholangitisAfkar30No ratings yet
- Alvine Discharge DiseasesDocument1 pageAlvine Discharge DiseasesApril Rose AlivioNo ratings yet
- Etiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDocument2 pagesEtiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis: Disease/Condition Differentiating Signs/Symptoms Differentiating TestsDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis: Disease/Condition Differentiating Signs/Symptoms Differentiating TestsJim Christian EllaserNo ratings yet
- Toxic Responses of The Liver: Hartmut JaeschkeDocument22 pagesToxic Responses of The Liver: Hartmut JaeschkeEduardo AnayaNo ratings yet
- Tropical SprueDocument3 pagesTropical SprueAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Small Bowels. Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diverticulosis of The Large Bowels. Tumors of The BowelsDocument10 pagesPathology of The Small Bowels. Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diverticulosis of The Large Bowels. Tumors of The BowelsMariam AlavidzeNo ratings yet
- Patophy of PudDocument4 pagesPatophy of PudClarence BravioNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument119 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseJoy LacunaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocument9 pagesPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors Etiology Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument13 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors Etiology Modifiable Risk FactorsgabbyNo ratings yet
- CHRONIC DIRRHEA FinalDocument93 pagesCHRONIC DIRRHEA FinalAtifNo ratings yet
- Alarm Findings For Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children - UpToDateDocument2 pagesAlarm Findings For Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children - UpToDateNatalia PidmurniakNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea - MRCEM SuccessDocument7 pagesDiarrhoea - MRCEM SuccessGazi Sareem Bakhtyar AlamNo ratings yet
- Selection 5232Document16 pagesSelection 5232Dilawar JanNo ratings yet
- GastroenteritisDocument4 pagesGastroenteritisJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- VI. Patho-Physiology: Removal of The Gallbladder?Document3 pagesVI. Patho-Physiology: Removal of The Gallbladder?Maui ReyesNo ratings yet
- Smart Sheet - MedAngle GITDocument6 pagesSmart Sheet - MedAngle GITRabia OwaisNo ratings yet
- GIT DiarrhoeaDocument40 pagesGIT DiarrhoeaOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Malabsorption ANGOLDocument30 pagesMalabsorption ANGOLAvramut IulianNo ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument13 pagesFood Poisoninglinna chinNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract DiseasesDocument35 pagesBiliary Tract DiseasesSoumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Semiology of The IntestineDocument37 pagesSemiology of The Intestinebear dianaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology 2Document62 pagesGastroenterology 2Mariam AlavidzeNo ratings yet
- Pathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Document3 pagesPathways Colitis Cerative Group 1Fuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- Doenças AvícolasDocument77 pagesDoenças AvícolasBergue OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Swmana 4 Teórico Digestive DisordersDocument43 pagesSwmana 4 Teórico Digestive DisordersAna Paula Hernández CarballoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisMay RodeoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Pathogens: Department of Clinical Microbiology Medical Faculty Universitas BrawijayaDocument56 pagesIntestinal Pathogens: Department of Clinical Microbiology Medical Faculty Universitas BrawijayaPipitNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMSDocument24 pagesMIDTERMSCherish Marie HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Gut Kidney Cross TalkDocument37 pagesGut Kidney Cross TalkAbdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- MS-2 GallbladderDocument2 pagesMS-2 Gallbladderelijahdale.guillergan-05No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument3 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseaseNikey LimNo ratings yet