0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views2 pagesChi-Square Test Significance Levels
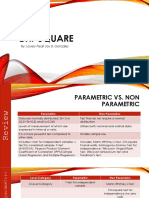
This document provides instructions for conducting a chi-squared test of independence. It explains that a chi-squared test is used to determine if two categorical variables are independent of one another. The document outlines the steps to 1) state the null and alternative hypotheses, 2) calculate expected values, 3) populate a table of observed and expected values, 4) calculate the chi-squared test statistic, 5) determine the degrees of freedom and significance level, 6) compare the test statistic to the critical value. An example is provided to demonstrate these steps.
Uploaded by
Antonia BornemannCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views2 pagesChi-Square Test Significance Levels
This document provides instructions for conducting a chi-squared test of independence. It explains that a chi-squared test is used to determine if two categorical variables are independent of one another. The document outlines the steps to 1) state the null and alternative hypotheses, 2) calculate expected values, 3) populate a table of observed and expected values, 4) calculate the chi-squared test statistic, 5) determine the degrees of freedom and significance level, 6) compare the test statistic to the critical value. An example is provided to demonstrate these steps.
Uploaded by
Antonia BornemannCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd