Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sheet 5 E1 ازهر
sheet 5 E1 ازهر
Uploaded by
magdy kamelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sheet 5 E1 ازهر
sheet 5 E1 ازهر
Uploaded by
magdy kamelCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet (5)
Tegara English
First year
ازهر
Financial Chapter
Accounting
5
The king of Accounting
Edited by Dr/ Magdy Kamel
Tel/ 01273949660
1 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Complete chapter (5)
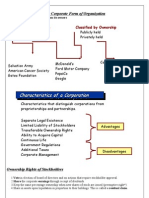
The corporation form of organization:
The legal interpretation of a corporation is an entity separate and distinct
from its owners
A corporation may be organized for the purpose of making profit or it may be
nonprofit seeking
Classification by ownership distinguishes between publicly held and privately
held corporations
A publicly held corporation may have A privately held corporations often
thouthands of stockholders, and its stock is referred to as a closely retated held
regularly traded on a national securities corporation, usually has only a few
exchanges. stockholders and doesn’t offer its stock for
sale to the general public.
Characteristics of a corporation :
1- separate legal existence كيان قانونى منفصل
As an entity separate and distinct from its owners, the corporation acts under
its own name rather than in the name of its stockholders .
2) limited liability of stockholders: التزام محدود لحاملى االسهم
Since a corporation is a separate legal entity , creditors have resources only to
compare assets to satisfy their claims.
3) transferable ownership rights حقوق ملكية متنقلة من شخص الخر
Ownership of a corporation is held in shares of capital stock, which are
transferable units.
4) ability to acquire capital سهوله تجميع راس المال
It is relatively easy for a corporation to obtain capital through the issuance of
stock
Stockholder has limited liability and shares of stock are readily transferable
2 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
5) continuous life عمر الشركة مستمر
The life of a corporation is stated in its charter.
The life may be perpetual or it may be limited to a specific number of years
6) corporation management اداره الشركة
Stockholders legally own the corporation. But they manage the
corporation indirectly through a board of directors they elect.
يمتلك اصحاب االسهم قانونا الشركه ولكنهم يديرون الشركه بصوره غير مباشره من خالل مجلس اداره ينتحبونه
The board, in turn, formulates the operating policities for the company.
board also selects officiers to execute policy and perform daily management
functions
االداره اليوميه,يقوم مجلس االداره باختيار الموظفين وتنفيز الوظائف
7) government regulations القيود والتنظيمات الحكومية
A corporation is subject to numerous state and federal regulations
Governmental regulations are designed to protect the owners of the corporation
8) additional taxes الضرائب المضاعفة
Corporation must pay federal and state income taxes as a separate legal entity
These taxes are substantial : they can amount to more than 40% of taxable income
Forming a Corporation
A corporation is formed by grant of a state charter
which describes the name and purpose of the corporation ,
the types and number of shares of stock that are authorized to be issues,
the name of the individuals that formed the company
it is to a company’s advantage to incorporate in a state whose laws are
favorable to the corporation form of business organization.
Corporations engaged in interstate commerce must also obtain a license
from each state in which they do business
Costs incurred in the formation of a corporation are called organization costs.
These costs include legal and state fees, and promotional expenditures
3 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Ownership rights of stockholders حقوق الملكيه لحاملى االسهم
Stockholders have the right to:
1) Vote in election of board of directors at annual meeting and vote on actions
that require stockholder approval.
2) Share the corporate earnings through receipt of dividends.
3) Keep the same percentage ownership when new shares of stock are issued
(preemptive right) حق الشفعه
4) Share in assets upon liquidation in proportion to their holdings. This is called
a residual claim:
Stock issue Considerations
Authorized Stock
The charter indicates the amount of stock that a corporation is authorized to sell
تم تحديد كميه االسهم التى الشركه صرحت ببيعها: بمعنى وفقا لقرار تاسيس الشركه:اسهم جاهزه للبيع
Issuance Of Stock اسهم تم بيعها
A corporation can issue common stock directly to investors. /Or it can issue
the stock indirectly through an investment banking firm that specializes in
bringing securities to market.
شركه مصرفيه استثماريه,يمكن للشركه ان تبيع االسهم مباشرا للمستثمرين او بطريقه غير مباشره عن طريق
Market value per stocks
The stock of publicly held companies is traded on organized exchanges.
The dollars price per share are established by the interaction between buyers
and sellers.
Par and no par value stocks
Par value stock is capital stock to which the charter has assigned a value
per share most states required the corporation to sell its shares at par
No-par value stock is capital stock to which the charter has not assigned a
value .In many states the board of directors assigns a stated value to no-
par shares
4 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Corporate capital
Owners’ equity is identified by various names:
stockholders’ equity, shareholders’ equity, or corporate capital.
The stockholders’ equity section of a corporation’s balance sheet consists of two parts: (1)
paid-in (contributed) capital and (2) retained earnings (earned capital).
1) Paid-In Capital
Paid-in capital is the total amount of cash and other assets paid in to the corporation by
stockholders in exchange for capital stock. As noted earlier, when a corporation has only
one class of stock, it is common stock.
2) Retained Earnings
Retained earnings is net income that a corporation retains for future use. It is often referred
to as earned capital
First: accounting for common stock issues
1) The primary objectives in accounting for the issuance of common stock are :
a) to identify the specific sources of paid in capital
b) to maintain the distinction between paid in capital and retained earnings
2) when the issuance of common stock for cash is recorded, the par value of the shares is
credited to common stock, The portion of the proceeds that is above or below par
value is recorded in a separate paid in capital account.
3) when no par common stock has a stated value, the entires are similar to those for par
value common stock.
4) when no par common stock doesn’t have a stated value, the entire proceeds from the
issue become legal capital and credited to common stock.
Example (1)
Boomer corporation issues, 2,000 shares of common stock at $ 10 per shares.
Stock has $ 4 par value Stock has no par value
Cash 20,000 Cash 20,000
Common stock (4 × 2,000) 8,000 Common stock 20,000
Paid in capital in excess of (2,000 × 10)
par value (6 × 2,000) 12,000
Stock has $ 4 stated value Stock has no stated value
Cash 20,000 Cash 20,000
Common stock (4 × 2,000) 8,000 Common stock 20,000
Paid in capital in excess of (2,000 × 10)
stated value (6 × 2,000) 12,000
5 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Second : treasury stock
1) treasury stock is a corporation’s own stock that has been issued fully paid for , &
reacquired by the corporation but not retired.
هى اسهم تمتلكها الشركه ومصدره فعال وثمنها ادفع بالكامل والشركة هتعيد امتالكها مره اخرى
2) treasury stock is generally accounted for by the cost method , under this method ,
treasury stock is debited for the price paid to require the shares & the same amount is
credited to treasury stock when the share are disposal of
3) when the selling price of treasury stock is greater than its cost, the difference is credited
to paid in capital from treasury stock, when treasury stock is sold below its cost, paid in
capital from treasury stock is debited for its remaining balances and retained earnings is
debited for any additional excess of cost over selling price
Example :
On January 1, 2010, the stockholders' equity section of Nunez Corporation shows:
Common stock ($5 par value) $1,500,000
paid-in capital in excess of par value $1,000,000
and retained earnings $1,200,000
During the year, the following treasury stock transactions occurred.
a) Mar. 1 Purchased 50,000 shares for cash at $15 per share.
July. 1 Sold 10,000 treasury shares for cash at $17 per share.
Sept. 1 Sold 8,000 treasury shares for cash at $14 per share.
b) Restate the entry for September 1, assuming the treasury shares were sold at $12 per
share.
Solution
a) Journal entries
Mar.1 Treasury stock (50,000 x $15) 750,000
Cash 750,000
July 1 Cash 170,000
Treasury stock (10,000 × $15) 150,000
Paid-in cap. from treasury stock 20,000
Sept. 1 Cash (8,000 x $14) 112,000
Paid-in cap. from treasury stock 8,000
Treasury stock (8,000 × $15) 120,000
b)
Sept. 1 Cash (8,000 x $12) 96,000
Paid-in cap. from treasury stock 20,000
Retained earnings 4,000 120,000
Treasury stock (8,000 × $15)
6 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
Third : accounting for preferred stock
1) a corporation may issue an additional class of stock (called preferred stock ) to appeal to
more potential investors.
2) preferred stock has contractual provision that give it priority over common stock in
certain areas.
Typically, preferred stock has a priority as to
a) distribution of earnings (dividends)
b) assets in the event of liquidation
3) preferred stock dividends preferences may be classified as:
Cumulative – both current year dividends and any unpaid prior year dividends must
be paid to preferred stockholders before common stockholders received any
dividends.
Preferred dividends not declared in a given period are called dividends in arrears.
Dividends in arrears are not considered a liability but they should be disclosed in the
notes to financial statements.
True or false
1. The cost method derives its name from the fact that the treasury stock
account is maintained at the cost of shares purchased
True false
2. When treasury stock is sold for an amount greater than its cost, the
difference should be credited to Gain on Sale of Treasury Stock and reported
as other income on the income statement.
True false
3. Stockholders' liability is generally unlimited; therefore, creditors have
recourse to stockholders' personal assets as well as corporate assets.
True false
4. Retained earnings is net income retained in a corporation and is often
referred to as earned capital
True false
7 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
5. A corporation is bound to a contract entered into by one of its stockholders.
True false
6. Issued shares of stock less outstanding shares equals treasury stock
True false
7. The cumulative feature of stock applies to preferred stock .
True false
8. Dividends in arrears are not considered a liability because no obligation exists
until the dividend is declared by the board of directors.
True false
9. Preferred stockholders have a priority as to dividends but not to assets in the
event of liquidation
True false
10. Treasury stock should be listed as an asset in the balance sheet.
True false
Muti choose question
1. Par value
a. represent what a share of stock is worth.
b. represent the original selling price for a share of stock.
c. is the legal capital established for a share of stock
d. is established for a share of stock after it is issued
2. If a company has 900,000 shares of common stock authorized, and has
750,000 shares issued, and holds 30,000 shares of common stock as treasury
stock, the general ledger account for common stock, $1 par value would have a
balance of.
a. $870,000.
b. $750,000.
c. $720,000.
d. $150,000.
8 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
3. All of the following balances are normally found in a corporation's
stockholders' equity section except
a. common stock
b. paid in capital in excess of par.
c. retained earnings
d. dividends in arrears
4. Preferred stock would least likely have which characteristic?
a. The right of the holder to vote at stockholders' meetings
b. the right of the corporation to redeem or retire the stock
c. preference as to assets upon liquidation of the corporation
d. preference as to dividends
5. A company purchases 1,500 shares of its $25 par value stock at $35 per share.
It then reissues 500 shares at $40 per share. The entry upon reissue of the stock
would include a credit to
a. cash for $2,500.
b. treasury stock for $2,500.
c. retained earnings for $2,500.
d. paid in capital from treasury stock for $2,500.
9 | Page Dr. Magdy Kamel
You might also like
- Summary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownFrom EverandSummary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownNo ratings yet
- CorpoLaw 2016Document12 pagesCorpoLaw 2016kathreenmonjeNo ratings yet
- ch (14) جامعه الازهرDocument26 pagesch (14) جامعه الازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Accounting For The Corporation Chapter 10Document51 pagesAccounting For The Corporation Chapter 10Rupesh PolNo ratings yet
- Equity FinancingDocument53 pagesEquity FinancingGaluh Boga KuswaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Review 11th EdDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Review 11th EdTin RanocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13Maya HamdyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document13 pagesChapter 13Mondy MondyNo ratings yet
- ch11 2Document58 pagesch11 2X YlmarixeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Stockholers Equity FinalDocument77 pagesChapter 7 Stockholers Equity FinalSampanna ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Recording Capital Stock & Reverses TransactionDocument49 pagesCAPE Recording Capital Stock & Reverses TransactionOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders' EquityDocument15 pagesChapter 11 - Reporting and Analyzing Stockholders' EquityElaiza RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Capital+Stock+TransactionsDocument17 pagesAccounting Capital+Stock+TransactionsOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting 2 Organization and Capital Stock TransactionsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Accounting 2 Organization and Capital Stock Transactionsalice horanNo ratings yet
- Stock KKDocument7 pagesStock KKamir rabieNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Rajesh PathakDocument25 pagesFinancial Accounting Rajesh PathakJHANVI LAKRANo ratings yet
- Corporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and DividendsDocument37 pagesCorporations: Organization, Stock Transactions, and Dividendsjoseph christopher vicenteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2杰克 l孙No ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument11 pagesCorporate FinanceTim GNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five-CorporationDocument6 pagesChapter Five-Corporationbereket nigussieNo ratings yet
- Corporate Accounting PDFDocument193 pagesCorporate Accounting PDFK GanesanNo ratings yet
- Companies (Theory)Document10 pagesCompanies (Theory)Dayaan ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 11 SummaryAreeba QureshiNo ratings yet
- Common and Preferred StockDocument12 pagesCommon and Preferred StockAmna ImranNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Corporate Form of Business Organizations Chapter OutlinesDocument11 pagesAccounting For Corporate Form of Business Organizations Chapter Outlinesdejen mengstieNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Equity: Key Terms and Concepts To KnowDocument27 pagesAccounting For Equity: Key Terms and Concepts To KnowJohn Paul N FornesteNo ratings yet
- AKW104 Chapter 13Document8 pagesAKW104 Chapter 13Chong Wan YunNo ratings yet
- SHE JeromeDocument3 pagesSHE Jeromemark_somNo ratings yet
- FA II CH 6 SHEDocument23 pagesFA II CH 6 SHEAbdlwahid AbdlberNo ratings yet
- Corporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transactions: Weygandt - Kieso - KimmelDocument54 pagesCorporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transactions: Weygandt - Kieso - Kimmelkey aidanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Core Concepts of Accounting Raiborn 2nd EditionDocument18 pagesSolution Manual For Core Concepts of Accounting Raiborn 2nd EditionJacquelineFrancisfpgs100% (38)
- Chapter 9 - Corporations - Organization and Share Capital Transactions Exercises T3AY2021Document5 pagesChapter 9 - Corporations - Organization and Share Capital Transactions Exercises T3AY2021Carl Vincent BarituaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 1Document26 pagesChapter 17 1Diệu Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Taller Cuatro Acco 112Document35 pagesTaller Cuatro Acco 112api-274120622No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Shareholders' Equity: Paid-In Capital Fundamental Share RightsDocument9 pagesChapter 18 Shareholders' Equity: Paid-In Capital Fundamental Share RightsSteeeeeeeephNo ratings yet
- Live TanyaaaayaDocument7 pagesLive Tanyaaaayaamir rabieNo ratings yet
- Meeting 9 - Company Financial StatementsDocument42 pagesMeeting 9 - Company Financial StatementsHelen FebrianaNo ratings yet
- Company Accounts Issue of Shares Par Premium DiscountDocument20 pagesCompany Accounts Issue of Shares Par Premium DiscountDilwar Hussain100% (1)
- Corporations: Organization, Capital Stock Transactions, and DividendsDocument64 pagesCorporations: Organization, Capital Stock Transactions, and DividendsDesta MaldinaNo ratings yet
- Finance Management 4Document26 pagesFinance Management 4charithNo ratings yet
- Stock TransactionDocument9 pagesStock TransactionShawon RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dividends - and - Share - Repurchases - Basics - SlidesDocument19 pagesDividends - and - Share - Repurchases - Basics - Slideszaheer9287No ratings yet
- Libby Chap 11 Study NotesDocument16 pagesLibby Chap 11 Study Noteshatanolove100% (4)
- Survey of Accounting 4Th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesSurvey of Accounting 4Th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFzanewilliamhzkbr100% (6)
- Survey of Accounting 4th Edition Edmonds Solutions ManualDocument62 pagesSurvey of Accounting 4th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manualdariusarnoldvin100% (32)
- Grade 11 Math Mod 8Document8 pagesGrade 11 Math Mod 8John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document4 pagesCH 11pablozhang1226No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5Jimmy LojaNo ratings yet
- CFAB Accounting Chapter 11. Company Financial StatementsDocument43 pagesCFAB Accounting Chapter 11. Company Financial StatementsHuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Corporation Is: Separate Legal Entity Created by Law: Corporations and Stockholders EquityDocument25 pagesCorporation Is: Separate Legal Entity Created by Law: Corporations and Stockholders EquityCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Solution of Fundamental of Financial Accouting by EDMONDS (4th Edition)Document141 pagesChapter 11 Solution of Fundamental of Financial Accouting by EDMONDS (4th Edition)Awais Azeemi67% (3)
- Edited CorporationDocument13 pagesEdited CorporationMesele AdemeNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2 - Chapter 13 - Notes - MiuDocument5 pagesAccounting 2 - Chapter 13 - Notes - MiuAhmad Osama MashalyNo ratings yet
- Stock Holders EquityDocument23 pagesStock Holders EquitySofia MuneerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CorporationDocument12 pagesChapter 5 CorporationMamaru SewalemNo ratings yet
- Ocampo, Maricris - AE100 - COA - BLK - 1H 10.5.1 Practice Questions: Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesOcampo, Maricris - AE100 - COA - BLK - 1H 10.5.1 Practice Questions: Answer The Following Questionsmaricris ocampoNo ratings yet
- The Corporate Form of OrganizationDocument7 pagesThe Corporate Form of OrganizationRabie HarounNo ratings yet
- Corporation Is: Separate Legal Entity Created by Law: Corporations and Stockholders EquityDocument25 pagesCorporation Is: Separate Legal Entity Created by Law: Corporations and Stockholders EquityDhafra Sanchez'sNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide to Stock Market: Investment, Types of Stocks, Growing Money & Securing Financial FutureFrom EverandA Beginners Guide to Stock Market: Investment, Types of Stocks, Growing Money & Securing Financial FutureNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 E1 ازهرDocument13 pagesSheet 4 E1 ازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- تلخيص لغة تانيه 20233Document4 pagesتلخيص لغة تانيه 20233magdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Sales RevenueDocument1 pageSales Revenuemagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- تلخيص سنه اولىDocument1 pageتلخيص سنه اولىmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- sheet (6) ازهر E1Document10 pagessheet (6) ازهر E1magdy kamelNo ratings yet
- ch (14) جامعه الازهرDocument26 pagesch (14) جامعه الازهرmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Alison Krauss CompanyDocument3 pagesAlison Krauss Companymagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Sheet (5) Part (2) Chapter (3) Costing and Control of Materials and LaborDocument11 pagesCost Accounting Sheet (5) Part (2) Chapter (3) Costing and Control of Materials and Labormagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Sheet (8) Intermediate Accounting: InventoriesDocument12 pagesSheet (8) Intermediate Accounting: Inventoriesmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Cayetano V MonsodDocument15 pagesCayetano V MonsodKareen BaucanNo ratings yet
- Rules in RCC and OCC RequiredDocument8 pagesRules in RCC and OCC RequiredXNo ratings yet
- 20 PIONEER INSURANCE SURETY CORPORATION VDocument2 pages20 PIONEER INSURANCE SURETY CORPORATION VKingNo ratings yet
- Corporation Hand Out - RevisedDocument21 pagesCorporation Hand Out - RevisedAnnie RapanutNo ratings yet
- TN Smart Start Up GuideDocument82 pagesTN Smart Start Up GuideGold SunriseNo ratings yet
- Chua vs. Court of AppealsDocument18 pagesChua vs. Court of AppealsCourt JorsNo ratings yet
- Commrev Online LecturesDocument88 pagesCommrev Online LecturesTinn ApNo ratings yet
- Bsoa Buss Law 2024 SyllabusDocument4 pagesBsoa Buss Law 2024 SyllabuselmocariangaNo ratings yet
- Alliance For Alternative Action: The Adonis Cases 2011Document171 pagesAlliance For Alternative Action: The Adonis Cases 2011Vince Llamazares LupangoNo ratings yet
- Abm 501 NotesDocument3 pagesAbm 501 NotesLeodian Diadem MercurioNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources and Environmental Law 13: GR No. 98332Document6 pagesNatural Resources and Environmental Law 13: GR No. 98332King RodilNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The RCCDocument45 pagesSalient Features of The RCCSunny DaeNo ratings yet
- Lao Vs LaoDocument1 pageLao Vs LaoCharisma Michelle L. De JesusNo ratings yet
- GN Poli - PubcorpDocument47 pagesGN Poli - PubcorpKia BiNo ratings yet
- (Succession) 73 - Lim Vs CA - PenafielDocument2 pages(Succession) 73 - Lim Vs CA - PenafielEon PenafielNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship in Tourism and Hospitality Module 7Document21 pagesEntrepreneurship in Tourism and Hospitality Module 7Elizar Insuma AsiasticoNo ratings yet
- Delaney v. Fidelity Lease LimitedDocument1 pageDelaney v. Fidelity Lease LimitedMond Ramos100% (1)
- 2022 Entrepreneurship & SBM 731 - CA Test 2 Review Questions - MergedDocument182 pages2022 Entrepreneurship & SBM 731 - CA Test 2 Review Questions - MergedMaria LettaNo ratings yet
- Creditor Bond - $12,348,000 Living Clerk Tribunal Ministries 236003062 - Bond-Created-MARCH 12-2024Document15 pagesCreditor Bond - $12,348,000 Living Clerk Tribunal Ministries 236003062 - Bond-Created-MARCH 12-2024akil kemnebi easley elNo ratings yet
- PNB v. Ritratto - G.R. No. 142616 - 362 Scra 216Document3 pagesPNB v. Ritratto - G.R. No. 142616 - 362 Scra 216lord wally100% (1)
- Final Project Bus 206 Lydia HarrisDocument21 pagesFinal Project Bus 206 Lydia Harrisapi-352111965No ratings yet
- Article Xii - National Economy and PatrimonyDocument9 pagesArticle Xii - National Economy and PatrimonyroseNo ratings yet
- SEC Opinion No. 40-04 Establishment Security AgencyDocument2 pagesSEC Opinion No. 40-04 Establishment Security Agencyskylark74No ratings yet
- Bustos vs. Millians Shoe, Inc.Document12 pagesBustos vs. Millians Shoe, Inc.Krystal Grace D. PaduraNo ratings yet
- Delaware Exempt Articles of IncorporationDocument4 pagesDelaware Exempt Articles of IncorporationFreeman LawyerNo ratings yet
- 8-Iron and Steel Authority Vs CA 249 SCRA 538Document9 pages8-Iron and Steel Authority Vs CA 249 SCRA 538enan_intonNo ratings yet
- Sport Governance and Policy Development (1 - Introduction To Sport Organizations and Governance)Document18 pagesSport Governance and Policy Development (1 - Introduction To Sport Organizations and Governance)daniel.fabellaNo ratings yet
- Book of RecordsDocument396 pagesBook of RecordsareyoubeefinNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Bank v. Court of First Instance of RizalDocument2 pagesPhilippine National Bank v. Court of First Instance of RizalKayee KatNo ratings yet