Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Forging
Uploaded by
Sriharsha Sarma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views28 pagesForging is a metal forming process where compressive forces are applied to deform heated metal into a desired shape. It uses the plastic properties of metal when heated. Application of heat lowers the yield point, making deformation easier. There are two main types of forging: open die forging where the metal is compressed between two open dies, and closed die forging where cavities in the dies constrain the metal flow during compression into a specific shape. Closed die forging includes drop forging using a falling ram and press forging using continuous pressure. Defects can occur from issues like temperature differences, residual stresses, improper cooling, die misalignment, or insufficient metal flow into the dies.
Original Description:
Original Title
4-Forging
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentForging is a metal forming process where compressive forces are applied to deform heated metal into a desired shape. It uses the plastic properties of metal when heated. Application of heat lowers the yield point, making deformation easier. There are two main types of forging: open die forging where the metal is compressed between two open dies, and closed die forging where cavities in the dies constrain the metal flow during compression into a specific shape. Closed die forging includes drop forging using a falling ram and press forging using continuous pressure. Defects can occur from issues like temperature differences, residual stresses, improper cooling, die misalignment, or insufficient metal flow into the dies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views28 pages4 Forging
Uploaded by
Sriharsha SarmaForging is a metal forming process where compressive forces are applied to deform heated metal into a desired shape. It uses the plastic properties of metal when heated. Application of heat lowers the yield point, making deformation easier. There are two main types of forging: open die forging where the metal is compressed between two open dies, and closed die forging where cavities in the dies constrain the metal flow during compression into a specific shape. Closed die forging includes drop forging using a falling ram and press forging using continuous pressure. Defects can occur from issues like temperature differences, residual stresses, improper cooling, die misalignment, or insufficient metal flow into the dies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
Forging – The process
Metal forging is a metal forming process that involves applying
compressive forces to a work piece to deform it, and create a desired
geometric change to the material.
It is the process of shaping heated metal by the application of sudden
blows or steady pressure and makes use of the characteristics of
plasticity of material.
Application of heat lowers the yield point and makes deformation
easier.
Smithy is the best example for Forging.
Forging Products
Classification of Metal Forging Process
By the degree to which the flow of material is constrained -
1. Open die forging - In which the work is compressed between two
die that do not constrain the metal during the process.
2. Impression die forging / Closed Die forging - In which cavities
within the die restrict metal flow during the compression of the part,
causing the material to deform into a desired geometric shape.
Some material in impression die forging is not constrained by the
cavities and flows outward from the die, this metal is called flash. In
industrial metal forging, a subsequent trimming operation will be
performed to remove the flash.
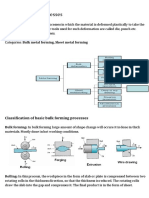
Closed and open die forging processes
Open- Die Forging
Closed- Die Forging
Impression- Die Forging
Classification of Closed Die Forging
1) Drop Forging
2) Press Forging
Classification of Closed Die Forging
1) Drop Forging
In this process, the forging is made by hammering a heated bar or billet
into aligned die cavities by allowing the ram to drop using Gravity
The forging equipment used for this is “Drop hammer”
Types of Drop hammer are –
1) Steam – air drop hammer
2) Board drop hammer
3) Belt drop hammer
4) Rope drop hammer
5) Chain drop hammer
2. Press Forging
• In press forging, the pressure is applied on the heated billet continuously
• Parts are made by plastically deforming a metal into die-cavities by a
slow squeezing action
• The presses used for press forging are-
Mechanical press (Crank, eccentric, knuckle or screw)
Upright hydraulic press
Forging Defects
Buckling, in upsetting forging - Subject to high compressive stress.
Surface cracking - due to temperature differential between surface and
centre, or excessive working of the surface at too low temperature.
Micro cracking - due to residual stress.
Flakes : internal rapture caused by improper cooling.
Forging Defects
Pitting - Caused by scale, which if not removed thoroughly from the die cavities is
worked into the surface of the forging.
Remedies – Frequent cleaning of dies
Die shift – Caused by misalignment between the top and bottom forging dies
Incomplete filling of the die – Caused by – wrong amount of metal, insufficient
number of blows during forging, forging the stock at too low temperature when it
has lost its plasticity
Hot tears and thermal cracking: these are surface cracks occurring due to non
uniform cooling from the forging stage or during heat treatment.
You might also like
- Forging - The Process: Metal Forging Is A Metal Forming Process That Involves ApplyingDocument25 pagesForging - The Process: Metal Forging Is A Metal Forming Process That Involves ApplyingAdityasinh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Asst. Professor University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Nitin LohaniDocument29 pagesAsst. Professor University of Petroleum and Energy Studies: Nitin LohaniRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument114 pagesUnit IIIManoj Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Metal FormingDocument20 pagesMetal FormingPrashant ShreshthaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Document93 pagesManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)beila.amu.22No ratings yet
- Metal Forming 1 PDFDocument6 pagesMetal Forming 1 PDFAlpha WolfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.1 To 14.4,14.6Document20 pagesChapter 14.1 To 14.4,14.6Lhekha RaviendranNo ratings yet
- U 4 P 1 MetalformingprocessesDocument82 pagesU 4 P 1 MetalformingprocessesAbhinandan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- We Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesDocument6 pagesWe Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesConnor WalshNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationDocument77 pagesUnit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationAkash akNo ratings yet
- Design of Dies - Unit 4Document149 pagesDesign of Dies - Unit 4210 SureshNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes: by Premchand Kumar Deoghar (Jharkhand)Document49 pagesManufacturing Processes: by Premchand Kumar Deoghar (Jharkhand)PremKumarNo ratings yet
- U-2 Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument76 pagesU-2 Mechanical Working of Metalsapi-271354682No ratings yet
- UNit 2 MEC 305Document32 pagesUNit 2 MEC 305Fuzzy is EasyNo ratings yet
- 4.3 ExtrusionDocument19 pages4.3 ExtrusionSiddharth RajendranNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes - FullDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processes - FullArjun NbNo ratings yet
- FMP 221 Lecture 9 Cold WorkingDocument34 pagesFMP 221 Lecture 9 Cold WorkingSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Submitted To: Miss Sobia Anwar Submitted By: Uzair Khan (2018-CH-01)Document12 pagesAssignment: Submitted To: Miss Sobia Anwar Submitted By: Uzair Khan (2018-CH-01)Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformation AssignmentDocument9 pagesBulk Deformation AssignmentMuhammad FasihNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document23 pagesCH 4huien ababuNo ratings yet
- ForgingDocument10 pagesForgingVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Pemilba CastingDocument8 pagesPemilba CastingRefky FNo ratings yet
- Project Group 3Document12 pagesProject Group 3GemedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document113 pagesChapter 4girma workuNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessDocument19 pagesMetal Forming ProcessragulnarayanNo ratings yet
- Extrusion ProcessesDocument6 pagesExtrusion ProcessesSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process 1 2Document70 pagesManufacturing Process 1 2MD Al-Amin100% (1)
- Lecture 11Document22 pagesLecture 11Huraira AbidNo ratings yet
- Bulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingDocument6 pagesBulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingAbdulfattah TawfiqNo ratings yet
- Special Casting ProcessesDocument25 pagesSpecial Casting ProcessesV Phanindra BoguNo ratings yet
- Forging DefectDocument4 pagesForging DefectRashmi Bhatt NautiyalNo ratings yet
- Applications & Processing of Metal AlloysDocument17 pagesApplications & Processing of Metal AlloysSohaibNo ratings yet
- MFG II 3182 Chapter 1Document58 pagesMFG II 3182 Chapter 1Naol EmanaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Working of Metals MaterialDocument40 pagesMechanical Working of Metals MaterialRoyalmechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metal Forming ProcessesDocument103 pagesChapter 3 Metal Forming Processesdagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Manufacturing Technology - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument30 pagesUnit 5 - Manufacturing Technology - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inROHIT MEHRANo ratings yet
- Extrusion LatestDocument27 pagesExtrusion LatestChanti ChaithanyaNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processrk_kamatchi3483No ratings yet
- Forging and Its TypesDocument9 pagesForging and Its TypesHarinath GowdNo ratings yet
- Hot & Cold WorkingDocument18 pagesHot & Cold WorkingMadushan MadushaNo ratings yet
- Forging DefectsDocument10 pagesForging DefectsnvemanNo ratings yet
- Casting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingDocument44 pagesCasting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Document111 pagesManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)AlemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFDocument62 pagesLecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFjawad khalidNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsDocument13 pages4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsHussein SaeedNo ratings yet
- 6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocument34 pages6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesZack MalikNo ratings yet
- 6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocument34 pages6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesMaida NurhidayahNo ratings yet
- Forming ProcessesDocument8 pagesForming ProcessesKishor PatilNo ratings yet
- Cold Forming of Metals: University of Southern Mindanao Kidapawan City Campus Sudapin, Kidapawan CityDocument40 pagesCold Forming of Metals: University of Southern Mindanao Kidapawan City Campus Sudapin, Kidapawan CitySanjay Kang ChulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PDFDocument20 pagesLecture 3 PDFيوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Forging NotesDocument71 pagesForging Notesmaddy_scribd100% (1)
- Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocument71 pagesBulk Deformation ProcessesHavenesh HaveNo ratings yet
- ExtrusionDocument81 pagesExtrusionAstha NiharikaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Manufacturing Processes 1Document19 pagesClassification of Manufacturing Processes 1Palaash Chaudhary86% (7)
- Hot & Cold WorkingDocument23 pagesHot & Cold WorkingzackaiedaNo ratings yet
- Hot and Cold Working Processes - 02Document16 pagesHot and Cold Working Processes - 02Itachi UchihaNo ratings yet
- Extrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarDocument27 pagesExtrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarAdityasinh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Forging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsFrom EverandForging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - SAWDocument8 pagesClass 7 - SAWSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Casting Question and SolutionsDocument2 pagesCasting Question and SolutionsSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class - Friction WeldingDocument15 pagesClass - Friction WeldingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 16 - SolderingDocument16 pagesClass 16 - SolderingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 20 - Gas WeldingDocument17 pagesClass 20 - Gas WeldingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 21 Gas Cutting MethodsDocument12 pagesClass 21 Gas Cutting MethodsSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - PAWDocument9 pagesClass 10 - PAWSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class5 - Types of CastingDocument94 pagesClass5 - Types of CastingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- High Fidelity Lithium Battery Modelwith Thermal EffectDocument9 pagesHigh Fidelity Lithium Battery Modelwith Thermal EffectSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- 8-Deep Drawing & Drawing and Punching and BlankingDocument20 pages8-Deep Drawing & Drawing and Punching and BlankingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- 3 ExtrusionDocument13 pages3 ExtrusionSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- 5-Processing of PlasticsDocument27 pages5-Processing of PlasticsSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class2 - Sand CastingDocument14 pagesClass2 - Sand CastingSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Class3 - PatternDocument57 pagesClass3 - PatternSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- 1791 Nonlinear Model Predictive Control For Thermal Management in Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesDocument15 pages1791 Nonlinear Model Predictive Control For Thermal Management in Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Computationally Efficient Stochastic Model Predictive Controller For Battery Thermal Management of Electric VehicleDocument13 pagesComputationally Efficient Stochastic Model Predictive Controller For Battery Thermal Management of Electric VehicleSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain-Based Architecture For Smart Healthcare System: A Case Study of Saudi ArabiaDocument8 pagesA Blockchain-Based Architecture For Smart Healthcare System: A Case Study of Saudi ArabiaSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: A Secure Resource For Development of Ladakh Region, IndiaDocument16 pagesGeothermal Energy: A Secure Resource For Development of Ladakh Region, IndiaSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Use of Geothermal Electric System For Remote Powering: A Case Study of Puga Geothermal FieldDocument5 pagesUse of Geothermal Electric System For Remote Powering: A Case Study of Puga Geothermal FieldSriharsha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Maquina de Anestesia Pelon Prima - sp2 - Service - ManualDocument110 pagesMaquina de Anestesia Pelon Prima - sp2 - Service - Manualperla_canto_1No ratings yet
- Supercritical Steam GeneratorDocument2 pagesSupercritical Steam Generatorrr1819No ratings yet
- Suction Side of Centrifugal PumpsDocument11 pagesSuction Side of Centrifugal PumpsTanishk KumarNo ratings yet
- SI Units and Dimensions: by Prof M BasannaDocument4 pagesSI Units and Dimensions: by Prof M Basannaembi76No ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument38 pagesHydrogenClaudio Ibarra Casanova0% (2)
- GravityLight Description of The Concept and Its RealizationDocument4 pagesGravityLight Description of The Concept and Its RealizationAhmad Fajar HumaidiNo ratings yet
- Lightning Protection CalculationDocument14 pagesLightning Protection Calculationgepewin2009100% (1)
- Exercise 4 Plastic Deformation by Oscillating Force and Observation of Strain Hardening On A CantileverDocument7 pagesExercise 4 Plastic Deformation by Oscillating Force and Observation of Strain Hardening On A CantileverSandip GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Spring Summer 2023 Technical Exams ListDocument10 pagesSpring Summer 2023 Technical Exams ListAshraf BadrNo ratings yet
- Bee PPT-1Document309 pagesBee PPT-1wondimagegn debebeNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog: Lighting The Led Revolution™Document76 pagesProduct Catalog: Lighting The Led Revolution™Fernando MolinaNo ratings yet
- Classical Physics Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 38Document27 pagesClassical Physics Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 38Anonymous 8f2veZfNo ratings yet
- Tariff Order 2019-20Document398 pagesTariff Order 2019-20Raghu VallabhuNo ratings yet
- Electrical InstallationsDocument51 pagesElectrical InstallationsCinthia Lidia Hidrogo Paulino100% (1)
- World Energy Issues Monitor 2022 - Global ReportDocument30 pagesWorld Energy Issues Monitor 2022 - Global ReportAhmedNo ratings yet
- Golbal Food PolocyDocument142 pagesGolbal Food Polocybmsvk1No ratings yet
- Labphys 6Document4 pagesLabphys 6Edyson CitraNo ratings yet
- B. 170 Volts: Supplementary ProblemsDocument7 pagesB. 170 Volts: Supplementary ProblemsDwight Jesser TolentinoNo ratings yet
- AOP605 Complementary Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorDocument7 pagesAOP605 Complementary Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorfrancicciusNo ratings yet
- Vapor Sensor: Installation GuideDocument12 pagesVapor Sensor: Installation GuideShalvaTavdgiridzeNo ratings yet
- Checklist Maintenance RobotDocument4 pagesChecklist Maintenance RobotTrần ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Enst Renewable Energy Syllabus 2015 1Document6 pagesEnst Renewable Energy Syllabus 2015 1api-303214818No ratings yet
- MM Meccalte Mec1275Document4 pagesMM Meccalte Mec1275HabibNo ratings yet
- Matlab CodeDocument3 pagesMatlab CodeAbdallAh ALi SmaDi50% (2)
- Diesel Fuel MSDS 2019Document12 pagesDiesel Fuel MSDS 2019bobNo ratings yet
- Diseño IntercambiadorDocument9 pagesDiseño IntercambiadorMateo VanegasNo ratings yet
- Et IsoDocument4 pagesEt IsoMizan Sarkar100% (1)
- TPG4175 Petrophysics: Course OverviewDocument8 pagesTPG4175 Petrophysics: Course OverviewAngela rismaNo ratings yet
- Relay Catalogue Feb 2015Document20 pagesRelay Catalogue Feb 2015Mahesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- 5000m3 LPG Tank FarmDocument2 pages5000m3 LPG Tank FarmLpgTankFarmNo ratings yet