100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views10 pagesLearning Episode 1 Educational Theories - PONIENTE
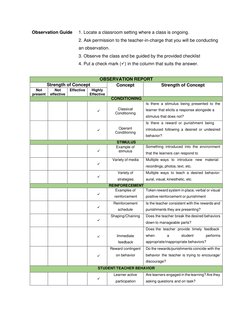
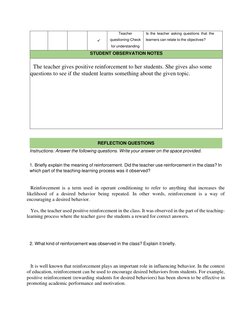
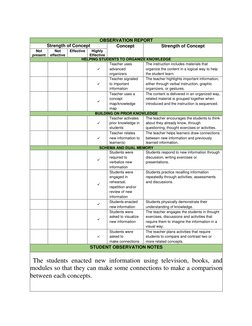
The teacher utilized operant conditioning in the classroom by providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors and removing privileges for undesired behaviors. A variety of media was used as stimuli to elicit responses from learners, including recordings, photos, and text. Positive reinforcement like rewards and praise were given to encourage participation and check for understanding. Overall, operant conditioning proved an effective approach for influencing student behavior.
Uploaded by
Cid PonienteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views10 pagesLearning Episode 1 Educational Theories - PONIENTE
The teacher utilized operant conditioning in the classroom by providing positive reinforcement for desired behaviors and removing privileges for undesired behaviors. A variety of media was used as stimuli to elicit responses from learners, including recordings, photos, and text. Positive reinforcement like rewards and praise were given to encourage participation and check for understanding. Overall, operant conditioning proved an effective approach for influencing student behavior.
Uploaded by
Cid PonienteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd