Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormone Notes
Uploaded by
laeticia schmiesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hormone Notes
Uploaded by
laeticia schmiesCopyright:
Available Formats
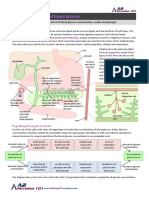
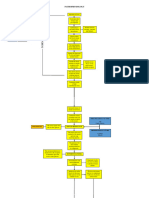
CE 3 GUC S
·
pancreas cells control blood
glucose concentration
deviation of blood glucose
level from Immol/L (80-g0mg/dL) lead to homeostasy process initrated
by moulin &
glucagon
hypotonic
·
too much too less celk become
or ,
or
hypertonic
pancreas two
glands
:
organ
in
exocrine trasue release
digestive enzymes Intestine
·
into
· endocrine trobue release hormones into blood Golets of
Langerhans
If blood
·
level fall below set point
Alpha celly
Synthesize + Secrete
glugon glucose
broken down
glycogen to
glucose in liver I released into blood
Beta 4 Secrete insulin if blood level rise point
Cells
Synthese glucose above set
Stimulate Skeletal muscle
uptake of glucose by various trosues ,
ie . a liver to convert to
glycogen
reduce blood
glucose con
insulin broken down
by cells It acts on
broken I are absorbed bloodstream
1. After meals, Carbohydrates are down into
glucose molecules into the
2 Cells that require
.
are in tissues that are
suddenly increasing the rate of respiration are
going to more
glucose than normal
You might also like
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- POGIL Control of Blood Sugar Levels PDFDocument5 pagesPOGIL Control of Blood Sugar Levels PDFJoey Ma63% (8)
- Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesDiabetes Mellitusfayeniwa100% (1)
- DM Type 1Document4 pagesDM Type 1Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- 041 LiverDocument3 pages041 Liveraistina100% (1)
- Scholarship Reinstatement Appeal Sample LettersDocument2 pagesScholarship Reinstatement Appeal Sample LettersZeejnA89% (9)
- Forbidden by God PDFDocument24 pagesForbidden by God PDFDesiderio IV Camitan100% (1)
- Models of Emotional IntelligenceDocument2 pagesModels of Emotional Intelligencegsgopalsamy100% (4)
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DMDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DMJisel-Apple Bulan100% (3)
- Physiology of HomeostasisDocument17 pagesPhysiology of HomeostasisRamadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Best Pediatric Neck MassesDocument116 pagesBest Pediatric Neck MassesOmar PeterNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Incidents RegisterDocument1 pageHazardous Incidents RegisterNitinNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control MechanismsDocument4 pagesFeedback Control MechanismsJividan SasidranNo ratings yet
- 28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SDocument5 pages28 Control of Blood Sugar Levels-SAaliya Nagori100% (1)
- HDHC Health Insurance PDFDocument5 pagesHDHC Health Insurance PDFNAYAN MEHTA0% (1)
- CBYDP SampleDocument3 pagesCBYDP SampleRenato Concepcion100% (1)
- Mimay MimaropaDocument1 pageMimay MimaropaErrol LlanesNo ratings yet
- Discovering The Self - The Digital SelfDocument27 pagesDiscovering The Self - The Digital SelfKen Ken CuteNo ratings yet
- Handling Appointment in Dental ClinicDocument19 pagesHandling Appointment in Dental ClinicNabila Bela100% (1)
- Thesis Statement of An Academic Text: Lesson 5Document15 pagesThesis Statement of An Academic Text: Lesson 5Vanessa NavarroNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFDocument3 pages1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFtiaraNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument34 pagesHomeostasisAwaid AsimNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalDocument21 pagesMetabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalMahendra Yudha NNo ratings yet
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 pagesBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms 2Document14 pagesFeedback Mechanisms 2Jade Mark PantuaNo ratings yet
- Endo-Doc LapakDocument3 pagesEndo-Doc LapakHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Biology Homestasis DiagramDocument1 pageBiology Homestasis DiagrammonteNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Lecture Note-6thDocument46 pagesDiabetes Lecture Note-6tholawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Schematic Pathophy DkaDocument2 pagesSchematic Pathophy DkaMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- DKA DrawioDocument2 pagesDKA DrawioSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesMedical Management: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Rev Notes ch18 eDocument3 pagesRev Notes ch18 eEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- AlgoDocument1 pageAlgoErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Vion - Feed Back LoopsDocument2 pagesVion - Feed Back Loopsfin vionNo ratings yet
- Type of Regulation ChartDocument6 pagesType of Regulation ChartmarNo ratings yet
- Dka PathophysiologyDocument1 pageDka PathophysiologyClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Fat in BodyDocument7 pagesGroup 2 - Fat in BodySisfa ShabelaNo ratings yet
- L11 Glucose RegulationDocument21 pagesL11 Glucose RegulationCheng FuNo ratings yet
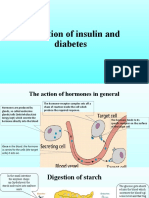
- The Action of Insulin and Diabetes PPT LLDocument12 pagesThe Action of Insulin and Diabetes PPT LLLili lengyelNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document1 pagePatho 1ricciNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document8 pagesPresentation 3mben4956No ratings yet
- Hormones and The Coordinating System of AnimalsDocument48 pagesHormones and The Coordinating System of AnimalsElaine MontealtoNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 13 - HormoneDocument11 pages(BIO) Chapter 13 - HormonewengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument31 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucoseLisandrea BrownNo ratings yet
- Glucose regulation-RSKDocument4 pagesGlucose regulation-RSKdevilalshingh9525No ratings yet
- Homeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in BloodDocument13 pagesHomeostatis Principles and Regulation of Glucose in Bloodk75544863No ratings yet
- Book Chapter Carbohydrate Storage and MetabolismDocument16 pagesBook Chapter Carbohydrate Storage and Metabolismq8laNo ratings yet
- Glucose Physiology, Normal.Document8 pagesGlucose Physiology, Normal.hajrahsuhardiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyjohnbech07No ratings yet
- Nursing - CS - Review of Insulin and Glucose Control - 01 1Document1 pageNursing - CS - Review of Insulin and Glucose Control - 01 1pattie29No ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanism Animal PhysiologyDocument27 pagesFeedback Mechanism Animal PhysiologyBacon ZenNo ratings yet
- Pathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionDocument6 pagesPathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionBrandt CajoconNo ratings yet
- P4-Obesity and The Regulation of Body MassDocument8 pagesP4-Obesity and The Regulation of Body MassOcta RenitaNo ratings yet
- Gluco Neo GenesisDocument6 pagesGluco Neo GenesisNizam YahyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSDocument1 pageBlood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSfatimaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Question Experiment 5Document6 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 5Skefadiuto100% (3)
- Gluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)Document28 pagesGluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)saadzubair0307No ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument8 pagesHomeostasisMeatball BananaNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinBobNo ratings yet
- HUBS191: Lecture 38: Revision and IntegrationDocument10 pagesHUBS191: Lecture 38: Revision and IntegrationCharissa HooiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Xid-31373689 2Document18 pagesXid-31373689 2Tan Yong MingNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab FinalsDocument10 pagesBiochem Lab FinalsAJ DuenasNo ratings yet
- OBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Document70 pagesOBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Hernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - Glycolysis-2Document8 pagesMetabolism - Glycolysis-2Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Irregularity of Glycogen Synthase Homeostasis Complications Hepatic and Neuro DefectsDocument11 pagesIrregularity of Glycogen Synthase Homeostasis Complications Hepatic and Neuro DefectsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Cap 8 Appleton Homeostasis de GlucosaDocument14 pagesCap 8 Appleton Homeostasis de GlucosaMariandré OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Dietary Management - Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesDietary Management - Diabetes MellitusReanne Mae AbreraNo ratings yet
- Matthew Recorr Resume 1Document3 pagesMatthew Recorr Resume 1api-264456532No ratings yet
- MWRC Policies & Procedures Manual 2020Document10 pagesMWRC Policies & Procedures Manual 2020Emma RyersonNo ratings yet
- SOAL English USBN 2022Document10 pagesSOAL English USBN 2022Amrina RosyadaNo ratings yet
- MCI Screening Test Result of Mbbs Universities AbroadDocument54 pagesMCI Screening Test Result of Mbbs Universities AbroadYukti Belwal100% (4)
- Spinal & Posture CorrectionDocument5 pagesSpinal & Posture CorrectionAmir HabibNo ratings yet
- Lifting, Moving and Rapid ExDocument13 pagesLifting, Moving and Rapid Expdfs.olpNo ratings yet
- G11 - PAG-ASA Teacher's GuideDocument1 pageG11 - PAG-ASA Teacher's Guidefatima naranjoNo ratings yet
- CALCUALTIONDocument2 pagesCALCUALTIONGeraldine MagnanaoNo ratings yet
- Artículo Grupo 3Document7 pagesArtículo Grupo 3antogallardovdlnNo ratings yet
- The FDA Group - The OTC Drug Manufacturer's Guide To CGMP Compliance and Quality ManagementDocument19 pagesThe FDA Group - The OTC Drug Manufacturer's Guide To CGMP Compliance and Quality ManagementAri CleciusNo ratings yet
- Gi 6.004-Near-Miss-Reporting-ProcessDocument5 pagesGi 6.004-Near-Miss-Reporting-ProcessAyman AdilNo ratings yet
- Diptiman Paramedical College and Hospital - 1Document48 pagesDiptiman Paramedical College and Hospital - 1DharmaNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesapi-643769053No ratings yet
- Medical 19.08.2023Document20 pagesMedical 19.08.2023Дмитрий ПирусNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document3 pagesCase 1Jeanny Lou Lago-FormosoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentDocument16 pagesModule 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentLaw HacksNo ratings yet
- 1964 Lawrence A. WeinbergDocument13 pages1964 Lawrence A. Weinberg謎超人No ratings yet
- Superintendents Contract 2023-26Document6 pagesSuperintendents Contract 2023-26Matthew SelfNo ratings yet
- Nuevo - NCP (Module 2)Document4 pagesNuevo - NCP (Module 2)Nuevo, Kayesha E.No ratings yet