100% found this document useful (1 vote)
895 views2 pagesDiltiazem
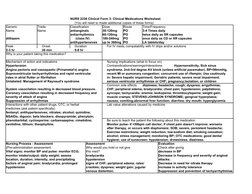
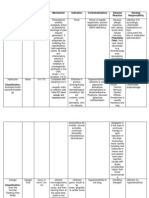
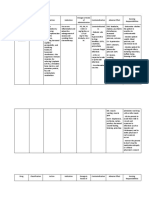
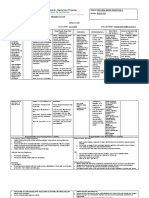
This document provides information about the medication diltiazem, including its classification, dosing, mechanisms of action, nursing implications, interactions, and monitoring. Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias. It works by vasodilation to decrease blood pressure and coronary vasodilation to reduce angina attacks. Nurses should monitor for side effects like hypotension, bradycardia, and heart failure and educate patients about drug interactions and signs requiring medical attention.
Uploaded by
ECopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
895 views2 pagesDiltiazem
This document provides information about the medication diltiazem, including its classification, dosing, mechanisms of action, nursing implications, interactions, and monitoring. Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias. It works by vasodilation to decrease blood pressure and coronary vasodilation to reduce angina attacks. Nurses should monitor for side effects like hypotension, bradycardia, and heart failure and educate patients about drug interactions and signs requiring medical attention.
Uploaded by
ECopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd