Professional Documents
Culture Documents
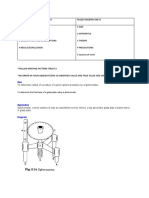
Determining radius of curvature using a spherometer
Uploaded by
Sahil LakhyaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Determining radius of curvature using a spherometer
Uploaded by
Sahil LakhyaniCopyright:
Available Formats
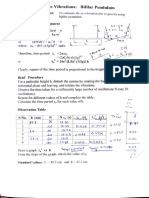
Blue Heaven Vidyalaya S 0 2 22
Experiment No.3 Dated:
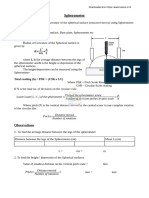
Aim: To determine radius ofcurvature of a given spherical surface by a spherometer.
Apparatus: Spherometer, a plane glass plate,
Diagram:
K
5
P
SpAoomte
Formula used:
The radius of curvature R of a spherical surface is given by
R a
6h
/here a the mean distance between the tips of legs ofthe spherometer., h= difference in the readings of the
spherometer when placed first on the plane surface and then on the convex surface.
Observations
() Leastcount (L.C.)= Pitch 0.1c 0.001 cm
number of divisions on circular scale (n) 100
(i) Mean (a) = 4 : + 4. S + 4 - = 4.s" ma
(ii) For h -
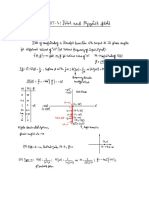
Reading on S.No. Mean Scale Circular scale Circularscale Total reading | Mean
reading conciding no. reading Z=X+y(cm) (cm)
X (cm) (n) Y=n x LC.
(cm)
Plane glass
plate (h,)
2. f.ol
ol
Convex
surface
1-2 6 O.09 296
l296
(ha) 2. 2 d 09 296
Calculations
h=ha-h = 294 -/.o1( 0 28S° Cm
Mean 'a' =atâzta3
3
4 5
* * * * * * * * *** ****s* s** **
'R=
6h
s) 0: 2025+0.142 l1y2 +0-142
6MO29S 2 710
1.84 Cur
Result: o ms e Curvatme a a 9Ave tphei cal Sa2JaA
by a p k u oniliv has beu tound I1-98 4 tm.
Precautions:(j)thescrew must be turned in one direction only to avolid error due to back lash.
(i) the proper just touch position should be obtained both on convex surface and the plane surface.
(ii) the legs of the spherometer should not be shaky and the screw should rotate freely.
You might also like
- Determine Radius & Thickness Using SpherometerDocument3 pagesDetermine Radius & Thickness Using SpherometerYash TandonNo ratings yet
- Determine Radius of Curvature Using SpherometerDocument3 pagesDetermine Radius of Curvature Using SpherometerKartikNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 DynamicsDocument5 pagesLab 1 Dynamicslp23mem4r06No ratings yet
- Basic Twist Drill Geometry: Helix and Clearance AnglesDocument30 pagesBasic Twist Drill Geometry: Helix and Clearance AnglesManish DasNo ratings yet
- IB Analysis and Approaches Formula SheetDocument1 pageIB Analysis and Approaches Formula SheetpaulaNo ratings yet
- The Sun Shadow Positioning: LimengchenDocument4 pagesThe Sun Shadow Positioning: LimengchenmimarilkerNo ratings yet
- To Determine Radius of Curvature of A Given Spherical Surface by A SpherometerDocument4 pagesTo Determine Radius of Curvature of A Given Spherical Surface by A SpherometerSandipan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Chew 1505 CH10Document73 pagesChew 1505 CH10lzyabc597No ratings yet
- Unit 5 SDDocument64 pagesUnit 5 SDGanapati Girish KamatNo ratings yet
- Finding The Refractive Index of Water and OilDocument15 pagesFinding The Refractive Index of Water and Oilpaceoflearning73825No ratings yet
- Alekh Physics3Document20 pagesAlekh Physics3guptaakash25999No ratings yet
- P2 2Document11 pagesP2 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Trig Functions & Reference AnglesDocument12 pagesTrig Functions & Reference AnglesLisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Turnpage1 PDFDocument18 pagesTurnpage1 PDFIrene BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Euler S DiskDocument4 pagesEuler S Disksanhthanh24091994No ratings yet
- Dome SynchronisationDocument20 pagesDome Synchronisationmaurice falzonNo ratings yet
- To find refractive indices of water and turpentine oilDocument15 pagesTo find refractive indices of water and turpentine oilSurianandhanNo ratings yet
- Ah Yd 4 VC VDocument22 pagesAh Yd 4 VC V918goodyNo ratings yet
- L-1/T-2/CE Date: 30/01/2012Document15 pagesL-1/T-2/CE Date: 30/01/2012SK Adnan IslamNo ratings yet
- Area Computation: Baharin AhmadDocument24 pagesArea Computation: Baharin AhmadFadzir AmirNo ratings yet
- Physics EXPERIMENTs Term2Document6 pagesPhysics EXPERIMENTs Term2cutuNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument3 pagesWavenaazarianaNo ratings yet
- NP2Document6 pagesNP2subhajana646No ratings yet
- Logarithm, Geometry, Progression and MensurationDocument2 pagesLogarithm, Geometry, Progression and MensurationAayan SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Simulation of The Detection of Underwater Objects From Air: A. A. Kovalev, A. A. Liberman, and S. A. MoskalyukDocument8 pagesSimulation of The Detection of Underwater Objects From Air: A. A. Kovalev, A. A. Liberman, and S. A. MoskalyukCarl FranksNo ratings yet
- CBSE_G+10_Areas+Related+To+Circles_EIQ importantDocument17 pagesCBSE_G+10_Areas+Related+To+Circles_EIQ importantyeahmevaibhaviNo ratings yet
- Estimation ManualDocument33 pagesEstimation Manualmerreik100% (1)
- Moment of Inertia PDFDocument16 pagesMoment of Inertia PDFRio ChanNo ratings yet
- SP Hero MeterDocument6 pagesSP Hero MeterReshan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MQP Ans 02Document9 pagesMQP Ans 02agrawalvidhesh0No ratings yet
- Grade-10_Mathematics_Chapter11_Areas-Related-To-Circles-1Document18 pagesGrade-10_Mathematics_Chapter11_Areas-Related-To-Circles-1raviskskskNo ratings yet
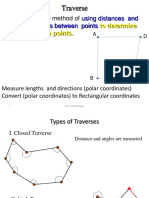
- Traverse: Using Distances and Directions of Lines Between PointsDocument26 pagesTraverse: Using Distances and Directions of Lines Between PointsIbrahim AdelNo ratings yet
- SRN Class Xii PhyDocument16 pagesSRN Class Xii Phybabumohana1979No ratings yet
- Solid Angle ProblemsDocument4 pagesSolid Angle Problemssandeep_sihag07No ratings yet
- Earth Quantities: Volumes and AreasDocument20 pagesEarth Quantities: Volumes and AreasChita ChibesakundaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectSourima DeyNo ratings yet
- Earth's Magnetic Field: College of Arts and Sciences Mathematics, Statistics and Physics Department Physics ProgramDocument4 pagesEarth's Magnetic Field: College of Arts and Sciences Mathematics, Statistics and Physics Department Physics ProgramAbdulNo ratings yet
- Computation of Added Mass and Damping Coefficients Due To A Heaving CylinderDocument14 pagesComputation of Added Mass and Damping Coefficients Due To A Heaving CylinderlapuNo ratings yet
- Hsslive_xi_spherometerDocument2 pagesHsslive_xi_spherometeraljalil089No ratings yet
- Investigation Natural Convection in Convergent Vertical ChannelsDocument9 pagesInvestigation Natural Convection in Convergent Vertical ChannelsSouadHadjadjNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsjhardik607No ratings yet
- It Should Be Less Than R /3 or 10mDocument5 pagesIt Should Be Less Than R /3 or 10mMawan BentzNo ratings yet
- Physics Project MDocument20 pagesPhysics Project Mvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- JW Chapter5solutionsDocument25 pagesJW Chapter5solutionsUp ToyouNo ratings yet
- Involute Gear InvolumetryDocument5 pagesInvolute Gear InvolumetrySafdar Ali NiaziNo ratings yet
- PlacasDocument23 pagesPlacasaugustopippiNo ratings yet
- Spectrometer Experiment ResultsDocument3 pagesSpectrometer Experiment ResultsgeetishaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Shubhra Nil DeyNo ratings yet
- Lec11 14Document24 pagesLec11 14Subrata Kumar DattaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry BasicsDocument11 pagesTrigonometry BasicsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Surveying: Basics of TraversingDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Surveying: Basics of TraversingReoeuele Duran CalzitaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- MATLAB Function for Disk Cam ProfileDocument3 pagesMATLAB Function for Disk Cam ProfilePatrick OguamaNo ratings yet
- ArchimedeDocument5 pagesArchimedestelios KontosNo ratings yet
- 35IJMPERDAPR201935Document14 pages35IJMPERDAPR201935TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocument17 pagesPhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex Lenshuertasdaniel60No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedJohn VincentNo ratings yet
- Lectures on the Arithmetic Riemann-Roch Theorem. (AM-127), Volume 127From EverandLectures on the Arithmetic Riemann-Roch Theorem. (AM-127), Volume 127No ratings yet
- Non-Linear Differential Equations: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsFrom EverandNon-Linear Differential Equations: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo ratings yet
- TRUMPF Genuine Parts Catalog enDocument116 pagesTRUMPF Genuine Parts Catalog encrazy hackerNo ratings yet
- WAEC PHYSICS SyllabusDocument59 pagesWAEC PHYSICS SyllabusSani MubarakNo ratings yet
- Bennett and Rabbetts Clinical Visual OpticsDocument472 pagesBennett and Rabbetts Clinical Visual OpticsShifan Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Telescopes in HistoryDocument3 pagesTelescopes in HistoryGovind GyawaliNo ratings yet
- Preboard MAPEHDocument20 pagesPreboard MAPEHChristaniel Langer100% (2)
- Physics Chapter 10 MCQSDocument2 pagesPhysics Chapter 10 MCQSYank Azhar100% (2)
- Full Download Test Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition PDF Full Chaptergenevieveprattgllhe100% (20)
- The Uses of Lenses in Optical DevicesDocument6 pagesThe Uses of Lenses in Optical DevicesAin NadiaNo ratings yet
- Orbis Guide To Ophthalmic EquipmentDocument16 pagesOrbis Guide To Ophthalmic EquipmentmohammedNo ratings yet
- Elective Photography01Document11 pagesElective Photography01Ar Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light: Notes and StuffsDocument42 pagesPhysics - Light: Notes and StuffsSijabuliso SibandaNo ratings yet
- 5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Document11 pages5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Rafael Marco ManubayNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument26 pagesMICROSCOPE09ANKIT MISHRANo ratings yet
- English 1 - Meeting 14 - ReviewDocument19 pagesEnglish 1 - Meeting 14 - ReviewRio HansNo ratings yet
- Liemke's Merlin 13 Thermal Imaging Clip-OnDocument7 pagesLiemke's Merlin 13 Thermal Imaging Clip-OnTwobirds Flying PublicationsNo ratings yet
- QS-Series Snap-In Panel Mount LED IndicatorsDocument4 pagesQS-Series Snap-In Panel Mount LED IndicatorsDanilo SantosNo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Determination of Unknown ResistanceDocument14 pagesMeter Bridge Determination of Unknown Resistancesujith kumarNo ratings yet
- Q On LensesDocument3 pagesQ On Lenseszendaya alisiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment 07 (Convex Mirror) - 1Document2 pagesPhysics Experiment 07 (Convex Mirror) - 1yubraj sethNo ratings yet
- Oculus: Pentacam Pentacam HRDocument20 pagesOculus: Pentacam Pentacam HRSaecio OpticoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Evolving Science Fourth EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology An Evolving Science Fourth Editionolivil.donorbipj100% (38)
- Forensic Photography DoneDocument40 pagesForensic Photography DoneRuffa Mayjade AvilaNo ratings yet
- Science 3 4 ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience 3 4 ReviewerAngelica VersolaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedDocument72 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedAishwarya PatilNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper 2021 2022 Science 10 MinDocument12 pagesCBSE Sample Paper 2021 2022 Science 10 MinPayoja RajNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22Document72 pagesSCIENCE - X Golden Sample Paper - 2021-22krish patelNo ratings yet
- What is a Dumpy Level and How is it Used in SurveyingDocument10 pagesWhat is a Dumpy Level and How is it Used in SurveyingStefani Ann CabalzaNo ratings yet
- Phys 103 A.Y. 2019-2020Document8 pagesPhys 103 A.Y. 2019-2020Jomar BacaniNo ratings yet
- Earth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test BankDocument38 pagesEarth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test Bankdylanyoung2tlm100% (12)
- Rimfire: Riflescope Owner'S GuideDocument28 pagesRimfire: Riflescope Owner'S Guidedavid churaNo ratings yet