Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Five BP2020
Uploaded by
Nelson OmondiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Five BP2020
Uploaded by
Nelson OmondiCopyright:
Available Formats
BUSINESS PLANNING
CHAPTER FIVE
FINANCIAL PLAN
In the financial plan you will deal with the financial aspects of your proposed business. To gauge
your future financial potential, you will prepare pro-forma balance sheets, pro-forma profit and loss
accounts and projected cash flow statement. You will also determine break-even level of sales and
calculate the expected profitability ratios of your business. Finally, you will indicate your
requirements and proposed capitalization.
Guidelines
In this chapter you will present information in tables, you will also be required to
write sets of assumptions governing every projection.
For every table indicate unit of currency i.e. Kshs.
Indicate dates for balance sheets, and cash flow projections
There should be minimal literature and mathematical workings in the tables just
provide worked figures (you may attach the calculations as appendices.
All tables must be done completely.
5.1 PRE-OPERATIONAL COSTS
Identifying your pre-operational costs.
What costs will you incur before you become operational? (Example professional fees,
installation costs, licenses, permits, deposits for water, electricity and telephones)
These are expenses that must be incurred before commencement of the business and they may
include but not limited to:
ITEM Cost Kshs
Transport
Market research
Assets(plant/properties)(from chapter four first table)
Consultation fess
Installations
Stationeries
Telephone
Licenses and Registrations
Rent deposit
TOTALS
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 1
BUSINESS PLANNING
5.2 WORKING CAPITAL
Estimating your working capital requirements for the first three years of operation
What working capital will you need over the first three years?
State any assumptions that you have made in arriving at your figures
WORKING CAPITAL FOR THE FIRST THREE YEARS
Item Year I Year II Year II
Current Assets
Stock of raw materials xxxx xxxx xxxx
Work in progress xxxx xxxx xxxx
Stock of finished goods
Closing stock xxxx xxxx xxxx
Debtors. xxxx xxxx xxxx
Cash in hand
Cash at Bank xxxx xxxx xxxx
(A) xxxx xxxx xxxx
Less Current Liabilities
Creditors xxxx xxxx xxxx
Loan repayment (One Year)
Un paid expenses xxxx xxxx xxxx
(B)
xxxx xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxxx xxxx
Working capital = A-B xxxx xxxx xxxx
Working capital = current Assets – Liabilities
Do not be in a hurry to do this part, do it after you have completed the balance
sheet. Use only entries that are relevant to your business, e.g. if you are not
manufacturing work in progress is unnecessary. Import entries from Bal sheet.
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 2
BUSINESS PLANNING
5.3(a) CASH FLOW PROJECTION FOR THE FIRST YEAR
Item Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Totals
Beginning Cash AC - - - - - - - - - - - AC
Cash Sales Y%
Debtors X%
Total cash TTLs
inflow(A) STT
Expenses
Purchases TTLs
SET
Rent OEB
Salaries/Wages OEB
Electricity bill OEB
Water bill OEB
Insurance OEB
Loan repayment OEB
Interest on loan OEB
Maintenance & OEB
Repair
Telephone OEB
Postage OEB
Stationery & OEB
Printing
Transportation OEB
Drawings OEB
Miscellaneous OEB
Total expenses
(B)
Net Cash=A-B
The beginning cash will be the total investment
Key AC- Approved Capital,Y%-Cash sales which should be >than X% where X% is the
proportion of goods sold on credit. Cash sales = TCI(A) – X% x TCI(A)
OEB-Operations Expense Budget (in chapter Two),
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 3
BUSINESS PLANNING
Remember some of these expenses are variable i.e. change while others are fixed per month.
TTLsSTT -Totals Sales Target Table
TTLs SET-Totals Sales Estimate Table, all in chapter Two.Page layout for 5.3a is landscape.
5,3(b) CASH FLOW PROJECTION FOR THE FIRST THREE YEARS
Item Year I ( Kshs) Year II (Kshs) Year III (Kshs)
Beginning cash AC AC +NCY1 AC=NCY1+NCY2
Cash Sales
Debtors
Total Cash Inflow (A) 5% of Year I 10% of Year I
Expenses
Purchases
Rent
Salaries/Wages
Electricity bill
Water bill
Insurance
Loan repayment
Interest on loan
Maintenance & Repair
Telephone
Postage
Stationery & Printing
Transportation
Drawings
Miscellaneous
Total cash outflow (B)
Net cash = A-B NCY1 NCY2 NCY3
Assumptions
Some expenses my NOT increase, instead they may decrease e.g. loan. Others may
remain constant e.g. Rent, & Salary depending on the business location and strategy.
NCY1, 2, 3-Net Cash Years 1, 2, &3
(Page layout is portrait)
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 4
BUSINESS PLANNING
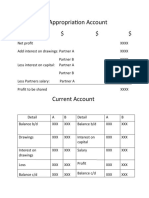
5.4 PROFORMA INCOME STATEMENT AS AT 31ST DECEMBER YEAR I
Item Year I Year II Year III
Sales TCI(A) 5.3b TCI(A) 5.3b(1.05) TCI(A) 5.3b(1.1)
(Less purchase of stock)
Gross profit (A)
Expenses
Rent
Salaries/Wages
Electricity bill
Water bill
Insurance
Loan repayment
Interest on loan
Maintenance & Repair
Telephone
Postage
Stationery & Printing
Transportation
Drawings
Miscellaneous
Total expenses (B)
Profit before Tax
Provision for Tax
Net profit after Tax
Notes
The Proforma income statement is a summary of income and expenditure for the year
in Kshs.
The sales and purchases figures are the totals for the year
Net profit before Tax =Gross profit – Total expenses
Provision for Tax should be given at the current taxation rates and subjected to the
profit before Tax. (Page layout is portrait)
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 5
BUSINESS PLANNING
5.5 PROFORMA BALANCE SHEET FOR THE FIRST YEAR
Proforma balance sheet As 31st As at 31st De As at 31st Dec
Year III
Dec Year I Year II
Fixed assets (Kshs) (Kshs) (Kshs)
Motor Vehicle xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Machinery & Equipment xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Furniture & Fittings Xxxxx Xxxxx Xxxxx
Accumulated depreciation (%) xxxxx xxxxx
Current assets
Debtors xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Rates prepayments xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Insurance prepayments xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Cash @ Bank xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Cash @ hand xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Closing stock xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Current liabilities
Creditors xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Sundry xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Net assets xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Financed by
Capital xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Net Profit xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Less Drawings (xxxxx) (xxxxx) (xxxxx)
xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx
Notes (Page layout is portrait)
Assets =Capital + Liabilities
The machines and other assets should be depreciated at the rate of 5-10% per year. To test the
balance sheet, assets must be equal to liabilities. The totals of the balance sheets at the beginning of
the year should be equal to the total investments.
Caution: under Fixed Assets, use only entries that are relevant to
your business plan, extracted from table of facilities in chapter four.
Exported relevant entries to 5.2 once the balance sheet is complete.
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 6
BUSINESS PLANNING
5.6 CALCULATION OF BREAK EVEN POINT
Calculating the expected breakeven level for your business.
Fixed costs Amount Kshs
-
-
-
Total fixed costs
Variable cost Amount Kshs
-
-
-
Total variable cost
Notes
Fixed costs are constant expenses for a defined period of time say one year e.g. Rent,
Licenses, salaries, Goodwill, insurance, depreciation, loan repayment etc.
Variable expenses are those that fluctuate within a specified period of time e.g. water
bills, allowances, recruitment costs, advertising costs, electricity bills, water bills
miscellaneous etc.
To obtain the breakeven point (level), you have to calculate the contribution margin
thus
Contribution Margin = Total sales – Total variables x100
Total Sales
Breakeven Level = Fixed Cost
Contribution margin %
5.7 CALCULATIONS OF PROFITABILITY RATIOS
(a) Gross profit percentage = Gross profit x100
Sales
(b) Return on Equity = Net profit after Tax x 100
Owners’ contribution
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 7
BUSINESS PLANNING
(c) Return on investment = Net profit Tax x 100
Total investment
5.8 DESIRED FINANCING
DESCRIPTION AMOUNT IN (KSHS)
Pre operational costs 5.1
Initial working capital AC - Pre Operational costs)
TOTAL AC
5.9 PROPOSED CAPITALIZATION
ITEM AMOUNT IN KSHS
Equity (own contributions, relatives etc)
Bank loan
Total AC
REFERENCES
Stokes and Wilson: Small Business Management and Entrepreneurship, 7th Edition (2010) south
western
Salemi: Entrepreneurship-Simplified: 6th Edition
Nickels and McHugh: Understanding Business: 4th Edition (2004) IWRIN
LECTURER MR.I.M.IMBISI © 2020
NOTES BY MR.ISAACK IMBISI ©2020 EDITION Page 8
You might also like
- AP US History TimelineDocument16 pagesAP US History TimelineJohn VR100% (5)
- POA Formats and Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesPOA Formats and Financial StatementsWilliNo ratings yet
- Tender Document STPDocument289 pagesTender Document STPvikas patelNo ratings yet
- Hydro Project Checklist CDMDocument6 pagesHydro Project Checklist CDMlunashim100% (1)
- Capital Asset Investment: Strategy, Tactics and ToolsFrom EverandCapital Asset Investment: Strategy, Tactics and ToolsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument2 pagesIndustrial ElectronicsMartinFS110380% (5)
- The Role of Financial System in The EconomyDocument15 pagesThe Role of Financial System in The Economymubarek100% (2)
- Accounting-Formats For Cambridge IGCSEDocument11 pagesAccounting-Formats For Cambridge IGCSEmuhtasim kabir100% (9)
- Geojit Financial Services Pay SlipDocument1 pageGeojit Financial Services Pay Slipsanjit deyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Government Banking InstitutionsDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Government Banking InstitutionsChichay KarenJoyNo ratings yet
- Credit Appraisal Process ReportDocument44 pagesCredit Appraisal Process ReportMuskan Maheshwari100% (2)
- Angel Jose Warehousing Co., Inc., Plaintiff-Appellee, V. Chelda Enterprises and David Syjueco, Defendants-Appellants.Document1 pageAngel Jose Warehousing Co., Inc., Plaintiff-Appellee, V. Chelda Enterprises and David Syjueco, Defendants-Appellants.elle cotocoNo ratings yet
- CouseDocument10 pagesCouseMagdy KamelNo ratings yet
- Mepa Unit 5Document18 pagesMepa Unit 5Tharaka RoopeshNo ratings yet
- Final AccountsDocument8 pagesFinal AccountsDananjaya RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries for Financial StatementsDocument90 pagesAdjusting Entries for Financial StatementsBadal singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- MEFA 5 UnitDocument30 pagesMEFA 5 UnitSuhasNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING FOR NON-CURRENT ASSETSDocument15 pagesACCOUNTING FOR NON-CURRENT ASSETSRECALL JIRIVENGWANo ratings yet
- 6 Branch AccountingDocument48 pages6 Branch AccountingsmartshivenduNo ratings yet
- Advanced Financial AccountingDocument102 pagesAdvanced Financial AccountingYash WanthNo ratings yet
- Drawing Financial Statements and ProjectionsDocument36 pagesDrawing Financial Statements and ProjectionsAaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and financial management group 8Document4 pagesEntrepreneurship and financial management group 8Aaron MushunjeNo ratings yet
- Notes of Financial Statements or Final AccountsDocument11 pagesNotes of Financial Statements or Final Accountsrxcha.josephNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet NotesDocument4 pagesBalance Sheet NotesAudrey RolandNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Topic FiveDocument14 pagesFinancial Accounting Topic FiveGABRIEL KAMAU KUNG'UNo ratings yet
- Notes-Unit-3-Final Accounts - (Partial)Document12 pagesNotes-Unit-3-Final Accounts - (Partial)happy lifeNo ratings yet
- Partnership Final Accounts PDFDocument97 pagesPartnership Final Accounts PDFKaushik Patel75% (4)
- Machinery Services: TemplateDocument2 pagesMachinery Services: TemplategazanNo ratings yet
- 4 Branch AccountsDocument18 pages4 Branch AccountsBAZINGANo ratings yet
- Partnership Lecture Handout With IllustrationDocument23 pagesPartnership Lecture Handout With IllustrationMichael Asiedu100% (3)
- Lect 11c Depreciation-Disposals (Part 3)Document17 pagesLect 11c Depreciation-Disposals (Part 3)11Co sarahNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Published Financial StatementsDocument19 pagesPreparation of Published Financial StatementsRuth Nyawira100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - PL & BS (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - PL & BS (Compatibility Mode)Riyasat khanNo ratings yet
- Accounting 0452 Notes-Ch8Document3 pagesAccounting 0452 Notes-Ch8Huma PeeranNo ratings yet
- SYJCBKLMRDocument33 pagesSYJCBKLMRghostinhouse223No ratings yet
- Navneet Model Practice-2Document7 pagesNavneet Model Practice-2Rudra ShahNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 2Document89 pagesFinancial Accounting 2Colince johnson0% (1)
- Session 1 - Finance For Non-Finance (19.08.2023)Document17 pagesSession 1 - Finance For Non-Finance (19.08.2023)Saroj AndhariaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Session 3: Financial StatementsDocument45 pagesBusiness Finance: Session 3: Financial StatementsXia AlliaNo ratings yet
- Tally Trading and Profit Loss Acc Balance SheetDocument14 pagesTally Trading and Profit Loss Acc Balance Sheetsuresh kumar10No ratings yet
- Psa VDocument5 pagesPsa Vsunkanmi4890No ratings yet
- ABC Club financial report breakdownDocument9 pagesABC Club financial report breakdownJoemar Legreso100% (1)
- MANUFACTURING AND NON-MANUFACTURING ENTITIES FINAL ACCOUNTSDocument13 pagesMANUFACTURING AND NON-MANUFACTURING ENTITIES FINAL ACCOUNTSRahul NegiNo ratings yet
- 4 General Accounts of Partnership FirmDocument16 pages4 General Accounts of Partnership FirmNisarga T DaryaNo ratings yet
- Tugas - Kadek SudianggartawanDocument8 pagesTugas - Kadek Sudianggartawan11Kadek SudianggartawanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Published Financial StatementsDocument46 pagesPreparation of Published Financial StatementsBenard Bett100% (2)
- Financial Statements Part A&bDocument6 pagesFinancial Statements Part A&b16115dxbpNo ratings yet
- IFRS - Lecture Cash Flow (For Self-Srudy)Document77 pagesIFRS - Lecture Cash Flow (For Self-Srudy)KristenNo ratings yet
- CH7 - DiscussionDocument8 pagesCH7 - DiscussionRichell ArtuzNo ratings yet
- +1 Acc Model Hly Ans (EM) 2022Document7 pages+1 Acc Model Hly Ans (EM) 2022BABA AssociatesNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Companies Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesSession 2 Companies Financial StatementsEraldo BoechatNo ratings yet
- Public Sector Accounting and ReportingDocument9 pagesPublic Sector Accounting and Reportingsunkanmi4890No ratings yet
- An Income Statement and A Statement of Financial Position For LawyersDocument5 pagesAn Income Statement and A Statement of Financial Position For Lawyerstapiwa mafunduNo ratings yet
- Corporate Unit 3Document497 pagesCorporate Unit 3bhavu aryaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument5 pagesCash Flow StatementDebaditya SenguptaNo ratings yet
- CASH FLOWS STATEMENTDocument6 pagesCASH FLOWS STATEMENTNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Syllabus (26.08.2023)Document8 pagesSession 2 - Syllabus (26.08.2023)Saroj AndhariaNo ratings yet
- Fund Flow - RevisedDocument11 pagesFund Flow - RevisedModhish NothumanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-Final Accounts - 2Document23 pagesUnit 7-Final Accounts - 2anamikarajendran441998No ratings yet
- Format SOCI SOFP For Servicing OperationDocument2 pagesFormat SOCI SOFP For Servicing OperationNUR ADLIN ZAFIRAH BINTI NORAZLI KTNNo ratings yet
