Professional Documents
Culture Documents
THERA EX - RANGE OF MOTION Laboratory
Uploaded by
Marili Camille CoquiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
THERA EX - RANGE OF MOTION Laboratory
Uploaded by
Marili Camille CoquiaCopyright:
Available Formats
RANGE OF MOTION
THERA EX / LABORATORY
● Shoulder Internal Rotation - External
OUTLINE
Rotation
I. Spine ROM 1. Grasp the hand and the wrist with
II. Shoulder, Elbow, Forearm your index finger between the
III. Wrist and Hand patient’s thumb and index finger
IV. Lower Extremity 2. Place your thumb and the rest of your
fingers on either side of the wrist
thereby stabilizing the wrist
SPINE ROM 3. With the other hand, stabilize the
Cervical Spine ROM elbow. Then rotate the humerus by
● Cervical Flexion moving the arm like a spoke on a
o patient in supine wheel
● Cervical Extension
o patient in supine ● Shoulder Horizontal Adduction -
● Cervical Lateral Flexion Abduction
o patient in supine and do it in both sides 1. Hand placement is the same as with
● Cervical Rotation flexion but turn your body and face
o do in both sides the patient’s head as you move the
patient's arm out to the side and then
Lumbar Spine ROM across the body
● Lumbar Flexion
● Lumbar Rotation ● Shoulder Extension
● Lumbar Extension 1. To obtain extension past zero, position
the patient side-lying and move the
SHOULDER, ELBOW, FOREARM arm through the available range and
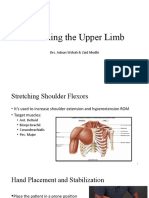
● Shoulder Flexion return. (can also be done supine at the
1. Grasp the patient’s arm under the edge of the bed, prone or sitting)
elbow with your lower hand
2. With the top hand, cross over and ● Elbow Flexion - Extension
grasp the wrist and palm of the 1. Hand placement is the same as with
patient’s hand the shoulder flexion except the
3. Lift the arm through the available motion occurs at the elbow as it is
range and return flexed and extended.
2. One can perform elbow flexion and
● Shoulder Abduction - Adduction extension with the forearm pronated
1. Use the same hand placement as with as well as supinated
flexion, but move the arm out to the
side. The elbow may be flexed ● Forearm Pronation - Supination
1. Grasp the patient’s wrist, supporting
the hand with the index finger, and
placing the thumb and the rest of the
fingers on either side of the distal
forearm
✨| satou puas PROM
1
polaroid love ੈ✩‧₊˚
THERAPEUTIC EXERCISE – RANGE OF MOTION LABORATORY
2. Stabilize the elbow with the other - PIP -> Stabilize the 5th proximal
hand phalanx and move the 5th middle
3. The motion is a rolling of the radius phalanx
around the ulna at the distal radius - DIP -> stabilize the 5th middle
phalanx and moving 5th distal
WRIST AND HAND phalanx
● Wrist Flexion - Extension - Alternative: Do the motions
- Locate the wrist joint and Stabilize the simultaneously (stabilize all the joints
distal forearm possible)
- Move the hand towards flexion 10
times ● Elongation of the Extrinsic Muscles of the
- Move the hand posteriorly (extension) Wrist and Hand (Flexor/Extensor
for 10 times Digitorum)
- Alternative: doing both extension and - make sure to follow the distal to
flexion simultaneously proximal patterns
- stabilize the distal forearm
● Wrist Radial - Ulnar Deviation
- same hand placement and stabilize LOWER EXTREMITIES
the distal forearm ● Hip Flexion with Knee extension
- Repeat each motion for 10 times - patient must be at the side of the table
and the PT must be at the middle of
● Cupping and Flattening of the Arch of the the table (to be able to provide good
Hand leverage)
- trying to move the carpometacarpal - One hand under the heel and one on
and intermetacarpal joint the top of the knees
- make sure to maximize the cupping - Move the toes towards the ceiling
and flattening (until the available range of motion)
- Do it 2 - 3 times
● 1st CMC Joint Flexion - Extension -
Abduction - Adduction ● Hip Extension
- stabilize the trapezius while doing the - Prone position and sidelying position
motion
Sidelying position
● 1st MCP Joint Flexion - Extension - try to slightly bend the legs and the
- stabilize the 1st metacarpal and move stabilization is under the legs
the proximal phalanx of the first digit supporting the knee joint
- another hand is on the pelvic region
● 1st IP Joint Flexion - Extension - try to sway the leg back
- stabilize the proximal phalanx of the
first digit Prone position
- hold it on the lateral aspect - the stabilizing hand must be on the
pelvic area and the supporting hand
● 5th MCP, PIP, DIP Joint Flexion - must cradle the leg and thigh
Extension (2nd - 4th MCP, PIP, DIP) - extension
- MCP -> stabilize the 5th metacarpal
and move the 5th proximal phalanx ● Hip Abduction - Adduction
- patient on supine and PT on the side of
the table
✨| satou puas PROM
2
polaroid love ੈ✩‧₊˚
THERAPEUTIC EXERCISE – RANGE OF MOTION LABORATORY
- the PT must be supporting the ankle
and the other hand is in the medial
aspect of the thigh
- make sure that the knee is in an
extended position
● Hip Internal Rotation and External
Rotation
- patient on supine
- dominant hand of PT must be
supporting the heel of the patient and
the non-dominant hand must be on
the distal part of the thigh
- hip is in 90 degrees hip and knee
flexion
- when the hip is unstable: cradle it
● Knee Flexion and Extension
- patient in prone position
- hold the distal part of the leg and
stabilize the pelvic region
● Ankle Dorsiflexion and Plantarflexion
- patient in supine position and at the
edge of the table
- hold the ankle and move it upward
(dorsiflexion)
● Subtalar Inversion and Eversion
- patient in supine
- dominant hand of PT supporting the
heel of the client
- non dominant hand of PT supporting
the distal part of the leg
● Toes Flexion and Extension
- patient in supine
- stabilize the metatarsalphalengeal
joint and hold the toe (and move it)
References:
● Maam Keith video presentation
● Maam Mheg video presentation
● Maam Ethley video presentation
● Sir ER video presentation
✨| satou puas PROM
3
polaroid love ੈ✩‧₊˚
You might also like
- Principles of Body Mechanics:: Rom& Isometric ExercisesDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Body Mechanics:: Rom& Isometric ExercisesRose Antonette BenitoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Prelab Homework - AnswersDocument12 pagesWeek 4 Prelab Homework - AnswerswilliamsdevanelNo ratings yet
- Warm Up SessionDocument7 pagesWarm Up SessionDIABLA FFNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Stretching and Strengthening: IMG Physical TherapyDocument8 pagesShoulder Stretching and Strengthening: IMG Physical TherapyRushabh PatelNo ratings yet
- 2 - Stretching of The Trigger PointDocument17 pages2 - Stretching of The Trigger PointLolyNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Stretching 1Document26 pagesLab 4 Stretching 1Ibraheem MohdNo ratings yet
- Range of MotionDocument59 pagesRange of MotionIsrael Jiel Fedelicio100% (1)
- Passive Range of Motion Exercises GuideDocument7 pagesPassive Range of Motion Exercises GuideFreisan ChenNo ratings yet
- Manipulasi ShoulderDocument37 pagesManipulasi ShoulderVikborn TjgNo ratings yet
- Muscular - Active Assistive Range of Motion (AAROM)Document4 pagesMuscular - Active Assistive Range of Motion (AAROM)mksayshiNo ratings yet
- Scapular Ax in NeuroDocument6 pagesScapular Ax in NeurolavanyaphdNo ratings yet
- SCI and TBI ManagementDocument40 pagesSCI and TBI ManagementAlif AndiniNo ratings yet
- Knee PP Revision:: 1. Flexion (0 - 135)Document13 pagesKnee PP Revision:: 1. Flexion (0 - 135)senoNo ratings yet
- 5 Shoulder MovmentsDocument70 pages5 Shoulder Movmentsalinaziyad3No ratings yet
- Stretch and Flex PosterDocument1 pageStretch and Flex Postermaricor aranNo ratings yet
- Throwers Ten 0Document7 pagesThrowers Ten 0nerat pamNo ratings yet
- Stretch and strengthen lower back musclesDocument5 pagesStretch and strengthen lower back musclesAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- EXERCISESDocument14 pagesEXERCISESKasapharma y Kasanacorp Victor H. Zuñiga TapiaNo ratings yet
- Central Integration of Motor FunctionDocument3 pagesCentral Integration of Motor FunctionM51785No ratings yet
- LeafletDocument2 pagesLeafletAndikaNo ratings yet
- LeafletDocument2 pagesLeafletAndikaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Elbow (Lanjutan) : Presentan: Dr. Sylvia Evelyn Aritonang Pembimbing: Dr. Tri Damiati Pandji, SPKFRDocument45 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Elbow (Lanjutan) : Presentan: Dr. Sylvia Evelyn Aritonang Pembimbing: Dr. Tri Damiati Pandji, SPKFRsingle_ladyNo ratings yet
- Dumbbell Step-Up: ExecutionDocument10 pagesDumbbell Step-Up: ExecutionDavid RomeroNo ratings yet
- MSKII Elbow OE - StudentDocument49 pagesMSKII Elbow OE - StudentPeter YipNo ratings yet
- 6 Elbow and WristDocument76 pages6 Elbow and Wristalinaziyad3No ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument2 pagesPathfit ReviewermicahaalliyahazoresNo ratings yet
- Rollbord With Flat Sheet For Lateral Transfer Instructions - SMGHDocument1 pageRollbord With Flat Sheet For Lateral Transfer Instructions - SMGHAhata Sham NewazNo ratings yet
- 10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionDocument36 pages10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionzelinaokiNo ratings yet
- GONIOMETRYDocument185 pagesGONIOMETRYsunil patelNo ratings yet
- Base Workout 1Document1 pageBase Workout 1Lewis SermanNo ratings yet
- 7 Muscle Length TestingDocument8 pages7 Muscle Length Testingbuhlembatha304No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Prosthetics Body LandmarksDocument7 pagesUpper Extremity Prosthetics Body Landmarksد.موسى التويتيNo ratings yet
- Preparation Rationale/ CommentsDocument4 pagesPreparation Rationale/ CommentsPrince TulauanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris TK IiDocument5 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris TK IiNurharwati WanthyNo ratings yet
- Prom 2Document2 pagesProm 2Jose MarzanNo ratings yet
- Rehab. Following AmputationDocument27 pagesRehab. Following Amputationyosra adamNo ratings yet
- Lecture III LL. Lumbar Spine Self Vassissted ROM (Autosaved) PDFDocument51 pagesLecture III LL. Lumbar Spine Self Vassissted ROM (Autosaved) PDFAhmed NaeemNo ratings yet
- AnkleDocument12 pagesAnkleArianne Mari BalingitNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Ex 5-12Document5 pagesUnit 7 Ex 5-12Cosmina CorbeanuNo ratings yet
- C5 Elbow Flexors - Biceps Brachii, BrachialisDocument17 pagesC5 Elbow Flexors - Biceps Brachii, BrachialismayraNo ratings yet
- FitnessDocument31 pagesFitnessjmNo ratings yet
- 5-Flexibility TestsDocument62 pages5-Flexibility TestsMr. MixerNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy Techniques for the Lower ExtremitiesDocument11 pagesManual Therapy Techniques for the Lower ExtremitiesSaumitra Phadke100% (2)
- Exercise Manual FinalDocument57 pagesExercise Manual FinalkendallhalesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle AnatomyDocument21 pagesSkeletal Muscle AnatomyPeterNo ratings yet
- Dry Land Workout PlanDocument2 pagesDry Land Workout PlanMaryvan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Derived PositionDocument14 pagesDerived Positionbhavesh jain83% (18)
- MIDTERM - 2 - Brunnstrum - Chapter 3 Traning Procedure For The Trunk and Upper Extremity - 03-14-22Document12 pagesMIDTERM - 2 - Brunnstrum - Chapter 3 Traning Procedure For The Trunk and Upper Extremity - 03-14-22Mariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- Block 1 Practical 1Document14 pagesBlock 1 Practical 1joe doweNo ratings yet
- Facilitated Positional Release FPRDocument12 pagesFacilitated Positional Release FPRcoahuiltecoNo ratings yet
- Brunnstrom Approach (Hashir)Document20 pagesBrunnstrom Approach (Hashir)Hemanth SNo ratings yet
- Ballard Scoring: Component Description How To IllicitDocument4 pagesBallard Scoring: Component Description How To IllicitDoc Prince CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Stretch Strap InstructionsDocument7 pagesStretch Strap Instructionsromeo_malaya100% (1)
- Deltoid Muscle: 13 Main Muscle and Type ExercisesDocument10 pagesDeltoid Muscle: 13 Main Muscle and Type ExercisesCharise R. FortichNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy - Stroke - Arm ExercisesDocument5 pagesPhysiotherapy - Stroke - Arm Exercisesayeshamumtazkakakhel322No ratings yet
- Home Exercise Program: Created by Namratha C Prabhu PT May 27th, 2015Document3 pagesHome Exercise Program: Created by Namratha C Prabhu PT May 27th, 2015Ravindra Nadh Chowdary KammaNo ratings yet
- Lower Body Exercises for Strong Legs and GlutesDocument8 pagesLower Body Exercises for Strong Legs and GlutesLovelyNo ratings yet
- PTY 210 Exercise Therapy & Massage FoundationsDocument22 pagesPTY 210 Exercise Therapy & Massage FoundationsMayank kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Radio Taiso Routine 2: More Exercises for Health & Vitality: Radio Taiso, #2From EverandRadio Taiso Routine 2: More Exercises for Health & Vitality: Radio Taiso, #2No ratings yet
- THERA EX - Patient Management and Clinical Decision MakingDocument11 pagesTHERA EX - Patient Management and Clinical Decision MakingMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of the Head and NeckDocument49 pagesMuscles of the Head and NeckMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Repair PTDocument41 pagesInflammation Repair PTMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- AS # 3 Lecture - Range of MotionDocument1 pageAS # 3 Lecture - Range of MotionMarili Camille CoquiaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Biomechanics 2Document24 pagesMuscle Biomechanics 2Murad KurdiNo ratings yet
- .Aj PW Masterclass Vol1 Members PDFDocument4 pages.Aj PW Masterclass Vol1 Members PDFPhatanan KhamkaewNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease: SynonymsDocument35 pagesLegg Calve Perthes Disease: SynonymsAsad ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health 1: First Semester - Module 6 AerobicDocument7 pagesPhysical Education and Health 1: First Semester - Module 6 AerobicMarissa UrnosNo ratings yet
- Surprising Causes of Chest PainDocument4 pagesSurprising Causes of Chest PainRaprnaNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Tibial Plateau FractureDocument29 pagesRehabilitation of Tibial Plateau FractureJansen LeeNo ratings yet
- Bodybuilding - The Rock Hard Challenge (Month 2 Training)Document10 pagesBodybuilding - The Rock Hard Challenge (Month 2 Training)jwarswolvesNo ratings yet
- Interchange of Affirmative and Negative Sentences ExercisesDocument3 pagesInterchange of Affirmative and Negative Sentences ExercisesChandan SahaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Athleticism - Yuri ShaposhnikovDocument113 pagesSecrets of Athleticism - Yuri ShaposhnikovDan Lurie100% (11)
- IELTS Reading Academic Test 1Document14 pagesIELTS Reading Academic Test 1Penguin 200350% (6)
- From The ShadowDocument376 pagesFrom The ShadowSean Cutler100% (2)
- Total Gym Titanium - ManualDocument20 pagesTotal Gym Titanium - ManualJerryNo ratings yet
- CH - 1, P. Edu CLASS 11Document22 pagesCH - 1, P. Edu CLASS 11soniadhingra1805No ratings yet
- Reviewer in PeDocument10 pagesReviewer in PeJaspher BalanonNo ratings yet
- TechnoGym - Professional Wellness CollectionDocument332 pagesTechnoGym - Professional Wellness CollectionPeter DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Dancing for Fitness in the New NormalDocument29 pagesDancing for Fitness in the New NormalAndrelle Josh RosaceñaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 29Document11 pagesLesson 29Nhung HồngNo ratings yet
- A. Sequential Steps For Designing A Resistance Training ProgramDocument62 pagesA. Sequential Steps For Designing A Resistance Training ProgramNicole Ba�ares100% (1)
- Answers To Workbook Exercises: Unit 3 Living Things in Their Environment Exercise 3.1 Animal AdaptationsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Workbook Exercises: Unit 3 Living Things in Their Environment Exercise 3.1 Animal AdaptationsBhawana Singh50% (2)
- Trinity GESE Grade 6 SummaryDocument6 pagesTrinity GESE Grade 6 SummaryArianey1100% (1)
- Physical Fitness Midterm Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesPhysical Fitness Midterm Exam ReviewYheva Sanchez100% (1)
- CrossFit WODsDocument11 pagesCrossFit WODsmoxbyers7922100% (8)
- How To Keep Your Mind SharpDocument1 pageHow To Keep Your Mind Sharpkhalid.ehsNo ratings yet
- Fit After 50 For MenDocument28 pagesFit After 50 For Menmkptec0% (1)
- Getting fit through joggingDocument6 pagesGetting fit through joggingNguyen Thanh ThinhNo ratings yet
- Poliquin Ed 3Document198 pagesPoliquin Ed 3Louis Trần100% (1)
- Katz enDocument71 pagesKatz enAyush MauryaNo ratings yet
- STC ManualDocument56 pagesSTC ManualRussell ShacklefordNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 7 Quarter 4Document3 pagesMapeh 7 Quarter 4Rochen Apao Villapaña CarreonNo ratings yet
- Achievement Test 3. Listening Exercise 1 Recording 5Document3 pagesAchievement Test 3. Listening Exercise 1 Recording 5FernandoNo ratings yet