Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L12. Endocrine System Drugs
Uploaded by
sabahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L12. Endocrine System Drugs
Uploaded by
sabahCopyright:
Available Formats
LECCTURE OF PHARMACOLOGY
MADE BY NURSING ZONE TEAM
L12. Endocrine System drugs
THIRD YEAR
@Nursing_Zone39
• Pancreas: is a mixed exocrine (secrets digestive enzymes) & endocrine
Oral
of Langerhans) glands. Rectal SC
Hmmmm
(islets
• Islets
or ofEasy
Langerhans secrets:
1.orInsulin:
Verity from B or cells
2. Glucagon: from A or cells Bypasses liver
(hyperglycemic effect) Patient can
or Compact
3. Somatostatin: from DErratic
or cellsabsorption low
/ hypothalamus administer
Convenient
4. Amylin: from B or cells compliance Complete
First pass effect
absorption
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
Differentiate between glucose, glycogen & glucagon Pain full
• Sublingual-Buccal
Glycogen is a stored form of energy. IV IM
• Glucagon signals the body to convert the stored glycogen back into glucose.
TI Rapid absorption
Stability of drug
I Rapid TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate K Sustained release
E Can’t be retrieved (DM) possible
Inconvenient
IXHyperglycemia
XI Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses
only
& Glucagon
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
Insulin
Work as a team (opposite to each other), and they’re the most
important regulators of normal fuel metabolism (glucose).
Complementary interaction of glucagon and insulin
Best of luck
Blood glucose Blood glucose
β-cell
α-cell α-cell β-cell
Glucagon Insulin Glucagon Insulin
Blood glucose to normal
Blood glucose to normal
• Somatostatin: inhibits both glucagon & insulin secretion by a paracrine
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
mechanism.
or Easy inhibits both glucagon
• Somatostatin:
& insulin secretion by a paracrine
or Verity
mechanism. Patient can
Bypasses liver
or Compact
• Amylin: delays gastric emptying, and opposes insulin by stimulating
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient
glycogen breakdown.
compliance Complete
First pass effect
absorption
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
Inappropriate glucose homeostasis Pain full
Diabetes Mellitus
Sublingual-Buccal IV IM
TI Rapid absorption
• The most common
Stability of drug
I Rapid
endocrinological disorder. TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E
• IsHigher
a group I Accurate
of syndromes characterized
bioavailability by: K Sustained release
E
◦Hyperglycemia
Inconvenient
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Expensive Trained personnel
◦Altered metabolism of lipid, carb., protein
What is Diabetes Mellitus
Small doses only
◦ risk of complicationsEXRequires trained personnel
from vascular Erratic absorption
diseases (include
Can’t be swallowed
atherocalarosis)
• Differentiated from Diabetes insipidus (deficiency/imbalance of ADH)
• Complications:
◦Autonomic neuropathy.
◦Hypertension.
Best of luck
◦Cardiovascular disease.
◦Dyslipidemia.
◦Gastropathy.
◦Peripheral vascular disease.
◦Erectile dysfunction.
◦Renal disease.
◦Peripheral neuropathy.
Retinopathy/Macular edema.
