Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Model Paper 9th Physics Merged
Uploaded by
BILAL AKHTARCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Model Paper 9th Physics Merged
Uploaded by
BILAL AKHTARCopyright:
Available Formats
TEST 1 PHYSICS 9th T.
MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
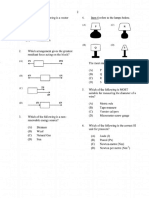
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) A type of motion in which a body mover about its own axis is called: I
(A) Vibratory (B) Circular (C) Random (D) Rotatory
II) A change in position in proper direction is called: II
(A) Velocity (B) Speed (C) Distance (D) Displacement
III) Least count of metre rod is ____. ___
III
(A) 1cm (B) 1mm (C) 0.1mm (D) 0.01mm
IV) By dividing displacement of a moving body with time, we obtain: :
IV
(A) Declaration (B) Velocity (C) Acceleration (D) Speed
V) Base unit is___. V
(A) Watt (B) Newton (C) Kilogram (D) Pascal
VI) 0.027 has significant digits. 0.027 VI
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define base quantity and write its names. I
II) Differentiate between rotatory and vibratory motion. II
III) Differentiate between scaler and vector and give example. III
IV) Differentiate between displacement and distance.
IV
V) What do you mean by zero error and zero correction. V
VI) Write the names of four derived units. VI
VII) Drive first equation of motion with the help of graph. VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Drive second equation of motion with the help of graph. 1
2) Write a note on 4 branches of physics. 4
2
TEST 1 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The study of internal structure of the earth is called: I
(A) Heat (B) Earth physics
(C) Geo physics
(D) Atomic physics
II) Which is not a derived unit? II
(A) Watt (B) Newton (C) Kilogram (D) Pascal
III) Which quantity is scaler: III
(A) Torque (B) Velocity (C) Power (D) Force
IV) A change in position is called: ____ IV
(A) Distance (B) Velocity (C) Speed (D) Displacement
V) Least count of vernier callipers is: V
(A) 1cm (B) 1mm (C) 0.01cm (D) 0.01mm
VI) A ball is thrown vertically upward, its velocity at the highest point is: VI
(A) (B) (C) (D) Zero
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define Plasma physics and Geo physics.
I
II) Differentiate between speed and velocity. II
III) Write down the formula and unit to find acceleration. III
IV) Define least count and write least count of metre rod.
IV
V) Define vibratory motion and give example. V
VI) Differentiate between machenical and digital stop watch VI
A sprinter completes its 100 meter race in 12 seconds. Find 10012 VII
VII)
his average speed.
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Write SI units of base quantities. SI 1
2) Drive third equation of motion with the help of graph. 2
TEST 1 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
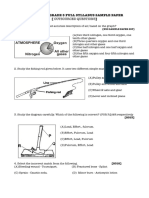
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Which of the following is a vector quantity? I
(A) Power (B) Distance (C) Speed (D) Displacement
II) Amount of a substance in terms of number is measured in: ___ II
(A) Mole (B) Newton (C) Kilogram (D) Gram
III) The number of significant figures in 0.00580 is: 0.00580 III
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 5 (D) 6
IV) a=_____? a=______? IV
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) The acceleration of a body falling down freely is approximately: V
(A) (B) (C) (D)
VI) The number of base units in SI is: (SI) VI
(A) 3 (B) 6 (C) 7 (D) 8
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define gravitational acceleration and write its value is SI Unit SI I
II) Define base and derived quantities. II
Why is the use of zero error necessary in a measuring
III) III
instrument?
IV) Differentiate between circular and rotatory motion. IV
V) Can a body moving at a constant speed have acceleration? V
VI) Write the least count of Screw Gauge. VI
VII) A car traveling at acceleration uniformly at VII
Calculate its velocity after 5 seconds. 5
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Define motion and explain its types 1
2) Write a note on Screw Gauge. 2
TEST 2 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Inertia depends on: ___ I
(A) Velocity (B) Mass (C) Net force (D) Force
II) The unit of weight in System International is: II
(A) Newton (B) Pound (C) Kilogram (D) Dyne
III) The force oppose the motion of a moving object is called: III
(A) Work (B) Power (C) Friction
(D) Momentum
IV) If velocity of the body becomes double, then centripetal force will be:
IV
(A) Half (B) Double greater (C) Triple greater (D) Four time greater
V) Unit of momentum is: V
(A) (B) (C) (D)
VI) The weight of a body is 147N. its mass will be when 147N VI
(A) 147Kg (B) 0.147Kg (C) 14.7Kg (D) 1.47Kg
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Differentiate between force and inertia. I
II) State Newton first law of motion and give equation. II
III) What is the law of conservation of momentum? III
IV) Write two advantages and two disadvantages of friction. IV
V) How cream seperator work? V
VI) The weight of a body is 147N. What is its mass? 147N VI
VII) Find the acceleration that is produced by 20N force in a 20 8 VII
mass of 8kg.
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) State Newton second law and drive equation. 1
2) Write a note on friction and its types. 2
TEST 2 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The centripetal acceleration is inversely proportional to:
I
(A) Mass (B) Radius (C) Both (D) Velocity
II) The equation of momentum is: II
(A) p=mv (B) (C) (D)
III) The force required to move the car in a curved path is: __ III
(A) Tention (B) Centripetal (C) Centrifugal (D) Gravitational
IV) Coefficient of friction between the tyre and wet road is: IV
(A) 1 (B) 0.8 (C) 0.6 (D) 0.2
V) Which of following material lowers friction when pushed between
V
metal plates.
(A) Oil (B) Air (C) Water (D) Marble powder
VI) When a horse pulls a cart, the action is on the: VI
(A) Cart (B) Horse (C) Earth (D) Cart and Earth
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define force and write its SI unit. SI I
II) State Newtion third law and give one example. II
III) How seat belts are useful at the time of driving? III
IV) Define momentum and write its equation. IV
V) Write the advantage of banking of road. V
VI) Differentiate between centripetal force and centrifugal force.
VI
VII) A mass of 5kg is moving with the velocity of . Find 5 VII
the force which is required to stop it in 2 seconds. 2
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Find the tention and acceleration in string when two bodies
1
attached with string move vertically.
2) State and explain Newton third law of motion. 2
TEST 2 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Rate of change of momentum is equal to: I
(A) Distance (B) Mass (C) Force (D) Torque
II) Newton first law of motion is valid only in the absence of: II
(A) Force (B) Torque (C) Friction (D) Momentum
III) A string is stretched by two equal and opposite forces 10N each. III
The tention in the string is: 10N
(A) 5N (B) 10N (C) 20N (D) Zero
IV) When the cyclist stops pedaling bicycle stops due to: __ IV
(A) Mass (B) Weight (C) Friction (D) Momentum
V) A mass of 6kg is moving with acceleration of . Force action on it is: V
6kg
(A) 3N (B) 4N (C) 8N (D) 12N
VI) How much acceleration is produced by force of 100N in mass of 50Kg?
100N50Kg
VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Why rolling friction is less than sliding friction?
I
II) Action and reaction are always equal and opposite, then II
how does a body move?
III) Define dynamics. III
IV) What is meant by coefficient of friction?
IV
V) What is meant by banking of road? V
VI) Define force and write its SI unit. SI VI
How much force is needed to prevent a body of mass 10kg from
VII) 10 VII
falling?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Define rate of change of momentum and also drive its equation. 1
2) Define centripetal force and write its equation and write factors
2
on which it depends.
TEST 3 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
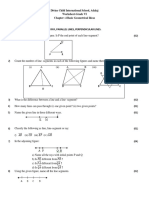
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Two equal but unlike parallel forces having different line of action produce I
(A) Couple (B) Torque (C) Equilibrium (D) Neutral equilibrium
II) The centre of gravity of irregular shaped body can be found with help of:
_ II
(A) Metre rod (B) Wedge (C) Plumb line
(D) Screw gauge
III) The formula of Torque is: III
(A) E=F x L (B) T= F x L (C) E= F x T (D) L= F x E
IV) Horizontly placed pencil is the example of ___. ___ IV
Equilibrium Stable equilibrium Neutral equilibrium Unstable equilibrium
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) The number of vectors that can be added by head to tail rule is: V
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) Unlimited
VI) If 10N force is making an angle with x-axis then value of X 10 VI
vertical component is:
(A) 4N (B) 5N (C) 7N (D) 8.7N
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What are like and unlike parallel forces? I
II) What is resultant of forces? II
What do you meant by perpendicular components?
III) III
Write down the formula to find its direction.
IV) Define moment arm. IV
V) Explain 2nd condition of equilibrium. V
VI) Define torque and write its unit. VI
What will be the torque it a force of 150N is applied on
VII) 10cm 150N VII
a spanner of 10N?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain stable and unstable equilibrium with examples. 1
The steering of car has a radius 16cm. Find the torque 50N 16cm 2
2)
produced by a couple of 50N.
TEST 3 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
The perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation
I) I
and the line of action of force is called:
(A) Work (B) Momentum (C) Torque (D) Moment Arm
II) The types of equilibrium are: II
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
III) Number of factors on which Torque depends: III
(A) Mass and Velocity (B) Force and Mass (C) Force and Velocity (D) Force and Moment arm
IV) The turning effect of a force is called: IV
(A) Work (B) Pressure (C) Torque (D) Momentum
V) Mathematically first condition of equilibrium is represented as: V
(A) (B) (C) (D)
VI) The number of perpendicular components of a vector is: VI
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Differentiate between centre of mass and centre of gravity. I
II) Differentiate between stable and neutral equilibrium. II
III) What is meant by resultant vector? III
IV) Differentiate between axis of rotation and moment arm.
IV
V) On doubling the moment arm, what effect on value of torque V
VI) What is Head to tail rule? Explain with example. VI
How magnitude and direction of a force can be determined
VII)
VII
from its perpendicular components?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain 1st and 2nd condition of equilibrium & derive equation 1
A force of 100N is applied prependicularly on a spanner at a 10cm 100N 2
2)
distance of 10N from a nut. Find the torque produced by force.
TEST 3 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) An example of neutral equilibrium is: I
(A) Block (B) Foot ball (C) Pencil at its tip (D) Book on table
II
II) In isolated system the momentum after collision of two bodies is:
(A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Constant (D) Zero
III) First condition of equilibrium is: III
(A) (B) (C) (D)
IV) Racing cars are made stayable by: IV
(A) Increasing their speed (B) Decreasing their mass (C) Decreasing their width (D) Lowering their center of gravity
V) A body satisfies second condition for equilibrium if the resultant V
___ acting on it is zero. ___
(A) Force (B) Weight (C) Torque (D) Momentum
VI) The centre of gravity of a body is such a point where the whole VI
weight of body acts ____. ___
(A) Vertically upward (B) Vertically downward (C) At origin (D) Horizontally downward
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What is meant by neutral equilibrium? I
II) Define Torque and Rigid body II
III) State the principle of moments. III
IV) Differentiate between line of action of force and moment arm. IV
V) State first condition of equilibrium. V
VI) Why the height of racing vehicles is kept as lower? VI
Find the vertical components of force of 50N making an x 50N
VII)
angle of with x-axis. VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) What is meant by rosolution of forces and explain with example. 1
30 200N 2
A man is pulling a trolley on a horizontal road with a force of 200N making 30 degree with the road. Find horizontal
2)
and vertical components of its force.
TEST 4 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The value of gravitational field strength near the surface of earth is:
I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
II) At altitude h, the value of "g" can be determined by the formula: g h II
(A) (B) (C) (D)
III) Value of gravitational acceleration at 1000km above surface of earth is: 1000 III
(A) (B) (C) (D)
IV) The distance of Moon from Earth is nearly: IV
(A) 3800km (B) 37000km (C) 370,000km (D) 380,000km
V) Velocity of Geostationary satellite with respect to earth is: V
(A) (B) (C) Zero (D) None
VI) Formula to determine the value of gravitational acceleration is: VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define law of gravitation and write its equation. I
II) What is meant by the Force of gravitation? II
III) Write the value of and unit of gravitational constant "G" in SI units. g SI III
IV) Why is the value of "g" different at different places? g IV
V) On what factors the orbital speed of satellite depends? V
VI) Define geostationary orbit. VI
VII) Why law of gravitation is important to us? VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Determine the mass of Earth using the law of gravitation. 1
2) Explain motion of artificial satellites and drive the equation. 2
TEST 4 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The orbital speed of a low orbit satellite is: I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
The value of "g" at a height on Earth's radius above the
II) g II
surface of the Earth is:
(A) 2g (B) (C) (D)
III) Earth's gravitational force of attraction vaishes at: III
(A) 1000km (B) 42300km (C) 6400km (D) Infinity
IV) Mass of the Earth is: IV
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) The Moon completes its one revolution around the Earth in: V
(A) 25.3 (B) 27.3 (C) 29.3 (D) 31.3
The value of "g" on Moon's surface is . What
VI) 100kg g VI
will be the weight of a 10kg body on the surface of Moon?
(A) 10N (B) 16N (C) 100N (D) 160N
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
Define Gravitational field strength. What is its value near Earth? I
I)
II) If R is doubled then what will be change in ? R II
What is the height and speed of Geostationary satellite from
III) III
the surface of the Earth?
IV) With what force an apple weighting 1N attracts the Earth? 1 IV
V) State the difference between natural and artificial satellites.
V
VI) Prove that gravitational force is a field force? VI
VII) Why communication satellites are stationed at geostationary orbits VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain the variation of "g" with altitude. g
1
2) State Newton's law of gravitation and drive its equation. 2
TEST 5 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The work will be zero when the angle between the force and the distance is: I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
The work done lifting a brick of mass 2kg through a
II) 5 2 II
height of 5m above the ground will be:
(A) 2.5J (B) 10J (C) 50J (D) 100J
III) The energy stored in coal is ____ energy: ___ III
(A) Heat (B) Nuclear (C) Electrical (D) Chemical
IV) Which device converts light energy into electrical energy? IV
(A) Photo cell (B) Electric cell (C) Generator (D) Electric bulb
V) The efficiency percentage of an electric lamp is:
V
(A) 5% (B) 10% (C) 15% (D) 20%
VI) The kinetic energy of a body of mass 2kg is 25J. Its speed will be: 25J 2 VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define work and write its SI unit. I
II) Write the definition and equation of K.E and P.E
II
III) Write the names of four types of energy. III
IV) What is soil erosion? IV
V) Differentiate between machinal and chemical energy. V
VI) Why fossil fuels are called non-renewable from of energy? VI
VII) The kinetic energy of a body of mass 2kg is 25J. Find its speed.
25
2
VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Write a note on any four forms of energy. 1
A man lifts 200N weight up to the height of 10m.
2) 10m200N 2
Find its work.
TEST 5 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) At what angle between force and displacement the wrok will be zero
I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
II) If the velocity of a body becomes three times greater then kinetic energy will be
II
(A) Three times (B) Four times (C) Six times (D) Nine times
III) One jole is equal to: III
(A) (B) (C) (D) 1N 1m
IV) Capability to do work is called: IV
(A) Power (B) Momentum (C) Torque (D) Energy
V) Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the velocity of a body: V
(A) Square (B) Two times (C) Three times (D) Four times
VI) The energy in the stretched bow is: VI
(A) Kinetic
(B) Elastic (C) Both (D) Heat
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) When does a force work? I
II) Differentiate between kinetic energy and potential energy.
II
III) Define machinal energy and give two examples. III
IV) Define joule. IV
V) Define mass energy equation. V
VI) Why do we need energy? VI
VII) A car weighting 10kN has speed of . Find its K.E
12kN VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Write a note on major two sources of energy. 1
Calculate power of pump which can lift 200kg of water 6 10 200kg 2
2)
through a height of 6m is 10s.
TEST 5 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Rate of doing work is called: I
(A) Momentum (B) Power (C) Torque (D) Energy
II) Energy stored in a Dam's water is: II
(A) Kinetic (B) Electrical (C) Thermal (D) Potential
III) SI unit of work is: SI III
(A) Watt (B) Joule (C) Newton (D) Pascal
IV) The work will be maximum when angle between force and displacement is IV
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) The efficiency of solar cell is: V
(A) 3% (B) 6% (C) 8% (D) 12%
VI) 10 jole work is done by machine in 5 seconds. Its power will be: 105 VI
(A) 2W (B) 10W (C) 25W (D) 50W
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Define kinetic energy and write its equation. I
II) Define energy and write any two kinds. II
III) What is meant by efficiency? III
IV) Write a short note on solar cell. IV
V) Define potential energy and write its equation.
V
VI) Define mass energy equation. VI
A body of mass 50kg is raised to height of 3m. What is its 3m
50
VII) VII
potential energy?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Write a note on any three renewable sources of energy. 1
A mass of 500g strikes the ground with. How much kinetic 500g 2
2)
energy velocity of stone at time it strikes ground?
TEST 6 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) In which state molecules do not leave their position? I
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) Plasma
II) The upthrust of liquid is given by: II
(A) ga (B) pgf (C) pg (D) pgh
III) Works on pascal's law: III
(A) Wedge (B) Screw gauge (C) Hydraulic press (D) Vernier callipers
IV) One pascal is equal to: IV
(A) 1Nm (B) (C) (D)
V) Hydraulic press works on: V
(A) Pascal's law (B) Newton's law (C) Hooke's law (D) Archimedes principle
VI) The density of 500g stone having volume will be:
200 500 VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Write some important features of kinetic molecular model of matter.
I
II) Which law is used in breaking system of cars and buses? II
III) State Archimedes principle. III
IV) Write a short note on plasma. IV
V) Define density and write its SI unit. SI V
VI) Define young modolus. VI
Why does a piece of stone sink in water but a ship with a huge VII
VII)
weight floats. Why?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain the working of hydrolic press on the basis of Pascal's law. 1
2) Define stress and tensile strain and also write their formulas. 2
TEST 6 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) In SI system, unit of density is: SI I
(A) kgm (B) (C) (D)
II) At sea level, the atmospheric pressure is about:
II
(A) 100130 Pa (B) 103100 Pa (C) 110300 Pa (D) 101300 Pa
III) One pascal is equal to: III
(A) (B) (C) (D)
What should be the approximate length of glass tube to
IV) IV
construct a water barometer?
(A) 0.5m (B) 1m (C) 2.5m (D) 11m
V) Which of the substance is the lightest one? V
(A) Lead (B) Aluminum (C) Mercury (D) Coper
VI) If force will be applied on smaller area, pressure will be come: VI
(A) Less (B) More (C) Much less (D) Zero
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) State the Pascal's law. I
II) Why water is not suitable to be used in a barometer? II
III) Why does atmospheric pressure vary with height? III
IV) On what factors pressure of a liquid depends? IV
V) Define elasticity. V
VI) What do you meant by Elastic limit? VI
Calculate the volume of a gold bar of mass 0.2kg. The 0.2 VII
VII)
density of gold is .
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain kinetic molecular model of matter.
1
2) Prove that pressure in a liquid increases with depth. 2
TEST 6 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) In SI unit of pressure is: I
(A) J (B) N (C) Nm (D)
II) The fourth state of matter is called: II
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) Plasma
III) In S.I system, the unit of Young modulous is: III
(A) Nm (B) (C) (D)
IV) Constant= Stress / Strain /= IV
(A) Newton's law (B) Pascal's law (C) Hook's law (D) Archimedes law
V) Mercury is ___ times denser the water. ___ V
(A) 10.34 (B) 12.6 (C) 13.6 (D) 16.8
VI) Density =______ ______= VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What is a barometer? I
II) State Hook's law. II
III) Write properties of fourth state of matter. III
IV) Write the term of pressure and write the factors on which it depends. IV
V) How a submarine moves up the water surface and down into water? V
VI) Can we use a hydrometer to measure the density of milk? VI
VII) The mass of of stone is 500g. Find its density.
500g VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
State Archemedus principle and prove it and
1) 1
derive equation of upthrust of liquid.
2) Explain variation in atmospheric pressure. 2
TEST 7 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Degree is hotness or coldness of the body is called: I
(A) Heat (B) Heat capacity (C) Temperature (D) Thermal conductivity
II) Which material has large specific heat?
II
(A) Mercury (B) Water (C) Ice (D) Copper
III) Letest heat of fusion of ice is given by: III
(A) (B) (C) (D)
IV) Mercury is denser than water: IV
(A) 10 times (B) 12.5 times 12.5 (C) 13 times (D) 13.6 times 13.6
V) Unit of specific heat capacity in SI system is: SI V
(A) (B) (C) (D)
VI) Water freezes at: VI
(A) 0K (B) -273 k (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What is difference between temperature and heat? I
II) Why heat is transferred from hot body to cold body? II
III) Define internal energy. III
IV) Define thermal equilibrium. IV
V) Write the uses and range of clinical thermometer.
V
VI) Define lower and upper fixed points. VI
VII) Define co-efficient of linear thermal expansion and write its SI unit. SI VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Convert normal body temperature into celsius and kelvin scale 1
2) How much heat is required to increase the temperature of 0.5kg of water 0.5 2
from to .Specific heat of water is
TEST 7 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) The specific heat of iron in joules per kilogram per kelven is: I
(A) 387.0 (B) 470.0 (C) 503.0 (D) 920.0
II) Rate of flow of heat is equal to: II
(A) Q x t (B) (C) (D)
III) Which gas is used in spite of frozen gas in refrigerator: III
(A) (B) (C) (D)
IV) The co-efficient of linear expansion and volume expansion are
IV
related by the equation:
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) Which of the following affects evaporation: V
(A) Temperature (B) Surface area of liquid (C) Wind (D) All
VI) On celsius scale is equal on Fahrenheit scale to:
VI
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) How temperature determines the direction of flow of heat? I
II) Change 300K temperature on kelvin into Celsius scale. 300K II
III) Write two characteristics of the liquid used in thermometer. III
IV) What are Kelvin scale and Fahrenheit scale? IV
V) What is latent heat of vaporization? Write its equation. V
VI) How does heating effects the motion on molecules of the gas? VI
VII) Convert into foreheit temperature scale. VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain linear thermal expansion in solids. 1
2) How much ice will 50,000J of heat? while latent heat of 50,000 2
fosion of ice is .
TEST 7 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Normal human body temperature is: I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
II) On Celsius scale, the temperature 300k will be: 300k
II
(A) (B) (C) (D)
III) Absolute zero temperature is: III
(A) (B) (C) (D) 100K
IV) The temperature at which a solid starts melting is called__point: IV
(A) Boiling (B) Freezing
(C) Fusion (D) None
V) in Celsius scale equals to: V
(A) (B) (C) (D)
VI) Heat always flow from___: VI
(A) Cold body to hot body (B) Hot body to cold body (C) Both of these (D) None of these
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Describe relation between heat capacity and quantity of substance. I
II) Differentiate between Heat and Internal energy. II
III) Write the values of latent heat of fusion of aluminum and copper. III
IV) Write factors on which evaporation of a liquid depends. IV
V) What is the effect of temperature on evaporation? V
VI) Define co-efficient of volume expansion and write its SI unit. VI
SI
VII) Explain specific heat capacity. VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Convert 300K into celsius and fahren heit scale. 300K 1
2) What is of water in a baker is its value in fahrenheit 2
scale and kelvin scale.
TEST 8 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) In solid, heat is transferred by: I
(A) Convection (B) Conduction (C) Absorption (D) Radiation
II) Example of a bad conductor is: II
(A) Graphite (B) Wool (C) Iron (D) Gold
III) Land breez and sea breez are result of: III
(A) Convection (B) Conduction (C) Absorption (D) Radiation
IV) What happens to the thermal conductivity of a wall if its thickness is doubled: : IV
(A) Becomes half (B) Remain same (C) Becomes double
(D) Becomes on fourth
V) Worst absorber of heat is: V
(A) White surface (B) Coloured surface (C) Dull black surface (D) Shining silvered surface
VI) In gases, heat is mainly transferred by: VI
(A) Radiation (B) Conduction (C) Convection (D) Molecular collision
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What is meant by transfer of heat? I
II) Write the uses of conductors and non-conductors. II
III) Define land breeze and sea breeze. III
IV) Why bottoms of cooking pots are made black? IV
V) What causes of glider to remain in air? V
VI) Define radiation. VI
VII) What is meant by conduction? VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain the applications and consequencesof radiations. 1
2) What is meant by convection currents and write its uses? 2
TEST 8 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Reason of glider toremain in air is: I
(A) Conduction (B) Convection (C) Radiation (D) Power
II) Heat transfers through fluids by the method called: II
(A) Conduction (B) Convection (C) Radiation (D) Absorption
III) The major source of heat energy is: III
(A) Sun (B) Earth (C) Moon (D) Nuclear fules
IV) Thermal conductivity of rubber is: IV
(A) (B) (C) (D)
V) The ways by which transfer of heat takes place are: V
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
VI) Rooms are heated using gas heaters by ____: ___ VI
(A) Radiation (B) Convection (C) Both (D) Conduction
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) What is thermal conductivity? I
II) Write uses of non-conductors. II
III) What is green house effect?
III
IV) Describe relation of radiation of heat and surface area. IV
V) Why transfer of heat in fluids takes place by convection? V
VI) Write the ways by which transfer of heat takes place. VI
VII) On what factors radiations depends? VII
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Define thermal conductivity and derive its equation. 1
2) Write uses of conductors and non-conductors. 2
TEST 8 PHYSICS 9th T.MARKS 30
NAME ROLL NO SECTION
TEST TYPE 8TH DIVISION WISE DATE ____/____/____ CHECKED BY
Circle the Correct Option 1X6=06 1
I) Thermal conductivity is directly proportional to: I
(A) Time
(B) Area (C) Temperature (D) Length of conductor
II) Which of the following birds are expert thermal climbers: II
(A) Eagle (B) Hawks (C) Vultures (D) All
III) The thermal conductivity of dry air in is: III
(A) 0.08 (B) 0.03 (C) 0.2 (D) 0.026
IV) Water is ___ conductor of heat: ___ IV
(A) Poor
(B) Good (C) Both (D) Exceptional good
V) ______ is good radiator of heat. V
(A) White surface (B) Green colored surface (C) Dull black surface (D) Shining silvered surface
VI) False ceiling is done to: VI
(A) Keep the ceiling clean (B) Lower the height of ceiling (C) Insulate the ceiling (D) Cool the room
Write short answers of the following 2X7=14 2
I) Why conduction of heat does not take place in gases? I
II) Write two examples of good and bad conductors each. II
III) How does heat reaches us from the sun? III
IV) Why we avoid wear dark colour dresses in summer season? IV
V) Write use of Styrofoam. V
VI) Define convection and write its two examples. VI
VII) Deserts soon get hot during sunrise and soon get cold VII
after sunset. Why?
Write detailed answers of the following 5X2=10 3
1) Explain the reason of sea breeze blows during the day and
1
land breeze blows during night.
2) What is rate of flow of heat? Explain different factors on 2
which it depends.
You might also like
- Test 1 Chemistry 9Th T.MARKS 30Document24 pagesTest 1 Chemistry 9Th T.MARKS 30Mohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise 9th Chemistry v1Document24 pagesChapter Wise 9th Chemistry v1a.basheer089No ratings yet
- Physice 10th Test PDFDocument20 pagesPhysice 10th Test PDFMuhammad Naseer ud dinNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chemistry Test Paper 3Document1 page9th Class Chemistry Test Paper 3amnaarif135No ratings yet
- 9th Class Math Test Paper 4Document1 page9th Class Math Test Paper 4sajjadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10th TestDocument24 pagesChemistry 10th TestMohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10th TestDocument24 pagesChemistry 10th TestR razaaliNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Physics Test Paper 6Document1 page9th Class Physics Test Paper 6Muneeb SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise 9th MathsDocument24 pagesChapter Wise 9th MathssurprisinglysarahytNo ratings yet
- Math 10th TestDocument23 pagesMath 10th TestMuhammad Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise 10th MathsDocument23 pagesChapter Wise 10th MathssaimmarketingseoNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Physics English Medium Chapter WiseDocument9 pages9th Class Physics English Medium Chapter WiseMr IQBALNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Math Test Paper 1Document1 page9th Class Math Test Paper 1rememi1794No ratings yet
- 9th Class Biology Test Paper 2Document1 page9th Class Biology Test Paper 2Syed Sibtain RazaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Practice SheetDocument2 pagesFiitjee: Practice SheetVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Hwa Jalan Atas Banggol, 15000 Kota Bharu, Kelantan Tel: (603) - 89486358 Faks: (603) - 89482117Document3 pagesSMJK Chung Hwa Jalan Atas Banggol, 15000 Kota Bharu, Kelantan Tel: (603) - 89486358 Faks: (603) - 89482117AzriNo ratings yet
- 12th Science Model Question Papers With Solutions MH Board Solutions PDFDocument390 pages12th Science Model Question Papers With Solutions MH Board Solutions PDFShashank RautNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics - Test Maker @Document4 pages11 Physics - Test Maker @ashfaq4985No ratings yet
- 1st Years Test Chapter 1 and 6Document2 pages1st Years Test Chapter 1 and 6Usman BahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics 1stDocument4 pagesPhysics 1stAbdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneDocument3 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics - Test Maker @Document2 pages11 Physics - Test Maker @Ahsan YasinNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper - Match 2023 - 6414657a7e37dDocument4 pagesBoard Question Paper - Match 2023 - 6414657a7e37dshubhamatilkar04No ratings yet
- Physics Multiple Choice 1Document11 pagesPhysics Multiple Choice 1lolipop kissezNo ratings yet
- Physics Half BookDocument2 pagesPhysics Half Bookعاطف محمودNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2020 P1Document18 pagesCSEC Physics June 2020 P1tony suchit100% (1)
- Ch#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)Document2 pagesCh#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)QamarNo ratings yet
- Css Physics1 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesCss Physics1 2010 PDFanwarNo ratings yet
- BArch M 15Document99 pagesBArch M 15vaishnavi hulsureNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneDocument2 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- Jan 2007 p1Document12 pagesJan 2007 p1Royan. O. BarnabyNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Physics Test Paper 8Document1 page9th Class Physics Test Paper 8Muhammad Mubashir ul hassanNo ratings yet
- 9 Physics - Test Maker @Document2 pages9 Physics - Test Maker @m.danishNo ratings yet
- 1st Year (Advance)Document1 page1st Year (Advance)QamarNo ratings yet
- D0679sci Part1 QR 2020 FinalDocument20 pagesD0679sci Part1 QR 2020 FinalEND GAMINGNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2002 P1Document11 pagesCSEC Physics June 2002 P1Nakalia HansonNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 1Document4 pagesPhysics Set 1Krishna PawarNo ratings yet
- 2013 Csec Physics Paper 1 PDFDocument12 pages2013 Csec Physics Paper 1 PDFNarvelle FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Ix Icse Physics Set A (QP)Document5 pagesIx Icse Physics Set A (QP)With DeboNo ratings yet
- Kepkpo Youth AssociationDocument6 pagesKepkpo Youth Associationsimon dzisenuNo ratings yet
- IV Mechanics IIA2010 UoSDocument3 pagesIV Mechanics IIA2010 UoSKashf e AreejNo ratings yet
- 01 Board Question Paper - July 2022 - 6582ac671517eDocument3 pages01 Board Question Paper - July 2022 - 6582ac671517ejuthani100No ratings yet
- 5 Pfy Physics T-2 03-09-2022Document1 page5 Pfy Physics T-2 03-09-2022noon noonNo ratings yet
- Algorithms Test 1: Best Case Average Case Worst Case I. O (N) O (N) O (N) II. O (N Log N) O (N Log N) O (N Log N)Document7 pagesAlgorithms Test 1: Best Case Average Case Worst Case I. O (N) O (N) O (N) II. O (N Log N) O (N Log N) O (N Log N)AKASH PALNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2013 P1Document12 pagesCSEC Physics June 2013 P1Leeyos78% (9)
- CSEC Physics January 2007 P1Document12 pagesCSEC Physics January 2007 P1Sachin MarajNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: July 2018: PhysicsDocument3 pagesBoard Question Paper: July 2018: PhysicsMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Ut1 PhyDocument3 pagesUt1 PhyNickulNo ratings yet
- p1 2009-2022Document189 pagesp1 2009-2022Timothy SeyaramNo ratings yet
- 2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Document13 pages2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Naps LibraryNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatisticsM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- 11 ScienceDocument8 pages11 Sciencewerg62856No ratings yet
- Physics P Ix 2021Document3 pagesPhysics P Ix 2021batmanNo ratings yet
- s1 2021 DecDocument3 pagess1 2021 Decjuthani100No ratings yet
- Bahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of MCQ's (F.B.I.S.E)Document71 pagesBahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of MCQ's (F.B.I.S.E)Zaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics FB MCQs With KeysDocument29 pages11th Physics FB MCQs With Keyssamyafarooq504No ratings yet
- LVL 2 Sample NsoDocument5 pagesLVL 2 Sample NsoBhishma PandyaNo ratings yet
- 9 Chapter 1Document1 page9 Chapter 1Muhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Divine Child International School, Adalaj Worksheet-Grade VI Chapter: 4 Basic Geometrical IdeasDocument3 pagesDivine Child International School, Adalaj Worksheet-Grade VI Chapter: 4 Basic Geometrical IdeasNatasha VidhaniNo ratings yet
- Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry and Its ApplicationsFrom EverandQuadrupole Mass Spectrometry and Its ApplicationsPeter H. DawsonNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 7: Kinematics 1 (Constant Acceleration)Document2 pagesMechanics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 7: Kinematics 1 (Constant Acceleration)HuzaifahNo ratings yet
- Yo YoDocument3 pagesYo Yoitaiorr100% (1)
- Parkworld PlotDocument2 pagesParkworld PlotJessica FerrellNo ratings yet
- Cb7b170c 080e 465f A881 60caacc97670N.L.M Exercise With Solution DoneDocument24 pagesCb7b170c 080e 465f A881 60caacc97670N.L.M Exercise With Solution DoneShuvanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- QWQWQQDocument15 pagesQWQWQQgurdeepsingh1296No ratings yet
- Answers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Document5 pagesAnswers To IGCSE Physics Revision Q's 26-01-2013Yaw Kean HuatNo ratings yet
- Ce Correl Dynamics Situation 1Document3 pagesCe Correl Dynamics Situation 1Glenn Frey LayugNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fisika - 2Document4 pagesTugas Fisika - 2bellina yunitasariNo ratings yet
- Extra High Voltage Ac Transmission Engineering by R D Begamudre PDFDocument2 pagesExtra High Voltage Ac Transmission Engineering by R D Begamudre PDFAllison67% (3)
- 60 ProblemsDocument40 pages60 ProblemsAttar Raha100% (1)
- Free Fall 2Document5 pagesFree Fall 2Mohd Äwiw Vießar AvondrahNo ratings yet
- 02 Kinematics PHY1012F-drg2021Document69 pages02 Kinematics PHY1012F-drg2021Simlindile Ngobela100% (1)
- Work, Power and EnergyDocument11 pagesWork, Power and EnergyMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- 78 Fuji SanyoDocument4 pages78 Fuji SanyoBAAAK100% (2)
- Syllabus For The National Physics Olympiad of BangladeshDocument2 pagesSyllabus For The National Physics Olympiad of BangladeshStanwood CoxNo ratings yet
- Notes On VA, EF & EFMDocument23 pagesNotes On VA, EF & EFMUtsav PathakNo ratings yet
- CT 3 JEE Adv 12-05-2013 Solution EnglishDocument12 pagesCT 3 JEE Adv 12-05-2013 Solution EnglishPrashantNo ratings yet
- Integer LOMDocument8 pagesInteger LOMAyushBhattNo ratings yet
- Rotational Inertia Lab ReportDocument8 pagesRotational Inertia Lab Reportcourtneypaxson100% (2)
- Options:: Useful Formulas Formulas Transformer FormulasDocument5 pagesOptions:: Useful Formulas Formulas Transformer FormulasMustafaMirNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square LawDocument16 pagesInverse Square Lawfushiguro megumiNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 004 Work Energy and Power PDFDocument27 pages004 Work Energy and Power PDFNIEVA LOU ORBOCNo ratings yet
- ME2307 Lab ManualDocument14 pagesME2307 Lab ManualAnirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 4 PDFDocument49 pagesPhysics Unit 4 PDFJhon ThomasNo ratings yet
- Forces Igcse PhysicsDocument5 pagesForces Igcse PhysicsAditi AnantNo ratings yet
- Self Test - Answers: 1. GravitationDocument4 pagesSelf Test - Answers: 1. GravitationAvishkar Patil100% (1)
- Unit 1 Review Package Conceptual QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Review Package Conceptual QuestionsasmipinkiNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy Worksheet #1 Answers - 1Document3 pagesConservation of Energy Worksheet #1 Answers - 1Fitz Baniqued67% (3)