Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESS
Uploaded by
Cielo PetilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESS
Uploaded by
Cielo PetilCopyright:
Available Formats
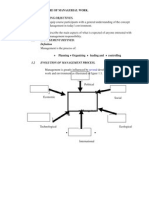
LESSON 4: Functions, Roles and Skills of a Manager
Manager is one who plans, organizes, leads and controls other individuals in the process of
pursuing organizational goals.
Level of Managers (by size of organization)
Top Managers – are responsible for the overall performance of the organization. They
formulate strategies, provide leadership,evaluate and shape the method of organizing and control the
direction of the organization in the effort to accomplish goals.
Middle Managers – direct the activities of other manager and sometimes also those operating
employees. They work with top managers and coordinate with peers to develop and implement
action plans to accomplish organizational objectives.
Lower level managers – are responsible for leading employees in the day to day task which
contribute to the organization’s goals.
TYPES OF MANAGERS
1. Line Managers – directly concerned with accomplishing the goals of the organization. The
decision they make with regards to operation are expected to be final and must be implemented.
2. Staff Managers – are in charge of units that provide support to the line units., they use
special expertise to advise the line workers.
3. Administrators – managers working in government or in non-profit organizations
MANAGERIAL ROLES
Role - is defined as an expected set of activities of behaviors stemming from a job.
1. INTERPERSONAL ROLES
The managerial roles in this category involve providing information and ideas. It involves
human interaction inside and outside work unit.
a. Figurehead
when the manager perform this role, he/she acts as the symbolic head of the
organization and as a result he expected to perform a number of duties of a legal or social
nature.
expected to be a source of inspiration.
b. Leader – this role makes the manage responsible for the motivation and activation of
subordinates. He is responsible for action in staffing, training and other associated duties.
c.Liaison – in assuming the liaison role, the manager makers contacts with individuals in and
out of the organization to facilitate the accomplishment of work in his department.
Managers must communicate with internal and external contacts. You need to be able to
network effectively on behalf of your organization.
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 1
2. INFORMATIONAL ROLES
The managerial roles in this category involve processing information
- a very important aspect of the manager’s job is to receive and communicate information.
- On receiving and sharing information, the manager assumes three specific roles.
1. Monitor – concern in various aspects of an organization, the manager is expected to collect
information that will be useful in performing his job.
In monitor, he handles all mails and contacts categorized as concerned primarily with
receiving information using such sources as news bulletin, special magazines and observation tours.
In other words, as a manager you regularly seek out information related to your organization
and industry, looking for relevant changes in the environment. You also monitor your team, in terms
of both their productivity and their well-being.
2. Disseminator – there are certain type of information that the manager may consider useful
to his subordinates. Some of the information may be factual and some may involve interpretation and
integration. As information disseminator, the manager sees to it that the relevant incoming
information is properly shared with subordinates.
3. Spokesperson – To effectively perform the role of spokesperson the manager sees to it that
his views are heard on occasions requiring his presence such as board meetings.
Managers represent and speak for their organization. In this role, you're responsible for
transmitting information about your organization and its goals to the people outside it.
3. DECISIONAL ROLES
The managerial roles in this category involve using information.
A. Entrepreneur – managers searches the organization and its environment for opportunities and
initiates projects to bring about positive change.
B. Disturbance handler
being a manager, he expected to respond to unwelcome pressures by formulating strategies
and reviewing such disturbances.
When an organization or team hits an unexpected roadblock, it's the manager who must take
charge. You also need to help mediate disputes within it.
C. Resource Allocator
The manager is responsible for the allocation of organizational resources of all kind such as
personnel, funds, machines or buildings and facilities to individual employees or units.
D. Negotiator
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 2
You may be needed to take part in, and direct, important negotiations within your team,
department, or organization. Negotiating in that the manager has to be the middle person in dealing with
the human resources and the business affiliates.
LESSON 5: MANAGAMENT SKILLS
Skills – an ability coming from someone’s knowledge, practice and aptitude to do something
well,as well as to translate that something into action that results in desired performance.
