Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intrinsic Extrinsic Pathway
Uploaded by
Angni, AsnoraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intrinsic Extrinsic Pathway
Uploaded by
Angni, AsnoraCopyright:
Available Formats
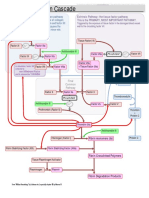
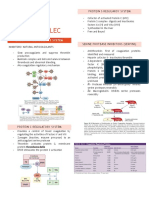
INTRINSIC
PATHWAY
Factor XII Factor XIIa
Factor XII (Hageman Factor,
Contact Factor)
Factor XII plays a primary role in
initiation of the contact or intrinsic
pathway of coagulation upon
binding with substances such as
glass or kaolin. The contact pathway
is the basis for the APTT clotting
assay. Specifically, factor XII is a clotting
factor. Clotting factors are specialized
proteins that are essential for proper
clotting, the process by which blood
clumps together to plug the site of a
wound to stop bleeding.
FACTOR XI FACTORS XIa
PLASMA THROMBOPLASTIN Factor XIIA acts as a catalyst to
ANTECEDENT (PTA, factor XI) activate factor XI to Factor XIA.
Factor XIA then goes on to activate
FACTOR XI is a plasma protein
factor IX to factor IXA. Factor IXA
functionally deficient in plasmas of
goes on to serve as a catalyst for
patients with congenital PTA
turning factor X into factor Xa.
deficiency. This agent participates early
This is known as a cascade.
in the intrinsic pathway of blood
coagulation.
FACTOR IX FACTOR IXa
Endothelial collagen is only exposed
when endothelial damage occurs. Factor
The Christmas factor (IX) is XIIA acts as a catalyst to activate factor
produced from the liver. Its XI to Factor XIA. Factor XIA then goes
production is activated by on to activate factor IX to factor IXA.
clotting factor XI (plasma Factor IXA goes on to serve as a
prothromboplastin antecedent) catalyst for turning factor X into factor
and calcium. Xa.
FACTOR X FACTOR Xa
Factor X is a clotting protein (also called Coagulation factor Xa is a protein
a clotting factor). Clotting factors are that reverses the effects of certain
specialized proteins that are essential for anticoagulant medications that are
proper clotting, the process by which used to treat or prevent blood clots.
blood clumps together to plug the site of Reversing anticoagulant medicine is
a wound to stop bleeding. Clotting necessary if you have uncontrolled or
requires a series of reactions to ultimately life-threatening bleeding as a result of
form a clot to plug a wound. how that medicine works.
EXTRINSIC
PATHWAY
FACTOR VII FACTOR VIIa
+
Once the damage to the
vessel is done, the epithelial TISSUE FACTOR
cells release tissue factor
which goes on to activate the (THROMBOPLASTIN)
factor VII to factor VIIa
Upon contact with blood plasma,
the damage extravascular cells,
release the thromboplastin. Ca2+
then the factor VII is activated and
forming an enzyme complex
FACTOR X FACTOR IXa
It can be activate by the factor VIIa –
TF(tissue factor) and Ca2+complex FACTOR VIIIa
via an extrinsic pathway and by
factor IXa in the presence of Ca2+ via (cofactor for IXa)
an intrinsic pathway of blood
coagulation system activation.
FACTOR X FACTOR Xa
The enzyme complex Factor VIIa goes on to activate
leads to the activation of factor X and Factor Xa this is the
factor X (Stuart-Power point where both extrinsic and
Factor) which activates intrinsic pathways become one.
the common pathway
You might also like
- HematologySlides2020 FullSizeDocument812 pagesHematologySlides2020 FullSizeNikos SyrigosNo ratings yet
- Platlets DisorderDocument177 pagesPlatlets DisorderFatimah A Al-dawoodNo ratings yet
- Use of Fresh Blood For Quality Control: Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument6 pagesUse of Fresh Blood For Quality Control: Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateTriana AmaliaNo ratings yet
- CSF SopDocument19 pagesCSF SopdeblackaNo ratings yet
- RBCDocument66 pagesRBCFarah mansourNo ratings yet
- Cobas 8000 Data ManagerDocument278 pagesCobas 8000 Data Manageradvanced techNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell Morphology Controversies and Alternativ PDFDocument137 pagesBlood Cell Morphology Controversies and Alternativ PDFWa Nur Arlin RahmadhantyNo ratings yet
- Validation Cell AnalyzersDocument45 pagesValidation Cell AnalyzerscandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- "Westgard Rules" and MultirulesDocument27 pages"Westgard Rules" and MultirulesNurul Aeni FitriyahNo ratings yet
- 300-5208 B BFM Clsi SopDocument23 pages300-5208 B BFM Clsi SopnjujjnjnjjnnjNo ratings yet
- DI-60 Integrated Slide Processing System BrochureMKT-10-1196 - Rev4Document12 pagesDI-60 Integrated Slide Processing System BrochureMKT-10-1196 - Rev4Hw XuNo ratings yet
- Techtalk August2010Document2 pagesTechtalk August2010Abu KhalidNo ratings yet
- Slide Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid For Cytological ExaminationDocument3 pagesSlide Preparation of Cerebrospinal Fluid For Cytological ExaminationMurshed HaidarNo ratings yet
- CC1 - Topic 1Document11 pagesCC1 - Topic 1Marie MontemarNo ratings yet
- Sysmex HemostasisDocument11 pagesSysmex HemostasisElyza L. de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis UNseries14pp 20072020 1Document13 pagesUrinalysis UNseries14pp 20072020 1Nurmi SyahidahNo ratings yet
- c8k Quick Reference Guide en 2.0Document36 pagesc8k Quick Reference Guide en 2.0advanced techNo ratings yet
- Hemophilia and Factor Assay PDFDocument17 pagesHemophilia and Factor Assay PDFSumaira JunaidNo ratings yet
- AutoverificationDocument5 pagesAutoverificationRuny RunyNo ratings yet
- CE (Ra) F (SH) PF1 (MJ GG) PFA (PR SS)Document4 pagesCE (Ra) F (SH) PF1 (MJ GG) PFA (PR SS)Krishna DubeyNo ratings yet
- Auto-Release: David Plaut Beth Friedt & Tammy TaylorDocument51 pagesAuto-Release: David Plaut Beth Friedt & Tammy TaylorasclswisconsinNo ratings yet
- The Peripheral Blood FilmDocument5 pagesThe Peripheral Blood FilmanggaririnNo ratings yet
- Product Introduction: Cellavision Dc-1 Loading Capacity: 1 Slide Throughput: 10 Slides/Hr Technical SpecificationsDocument12 pagesProduct Introduction: Cellavision Dc-1 Loading Capacity: 1 Slide Throughput: 10 Slides/Hr Technical SpecificationsElyza L. de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Morphology of HematologyDocument11 pagesMorphology of HematologyChabNo ratings yet
- CBC Referenge Range ADULTDocument2 pagesCBC Referenge Range ADULTCarl DevinNo ratings yet
- Nephelometry LODocument8 pagesNephelometry LOSantiagoAFNo ratings yet
- Identification of Normal and Abnormal Forms of RedDocument32 pagesIdentification of Normal and Abnormal Forms of RedNada hasanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Approach in HematologyDocument33 pagesStatistical Approach in HematologycandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaDocument30 pagesMicroscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Sysmex SEED 4 2013 Automated Haematology Sample Interferences Flagging and Results Interpretation - Part 1 enDocument8 pagesSysmex SEED 4 2013 Automated Haematology Sample Interferences Flagging and Results Interpretation - Part 1 enPieter Du Toit-Enslin50% (2)
- Laboratory Hematology CriteriaDocument7 pagesLaboratory Hematology CriteriaRosNo ratings yet
- Pro64-E-01 Body Fluid SOPDocument14 pagesPro64-E-01 Body Fluid SOPmmNo ratings yet
- Coag Made EasyDocument16 pagesCoag Made EasyBrian RobertsNo ratings yet
- Blood ReportDocument39 pagesBlood Reportputri Mentari100% (1)
- RBC MorphologyDocument9 pagesRBC MorphologybiancsNo ratings yet
- ICSH Guidelines For The Evaluation of Blood Cell AnalysersDocument16 pagesICSH Guidelines For The Evaluation of Blood Cell Analyserssellappan marappanNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell AbnormalitiesDocument9 pagesRed Blood Cell AbnormalitiesIez FatihahNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDocument7 pagesBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Hema II Chapter11 - QA in HematologyDocument29 pagesHema II Chapter11 - QA in HematologyAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- ADVIA-2120i Hematology TrainingDocument73 pagesADVIA-2120i Hematology TrainingLoay TibiNo ratings yet
- Platelet CountsDocument35 pagesPlatelet Countsshikhar623No ratings yet
- Data Interpretation - Factor Assays - AnswersDocument47 pagesData Interpretation - Factor Assays - AnswersSafdar Shabir Awan100% (1)
- Diagnosis of HemophiliaDocument150 pagesDiagnosis of HemophiliaresmasmanNo ratings yet
- 5-Westgard Quality Control 4 SlidesDocument9 pages5-Westgard Quality Control 4 SlidesPaul Avelino CallupeNo ratings yet
- The Diagnostic Use of ADVIA 2120i Siemens and An "APL Criteria" CanDocument9 pagesThe Diagnostic Use of ADVIA 2120i Siemens and An "APL Criteria" CananggaririnNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnosis in HaematologyDocument23 pagesMolecular Diagnosis in HaematologyUmar'Farouq Oni100% (1)
- 5 - Introducing XN and XN-L - Sudan PDFDocument57 pages5 - Introducing XN and XN-L - Sudan PDFAl- ImanuddinNo ratings yet
- Lipemia: Causes, Interference Mechanisms, Detection and ManagementDocument16 pagesLipemia: Causes, Interference Mechanisms, Detection and ManagementkartikaparamitaNo ratings yet
- RBCs Abnormal Morphology FinalDocument33 pagesRBCs Abnormal Morphology FinalInahkoni Alpheus Sky OiragasNo ratings yet
- 03 - Approach Hematolymphoid NeoplasmsDocument119 pages03 - Approach Hematolymphoid NeoplasmscandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Hemolysis Lipemia and High Bilirubin Effect On Laboratory Tests 2013 Accurate Results in The Clinical LaboratoryDocument10 pagesChapter 5 Hemolysis Lipemia and High Bilirubin Effect On Laboratory Tests 2013 Accurate Results in The Clinical LaboratoryCristina Gaidargi100% (1)
- Criteria For Specimen AcceptabilityDocument3 pagesCriteria For Specimen AcceptabilityFatwa100% (1)
- Red Blood Cell MorphologyDocument5 pagesRed Blood Cell MorphologyRyan KadavilNo ratings yet
- Endomitosis. EndomitosisDocument22 pagesEndomitosis. EndomitosisRUBEN DAMAYO100% (1)
- 1983 Senate Hearing TranscriptDocument1,037 pages1983 Senate Hearing TranscriptStephen LoiaconiNo ratings yet
- WBC Histogram Interpretations of 3-Part Differentiation: Sysmex Xtra Online - July 2011Document5 pagesWBC Histogram Interpretations of 3-Part Differentiation: Sysmex Xtra Online - July 2011ripangaNo ratings yet
- Blood BankingDocument7 pagesBlood BankingRoiland Atienza BaybayonNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology MainDocument68 pagesBlood Physiology MainOmenaalaNo ratings yet
- A Cell-Based Model of Coagulation and The Role of Factor VIIa - Blood Review 2003Document5 pagesA Cell-Based Model of Coagulation and The Role of Factor VIIa - Blood Review 2003Oscar Echeverría OrellanaNo ratings yet
- 10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFDocument21 pages10-Platelet Structure and Function PDFAnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageDocument5 pagesOvercoming Protein Instability Problems During Fusion Protein CleavageAsmaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Hemophilia - An OverviewDocument9 pagesReview Article: Hemophilia - An OverviewNelly Lutfieta SariNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants: Pharmacokinetics, Mechanisms of Action, and IndicationsDocument13 pagesAnticoagulants: Pharmacokinetics, Mechanisms of Action, and IndicationsNathali MorenoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in StrokeDocument93 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Used in StrokemehakNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Platelet FunctionDocument17 pagesHemostasis and Platelet FunctionUzama Binu AliNo ratings yet
- Coagulation CascadeDocument5 pagesCoagulation Cascadepieterinpretoria391100% (1)
- Week 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 11 - Hema Lec Major Anticoagulants SystemCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- LSM3212 - Lecture 2-4 BloodDocument59 pagesLSM3212 - Lecture 2-4 BloodAbraham KangNo ratings yet
- Thromboelastography Guide Trans 0413 p127 132Document6 pagesThromboelastography Guide Trans 0413 p127 132MarcelliaNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument135 pagesHemophiliaDivyashri Baraniya100% (1)
- Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladDocument82 pagesHemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Adelina VladLoly SinagaNo ratings yet
- Interferences From Blood Collection Tube Components On Clinical Chemistry Assays - Biochemia MedicaDocument8 pagesInterferences From Blood Collection Tube Components On Clinical Chemistry Assays - Biochemia MedicaBeatThe BeadNo ratings yet
- Zanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataDocument4 pagesZanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataasgooNo ratings yet
- DR Ip (Perbedaan Profil Perdarahan Pemberian Antiplatelet Pada Pasien Stroke Iskemik - Mukernas Perdossi Yogyakarta 27-30 Juli 2017Document15 pagesDR Ip (Perbedaan Profil Perdarahan Pemberian Antiplatelet Pada Pasien Stroke Iskemik - Mukernas Perdossi Yogyakarta 27-30 Juli 2017fajarrudy qimindraNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsTypes, Mode of Action and Preparation of Anticoagulant Bottles.Document40 pagesAnticoagulantsTypes, Mode of Action and Preparation of Anticoagulant Bottles.Arslan Arshad100% (1)
- 41042-Article Text-198327-1-10-20221205 PDFDocument8 pages41042-Article Text-198327-1-10-20221205 PDFCindy PramudinaNo ratings yet
- Animal Venoms in MedicineDocument9 pagesAnimal Venoms in MedicinelimperbiscuitNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewerDocument15 pagesHematology ReviewerNichol Villalba100% (1)
- Anticoagulants, Fibrinolytics, AntiplateletsDocument88 pagesAnticoagulants, Fibrinolytics, Antiplateletspmuawiyah25No ratings yet
- DVT (DR Dono)Document67 pagesDVT (DR Dono)Asmie Utamy AsfarNo ratings yet
- DOAC - Review Article Direct Oral AnticoagulantsDocument12 pagesDOAC - Review Article Direct Oral AnticoagulantsborstNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Cascade (Hema)Document4 pagesCoagulation Cascade (Hema)MarjoNo ratings yet
- HRM Week 2 - Introduction 2020 - PrintDocument34 pagesHRM Week 2 - Introduction 2020 - PrintShiv SookunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 - Drugs Affecting Blood CoagulationDocument12 pagesChapter 48 - Drugs Affecting Blood CoagulationJonathon100% (1)
- NATTOKINASEDocument18 pagesNATTOKINASESeng Kong YeohNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Hemostasis by Dr. RoomiDocument43 pagesLecture On Hemostasis by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- 2.7.2. Microbiological Assay of AntibioticsDocument7 pages2.7.2. Microbiological Assay of AntibioticsAshen NirodyaNo ratings yet