- Business FinanceDocument6 pagesBusiness FinanceHassan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Financial Statements-Manufacturing AccountsDocument7 pagesPreparation of Financial Statements-Manufacturing AccountsHeavens MupedzisaNo ratings yet
- Final Accounts of SoletradersDocument9 pagesFinal Accounts of SoletradersShanavaz AsokachalilNo ratings yet
- Spicemen Income StatementDocument19 pagesSpicemen Income StatementHussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing A/c For The Year Ended .31.03.2016: XXX XXXDocument2 pagesManufacturing A/c For The Year Ended .31.03.2016: XXX XXXsubhash dalviNo ratings yet
- 2016-12 ICMAB FL 001 PAC Year Question December 2016Document3 pages2016-12 ICMAB FL 001 PAC Year Question December 2016Mohammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 12 AccountancyDocument10 pages12 AccountancyBhaswati SurNo ratings yet
- MJ17 Hybrids F9 Clean ProofDocument6 pagesMJ17 Hybrids F9 Clean ProofVinny Lu VLNo ratings yet
- 123455Document1 page123455Nelson OmondiNo ratings yet
- Chess Technologies 0707617530Document8 pagesChess Technologies 0707617530Nelson OmondiNo ratings yet
- Act 7Document12 pagesAct 7mappu08No ratings yet
- 1607 - Battle at El AddeDocument12 pages1607 - Battle at El AddeNelson OmondiNo ratings yet
- Omndi Nelson OkeloDocument1 pageOmndi Nelson OkeloNelson OmondiNo ratings yet
- M2MRates Jul 2015 Jun 2016Document404 pagesM2MRates Jul 2015 Jun 2016Hazbar AsifNo ratings yet
- CSR of Banking IndustryDocument2 pagesCSR of Banking Industryzany_sNo ratings yet
- Indemnity Bond ExplainedDocument4 pagesIndemnity Bond ExplainedEhtmam KhanNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis 13Document292 pagesPHD Thesis 13Prince PatelNo ratings yet
- Check List To Educational Loan Proposals Under IBA Scheme For Studies in India/AbroadDocument1 pageCheck List To Educational Loan Proposals Under IBA Scheme For Studies in India/AbroadAnbarasan AnandhanNo ratings yet
- NISM-Series-VI-Depository Operations-May 2021 VersionDocument224 pagesNISM-Series-VI-Depository Operations-May 2021 VersionLohit BharambeNo ratings yet
- Costram Fa3Document3 pagesCostram Fa3ban1ksNo ratings yet
- Polaris Project Business Analyst Role and Payment SystemsDocument18 pagesPolaris Project Business Analyst Role and Payment SystemsGigish ThomasNo ratings yet
- 4-Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument20 pages4-Capital Budgeting TechniquesnoortiaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Implications for Educational PlanningDocument3 pagesBudgeting Implications for Educational PlanningBenedict LumagueNo ratings yet
- Managing FOREX ExposureDocument23 pagesManaging FOREX ExposureCijil Diclause0% (1)
- Management Accounting Lecture Notes, Ebook For BCom Third Year - PDF Download PDFDocument101 pagesManagement Accounting Lecture Notes, Ebook For BCom Third Year - PDF Download PDFNithya RajendranNo ratings yet
- Fincfriends PVT LTD: Sub: in Principle Sanction LetterDocument2 pagesFincfriends PVT LTD: Sub: in Principle Sanction LetterDílìp ÎñdúrkãrNo ratings yet
- Post-Closing Trial BalanceDocument8 pagesPost-Closing Trial BalanceNicole Andrea TuazonNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Help Southwest Airlines Hedge Fuel CostsDocument35 pagesDerivatives Help Southwest Airlines Hedge Fuel Costsnirali100% (1)
- Capiz NGO/PO Network For Enterprise Development (CapizNED), Inc.Document56 pagesCapiz NGO/PO Network For Enterprise Development (CapizNED), Inc.Capizned Capizned CapiznedNo ratings yet
- UTI and Reliance Capital: India's leading financial organizationsDocument4 pagesUTI and Reliance Capital: India's leading financial organizationsKarishma KolheNo ratings yet
- BIC CodesDocument12 pagesBIC CodesJaccoNo ratings yet
- Accounting firm offers tax helpDocument1 pageAccounting firm offers tax helpYanetNo ratings yet
- Kinney CH 02Document19 pagesKinney CH 02sweetmangoshakeNo ratings yet
- Turnover RatiosDocument10 pagesTurnover RatiosBOSENo ratings yet