Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence On Thefisheries Around North Eastern Part of Lake Tana Ethiopia 2332 2543 1000189
Uploaded by
banitessew82Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence On Thefisheries Around North Eastern Part of Lake Tana Ethiopia 2332 2543 1000189
Uploaded by
banitessew82Copyright:
Available Formats
Journal of Biodiversity & Endangered
Species Asmare, J Biodivers Endanger Species 2017, 5:2
DOI: 10.4172/2332-2543.1000189
Research Article OMICS International
Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence on the
Fisheries around North Eastern Part of Lake Tana, Ethiopia
Erkie Asmare*
Bahir Dar Fisheries and Other Aquatic Life Research Center, Bahir-Dar, Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Erkie Asmare, Bahir Dar Fisheries and Other Aquatic Life Research Center, Bahir-Dar, Ethiopia, Tel: 251 918271253; E-mail:
erkie.asmare@yahoo.com
Received date: Jan 02, 2017; Accepted date: June 23, 2017; Published date: June 30, 2017
Copyright: © 2017 Asmare E. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use,
distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
The study was conducted from June, 2015 to October, 2016 to assess the effect of water hyacinth on fishing and
fishers around the North-Eastern part of Lake Tana. The presence of water hyacinth in Lake Tana has been
recognized in 2011. Starting from the last five years, especially after 2014, fishing in the study area becomes tiring
due to the expansion of this invasive weed. Water hyacinth entangles the fishing nets and boats’ propeller, making it
difficult to fish and resulting in reduced fish catches. Hence, a reduced fish catch would have an adverse effect on
the quality of life of the communities around the lake and consequently affect sustainable development in the region.
Despite the fact that several efforts have been made by different parties, water hyacinth in Lake Tana continues to
expand itself year after year. Therefore, o its expansion is not easy to manage and complete eradication is
unimaginable. Therefore, if the expansion of water hyacinth continues in this trend, it can negatively affect the
livelihood of fishers in both directions by increasing costs of fishing and reducing the amount of fish caught.
Keywords: Livelihood; Inefficient fishing; Water hyacinth expansion; The Lake Tana and the adjacent wetlands provide directly and
Big threat indirectly a livelihood for more than 500,000 people [14]. In Lake Tana
fisheries, there are ten districts that have a potential for fishing and
Introduction more than 5400 fishers have been engaged in fishing in a seasonal and
full time basis at this time. Moreover, the poorest rely in a larger
Invasive species are widely accepted as one of the leading causes of proportion on fishing activities while the better off, mainly rely on
biodiversity loss and can have significant effects on resource agricultural activities and fishing as a supplementary [15,16].
availability and can suppress the relative abundance of native species
[1,2]. In Ethiopia, close to 35 invasive alien plant species are posing Even if a tremendous amount of human labor, time and money has
negative impacts on native biodiversity, agricultural lands, rangelands, been exerted each year by both surrounding community and
national parks, waterways, lakes, rivers, power dams, roadsides, urban government, its coverage continues to escalate from 20 ha in 2012 to
green spaces with great economy and social consequences [3]. They more than 50,000 ha in 2014. In addition, the 2014 assessment study
may also alter biological communities and ecosystem structure and shows that close to one-third or more than 30% of the shoreline of the
processes in terms of food web structure and energy flow [4]. north-eastern part of the Lake’s shore is now invaded by water hyacinth
[17]. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the impact of water hyacinth
At present Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipses) have been ranked on fishers around Lake Tana.
as one of the world’s worst invasive weeds [1,5] causing problems for
millions of users of water resources. It is known as “Blue Devil” or Materials and Methods
“Bengal terror” in India, “Florida devil” in South Africa, “German
weed” in Bangladesh and “Water terror” by South Western Nigeria The study was conducted from June, 2015 to October, 2016 in the
with its disruptive impacts on aquatic ecosystems, agriculture, North-Eastern part of Lake Tana. Based on the expansion magnitude
fisheries, transportation, living conditions and social structures [1]. of water hyacinth, purposive sampling method was used to select
Water hyacinth is justifiably called the world’s worst aquatic weed due Fogera, Libo-kemkem, Gondar Zuriya and Dembia districts.
to its ability to rapidly cover whole waterways. Qualitative data, focusing on the current status of water hyacinth
infestation and its possible impact on fishing activities was collected
Under favorable conditions, water hyacinth can double its mass
using PRA tools such as: Focus group discussion, key informant
every 5 days and it also grows from seed, which can remain viable for
interview and direct observation.
20 years or longer [2,6]. Due to its high reproduction rate, the complex
root structure and the formation of dense mats with up to two million In addition, consultancy workshop on the issues of water hyacinth
plants per hectare [7]. In Ethiopia, water hyacinth was officially and related Lake Tana threats were also held at Dembia, Gondar zuriya
reported in 1956 in Koka Lake and the Awash River [4,8-10]. In and Fogera districts with a total of 182 (31.5% of them were female)
addition, water hyacinth has been recognized as the most damaging participants. During the workshop, the participants in the group
aquatic weed in Ethiopia since 1965 [4]. However, in the case of Lake discussion were ranging from the highest officials to the lower local
Tana its presence has been recognized since 2011 [4,11-13]. experts and fishers. Moreover, secondary data were reviewed from
literatures and annual reports. Finally, the collected data were analyzed
and narrated qualitatively.
J Biodivers Endanger Species, an open access journal Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000189
ISSN: 2332-2543
Citation: Asmare E (2017) Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence on the Fisheries around North Eastern Part of Lake
Tana, Ethiopia. J Biodivers Endanger Species 5: 189. doi:10.4172/2332-2543.1000189
Page 2 of 4
Results and Discussion increasing fishing costs because of the time and effort spent in clearing
waterways, and causing loss of nets. It had inflicted heavy financial
Fisheries of Lake Tana and water hyacinth expansion burden on the surrounding fisher folk, who complained that their
fishing ground was infested with the weed, fish landings had dwindled
Even though fish catch from Lake Tana is not as the previous, and that even navigation had become impossible in the infested areas.
fisheries of Lake Tana serves as a source of direct cash for more than Similarly, Aloo et al. [22] reported that many landing sites have been
5400 fishers. Now a day, anthropogenic activities and the newly abandoned and income-generation from the sale of fish has been
emerged water hyacinth [18] poses a big threat on the fisheries of Lake negatively affected.
Tana. Important feeding and spawning grounds of the fish are reduced
A study by Kateregga and Sterner [23] confirmed that fish stocks
or lost altogether. When the fish in question are unique endemic ones,
decline have been at least temporarily halted by the declining catch
the problem is compounded. This is indeed true for the barbs of Lake
ability of fish because of the growing abundance of water hyacinth. A
Tana, which are facing imminent extinction as the food web of Lake
study in Lake Victoria by Bhattacharya et al. [1] also showed fish catch
Tana changes in time. The decline of barbs has been observed presently
rates decreased by 45% because water hyacinth mats blocked access to
in Eastern shore of the Lake Tana, which is shallower and where
fishing grounds, delayed access to markets and increased costs (effort
extensive removals of papyrus and nutrient inputs have been observed
and materials) of fishing. Similarly, Mitchel [21] and Mailu [24] stated
[13]. As a result, Catch Per Unit of Effort (CPUE ) of Labeobarbus in
that the hyacinth mats reduced their catch by covering fishing grounds,
2010 had dropped to an alarming 6 kg/trip in comparison with 28 kg/
delaying access to markets due to loss of output, increasing fishing
trip in 2001 and 63 kg/trip in 1991-1993 (63 kg/trip) [19].
costs due to the time and effort spent clearing waterways, forcing
In 2012, water hyacinth had proliferated and covered about 15% of translocation, and causing loss of nets.
the Northern shore of the Lake. Due to this infestation, a massive
annual removal campaign was organized by the regional government Effects of water hyacinth on fishing equipment’s
in 2013 and more than 40,000 farmers were involved [13]. Even though
such a massive physical removal was implemented, water hyacinth Access to sites becomes difficult when weed infestation is present,
flourishes alarmingly year to year. According to a 2014 assessment loss of fishing equipment often results when nets or lines become
study of Wassie et al. [17] close to one-third or more than. tangled in the root systems of the weed. Therefore, fishers turn back to
Furthermore, the reports of Bahir Dar fisheries and other aquatic life the landing site after they lost a lot of extra fuel and labour without any
research center (annual report) (2015) and [12] showed the current or with a minimum catches. Furthermore, each branch of water
(2015) estimate of water hyacinth infestation coverage is approximately hyacinth becomes attached to the fishing net, and when the fishers pull
34,500 ha (3,000 ha thick, 2,500 ha intermediate and 29,000 ha their fishing net (mostly monofilament gillnet) during fishing it
scattered). However, thick mat covered areas are smaller in the 2015 becomes damaged. Besides repairing the damaged fishing net, fishers
survey than in 2014, this is largely as a result of the community based invest considerable amount of time on detaching water hyacinth parts
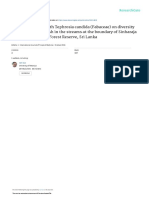
mass physical removal campaign and to some extent long dry season (branches) from gillnet after catching or fish (Figure 1). According to
dormancy (Figure 1). an interview with a key informant by Mitchel [21] ‘fishers experience
loss of fishing gear, time wasting during fishing and difficulty in
Effects of water hyacinth expansion on fishing activities movement, and even sometimes prevent people from fishing’. All these
lead to reduction in fish catch and subsequent loss of livelihood.
According to Opande et al. [20] when water hyacinth infestation is
present, access to fishing sites become difficult for riparian
communities which rely solely on fishing as their main economic
activity. Similarly, a study by Frezina [6] also reported that water
hyacinth can present many problems for the fishers. On the other
hand, water hyacinth provides highly complex habitat structure by
restricting the growth of other submersed macrophytes. This
modification and habitat complexity at the surface of the water are
likely affect fishing (Figure 2).
Starting from the last five years, especially after 2014, fishing in the
study area becomes tiring due to the expansion of this invasive weed.
In the area of severe infestation, especially around the shore area
fishing is therefore too much difficult. This results in blockage of fish
landing sites and destruction of fishing gear [20]. Hence, as much as Figure 1: Fishing net entangled by water hyacinth at the landing site
water hyacinth is viewed; it has had a negative impact on fishing, as it (a) and fishing at area free from water hyacinth (b).
causes difficulty in fishing [21]. Water hyacinth can also greatly affect
fish catch rates, because mats of water hyacinth can block access to
fishing grounds and clog eye of the net (Figure 2). On the other hand, an area of sparsely infested water hyacinth
As a result, fish production in the Lake has declined since the weed dawdles the speed of the fishing boat by ravelling the propeller. This
has blocked many fishing grounds. In this regard, Nabega Kebele in reduces the energy of the motorized boat without reducing the amount
Fogera district is an indicator that all fishers change their landing site of fuel consumed. This leads to increase in their expenditure on fuel for
to the neighboring district Libo-Kemkem because of water hyacinth their boat’s engine. However, in a densely infested area (Figure 2)
expansion obstructs their fishing activities. Therefore, for fishermen, fishing by using both types of boats (motorized and reed boat) is
the hyacinth mats have reduced their catch by covering the grounds, unimaginable. According to the focus group discussion and key
J Biodivers Endanger Species, an open access journal Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000189
ISSN: 2332-2543
Citation: Asmare E (2017) Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence on the Fisheries around North Eastern Part of Lake
Tana, Ethiopia. J Biodivers Endanger Species 5: 189. doi:10.4172/2332-2543.1000189
Page 3 of 4
informant interview, artisanal fishers, who couldn’t enter into the References
pelagic area using reed boat, are highly vulnerable to the problems
derived by water hyacinth. Therefore, water hyacinth affects 1. Bhattacharya A, Haldar S, Chatterjee PK (2015) Geographical
distribution and physiology of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipses) the
smallholder fishers by increasing costs of fishing and reducing the
invasive hydrophyte and a biomass for producing xylitol. Int J ChemTech
amount of CPUE. Res 7: 1849-1861.
2. Patel S (2012) Threats management and envisaged utilizations of aquatic
weed Eichhornia crassipes: An overview. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 11:
249-259.
3. Rezene F, Taye T (2014) Alien plant species invasions in Ethiopia:
challenges and responses.
4. Wondie Z (2013) Assessment of water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes
(Mart) Solms) in relation to water quality, composition and abundance of
plankton and macro-invertebrates in the north-eastern part of Lake Tana,
Ethiopia.
5. Villamagna A, Murphy BR (2016) Ecological and socio-economic impacts
of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) A review ecological and
Figure 2: Shore area infested by water hyacinth at Serava kebele.
socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes)
a review. Freshwater Biology 55: 282-298.
Furthermore, some fishers around Gorgora states that, fishing in the 6. Frezina NCA (2013) Assessment and utilization of water hyacinth in the
water bodies of Tamil Nadu. IJSRP 2: 58-77.
areas that are highly infested by water hyacinth (Figure 2) are risky
7. Rakotoarisoa TF, Waeber PO, Richter T, Mantilla Contreras IJ (2015)
because of the weed slow down the speed of the boat and we couldn’t Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) any opportunities for the Alaotra
escape from a hippopotamus. Even though originally perceived as a wetlands and livelihoods. MCD 10: 128-136.
practical problem for fishing and navigation, recent research indicates 8. Daniel W, Feleke Z, Seyoum L (2011) Potential of water hyacinth
that aquatic weeds are now also considered a threat to biological (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms) for the removal of chromium from
diversity affecting fish fauna, plant diversity and other freshwater life tannery effluent in constructed pond system. SINET Ethiop J Sci 34:
and food chains Mitchel [21]. Moreover, Gichuki et al. [25] reported 49-62.
that the weed forms thick mats over the infested water bodies causing 9. Tegene S, Ayele N (2014) Prevalence and intensity of water hyacinth
obstruction to economic development activities and impacting infestation in the water bodies of rift valley Ethiopia. TJANRS 1: 118-126.
negatively on the indigenous aquatic biodiversity. 10. Firehun Y, Struik PC, Lantinga EA, Taye T (2014) Water hyacinth in the
rift valley water bodies of Ethiopia its distribution socioeconomic
Eventually, further expansion of this plant may lead to drying up importance and management. IJCAR 3: 67-75.
and shrinking of the lake. Depending on the degree of evapo- 11. Dereje T (2015) Preliminary survey of water hyacinth in Lake Tana
transpiration and the lake size, there would be completely dry-up and Ethiopia. Glob J Allergy 1: 13-18.
disappearance of the Lake. Aba Samuel reservoir is a small lake near 12. Wassie A, Dereje T, Addisalem A, Abebaw Z, Befta T, et al. (2015) Water
Addis Ababa was chocked with water hyacinth and completely dried hyacinth coverage survey report on Lake Tana biosphere reserve
up in recent memory [13]. Technical survey report series 2.
13. Seyoum M (2013) Will water hyacinth become established in Lake Ziway?
In: Brook L, Seyoum M, Elias D, Zenebe T, and Tadesse F (eds.) Trends in
Conclusion and Recommendations the conservation and utilization of the resources of the Ethiopian rift
Like climate change and other anthropogenic activities, the newly valley Lakes, paper presented at the 5th annual conference of the
Ethiopian Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences Association (EFASA), Hawassa
emerged water hyacinth becomes a big threat for Lake Tana in general
pp: 50-78.
and the fishers in particular. effects of water hyacinth are dependent on
the extent of the invasion, the uses of the impacted water body, and the 14. Vijverberg J, Sibbing FA, Dejen E (2009) Lake Tana source of the Blue
Nile. Springer: Netherlands pp: 163-192
controlling methods used. If the expansion of this aquatic invasive
15. Asmare E, Tewabe D, Mohamed B, Hailu B (2015) Pre-scaling up of solar
weed continues at this rate, the livelihood of subsistence fishers could tent fish drier in northern and north western part of Lake Tana Ethiopia.
be endangered because of water hyacinth strongly reduces the IJFAR 1: 48-53.
efficiency of fishing. Unless a well-designed and organized preventive 16. Asmare E, Demissie S, Tewabe D (2016) Fisheries of Jemma and Wonchit
approach is followed, the expansion of water hyacinth could endanger Rivers as a means of livelihood diversification and its challenges in North
not only fishers and surrounding community but also the sustainability Shewa Zone. Ethiopia 7.
of the Lake. The local community around Lake Tana are at risk of 17. Wassie A, Minwuyelet M, Ayalew W, Dereje T, Woldegebrael W, et al.
losing their livelihood from fisheries following the infestation of the (2014) Water hyacinth coverage survey report on Lake Tana. Technical
Lake by water hyacinth. Once water hyacinth has established, it is very Report Series 1.
difficult to eradicate hence, continuous monitoring is very important 18. Erkie A, Sewmehon D, Dereje T, Mihret E (2016) Impact of climate
to reduce its rate of expansion. Farmers who are directly and indirectly change and anthropogenic activities on livelihood of fishing community
beneficial from Lake Tana considered water hyacinth as a curse and around Lake Tana Ethiopia. E-Cronicon 3: 548-557.
they are willing to participate in the prevention campaign. Therefore, 19. Brehan M, Martin deG, Leo N, Wassie A, Minwyelet M (2011) Lake
Tana’s (Ethiopia) endemic Labeobarbus spp. Flock an uncertain future
the government and other concerned stakeholders must surmount
threatened by exploitation, land use and water resources developments.
their facilitation and coordination role in the physical removal In: Brook L and Abebe G (eds.) Impacts of climate change and population
campaign. Moreover, conducting a multidisciplinary research to know on tropical aquatic resources, proceedings of the Third International
their effects on the aquatic systems, fish health and Lake’s productivity Conference of the Ethiopian Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences Association
is vital. (EFASA), Addis Ababa: AAU Printing Press pp: 285-297.
J Biodivers Endanger Species, an open access journal Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000189
ISSN: 2332-2543
Citation: Asmare E (2017) Current Trend of Water Hyacinth Expansion and Its Consequence on the Fisheries around North Eastern Part of Lake
Tana, Ethiopia. J Biodivers Endanger Species 5: 189. doi:10.4172/2332-2543.1000189
Page 4 of 4
20. Opande GO, Onyango JC, Wagai SO (2004) Lake Victoria The water 23. Kateregga E, Sterner T (2009) Lake Victoria fish stocks and the effects of
hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms) its socio-economic effects water hyacinth. J Environ Dev 18: 62-78.
control measures and resurgence in the Winam gulf. Limnologica 34: 24. Mailu AM (2001) Preliminary assessment of the social, economic and
105-109. environmental impacts of water hyacinth in the Lake Victoria basin and
21. Mitchel O (2014) Influence of water hyacinth on livelihoods of the the status of control major threats to Lake Victoria. In: Julien MH, Hill
riparian community of South West Seme location, Kisumu County, MP, Center TD, Jianqing D (eds.) Biological and integrated control of
University of Nairobi, Kenya. water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes pp: 130-139.
22. Aloo P, Ojwang W, Omondi R, Njiru JM, Oyugi D (2013) A review of the 25. Gichuki J, Omondi R, Boera P, Okorut T, Matano A, et al. (2012) Water
impacts of invasive aquatic weeds on the bio-diversity of some tropical hyacinth Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms-Laubach dynamics and
water bodies with special reference to Lake Victoria (Kenya). Biodivers J succession in the Nyanza Gulf of Lake Victoria (East Africa) implications
4: 471-482. for water quality and biodiversity conservation. Sci World J.
J Biodivers Endanger Species, an open access journal Volume 5 • Issue 2 • 1000189
ISSN: 2332-2543
You might also like
- Siné-Saloum Delta: An illustrated guide to Senegal’s remarkable mangrove estuary.From EverandSiné-Saloum Delta: An illustrated guide to Senegal’s remarkable mangrove estuary.No ratings yet
- Marine Mammals: Fisheries, Tourism and Management Issues: Fisheries, Tourism and Management IssuesFrom EverandMarine Mammals: Fisheries, Tourism and Management Issues: Fisheries, Tourism and Management IssuesNicholas GalesNo ratings yet
- Resource EconDocument5 pagesResource Econgetachew mulatNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Fish Parasites From Pangani Catchment and Lake Kitangiri in Singida, TanzaniaDocument11 pagesA Survey of Fish Parasites From Pangani Catchment and Lake Kitangiri in Singida, TanzaniaFred ChibwanaNo ratings yet
- "Wild Fish Are A Blessing": Changes in Fishing Practices and Folk Fish Cuisine Around Laguna Lake, Northern PhilippinesDocument11 pages"Wild Fish Are A Blessing": Changes in Fishing Practices and Folk Fish Cuisine Around Laguna Lake, Northern PhilippinesEricka De ClaroNo ratings yet
- Management of Overfishing in The Inland Capture Fisheries in NigeriaDocument6 pagesManagement of Overfishing in The Inland Capture Fisheries in NigeriaAbigail OmotolaNo ratings yet
- EJABF - Volume 24 - Issue 3 - Pages 181-191Document11 pagesEJABF - Volume 24 - Issue 3 - Pages 181-191ReCyoNo ratings yet
- Management of Inland Fisheries in NigeriaDocument17 pagesManagement of Inland Fisheries in NigeriaGeorge AtaherNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The Coastal Resources of Ibajay and Tangalan, Aklan - Implications For ManagementDocument72 pagesAn Assessment of The Coastal Resources of Ibajay and Tangalan, Aklan - Implications For ManagementYasmin H. Primavera-TirolNo ratings yet
- Fish Abundance Survey: WWF G M - C C PDocument44 pagesFish Abundance Survey: WWF G M - C C PKarun DewanNo ratings yet
- Fishing Condition and Fishers Income: The Case of Lake Tana, EthiopiaDocument4 pagesFishing Condition and Fishers Income: The Case of Lake Tana, EthiopiaPeertechz Publications Inc.No ratings yet
- Physics and Chemistry of The Earth: I. Naigaga, H. Kaiser, W.J. Muller, L. Ojok, D. Mbabazi, G. Magezi, E. MuhumuzaDocument11 pagesPhysics and Chemistry of The Earth: I. Naigaga, H. Kaiser, W.J. Muller, L. Ojok, D. Mbabazi, G. Magezi, E. MuhumuzaAngela JuliethNo ratings yet
- Mortality and Exploitation Rate of Some Reef Fish in Ternate Island WatersDocument7 pagesMortality and Exploitation Rate of Some Reef Fish in Ternate Island WatersaishiragreenNo ratings yet
- Report of Mass Fish Mortality Along The Eritrean Coast and IslandsDocument4 pagesReport of Mass Fish Mortality Along The Eritrean Coast and IslandsTeklehaimanot BerakiNo ratings yet
- Water Hyacinth Invasion in Lake TanaDocument4 pagesWater Hyacinth Invasion in Lake TanaThe Ethiopian AffairNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Condition Factor of Fish Species From Challawa Gorge DamDocument6 pagesBiodiversity and Condition Factor of Fish Species From Challawa Gorge DamNazeef SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Eutrophication Assessment and Bioremediation Strategy Using SeaweedsDocument8 pagesEutrophication Assessment and Bioremediation Strategy Using SeaweedsMarcus Adonai Castro da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pearl Spot 3 PDFDocument15 pagesPearl Spot 3 PDFAnjuNo ratings yet
- Nieves - An Assessment of Macro-Invertebrate Gleaning in Fisheries On The Albay GulfDocument9 pagesNieves - An Assessment of Macro-Invertebrate Gleaning in Fisheries On The Albay GulffurkonableNo ratings yet
- A Drivers Pressure State Impact Responses FrameworDocument20 pagesA Drivers Pressure State Impact Responses FrameworShaashooNo ratings yet
- Blast FishingDocument6 pagesBlast FishingAliyah Kahrine Chan CastilloNo ratings yet
- Permaculture Technology in Tropical Freshwater SwaDocument12 pagesPermaculture Technology in Tropical Freshwater SwatommyNo ratings yet
- Adoption and Consequences of New Light-Fishing Technology (Leds) On Lake Tanganyika, East AfricaDocument12 pagesAdoption and Consequences of New Light-Fishing Technology (Leds) On Lake Tanganyika, East AfricaGustave ZimmlerNo ratings yet
- Invasive Aquatic WeedDocument32 pagesInvasive Aquatic WeedYared Mesfin FikaduNo ratings yet
- Fishery Production System Southeastern OromiaDocument5 pagesFishery Production System Southeastern OromiaAlemu Lema AbeltiNo ratings yet
- Edward Paul Proposal Final.Document20 pagesEdward Paul Proposal Final.Edward paulNo ratings yet
- Farming Tilapia in Ponds in Central Luzon, Philippines A. Background 1. Scope and PurposeDocument16 pagesFarming Tilapia in Ponds in Central Luzon, Philippines A. Background 1. Scope and PurposeMichael ArligueNo ratings yet
- Tmp8e66 TMPDocument4 pagesTmp8e66 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Article4archives42008 1906Document10 pagesArticle4archives42008 1906Martia Putri GitrinNo ratings yet
- Deadly SprayDocument56 pagesDeadly SprayPerkumpulan TelapakNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Biodiversity of Lake Mainit, Southern PhilippinesDocument12 pagesAquatic Biodiversity of Lake Mainit, Southern PhilippinesRICA MAE LUMICTINNo ratings yet
- Survey On Socio-Economic Characteristics and Catch Assessment of Fisheries Traditional of The Northwestern Part of Lake Tanganyika in Uvira, DrcongoDocument8 pagesSurvey On Socio-Economic Characteristics and Catch Assessment of Fisheries Traditional of The Northwestern Part of Lake Tanganyika in Uvira, DrcongoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Growth Performanceof Green Mussel Pernaviridis Transplantedin Buguey Lagoon PhilippinesDocument6 pagesGrowth Performanceof Green Mussel Pernaviridis Transplantedin Buguey Lagoon Philippinesmarian almiaNo ratings yet
- 490 Ijar-30672Document5 pages490 Ijar-30672Ericka De ClaroNo ratings yet
- Culture-Based Fisheries in Rawa Lebak Lebung, South Sumatera, Is It Applicable?Document8 pagesCulture-Based Fisheries in Rawa Lebak Lebung, South Sumatera, Is It Applicable?FERLYNo ratings yet
- Informe GreenPeaceDocument26 pagesInforme GreenPeacefeshsmith2001No ratings yet
- The Ecological Balance of The Fish Community in An Aging ReservoirDocument9 pagesThe Ecological Balance of The Fish Community in An Aging Reservoiradventa sinta maritoNo ratings yet
- Lake Ontario Lakewide Management Plan Update 2008Document8 pagesLake Ontario Lakewide Management Plan Update 2008binational-netNo ratings yet
- Artisanal Fisheries Landings During PreDocument10 pagesArtisanal Fisheries Landings During PreSudesh RathodNo ratings yet
- TephrosiaDocument15 pagesTephrosiaProf. U.P.K. Epa - University of KelaniyaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture, Livestock FisheriesDocument13 pagesAgriculture, Livestock FisheriesStoic GeneralissimoNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper Presented To The Faculty of The Alcate, Victoria, Oriental Mindoro, PhilippinesDocument13 pagesA Research Paper Presented To The Faculty of The Alcate, Victoria, Oriental Mindoro, PhilippinesCrizhae OconNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Distribution of Freshwater Fish PDFDocument13 pagesDiversity and Distribution of Freshwater Fish PDFBob UrbandubNo ratings yet
- 192275-Article Text-487490-1-10-20200116 PDFDocument22 pages192275-Article Text-487490-1-10-20200116 PDFSylvestreYapoNo ratings yet
- The Gendered Effects of Climate Variability Change On Fisher Livelihoods and The Coping Strategies Opportunities in Mbita, Homa Bay County, KenyaDocument11 pagesThe Gendered Effects of Climate Variability Change On Fisher Livelihoods and The Coping Strategies Opportunities in Mbita, Homa Bay County, KenyaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- WWF Zambia Fisheries Summary August 2020 Final Web V 2Document20 pagesWWF Zambia Fisheries Summary August 2020 Final Web V 2Moses JuniorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Group 11Document32 pagesChapter 1-3 Group 11VIANCA JOY E MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Zooplankton and White Goby (Glossogobius Giuris Hamilton 1822) : Correlation and Fishers' Perception in Selected Sites in Laguna de Bay, Luzon Island, PhilippinesDocument18 pagesZooplankton and White Goby (Glossogobius Giuris Hamilton 1822) : Correlation and Fishers' Perception in Selected Sites in Laguna de Bay, Luzon Island, PhilippinesMutya, Rosemarie Kate N.No ratings yet
- Fish Species Diversity, Abundance and Distribution in The Major Water Bodies in Akwa Ibom State, NigeriaDocument7 pagesFish Species Diversity, Abundance and Distribution in The Major Water Bodies in Akwa Ibom State, NigeriaChikondi TemboNo ratings yet
- UJAS6 Mwebaza-NdawulaetalDocument16 pagesUJAS6 Mwebaza-NdawulaetalRonnie WartNo ratings yet
- Investigation of A Parasitic Outbreak of Lernaea Cyprinacea Linnaeus (Crustacea: Copepoda) in Fish From ZimbabweDocument10 pagesInvestigation of A Parasitic Outbreak of Lernaea Cyprinacea Linnaeus (Crustacea: Copepoda) in Fish From ZimbabweEdgar Solorio OrnelasNo ratings yet
- Inland Fisheries - NCSDocument36 pagesInland Fisheries - NCSShamim HussenNo ratings yet
- Field Trip Report - VietnamDocument12 pagesField Trip Report - VietnamGaluh Nur ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Exploitation of Coastal Resources: Group 6 VGLDocument19 pagesExploitation of Coastal Resources: Group 6 VGLRianna Angela PronNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Mangroves and Coastal Aquatic Biota: Journal of Physics: Conference SeriesDocument6 pagesThe Correlation Between Mangroves and Coastal Aquatic Biota: Journal of Physics: Conference SeriesSandy Wahyu DNo ratings yet
- Ecological Characteristics of Phytoplankton in Qin-Huangdao Waters During Red Tide PeriodDocument1 pageEcological Characteristics of Phytoplankton in Qin-Huangdao Waters During Red Tide PeriodSivagini KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- 4 6 37 889Document4 pages4 6 37 889Khoiril FuadNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Community On Fishery and Aquaculture Production in Central EthiopiaDocument4 pagesAwareness of Community On Fishery and Aquaculture Production in Central EthiopiaHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- 230937-Article Text-560487-1-10-20220831Document18 pages230937-Article Text-560487-1-10-20220831fireworkNo ratings yet
- Abundance and Diversity of Fishes in BayDocument17 pagesAbundance and Diversity of Fishes in BayRedgie PotenciandoNo ratings yet
- Eth20051503 PDFDocument19 pagesEth20051503 PDFbanitessew82No ratings yet
- 2022 Total Group Sat Suite of Assessments Annual ReportDocument18 pages2022 Total Group Sat Suite of Assessments Annual Reportbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Ethnc2 PDFDocument282 pagesEthnc2 PDFbanitessew82No ratings yet
- P15738coll2 3787Document1 pageP15738coll2 3787banitessew82No ratings yet
- BiH Inc Report PDFDocument196 pagesBiH Inc Report PDFbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Cop27 Presidency Vision Thematic Days Full ProgramDocument26 pagesCop27 Presidency Vision Thematic Days Full Programbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Anley Assignment1Document19 pagesAnley Assignment1banitessew82100% (1)
- ThesisDocument154 pagesThesisbanitessew82No ratings yet
- National Meteorological Agency: Proceeding Report of THE 40 Anniversary ofDocument78 pagesNational Meteorological Agency: Proceeding Report of THE 40 Anniversary ofbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Logistic in Value Chain Hadout (Cha-1&2) PDFDocument26 pagesLogistic in Value Chain Hadout (Cha-1&2) PDFbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Assignments-Design of Dam Appurtenant Structures-2023Document2 pagesAssignments-Design of Dam Appurtenant Structures-2023banitessew82No ratings yet
- Land Degrad Dev - 2017 - Dejen - The Decline of The Lake Tana Ethiopia Fisheries Causes and Possible SolutionsDocument10 pagesLand Degrad Dev - 2017 - Dejen - The Decline of The Lake Tana Ethiopia Fisheries Causes and Possible Solutionsbanitessew82No ratings yet
- Thesis and Dissertation Formating Guideline - IDRMFSS - BDU - Final - May2020 - 0Document43 pagesThesis and Dissertation Formating Guideline - IDRMFSS - BDU - Final - May2020 - 0banitessew82No ratings yet
- Model of The Pontic Shad Alosa Immaculata (Bennet, 1835) and Anchovy Engraulis Encrasicolus (Linnaeus, 1758) Catch in The Danube River and Black Sea For The Period 1920-2008Document6 pagesModel of The Pontic Shad Alosa Immaculata (Bennet, 1835) and Anchovy Engraulis Encrasicolus (Linnaeus, 1758) Catch in The Danube River and Black Sea For The Period 1920-2008daniel cretuNo ratings yet
- FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - Fishery and Aquaculture Country ProfilesDocument17 pagesFAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - Fishery and Aquaculture Country ProfilesAbduletif HeboNo ratings yet
- SPRO-Brochure-2022 Web ENDocument31 pagesSPRO-Brochure-2022 Web ENDragan MiloševićNo ratings yet
- FisheryDocument2 pagesFisheryKyle GalangueNo ratings yet
- Short Talk Summary: Phytoplankton Diversity and Abundance in Panguil Bay, Northwestern Mindanao, Philippines in Relation To Some Physical and Chemical Characteristics of The WaterDocument4 pagesShort Talk Summary: Phytoplankton Diversity and Abundance in Panguil Bay, Northwestern Mindanao, Philippines in Relation To Some Physical and Chemical Characteristics of The WaterEloisa Marie IglesiasNo ratings yet
- List of Lakes in India PDFDocument8 pagesList of Lakes in India PDFsoumo royNo ratings yet
- NNVS74356 WickedTunaOBX NorthernFury ScriptforCCDocument48 pagesNNVS74356 WickedTunaOBX NorthernFury ScriptforCCsupervikedNo ratings yet
- Balayan Marine Protected AreasDocument12 pagesBalayan Marine Protected Areasanakbalayan50% (2)
- Coastal Resources Depletion in Bolinao, Pangasinan (Case Study)Document14 pagesCoastal Resources Depletion in Bolinao, Pangasinan (Case Study)Desiree Mae FaisanNo ratings yet
- The Tragedy of The High Seas - The EconomistDocument3 pagesThe Tragedy of The High Seas - The EconomistFantastic DragonNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMultiple ChoiceMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- 50 GT Vessel Arrives in SindanganDocument2 pages50 GT Vessel Arrives in SindanganChristopher IgnacioNo ratings yet
- CM011 Research About RecyclingDocument16 pagesCM011 Research About RecyclingJohn VincentNo ratings yet
- The South Luconia ShoalsDocument1 pageThe South Luconia ShoalsFatin MinhatNo ratings yet
- 2023 C Atalo G: Nikko Kasei Co.,LtdDocument17 pages2023 C Atalo G: Nikko Kasei Co.,LtdFerran CongostNo ratings yet
- People OceanDocument3 pagesPeople OceanCristine Joy BalansagNo ratings yet
- Ammar. 2004 - Benthic Fauna of The Syrian CoastDocument1 pageAmmar. 2004 - Benthic Fauna of The Syrian CoastGabriele MacrìNo ratings yet
- Appendicularian Distribution and Diversity in The Southern Gulf of MexicoDocument10 pagesAppendicularian Distribution and Diversity in The Southern Gulf of MexicoJosé Manuel Martínez MontesNo ratings yet
- Wa0004Document15 pagesWa0004Daniel OscarNo ratings yet
- Daniel Weiss: Education G.P.A. 3.2/4.0Document2 pagesDaniel Weiss: Education G.P.A. 3.2/4.0api-638692198No ratings yet
- Coral Reef 1 SEDocument7 pagesCoral Reef 1 SEMohamoud OsobleNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Antara Kandungan Silika Dengan Kelimpahan Diatom Benthik Di Sepanjang Sungai Pelus Kabupaten BanyumasDocument7 pagesHubungan Antara Kandungan Silika Dengan Kelimpahan Diatom Benthik Di Sepanjang Sungai Pelus Kabupaten BanyumasZidan Asy'ariNo ratings yet
- Panulirus OrnatusDocument5 pagesPanulirus OrnatusadamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Principles of Oceanography and Marine Biology Class NotesDocument24 pagesModule 1 - Principles of Oceanography and Marine Biology Class Noteschris black MateusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlanktonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To PlanktonacroaliNo ratings yet
- ZP MPDocument2 pagesZP MPNagbhushan_cmNo ratings yet
- Rivers, Islands, Bays, Oceans, Strights...Document154 pagesRivers, Islands, Bays, Oceans, Strights...AzkaKhalidNo ratings yet
- Ocean WebquestDocument2 pagesOcean WebquestS354-Alaysia PickensNo ratings yet
- Bodies of Water in Your CommunityDocument4 pagesBodies of Water in Your CommunityCristina Gomez100% (1)
- MSC Go FishDocument7 pagesMSC Go FishHendri IlyasNo ratings yet