Professional Documents
Culture Documents
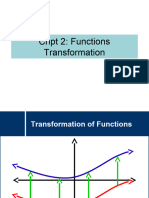
Transformations of A Parent Function
Uploaded by
Dab Dab litOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformations of A Parent Function
Uploaded by
Dab Dab litCopyright:
Available Formats
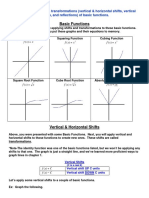
Transformations of the parent function of
f(x)
In mathematics, a transformation of a function is a process that alters the shape or appearance of the
graph of the function. There are several types of transformations that can be applied to a function,
including translations, reflections, dilations, and compressions.
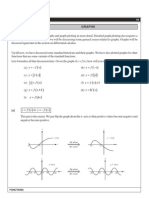
1. Translations: A translation is a transformation that shifts the graph of a function horizontally or
vertically. To translate a function f(x) horizontally, we can add a constant to the input x: f(x+c).
This shifts the graph of the function c units to the right if c is positive, and c units to the left if c is
negative. To translate a function f(x) vertically, we can add a constant to the output y: f(x)+c.
This shifts the graph of the function c units up if c is positive, and c units down if c is negative.
2. Reflections: A reflection is a transformation that flips the graph of a function over a line of
symmetry. To reflect a function f(x) over the x-axis, we can take the negative of the output y: -
f(x). This flips the graph of the function over the x-axis. To reflect a function f(x) over the y-axis,
we can take the negative of the input x: f(-x). This flips the graph of the function over the y-axis.
3. Dilations: A dilation is a transformation that stretches or shrinks the graph of a function. To
dilate a function f(x) by a factor of k, we can multiply the input x by k: f(kx). This stretches the
graph of the function horizontally by a factor of k if k is greater than 1, and shrinks it horizontally
by a factor of k if k is between 0 and 1.
4. Compressions: A compression is a transformation that compresses the graph of a function
horizontally. To compress a function f(x) by a factor of k, we can divide the input x by k: f(x/k).
This compresses the graph of the function horizontally by a factor of k.
It's important to note that these transformations can be combined and applied in any order to produce
a wide variety of different graphs. For example, we can translate a function horizontally and then reflect
it over the y-axis, or we can reflect a function over the y-axis and then dilate it horizontally.
You might also like
- Math Written TaskDocument6 pagesMath Written TaskKanika KumarNo ratings yet
- EER4 Notes PDFDocument6 pagesEER4 Notes PDFChien Manh NguyenNo ratings yet
- EER4 NotesDocument6 pagesEER4 NotesZia Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Graphs and TransformationsDocument2 pagesGraphs and TransformationsGrace CadagNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Sec3Document59 pagesChap1 Sec3Naqeeb khanNo ratings yet
- Math AnalysisDocument16 pagesMath Analysisapi-220275389No ratings yet
- Maths Quadratic GraphsDocument10 pagesMaths Quadratic GraphshaniaNo ratings yet
- Caq 2Document20 pagesCaq 2ThoughtsNo ratings yet
- New Functions From Old FunctionsDocument20 pagesNew Functions From Old FunctionsLaiba IftikharNo ratings yet
- Transformations of Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesTransformations of Exponential & Logarithmic FunctionsnooluoitNo ratings yet
- ShiftsDocument2 pagesShiftsdivakar.rsNo ratings yet
- Transformations of FunctionsDocument4 pagesTransformations of FunctionsCaribNo ratings yet
- 2.4: Transformations of Functions and GraphsDocument15 pages2.4: Transformations of Functions and GraphsSumant SumantNo ratings yet
- Transformations of FunctionsDocument35 pagesTransformations of FunctionsPHENYO SEICHOKONo ratings yet
- 1801 A Supp NotesDocument218 pages1801 A Supp NotesDodNo ratings yet
- 2 Graph SketchingDocument16 pages2 Graph Sketchingdmal88No ratings yet
- Transformation Parent FunctionsDocument15 pagesTransformation Parent Functionsqqvhc2x2prNo ratings yet
- G. Graphing Functions: 1. Right-Left TranslationDocument8 pagesG. Graphing Functions: 1. Right-Left Translation8310032914No ratings yet
- Transformations of Graphs: Name Description What To Look For in The Function How The Function ChangesDocument2 pagesTransformations of Graphs: Name Description What To Look For in The Function How The Function ChangesMindy DyarNo ratings yet
- Basic Transformation On GraphDocument14 pagesBasic Transformation On GraphPrinceNo ratings yet
- in This Section, We Will Study The Following Topics:: Families of GraphsDocument15 pagesin This Section, We Will Study The Following Topics:: Families of GraphsHenriel TambioNo ratings yet
- Transformation - FUNCTIONS - AAHL PDFDocument4 pagesTransformation - FUNCTIONS - AAHL PDFdivyNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Relation and FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Difference Between Relation and Functionbjkhaw75No ratings yet
- Lesson 17 - Exponential FunctionsDocument3 pagesLesson 17 - Exponential FunctionsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Sec Math Functions FunctiontransformationsDocument31 pagesSec Math Functions Functiontransformationsnellymanganyi62No ratings yet
- Function:: Chapter: 2. Functions and GraphsDocument13 pagesFunction:: Chapter: 2. Functions and GraphsDark Lord MJNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6153025579738585635Document65 pagesInbound 6153025579738585635Justin Ralph GanzonNo ratings yet
- M113 (Calculus) FormulasDocument68 pagesM113 (Calculus) FormulasTESLA - Harison NartatesNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Functions TransformationsDocument36 pagesGrade 12 Functions TransformationsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Transformations ExamDocument5 pagesTransformations ExamElaine LauNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Transformations of FunctionsDocument20 pages2.6 Transformations of FunctionsMuneer AlburayhNo ratings yet
- Transformations of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument3 pagesTransformations of Trigonometric FunctionsnooluoitNo ratings yet
- Graphs of FunctionsDocument13 pagesGraphs of FunctionsLennoxNo ratings yet
- Relations: Lines Connect The Inputs With Their Outputs. The Relation Can Also Be Represented AsDocument13 pagesRelations: Lines Connect The Inputs With Their Outputs. The Relation Can Also Be Represented AsCherisse MohammedNo ratings yet
- Quadratics and TransformationsDocument26 pagesQuadratics and Transformationsapi-236866849No ratings yet
- Composite and Inverse Functions: Mrs. Aldous, Mr. Beetz & Mr. Thauvette IB DP SL MathematicsDocument12 pagesComposite and Inverse Functions: Mrs. Aldous, Mr. Beetz & Mr. Thauvette IB DP SL MathematicsAnnanya GuhaNo ratings yet
- Function and LimitDocument87 pagesFunction and LimitVũ Thái Anh100% (1)
- Shifting of GraphsDocument8 pagesShifting of GraphsChampionip4pNo ratings yet
- Graph Exponential FunctionsDocument6 pagesGraph Exponential FunctionsminmenmNo ratings yet
- A Catalog of Essential Functions: Linear ModelsDocument27 pagesA Catalog of Essential Functions: Linear ModelsTuan Anh TranNo ratings yet
- Differential CalculusDocument2 pagesDifferential Calculusvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Math A 10FDocument9 pagesMath A 10FBrian MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Graphing Rational FunctionDocument9 pagesGraphing Rational FunctionJessel Jane LadraNo ratings yet
- Section - 9 Graphs: y FX y F XDocument31 pagesSection - 9 Graphs: y FX y F XrkshankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vocabulary ListDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Vocabulary ListLeetz123456No ratings yet
- PC Functions Transformations GraphingDocument4 pagesPC Functions Transformations GraphingHector R.No ratings yet
- Diffrentiation and Integration: Histor yDocument5 pagesDiffrentiation and Integration: Histor yVanvan Sinamban AliñoNo ratings yet
- MTH101 Lec#2Document29 pagesMTH101 Lec#2Omar HaroonNo ratings yet
- Functions and ModelsDocument59 pagesFunctions and ModelsWaqas AnwarNo ratings yet
- Asymptote Horizontal Asymptote: Horizontal Asymptotes Are Horizontal Lines To Which The Function IsDocument19 pagesAsymptote Horizontal Asymptote: Horizontal Asymptotes Are Horizontal Lines To Which The Function IsMohd Hazwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Function and LimitDocument98 pagesChapter 1 - Function and LimitAndDanNo ratings yet
- 8 The Slope Function RevisedDocument26 pages8 The Slope Function RevisedAlex SmithNo ratings yet
- Graph Transformations: Transformations "After" The Original FunctionDocument17 pagesGraph Transformations: Transformations "After" The Original FunctionLoewenherz7No ratings yet
- Cal141 The Partial DerivativeDocument4 pagesCal141 The Partial Derivativemarchelo_cheloNo ratings yet
- 2 - Transformations of Simple Polynomial FunctionsDocument18 pages2 - Transformations of Simple Polynomial Functionsjeremia yusNo ratings yet
- 11 FunctionsDocument76 pages11 FunctionsMahmoud Abdel-SalamNo ratings yet
- Affine Transformation: Unlocking Visual Perspectives: Exploring Affine Transformation in Computer VisionFrom EverandAffine Transformation: Unlocking Visual Perspectives: Exploring Affine Transformation in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Composite FunctionsDocument1 pageComposite FunctionsDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Laws of LogarithmsDocument1 pageLaws of LogarithmsDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- PEST AnalysisDocument1 pagePEST AnalysisDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Diamond eDocument1 pageDiamond eDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Scientific NotationDocument2 pagesScientific NotationDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- KSFsDocument2 pagesKSFsDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Laws of ExponentsDocument1 pageLaws of ExponentsDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Exponential EquationsDocument1 pageExponential EquationsDab Dab litNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument2 pagesCompleting The SquareDab Dab litNo ratings yet