Insulin dependent DM (IDDM)
Oral Rectal Type I
SC
Hmmmm
Sever / absolute lack of insulin
(10-20%)
or Easy
Verity with insulin
orTreated
Bypasses liver Patient can
or Compact
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient Type
compliance Complete
First pass effect Diabetes Mellitus
absorption
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
Pain full
Non-insulin dependent DM (NIDDM)
Sublingual-Buccal
Type II IV IM
(80-90%) Insulin resistance (⬇ sensitivity to its action)
TI Rapid absorption + lack of insulin
I Rapid TI Large volume
E Stability of drug
GBBBEmMgm
Accurate
ITreated K Sustained release
E Higher bioavailability by a range of drugs
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Inconvenient
Diagnosis Diabetes Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses only
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
Test Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG)*
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test*
(Preferred Test) Informal Plasma Glucose *
before taking food (no calories (common during pregnancy) after
Stage for at least 8h) taking food
Casual plasma glucose Two-hour plasma glucose
Diabetes FPG >126 mg/dl
Best of luck
>200 mg/dl (2hPG) >200 mg/dl
Impaired Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Impaired Fasting Glucose
Glucose (IGT) = 2HPG >140 ; and
(IFG)=FPG >100 and <126
Homeostasis <200 mg/dl
Normal FPG <100 mg/dl 2 hPG <140 mg/dl
• In absence of unequivocal hyperglycemia (=no confirmed diagnosis), these need to
be repeated on the second day
• All results are confirmed by the existence of symptoms
Glycated hemoglobin (Hb-A1c)
Oral
• Used to monitor the average Rectal
plasma glucose concentration & SC
HB over
Hmmmm
prolonged
or Easy periods of time (2-6months)
or Verity Patient can
HbA1c Bypasses
mmol/mol liver %
or Compact
Normal Below 42 mmol/mol Belowadminister
6.0%
Erratic absorption low
Convenient
Prediabetes compliance
42 to 47 mmol/mol Complete
6.0% to 6.4%
First pass effect
Diabetes 48 mmol/mol or over 6.5% absorption
or over
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
A1c (%) Pain full
Average Blood
Sugar (mg/dL)
Sublingual-Buccal IV 4 IM68
5 97
TI Rapid absorption Rapid
I TI Large volume
E Stability of drug
6 126
GBBBEmMgm
Accurate
I K Sustained152
release
E Higher bioavailability 7
IX Can’t be retrieved possible
XI Inconvenient Expensive 8 183
Trained personnel
Small doses only
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
Treatment of
Hyperglycemia
Treatment
Best of luck
Diet & Physical exercise
Anti-diabetic drugs
A. Parentral agents B. Oral hypoglycemic
agents
(Insulin)
A. Parentral agents (Insulin)
Oral
• Chemistry: Rectal SC
Hmmmm
◦A protein
or Easy
‣ MW ~6000
Verity
or ‣ C-poly-peptide (chain): A & B
Bypasses liver Patient can
◦A
or Compact
hormone: 51 a.a
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient
compliance Complete
First pass
• Action effect
& MoA:
absorption
◦Carb, inefficient
Sometimes fat, and protein metabolism
◦Storage of glucose (as glycogen in Small does
difficultly in swallowing
liver & skeletal muscles, and as Pain full
triglycerides in fat cells)
Sublingual-Buccal IV IM
• So insulin;
TI Rapid absorption
I Rapidin blood by:
◦Lowers concentration of glucose
Stability of drug
TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E Accurate (in liver).
Higher
‣ Stimulating glycogenI synthesis
bioavailability K Sustained release
E ‣ Increase glucose Can’t be
(inretrieved possible
Inconvenient
IXuptake muscle) by
XI glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT-4).
Expensive Trained personnel
Small ‣doses only gluconeogenesis (in liver).
Inhibiting
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
◦Stimulates DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
(essential for growth).
◦Facilitates the storage of triglyceride in
adipose tissue.
Best of luck
• Pharmacokinetics:
◦Not active orally (broken down in stomach)
◦Inactivated by insulinase in liver & kidney
◦50% is destroyed in a single passage to liver
◦IV has a t1/2 of less than 9min, so slow release preparations
◦Dose reduced in renal impairment
• Sources of Insulin:
1- Beef pancreas/ Pork pancreas
2- Human insulin: recombinant DNA origin
• Insulin preparations:
1-Oral Rectal
Very short, Rapid acting insulin (ultra-short, 3-5h):
SC
Hmmmm
Insulin Lispro, insulin Aspart
Easy
2-orShort acting insulin (6-10h):
Regular soluble insulin
Verity
3-orIntermediate acting insulin (10-12h):
Bypasses liver Patient can
or Compact
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn insulin (NPH)
Erratic absorption low administer
4-Convenient
Long acting insulin (24h): Ultra-Lente insulin, insulin Glargine.
compliance Complete
First pass effect
absorption
• Sometimes
Situations inefficient
in which short and long acting insulins should be used
together:in swallowing Small does
difficultly
1- for old and young patients where frequent injections are Pain
notfull
easy.
2- Before long flights.
Sublingual-Buccal IV IM
• Clinical uses of insulin:
TI Rapid absorption
1- life long IDDM.
Stability of drug
I Rapid TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E 2- NIDDM which is not controlled
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate K Sustained
by oral hypoglycaemic release
agents.
E 3- Gestational diabetes. Can’t be retrieved possible
Inconvenient
IX
XI4- Diabetic ketoacidosis (life Expensive
threatening). Trained personnel
Small doses only
5- Hyperosmolar coma.
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
6- Before major operations.
• Adverse effects:
◦Hypoglycemia.
◦Insulin allergy and insulin resistance.
Best of luck
◦lipodystrophy: Lipo-hypertrophy (accumulatio
of fat); and lipo-atrophy (repeated injections
in specific area).
◦Insulin edema.
◦Weight gain.
B. Oral hypoglycemic agents
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
1st generation:
Easy Chlorpropamide (t 1⁄2 60 hrs).
1- Sulfonylureas (oldest used Type II DM drug)
or
2nd generation: Glipizide.
or Verity
3rd generation: Glimiperide
Bypasses liver Patient can
Compact
◦Action and MoA:
or
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient
‣ I.Decrease blood glucose level by:
compliance Complete
First pass•effectIncrease of insulin release from functioning pancreatic β cell
• Increase in insulin receptors. absorption
Sometimes inefficient
• Reduction of serum glucagon concentration. Small does
difficultly‣ inII.swallowing
chlorpropamide has antidiuretic effect.
Pain full
◦Clinical uses of sulfonylureas:
Sublingual-Buccal
‣ Mainly for Type II DM patients. IV IM
‣ Chlorpropamide: promotes ADH release, used to treat diabetes insipidus.
TI Rapid
◦Adverse absorption
effects:
‣ Weight
Stability of drug
I Rapidin obese patients), TI
gain (not recommended
Large volume
hypoglycemia,
GBBBEmMgm
E
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate
cholestatic jaundice, allergic K Sustained
skin reaction, hemopoietic release
changes.
E ‣ Cross placenta. IX Can’t be retrieved possible
Inconvenient
XI ‣ Disulfiram-like reaction with
Expensive
alcohol. Trained personnel
Small‣ doses only
Chlorpropamide can cause water retention by increase release of ADH
EXRequires trained personnel Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
2- Meglitinides (Repaglinide, Nateglinide)
• Action and MoA:
Lowers blood glucose, and stimulates insulin release from B cells, causing
potassium k+ channel to close.
Best of luck
• Abs/Dist/Elim:
More rapidly acting and has shorter duration compared to sulfonylurea.
• Clinical uses:
◦Taken with each meal to stimulate insulin release.
◦Useful in patients with: type 2 DM and impaired renal function.
• Adverse effects:
◦Hypoglycemia.
◦Less weight gain
•
Action and MoA: Lowers blood glucose, increase of GLUT-4.
Oral Rapid oral absorption, Rectal SC
Hmmmm
Abs/Dis/Elim: • short t 1⁄2 7h.
Clinical EasyType 2 DM.
or use:•
Adverseor •
effects:
Verity
◦Weight gain, fluid retentionBypasses
which could Patient can
liver lead to heart failure.
or Compact
◦Low risk of hypoglycaemia. Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient
compliance Complete
First pass effect 3- Thiazolidinediones (Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone)
absorption
Sometimes inefficient
& Metformin) Small does
difficultly in swallowing • Action and MoA: Lowers blood glucose
Pain full
5- Metformin (Glucophage)
4- Biguanide compounds (Phenformin
• Action and MoA: concentration, via inhibiting
◦Inhibition of hepatic
Sublingual-Buccal IV
gluconegenesis by activating AMP.
IM
gluconeogenesis. • Abs/Dist/Elim: Given orally t 3 1⁄2 h.
◦Direct stimulation of
TI Rapid absorption avoided in patients with renal
Rapid
glycolysis.
Stability of drug
I insufficiency TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E
◦Decrease of
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate
• Clinical uses: K Sustained release
E intestinal absorption IX Can’t be retrieved possible
◦patients with refractory obesity .
Inconvenient
XI of glucose.
Expensive
◦certain non-obeseTrained
adult personnel
diabetics.
Small doses only
◦Inhibition of plasmaRequires trainedItpersonnel
EX does not causeErratic absorption
hypoglycemia.
Can’t be swallowed
glucagon levels. • Adverse effects:
◦Up-regulation of ◦lactic acidosis.
insulin receptors. ◦Anorexia, GIT disturbances,
including diarrhea weight loss.
Best of luck
• Action and MoA: Delays carboydrate absorption from intestine; via decrease
intestinal absorption by inhibiting the action of intestinal brush border α-
glucosidase, slows the absorption decrease the postprandial (after meals) rise in
plasma glucose in both normal and diabetic subjects.
• Abs/Dis/Elim: Metabolized in GIT by bacteria and digestive enzymes.T 1⁄2 2h.
• Clinical use: Type 2 DM not controlled by other drugs.
• Adverse effects: Flatulence & diarrhea.
6- Glucosidase inhibitors (acarbose and miglitol)
Treatment of hypoglycaemia
Oral Rectal SC
Hmmmm
or Easy
or Verity(IV).
1- Glucose Patient can
Bypasses liver
or Compact
Erratic absorption low administer
Convenient
2- Glucagon:
compliance Complete
First pass effect
◦Action: Increase blood glucose con. absorption
Sometimes inefficient
Small does
difficultly in swallowing
◦MoA: Glucagon activates adenylate cyclase = stimulatingPain full
hepatic
gluconeogenesis
Sublingual-Buccal IV IM
◦Abs/Dist/Elim: Given by injection t 5 1⁄2 min.
TI Rapid absorption
Stability of drug
I Rapid TI Large volume
GBBBEmMgm
E ◦Clinical use: Emergency treatment
Higher bioavailability
I Accurate of K Sustained release
E
Inconvenient
IX Can’t
hypoglycaemic (caused be retrieved
by insulin possible
XI overdose),. Expensive Trained personnel
Small doses only
Hypoglycaemia
EXRequires trained personnel
gtfo Erratic absorption
Can’t be swallowed
◦Adverse effects: uncommon
Best of luck
MADE BY NURSING ZONE TEAM
Pharma references
A- Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 13 E Paperback
Bertram Katzung (Author), Anthony Trevor (Author) Publisher: McGraw-Hill Medical; 13 edition
(December 23, 2014)
Language: English
ISBN13:97 0071825054
ISBN 10:0071825053
B. Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology 6th edition (Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Series)
Paperback
Karen Whalen PharmD BCPS (Author) Edition: Sixth, North American.
Edition Language: English. ISBN-13: 978-1451191776 ISBN-10: 1451191774
2. List Essential References Materials (Journals, Reports, etc.) British National Formulary (BNF)
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 9+10. Oral Antidabetic DrugsDocument3 pages9+10. Oral Antidabetic Drugsmohammed alrubaiaanNo ratings yet
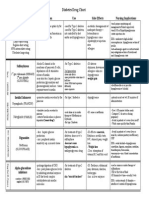
- Diabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MedicationDocument3 pagesDiabetes MedicationRuben Gutierrez-ArizacaNo ratings yet
- DM Type 1Document4 pagesDM Type 1Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsDocument59 pagesStep 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsMe back to MeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesDiabetes Mellitusfayeniwa100% (1)
- Diabetes Topic DiscussionDocument42 pagesDiabetes Topic Discussionapi-536649999No ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Nuno Nina CellWaterDocument21 pagesNuno Nina CellWatershanti08100% (1)
- Minimally Invasive Bariatric Surgery, Second EditionDocument535 pagesMinimally Invasive Bariatric Surgery, Second EditionSofia Isabel Teixeira100% (1)
- Krok2 - Medicine - 2013Document28 pagesKrok2 - Medicine - 2013ashighaNo ratings yet
- Evogliptin Conference PresentationDocument77 pagesEvogliptin Conference PresentationKrishna Chaitanya100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Overview and TreatmentsDocument36 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Overview and TreatmentsGlenn Nadine N. Masicampo100% (1)
- Pharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsDocument1 pagePharm - Endocrine - Anti-DiabeticsAbhineeth BhatNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-R4.2-Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsDocument14 pagesPHARMA-R4.2-Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic Drugscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy CalciumcarbonateDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Calciumcarbonateduane27fronterasNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Case Clue - 1 LinersDocument753 pagesCase Clue - 1 LinersOnly MrcpNo ratings yet
- L11 Glucose RegulationDocument21 pagesL11 Glucose RegulationCheng FuNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinBobNo ratings yet
- Endo-Doc LapakDocument3 pagesEndo-Doc LapakHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Sources of CHO: ACTIVITY No. 5 Blood Glucose TestDocument5 pagesSources of CHO: ACTIVITY No. 5 Blood Glucose TestCiara PamonagNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes PDFDocument4 pagesDrugs For Diabetes PDFDylan RastoNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Regulation 2Document11 pagesHormonal Regulation 2Manila MedNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pharmacology - Antidiabetic DrugsDocument13 pages2 - Pharmacology - Antidiabetic DrugsSoc Gerren TuasonNo ratings yet
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 pagesBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 12 Clin Path Exocrine and Endocrine Functions of The PancreasDocument13 pages12 Clin Path Exocrine and Endocrine Functions of The PancreasJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument34 pagesHomeostasisAwaid AsimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of DMDocument13 pagesNursing Care of DMItachi SanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For StrokeDocument7 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Strokegateway1119No ratings yet
- SGLT-2 InhibitorDocument41 pagesSGLT-2 InhibitorraraNo ratings yet
- Medication Used in Diabetes Mellitus 2Document3 pagesMedication Used in Diabetes Mellitus 2Joanna Maiden Gacias100% (1)
- Chapter 19 - Gluconeogenesis & Amp The Control of Blood GlucoseDocument14 pagesChapter 19 - Gluconeogenesis & Amp The Control of Blood Glucoserenzo041199No ratings yet
- 04-24-2014 Diabetes Drug Classes V0.01asDocument11 pages04-24-2014 Diabetes Drug Classes V0.01asashishhawkingNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicxx GamingNo ratings yet
- Gonzales, Elyhna Bsn2d Drugstudy Unit8Document3 pagesGonzales, Elyhna Bsn2d Drugstudy Unit8Elyhna GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Document27 pagesInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Hormone NotesDocument8 pagesHormone Noteslaeticia schmiesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part1Document6 pagesEndocrine Part1ahmed nasserNo ratings yet
- 4A Drug SheetDocument14 pages4A Drug SheetTherese PagayNo ratings yet
- Hunger Eating Thirst and Drinking Recorded LectureDocument5 pagesHunger Eating Thirst and Drinking Recorded LectureOnin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Obat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaDocument70 pagesObat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaHernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- Dka PathophysiologyDocument1 pageDka PathophysiologyClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Injectable Non-Insulin Medication Management of DiabetesDocument1 pageNursing CS Injectable Non-Insulin Medication Management of Diabetespattie29No ratings yet
- Glucagon and Control of Blood GlucoseDocument24 pagesGlucagon and Control of Blood GlucoseMdAbdulMateenNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSDocument1 pageBlood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSfatimaNo ratings yet
- A Pregnant Woman With Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 DiabetesDocument5 pagesA Pregnant Woman With Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Diabeteskenken the ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Novolin and HumulinDocument3 pagesNovolin and HumulinChynnaNo ratings yet
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 Si 2 2019Document106 pagesCurs 1 Si 2 2019Amelia PricopNo ratings yet
- GH Chap 78 - Insulin, Glucagon and DMDocument16 pagesGH Chap 78 - Insulin, Glucagon and DMShellz2428No ratings yet
- OBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Document70 pagesOBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Hernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Agents Used Thyroid and Glucose Metabolism - ClementeDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Agents Used Thyroid and Glucose Metabolism - ClementeJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesDiabetes MellitusLyra LoonNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic HormonesDocument3 pagesPancreatic HormonesShammyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For MBBS InsulinDocument49 pagesTutorial For MBBS Insulinuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Notes: Diabetes Mellitus Is A Group of Metabolic Disorders Characterized HyperglycemiaDocument14 pagesPathophysiology Notes: Diabetes Mellitus Is A Group of Metabolic Disorders Characterized HyperglycemiaHaifa ibrahimNo ratings yet
- The Science Of Glp-1 For Appetite Reduction And Weight Loss - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Appetite Management And Weight Loss StrategiesFrom EverandThe Science Of Glp-1 For Appetite Reduction And Weight Loss - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Appetite Management And Weight Loss StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Diabetes Research: Methods and TechniquesFrom EverandClinical Diabetes Research: Methods and TechniquesMichael RodenNo ratings yet
- Marco Antonio Rubino MR - Fantauzzi Canadian History Since World War I November 22, 2021Document3 pagesMarco Antonio Rubino MR - Fantauzzi Canadian History Since World War I November 22, 2021marco rubinoNo ratings yet
- English Reading PracticeDocument3 pagesEnglish Reading PracticeJovilis MajamiNo ratings yet
- FGHHJJDocument12 pagesFGHHJJRosalinaNo ratings yet
- Steroid Induced Diabetes and Hyperglycaemia Part 2 ManagementDocument5 pagesSteroid Induced Diabetes and Hyperglycaemia Part 2 ManagementAura DiscyacittaNo ratings yet
- Body Constitution - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument19 pagesBody Constitution - An Overview - ScienceDirect Topicsshawil71No ratings yet
- (Kannan Et Al., 2012) Thermal Burn of Palate in An Elderly Diabetic PatientDocument4 pages(Kannan Et Al., 2012) Thermal Burn of Palate in An Elderly Diabetic PatientAFINA MUTIAH TUHEPALYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101 (Eng) For TEX3701 2020Document38 pagesTutorial Letter 101 (Eng) For TEX3701 2020SleepingPhantoms0% (1)
- Full Download Book Arias Practical Guide To High Risk Pregnancy and Delivery PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Arias Practical Guide To High Risk Pregnancy and Delivery PDFrashad.nehring692100% (18)
- Avaliao de Ingles - EMDocument3 pagesAvaliao de Ingles - EMCarlos AndréNo ratings yet
- Brands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreDocument3 pagesBrands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreNanda Asyura RizkyaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Course During CCGDM.Document6 pagesAssignment On Course During CCGDM.Biman MondalNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Prediction Final ReportDocument31 pagesHeart Disease Prediction Final ReportMUSIC BY LOSTNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by TouhyDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhymargueriteaguilarhhcmd0100% (24)
- Manual Therapy: H. Wittink, R. Engelbert, T. TakkenDocument8 pagesManual Therapy: H. Wittink, R. Engelbert, T. TakkenJor ChavezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesDiabetes PathophysiologyRyan MulanoNo ratings yet
- DIACARE AbhilashDocument7 pagesDIACARE AbhilashKumaraguru ManickavasagamNo ratings yet
- What Diabetes Means? Type 1 Type 2Document47 pagesWhat Diabetes Means? Type 1 Type 2onevikasNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Da BombaDocument52 pagesProtocolo Da BombaEmerson SaNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Best Oral Diabetic Agents in t2 Diabetes Mellitusphysicians Challenge 2155 6156 1000797Document7 pagesChoosing The Best Oral Diabetic Agents in t2 Diabetes Mellitusphysicians Challenge 2155 6156 1000797silvanaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Care 4 U!: Enjoy The Posters!Document10 pagesDiabetes Care 4 U!: Enjoy The Posters!Mary ShermanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Wound Healing Expert GuideDocument13 pagesNutrition Wound Healing Expert GuideAlya JohNo ratings yet
- Storage of Insulin: Idf Europe Awareness PaperDocument12 pagesStorage of Insulin: Idf Europe Awareness PaperIndri AuraliaNo ratings yet
- Playbook v3Document34 pagesPlaybook v3Rufaida MudrikaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Diabetes by Pathophysiology, Natural History, and Prognosis PDFDocument15 pagesDifferentiation of Diabetes by Pathophysiology, Natural History, and Prognosis PDFHadi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Golden RetrieverDocument8 pagesGolden Retrieverpacho87No ratings yet