1. Technical Skills
- refers to the abilities to use special proficiency or expertise in performing specific tasks.
- they refer to the use of tools, techniques and specialized knowledge.
2. Human Skills/Interpersonal Skills
- refer to the abilities to work well in cooperation with other persons; whether they are
subordinates, peers and superiors. A person with good human skills will have a high degree of self-
awareness and a capacity for understanding or empathizing with feeling of others.
Communication skills are important component of interpersonal skills. And this skills is closely related
to person’s emotional intelligence.
3. Conceptual Skills/Analytical Skills – refer to the ability of the manager to see the organization as
a whole and to solve problems in was that benefit the total system. Specifically the manager who.
Possesses these skills is expected to analyze and solve complex problems. Thus the manager with
good conceptual skills will have the metal capacity to perform the following:
a. identify problems and opportunities
b. gather and interpret relevant information
c. execute problems solving decisions that serve the organization’s purpose.
*****
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 3
Chapter 2: The FIRM AND ITS ENVIRONMENT
Knowledge about management and organization is very useful especially in human endeavors like
operating a business firm.
A. Business defined as all profit-seeking activities and enterprises that provide goods and services to
an economic system.
Environmental Scanning
- process of identifying and analyzing the various forces or elements interacting and
influencing interacting with the organization.
Through this process, the organization decide how to can respond to the various issues and
challenges brought about by these forces.
VARIOUS FORCES/ELEMENTS OF EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
Of all the outside factors or influences that impact the operation of the business. The business
must act or react to keep up its flow of operations. The external environment can be broken down
into two types: the macro environment and micro-environment.
MACRO ENVIRONMENT
It consists of the most general elements that can potentially influence the strategic and long-term
decisions of the firm. These forces/elements are uncontrollable- the firm does not have any
control over them, but the firm can think of various ways to respond and adapt to the influences
that these may bring to the organization.
1. Demographic Conditions
It is the statistical study of people and the human population. Information such as age, sex,
marital status, family size, occupation, and the like are being gathered by businesses to forecast
future trends and consumption of the products and services that they may offer.
2. Economic conditions - It refers to the overall health of the economy. The economy can effect on
two essential aspects – your company’s levels of production and the decision-making process of your
customers.
3. Political - Legal conditions - It refers to national or local laws, international laws, and rules and
regulations that influence organizational management.
4. Technological Conditions- Refers to advancement and development in technology and its
availability and ability to help business prosper and operate more effectively.
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 4
5. Socio-cultural conditions – It refers to the structure and dynamics of individuals and groups and
how these affect their behaviors, belief, and lifestyles.
6. World and Ecological Environment conditions - This refers to the physical environment of the
organization and the resources available to be able to produce output. It also refers to how the firms
can meet the needs of their customers while advancing the well being of the natural environment.
MICRO ENVIRONMENT
It consists of all the actual organizations, groups, and persons with whom the organization interacts
and conducts business. It is also called a task environment or competitive environment
1. COMPETITORS
These includes rival firms within the same industry and the ways that they behave competitively
towards one another.
2. CUSTOMERS
Customers are those who patronize the organization’s products and services. Increasing customer
sophistication makes it necessary for managers of organizations to make crucial decisions regarding
the development of products with higher value and the improvement of their services to meet their
patrons’ increasing demand.
3. SUPPLIERS
Managing the supply chain and distribution network should also be a primary focus of businesses
that strive to be successful. A well-managed supply chain reduces operational costs and improves
efficiency. Some companies that have managed efficient supply chains have been able to pass the
savings to their customers.
4. SUBSTITUTE AND COMPLEMENTS
Products that can serve as an alternative to other product are called substitute.
Complements - those products that need to be used along with other products
This is based on the ability of consumers to find what they want from the sellers.
5. NEW ENTRANTS
These include new competitors entering the market and depend on the presence or absence of
barriers of entry into the market.
