100% found this document useful (1 vote)
577 views67 pagesRotary Kiln & ATOX Mill Maintenance
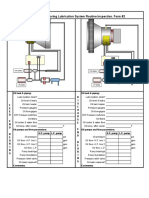
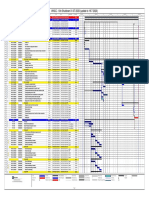
The document discusses advanced maintenance techniques for rotary kilns and raw mills. It covers different types of maintenance including reactive, preventive, predictive, and reliability-centered maintenance. Key components that require maintenance on rotary kilns are discussed in detail, including the kiln shell, supporting rollers and tyres, inlet/outlet seals, thrust rollers, and drive system. Condition monitoring techniques are recommended to predict failures and schedule maintenance to minimize downtime.
Uploaded by
Muhammad YaseenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
577 views67 pagesRotary Kiln & ATOX Mill Maintenance
The document discusses advanced maintenance techniques for rotary kilns and raw mills. It covers different types of maintenance including reactive, preventive, predictive, and reliability-centered maintenance. Key components that require maintenance on rotary kilns are discussed in detail, including the kiln shell, supporting rollers and tyres, inlet/outlet seals, thrust rollers, and drive system. Condition monitoring techniques are recommended to predict failures and schedule maintenance to minimize downtime.
Uploaded by
Muhammad YaseenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd