Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Between Autoregressive and Moving Average Models
Uploaded by
Deepak Padiyar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAn autoregressive (AR) model bases the current value on prior values, with an AR(1) using the immediately preceding value and AR(2) using the previous two. A moving average (MA) model creates averages of data subsets to smooth outliers. An ARIMA model combines AR and MA techniques to account for trends, cycles, seasonality in data when forecasting. ARIMA forecasting involves inputting time series data, identifying appropriate lags or differencing, checking for stationarity, and outputting results interpreted like a regression model.
Original Description:
Between Autoregressive and Moving Average Models
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn autoregressive (AR) model bases the current value on prior values, with an AR(1) using the immediately preceding value and AR(2) using the previous two. A moving average (MA) model creates averages of data subsets to smooth outliers. An ARIMA model combines AR and MA techniques to account for trends, cycles, seasonality in data when forecasting. ARIMA forecasting involves inputting time series data, identifying appropriate lags or differencing, checking for stationarity, and outputting results interpreted like a regression model.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBetween Autoregressive and Moving Average Models
Uploaded by
Deepak PadiyarAn autoregressive (AR) model bases the current value on prior values, with an AR(1) using the immediately preceding value and AR(2) using the previous two. A moving average (MA) model creates averages of data subsets to smooth outliers. An ARIMA model combines AR and MA techniques to account for trends, cycles, seasonality in data when forecasting. ARIMA forecasting involves inputting time series data, identifying appropriate lags or differencing, checking for stationarity, and outputting results interpreted like a regression model.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
What Are the Differences Between Autoregressive and
Moving Average Models?
ARIMA combines autoregressive features with those of moving averages.
An AR(1) autoregressive process, for instance, is one in which the current
value is based on the immediately preceding value, while an AR(2)
process is one in which the current value is based on the previous two
values. A moving average is a calculation used to analyze data points by
creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set to
smooth out the influence of outliers. As a result of this combination of
techniques, ARIMA models can take into account trends, cycles,
seasonality, and other non-static types of data when making forecasts.
How Does ARIMA Forecasting Work?
ARIMA forecasting is achieved by plugging in time series data for the
variable of interest. Statistical software will identify the appropriate number
of lags or amount of differencing to be applied to the data and check for
stationarity. It will then output the results, which are often interpreted
similarly to that of a multiple linear regression model.
You might also like
- Arima Modelling by Ankit BhandariDocument6 pagesArima Modelling by Ankit BhandariAnkitNo ratings yet
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving AverageDocument4 pagesAutoregressive Integrated Moving AverageJonhmark AniñonNo ratings yet
- Finance Workshop HondaDocument30 pagesFinance Workshop Hondaatul kumarNo ratings yet
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving AverageDocument2 pagesAutoregressive Integrated Moving AverageDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Models (Arima)Document2 pagesAutoregressive Integrated Moving Average Models (Arima)Ayush choudharyNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 Time Series Forecasting ARIMA ModelDocument19 pagesModule 3.1 Time Series Forecasting ARIMA ModelDuane Eugenio AniNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Sales Through Time Series ClusteringDocument18 pagesForecasting Sales Through Time Series ClusteringLewis TorresNo ratings yet
- End Term Project (BA)Document19 pagesEnd Term Project (BA)atmagaragNo ratings yet
- Stock Price Forecasting Using Arima and Fourier TransformsDocument8 pagesStock Price Forecasting Using Arima and Fourier TransformsRodro1608No ratings yet
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving AverageDocument10 pagesAutoregressive Integrated Moving AverageshanNo ratings yet
- ARIMA Model: This Acronym Is Descriptive, Capturing The Key Aspects of The Model Itself. Briefly, They AreDocument2 pagesARIMA Model: This Acronym Is Descriptive, Capturing The Key Aspects of The Model Itself. Briefly, They Areshivani khareNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument23 pagesModule 5 PDFJha JeeNo ratings yet
- CRD AssignmentDocument9 pagesCRD AssignmentSreenivasNo ratings yet
- What Is Nonlinear RegressionDocument4 pagesWhat Is Nonlinear RegressionSiti Julpah HartatiNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument30 pagesFinal ReportThương VănNo ratings yet
- ARIMA Models For Time Series Forecasting - Introduction To ARIMA ModelsDocument6 pagesARIMA Models For Time Series Forecasting - Introduction To ARIMA ModelsgschiroNo ratings yet
- ARIMA ModelsDocument2 pagesARIMA ModelsGasimovskyNo ratings yet
- Arima Modeling With R ListendataDocument12 pagesArima Modeling With R ListendataHarshalKolhatkarNo ratings yet
- Sas/Ets Procedures: Rajender Parsad and Manoj Kumar Khandelwal I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi - 110 012Document10 pagesSas/Ets Procedures: Rajender Parsad and Manoj Kumar Khandelwal I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi - 110 012jitenNo ratings yet
- ArimaDocument23 pagesArimaSanthosh Raghavan100% (1)
- C 18,21,38,39,51business ForecastingDocument8 pagesC 18,21,38,39,51business ForecastingPrince JoshiNo ratings yet
- Automatic Forecasting SnapStatDocument7 pagesAutomatic Forecasting SnapStatRodrigo Vallejos VergaraNo ratings yet
- Stata Guide 01Document9 pagesStata Guide 01Heather CarterNo ratings yet
- Box-Jenkins Methodology Forecasting BasicsDocument11 pagesBox-Jenkins Methodology Forecasting BasicsAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- ARIMA Vs SARIMA Vs LSTMDocument13 pagesARIMA Vs SARIMA Vs LSTMsahilgdwnNo ratings yet
- Box JerkinDocument7 pagesBox Jerkinyash523No ratings yet
- Ads Phase5Document10 pagesAds Phase5RAJAKARUPPAIAH SNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Amit Thakur C-06 Anoop C C-08 Ashish Singh C-16 Dhirender Singh C-19 Sajin Sunny C-66Document8 pagesPresented By: Amit Thakur C-06 Anoop C C-08 Ashish Singh C-16 Dhirender Singh C-19 Sajin Sunny C-66Prince JoshiNo ratings yet
- ML Activity 2 - 2006205Document3 pagesML Activity 2 - 2006205tanishk ranjanNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To Time Series AnalysisDocument18 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Time Series AnalysisAdriano Marcos Rodrigues FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Exponential SmoothingDocument2 pagesExponential SmoothingHitesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- WiproDocument21 pagesWiproJatinNo ratings yet
- Chap21 SDocument55 pagesChap21 SRaghad AlnajimNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument6 pagesClass NotesNirmal SamuelNo ratings yet
- Equipment Fault Forecasting Based On ARMA ModelDocument5 pagesEquipment Fault Forecasting Based On ARMA ModelClaudio RobertoNo ratings yet
- Codigos para STATADocument9 pagesCodigos para STATAPilar CarterNo ratings yet
- ARIMA PaperDocument3 pagesARIMA PaperroziahzailanNo ratings yet
- Slide 8Document6 pagesSlide 8RJ RajpootNo ratings yet
- ARIMA Modelling and Forecasting: by Shipra Mishra InternDocument17 pagesARIMA Modelling and Forecasting: by Shipra Mishra InternShipraMishraNo ratings yet
- MATLAB, Step by StepDocument5 pagesMATLAB, Step by StepNidhi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Mastering Data Analytics - Data Science TermsDocument7 pagesMastering Data Analytics - Data Science TermsPhong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Automatic ForecastingDocument11 pagesAutomatic ForecastingOmar DSNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance ManagementDocument9 pagesQuality Assurance Managementselinasimpson0301No ratings yet
- Pom - Forecasting TechniquesDocument13 pagesPom - Forecasting TechniquesSuganya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Questions (#Day13)Document10 pagesData Science Interview Questions (#Day13)Sahil GouthamNo ratings yet
- Meow Meow Hehe CuteDocument1 pageMeow Meow Hehe CuteunggoypatotoyNo ratings yet
- Predictive AnalyticsDocument9 pagesPredictive Analyticsmattew657No ratings yet
- 3.1.1 The Three Stages of ARIMA ModellingDocument3 pages3.1.1 The Three Stages of ARIMA ModellingSnooky Benitez QuisilNo ratings yet
- Forecast Models and CalculationsDocument33 pagesForecast Models and CalculationsShashikanth Sammiti100% (2)
- Manuscript AIP 116 RevisedDocument13 pagesManuscript AIP 116 Revisedsenthil.jpin8830No ratings yet
- Chat GPTDocument24 pagesChat GPTpoorvaja.rNo ratings yet
- Timeseries AnalysisDocument5 pagesTimeseries AnalysisFuad Hasan GaziNo ratings yet
- Data Quality Management ToolsDocument7 pagesData Quality Management Toolsselinasimpson1601No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - DSADocument9 pagesUnit 4 - DSARoshanaa R100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Guide To Time Series AnalysisDocument26 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Time Series AnalysisMartin KupreNo ratings yet
- Marketing Analytics - Group 7Document9 pagesMarketing Analytics - Group 7ankitNo ratings yet
- Be A 65 Ads Exp 8Document10 pagesBe A 65 Ads Exp 8Ritika dwivediNo ratings yet
- Similarity Flooding: A Versatile Graph Matching Algorithm and Its Application To Schema MatchingDocument12 pagesSimilarity Flooding: A Versatile Graph Matching Algorithm and Its Application To Schema MatchingimmortalriderNo ratings yet
- Time Series Analysis and ForecastingDocument13 pagesTime Series Analysis and ForecastingSiectio DickoNo ratings yet
- Distance MeasuresDocument11 pagesDistance MeasuresDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Geometric Explanation of PCADocument5 pagesGeometric Explanation of PCADeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Geometric Explanation of PCADocument5 pagesGeometric Explanation of PCADeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Principal Component AnalysisDocument4 pagesPrincipal Component AnalysisDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Example of How To Use Multiple Linear RegressionDocument4 pagesExample of How To Use Multiple Linear RegressionDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
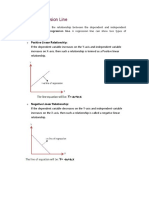
- Linear Regression LineDocument1 pageLinear Regression LineDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Score PlotsDocument5 pagesInterpreting Score PlotsDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Vs Logistic RegressionDocument2 pagesLinear Regression Vs Logistic RegressionDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Types of RegressionDocument3 pagesTypes of RegressionDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear VS Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesNonlinear VS Linear RegressionDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesMultiple Linear RegressionDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Linear Best FitDocument2 pagesLinear Best FitDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Multivariate DataDocument4 pagesVisualizing Multivariate DataDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Loadings and Scores CombineDocument2 pagesInterpreting Loadings and Scores CombineDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Loading PlotsDocument3 pagesInterpreting Loading PlotsDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Geometric Explanation of PCADocument5 pagesGeometric Explanation of PCADeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Direction VectorsDocument2 pagesDirection VectorsDeepak PadiyarNo ratings yet
- Detail Project Report SMDMDocument25 pagesDetail Project Report SMDMDeepak Padiyar100% (1)