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 5
ELEMENTS OF INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
Generally consists of those elements that exist within or inside the organization such as physical
resources, financial resources, human resources, information resources, technological resources,
organization’s goodwill, corporate culture, and the like.
1. Owners and Shareholders - Owners are people who invested in the company and have property
rights and claims on the organization. Owners can be an individual or group of persons who started
the company; or who bought a share of the company in the share market.
2. Board of Directors- The board of directors is the governing body of the company who is elected by
stockholders, and they are given the responsibility for overseeing a firm’s top managers such as the
general manager.
3. Employees - Employees or the workforce, the most important element of an organization’s internal
environment, which performs the tasks of the administration. Individual employees and also the
labor unions they join are important parts of the internal environment.
4. Organizational Culture - Organizational culture is the collective behavior of members of an
organization and the values, visions, beliefs, habits that they attach to their actions.
5. Resources of the Organization - An organization s resources can be discussed under five broad
heads: physical resources, human resources; financial resources, informational resources, and
technological resources. Physical resources include land and buildings, warehouses, all kinds of
materials, equipment, and machinery.
6. Organization’s image/goodwill - The reputation of an organization is a very valuable intangible
asset. High reputation or goodwill develops a favorable image of the organization in the minds of the
public
“No- reputation” cannot create any positive image. A negative image destroys the
organization’s efforts to attract customers in a competitive world.
*****
Reference
https://www.educba.com/how-to-apply-management-theories-at-workplace/
Organization and Management, Ng, Mark Francis
Organization and Management, Medina, Robert
INFORMATION SHEET OM_1st Sem19-
20 | 6
You might also like
- Mgt501 - Human Resource Management Mcqs Solved by Shining Star ($$)Document503 pagesMgt501 - Human Resource Management Mcqs Solved by Shining Star ($$)ZainNo ratings yet
- Summer InternshipDocument27 pagesSummer InternshipAfnain AmmanNo ratings yet
- Drucker's Five Basic Operations in The Work of Manager: A Manager Sets ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDrucker's Five Basic Operations in The Work of Manager: A Manager Sets ObjectivesAvery Jan Silos100% (1)
- Roles Skills of A ManagerDocument8 pagesRoles Skills of A ManagerDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Process in IfortisDocument83 pagesRecruitment and Selection Process in Ifortisravi singh75% (4)
- Overview of Management and OrganizationDocument50 pagesOverview of Management and OrganizationDennisBrionesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Principles of ManagementDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Principles of ManagementLisa GalinaNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM506 Assessment 5Document24 pagesBSBHRM506 Assessment 5Sunita Reddy100% (1)
- Organizational ManagementDocument5 pagesOrganizational Managementmae ledesmaNo ratings yet
- lecture 1Managers, decision making, management roles & chapetr 1Document4 pageslecture 1Managers, decision making, management roles & chapetr 1genshinislifeloveNo ratings yet
- Om Handouts Lesson 3Document24 pagesOm Handouts Lesson 3Prose Kate CutorNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management ReviewerDocument17 pagesOrganization and Management ReviewerMariedol RamelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document30 pagesLesson 2Thea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- OrgMgt QTR 1 Functions Roles and Skills of ManagersDocument18 pagesOrgMgt QTR 1 Functions Roles and Skills of Managersjustindimaandal8No ratings yet
- Management Functions ExplainedDocument43 pagesManagement Functions ExplainedPreeti Mishra DubeyNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Management AND OrganizationDocument39 pagesAn Overview of Management AND Organizationhey JoguNo ratings yet
- Q1 OM MODULE 3 Converted 1Document32 pagesQ1 OM MODULE 3 Converted 1Elaiza GaytaNo ratings yet
- Essay Es27 NotesDocument10 pagesEssay Es27 NotesJake LobrigasNo ratings yet
- Management of Small FirmsDocument3 pagesManagement of Small FirmsSurvi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Document3 pagesOrganization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1111)Document19 pagesChapter 1 (1111)Abdallah ShamelNo ratings yet
- Orma ReviewerDocument13 pagesOrma Reviewer21-50974No ratings yet
- Student'S Activity Sheet: Skills-And-Role/90741 MDocument9 pagesStudent'S Activity Sheet: Skills-And-Role/90741 MAizelle SalibayNo ratings yet
- Management PrinciplesDocument81 pagesManagement PrinciplesTheo Van Schalkwyk67% (3)
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State College: Alijis Campus - Binalbagan Campus - Fortune Towne Campus - Talisay CampusDocument11 pagesCarlos Hilado Memorial State College: Alijis Campus - Binalbagan Campus - Fortune Towne Campus - Talisay CampusErnest John Seguisabal100% (1)
- INTRO TO MGMT NOTES: DEFINITIONS, ROLES, SKILLS & FUNCTIONSDocument8 pagesINTRO TO MGMT NOTES: DEFINITIONS, ROLES, SKILLS & FUNCTIONSMohammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Course: Organizational BehaviorDocument12 pagesCourse: Organizational BehaviorABDUL KARIM ASLAMINo ratings yet
- Imem Unit IVDocument60 pagesImem Unit IVjanagyrama1No ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN QUẢN TRỊ HỌCtiếng anhDocument16 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN QUẢN TRỊ HỌCtiếng anhNguyễn Thị Mỹ LinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document2 pagesUnit 1Unsolved MistryNo ratings yet
- MBA Individual Assignment Roles in MISDocument9 pagesMBA Individual Assignment Roles in MISአረጋዊ ሐይለማርያምNo ratings yet
- Quản trị học tiếng anh - HI 47K DUE ZDocument16 pagesQuản trị học tiếng anh - HI 47K DUE ZThúy VyNo ratings yet
- ABMDocument7 pagesABMDUMALAG GENEVIEVENo ratings yet
- Organizational Design Apuntes FinalDocument68 pagesOrganizational Design Apuntes FinalMarinaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Manager: Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing & ControllingDocument9 pagesFunctions of Manager: Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing & ControllingMlyn100% (1)
- Chapter 1editedDocument13 pagesChapter 1editedMuktar jiboNo ratings yet
- Changing Nature of Managerial WorkDocument10 pagesChanging Nature of Managerial WorkakramNo ratings yet
- CFLM - Final Examination Reviewer JANUARY 3 - 9, 2022 Characteristics of A Good ManagerDocument2 pagesCFLM - Final Examination Reviewer JANUARY 3 - 9, 2022 Characteristics of A Good ManagerLeonard MaestrocampoNo ratings yet
- Roles of ManagerDocument7 pagesRoles of ManagerShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersDocument64 pagesWho Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersMansiNo ratings yet
- Business ManagementDocument8 pagesBusiness ManagementAvadhut PaymalleNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE mgDocument3 pagesCHAPTER ONE mgNikodimos yeshitilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Managing & ManagersDocument23 pagesChapter - 1: Managing & Managerscooldude690No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Management Today-DoneDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Management Today-Donebbypia johnNo ratings yet
- Notes MGTDocument62 pagesNotes MGTGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Leadership 2Document30 pagesLeadership 2Miko Paolo SanchezNo ratings yet
- MGMT 1001Document25 pagesMGMT 1001Joey XUNo ratings yet
- Management Principles MNG 2601 Summary of TextDocument82 pagesManagement Principles MNG 2601 Summary of Textpagieljcgmailcom80% (5)
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Josh LaxaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document13 pagesWeek 1Franco PagdonsolanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1Nishani wickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Quản trị học tiếng anh - HI 48K DUE ZDocument16 pagesQuản trị học tiếng anh - HI 48K DUE ZKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Teaching NoteDocument47 pagesTeaching NoteSandhya Darshan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Principles of ManagementDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Principles of ManagementWilfredo Jr CanilangNo ratings yet
- Difence University College of EngineeringDocument8 pagesDifence University College of Engineeringyisakabera0227No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Managers in The WorkplaceDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Managers in The WorkplaceMy KiềuNo ratings yet
- Business ManagementDocument64 pagesBusiness Managementshantel tinotendaNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENTDocument24 pagesMANAGEMENTMónika NémethNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes PPMDocument124 pagesLecture Notes PPMFadil RushNo ratings yet
- BBM1201 Principles of ManagementDocument8 pagesBBM1201 Principles of Managementwriter bestNo ratings yet
- A Study On Exit Interview in Relation To Employer BrandingDocument6 pagesA Study On Exit Interview in Relation To Employer BrandingPiyushNo ratings yet
- Changing Perspectives of HRMDocument5 pagesChanging Perspectives of HRMFrancine De veraNo ratings yet
- Answer A) Job Analysis: You May Also LikeDocument91 pagesAnswer A) Job Analysis: You May Also LikeSANTOSH GORENo ratings yet
- TranDocument24 pagesTrantapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- Northeastern College Graduate Term Paper on Staff Personnel ManagementDocument17 pagesNortheastern College Graduate Term Paper on Staff Personnel Managementsharon agustinNo ratings yet
- Hra Ai - 2 Human Resource Accounting Is A Method To Measure The Effectiveness of Personnel Management Activities and TheDocument8 pagesHra Ai - 2 Human Resource Accounting Is A Method To Measure The Effectiveness of Personnel Management Activities and The$!v@No ratings yet
- Personnel Planning and RecruitingDocument38 pagesPersonnel Planning and RecruitingMamun RashidNo ratings yet
- Market Oriented Strategic PlanningDocument52 pagesMarket Oriented Strategic PlanningSaadNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics For Mba HR StudentsDocument6 pagesDissertation Topics For Mba HR StudentsPapersWritingServiceUK100% (1)
- 5 6 7 Management of International Business ActivitiesDocument41 pages5 6 7 Management of International Business ActivitiesQuynh Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Using Iso 9001 To Improve Sales Operation Performance: A Case Study of Implementationf ISO 9001Document7 pagesUsing Iso 9001 To Improve Sales Operation Performance: A Case Study of Implementationf ISO 9001owngauravNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument23 pagesHuman Resource ManagementS M HashirNo ratings yet
- Igaming Salary Survey 2023Document16 pagesIgaming Salary Survey 2023Goran AndreevskiNo ratings yet
- JD-Payroll OfficerDocument3 pagesJD-Payroll OfficerElmer GwapoNo ratings yet
- The Hotel Paris Case StudyDocument3 pagesThe Hotel Paris Case StudyShafaq NigarNo ratings yet
- HR Armaan PDFDocument93 pagesHR Armaan PDFzomaan mirzaNo ratings yet
- Summary ReportDocument5 pagesSummary ReportCassia ィNo ratings yet
- Perspective Management - Group 10: Guided by Prof. Stephen D'SilvaDocument54 pagesPerspective Management - Group 10: Guided by Prof. Stephen D'SilvaNorman LewisNo ratings yet
- Management & Entrepreneurship Course CodeDocument97 pagesManagement & Entrepreneurship Course CodeKaushik Karthikeyan KNo ratings yet
- Current Trends in HR ManagementDocument18 pagesCurrent Trends in HR ManagementPROFESSOR DON DALIDNo ratings yet
- To Whomsoever It May ConcernDocument1 pageTo Whomsoever It May ConcernParvishMarmatNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Ventures in The PhilippinesDocument25 pagesEntrepreneurial Ventures in The Philippinescydralekaye.leyrosNo ratings yet
- 2012 Tillingate Living Case Study Feedback ReportDocument48 pages2012 Tillingate Living Case Study Feedback ReportVathasil VasasiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - HR Management and The SA Labour Legislation Framework V1Document36 pagesChapter 12 - HR Management and The SA Labour Legislation Framework V1Terilee PillayNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Amazon As An EmployerDocument2 pagesCase Analysis - Amazon As An EmployerDharampreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Figure 2.6 Organizational Structure: PartnersDocument4 pagesFigure 2.6 Organizational Structure: Partnersjanel anne yvette sorianoNo ratings yet