Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math problems involving geometry, algebra, trigonometry and calculus
Uploaded by
MJ Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math problems involving geometry, algebra, trigonometry and calculus
Uploaded by
MJ Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
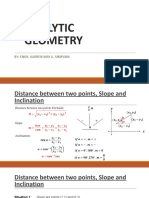
Example 1: If the point ( x, 3 ) is equidistant from ( 3, - 2 ) and ( 7, 4 ), find x.
Example 2: The vertices of an isosceles triangle are at A( 4, 5 ), B( 5, 0 ) and C( 9, y ). Find y if the equal sides are AB and AC.
Example 3: Given a line segment whose endpoints are P1( - 3, 5 ) and P2( 2, - 5 ).
1. Find the point which divides the line segment into 2 parts in the ratio 2:3. The point is nearer from P1 than from P2.
2. Extend the line segment from P1 to P2 by a distance equal to twice its length. Find the terminal point.
Example 4: Find the point which is three – fifths of the way from the point P1 ( 2, - 5 ) to the point P2( - 3, 5 )
Example 5: Given a line segment whose endpoints are P1( - 3, 5 ) and P2( 2, - 5 ). Find the midpoint of the line segment
Example 6: Find the area of a quadrilateral with vertices at ( 5, 6 ), ( 6, - 2 ), ( -1, 5 ) and ( - 4, -1 ).
Example 7: Find the value of x so that the slope of the line through ( x, 6 ) and ( 10, - 3 ) is – 3/2.
Example 8: Find the equation of the line through ( 4, 2 ) with the x – intercept twice the y – intercept.
Example 9: Find the equation of the line with normal angle 45 o and normal intercept 3.
Example 10: A line passes through ( 1, - 6 ) with slope 3/2.
1. Write the equation in the point – slope form.
2. Write the equation in the slope – intercept form.
3. Write the equation in the general form
Example 11: Find the distance between the parallel lines 3x – 4y + 7 = 0 and 3x – 4y – 8 = 0.
Example 12: Find the value of k so that the graphs of 3x + 4y + 5 = 0 and kx + 8y + 7 = 0 will not intersect?
Example 13: Write an equation of the line that is perpendicular to the line through ( 9, 10 ) and ( 3, - 2 ) and passes through the x –
intercept of that line.
Example 14: Two lines have equations of 2x – y + 2 = 0 and 2x + y – 4 = 0. Find the smallest angle between the 2 lines.
Example 15: Find the distance from 3x – 5y – 15 = 0 to the point ( 1, 2 )
Example 16: Two lines have equations of 2x – y + 2 = 0 and 2x – 4y – 11 = 0. Find the smallest angle between the 2 lines.
Example 17: Given the equation x 2 + y2 + 6x – 4y – 12 = 0.
1. Find the center and radius of the circle.
2. Find the length of the tangent from the point ( 10, 8 ) to the circle at the point of tangency.
3. Find the shortest distance from the point ( 10, 8 ) to the circle.
Example 18: Find the equation of the circle with center at C( 5, 2 ) and tangent to the line 2x – y + 7 = 0.
Example 19: Find the equation of the circle which passes through the points ( 0, 0 ), ( 6, 3 ) , and ( - 2, 4 )
Example 20: Find the radical axis of the given circles:
x 2 + y2 – 2x – 15 = 0
x 2 + y2 + 4x – 8y - 5 = 0
Example 21: Given the curve y 2 + 8x + 4y – 28 = 0.
1. Find the vertex
2. Find the focus
3. Find the length of the latus rectum
4. Find the directrix
Example 22: The cable of a suspension bridge hangs in the form of a parabola when the load is uniformly distributed horizontally. The
supporting towers are 40 m high and are spaced 240 m apart. The lowest point of the cable is 10 m above the roadway. Consider the
roadway as the x – axis and the axis of the parabola as the y – axis.
1. Find the equation of the cable( parabola ).
2. Find the vertical distance from the roadway to the cable at a point on the roadway 50 m from the center.
Example 23: Given the equation of the curve 9x2 + 25y2 – 18x + 250y + 409 = 0.
1. Find the center.
2. Find the distance between directrices.
3. Find the area and perimeter
Example 24: Find the equation of an ellipse with center at C( 3, 6 ), a focus at F( 3, 3 ) and second eccentricity equal to 3/4.
Example 25: The cross – section of a trough is a semi – ellipse with top width of 24 inches and a depth of 18 inches. It is filled with water to
a depth of 12 inches. Compute the width of the water surface
Example 26: Given the equation of the curve: 5y2 – 4x2 + 40y + 60 = 0. 1. Find the center. 2. Compute the eccentricity. 3. Compute the
length of the latus rectum.
Example 27: Find the equation of the hyperbola with center at ( 3, 1 ), one vertex at ( 6, 1 ) and latus rectum equal to 6.
Example 28: Plot the following points. a) A( 3, 30o ) c) P( - 2, 60o ) b) B( 2, - 60o ) d) Q( - 3, - 90o )
Example 28: A triangle has vertices at O( 0, 0o ), A( 6, 25o ) and B( 8, 72o ).
1. Find its area
2. Find its perimeter
3. Express the coordinates of A in rectangular form
Example 29: Find the polar equation of a circle with center at rectangular coordinates ( 3, 0 ) and tangent to the y – axis.
Example 30: Find the length of the latus rectum of the curve r = 4/(1 cos)
Example 31: Draw the graph of the curve with parametric equations
Example 32: Find the slope and y – intercept of the line x = 2t, y = t + 1.
Example 33: Find the eccentricity of the curve x = 3sin, y = 2cos.
You might also like
- Analytic GeometryDocument1 pageAnalytic GeometryNoxian TelicNo ratings yet
- 1b Important QuestionDocument3 pages1b Important QuestionSyed Salman85% (71)
- Analytic GeometryDocument1 pageAnalytic GeometrySo NnyNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document4 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1Mj AquinoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ProblemsDocument12 pagesMathematics ProblemsCelene Pia Ngo100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry ExamdbhbuBVJFBVUjbv;BSDUVNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry ExamOwen Radaza PiranteNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Practice Problems PDFDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Practice Problems PDFarthur guil-anNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Exammk07 natNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry ExamJomarCalacagNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Equations & ConceptsDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Equations & ConceptsDenNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Examreniel fabroNo ratings yet
- La RectaDocument6 pagesLa RectaJorge YarlequeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics GE REVIEW Session 4Document42 pagesMathematics GE REVIEW Session 4Broddett Bello Abatayo100% (2)
- Metro Karunagaran's 12th Std Maths Challenge for Centum - Top 50 3 Mark Questions Chapters 5,6,7,8Document12 pagesMetro Karunagaran's 12th Std Maths Challenge for Centum - Top 50 3 Mark Questions Chapters 5,6,7,8Gladson RennisNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument81 pagesAnalytic GeometryJohn Rofer CabantingNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry ExamDocument1 pageAnalytic Geometry Examcloud100% (1)
- Coordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesCoordinate GeometryVeera Venkata Sairam ChakravartulaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry IDocument3 pagesAnalytical Geometry IAnonymous Qq3Cd9hg0No ratings yet
- 10th Maths - 2 Mark (C, D Grade)Document4 pages10th Maths - 2 Mark (C, D Grade)nagarajuchalla0000No ratings yet
- 2013 Metrobank-MTAP - Dep-Ed Math Challenge 4th YearDocument7 pages2013 Metrobank-MTAP - Dep-Ed Math Challenge 4th YearChrisseMarthaGillesania100% (1)
- 4102600920398609Document6 pages4102600920398609yachemanenisNo ratings yet
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Analytic GeometrygregNo ratings yet
- Analytic ReviewDocument9 pagesAnalytic ReviewpsittacosisNo ratings yet
- Chapter: - Straight Lines and Conic SectionsDocument3 pagesChapter: - Straight Lines and Conic SectionsgritikaNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 6 Conic Sections PDFDocument8 pagesEXERCISE 6 Conic Sections PDFNurul SamsuddinNo ratings yet
- QB - Differentiation and Its ApplicationsDocument4 pagesQB - Differentiation and Its ApplicationsfgfgfNo ratings yet
- Anal Geom Exam-Questions2Document7 pagesAnal Geom Exam-Questions2Marcus McWile MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Problems and SolutionsDocument5 pagesAnalytic Geometry Problems and SolutionsJoyjoy C LbanezNo ratings yet
- Equations of circles and their propertiesDocument7 pagesEquations of circles and their propertiesBrijesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Assignment Solutions for Class 11Document7 pagesStraight Line Assignment Solutions for Class 11SAMEER.SHARMANo ratings yet
- 10th SA II Mathematics 1Document4 pages10th SA II Mathematics 1Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Ece Quiz 3-1Document9 pagesEce Quiz 3-1pclr07No ratings yet
- Math Quiz ReviewerDocument15 pagesMath Quiz ReviewerMarvin Rinon0% (1)
- Important Math Questions for Class XDocument8 pagesImportant Math Questions for Class X621220100% (1)
- Class X (Mathematics) : Holiday HomeworkDocument7 pagesClass X (Mathematics) : Holiday HomeworkSudhir AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Anal Geom Exam-QuestionsDocument7 pagesAnal Geom Exam-QuestionsMarcus McWile MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Anal Geom and Solid Geom Compilation Pinoy Bix GDocument63 pagesAnal Geom and Solid Geom Compilation Pinoy Bix GKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Question To Be Solved in ClassDocument6 pagesStraight Line Question To Be Solved in ClassSuryakanta JenaNo ratings yet
- 1 Stmathsbnew 2012Document3 pages1 Stmathsbnew 2012api-142567765No ratings yet
- Day 8 - Circle (Ok)Document18 pagesDay 8 - Circle (Ok)Daniel PiamonteNo ratings yet
- 25 Questions Maths Class 11thDocument3 pages25 Questions Maths Class 11thbansaljayash740No ratings yet
- X-M-Midterm-QP-A-E-21-22Document2 pagesX-M-Midterm-QP-A-E-21-22tmsssk23No ratings yet
- Circles: Equations, Properties and RelationshipsDocument15 pagesCircles: Equations, Properties and Relationshipskishangopi123No ratings yet
- 10th Maths Sample Paper 2011-2012 - 1Document3 pages10th Maths Sample Paper 2011-2012 - 1Alex ThomasNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument4 pagesStraight Linesblue_l1No ratings yet
- CBSE Class XI Straight Lines Assignment 3Document3 pagesCBSE Class XI Straight Lines Assignment 3Vishal Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cartesian Coordinate System and Conic Sections ReviewDocument65 pagesCartesian Coordinate System and Conic Sections ReviewAllen Kyle SayoNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Impq 11 Conic Sections Kvs PDFDocument6 pages11 Maths Impq 11 Conic Sections Kvs PDFSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- X Maths PaperDocument5 pagesX Maths Paperankurpapneja4100% (1)
- Problem Set 1 in Pre CalDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 in Pre CalAnthony AbesadoNo ratings yet
- Circle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDocument4 pagesCircle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaShubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Circles 240Document283 pagesCircles 240Faraz ZeyaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MergedDocument47 pagesModule 5 Mergedrikki angNo ratings yet
- Maths 1b 25-01-2016Document4 pagesMaths 1b 25-01-2016Bhanu KanatalaNo ratings yet
- Equation of Circles (Lesson 6Document19 pagesEquation of Circles (Lesson 6Roy Vinzon Martin Arceo100% (1)
- Sample Paper - 01 (For 2012) Class - X, SA-II Subject - MATHEMATICS (Code-041)Document5 pagesSample Paper - 01 (For 2012) Class - X, SA-II Subject - MATHEMATICS (Code-041)Rukmini SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transportation Engineering and Planning - Term PaperDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Transportation Engineering and Planning - Term PaperMJ Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Principles of Transportation Engineering Research WorkDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Transportation Engineering Research WorkMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 of Geotechnical Book SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 2 of Geotechnical Book SummaryMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Transport Policy Analysis and PlanningDocument2 pagesTransport Policy Analysis and PlanningMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- StrucTheor FormulasDocument3 pagesStrucTheor FormulasMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Steel DesignDocument4 pagesPractice Problems Steel DesignMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Combined Stress Sample ProblemsDocument1 pageCombined Stress Sample ProblemsMJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Show PDFDocument17 pagesShow PDFVineel KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Circle-02 - Solved ExampleDocument17 pagesCircle-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- The Magnetic Field Produced at A Focus of A Current Carrying Conductor in Shape of A Conic SectionDocument3 pagesThe Magnetic Field Produced at A Focus of A Current Carrying Conductor in Shape of A Conic SectionArchisman PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Learning Competencies TrackingDocument1 pageConic Sections Learning Competencies TrackingJonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Graphing Parabolas - Standard FormDocument12 pagesGraphing Parabolas - Standard FormdevikaNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING DRAWING LECTURE NOTES ON MECHANICS OF FLUIDSDocument212 pagesENGINEERING DRAWING LECTURE NOTES ON MECHANICS OF FLUIDSrangavaliNo ratings yet
- SLK Precalculus Quarter 1 Unit 1Document55 pagesSLK Precalculus Quarter 1 Unit 1Nikkaa XOX100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry 2Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 2Christopher Lennon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument3 pagesEngineering DrawingLeonel ZurbitoNo ratings yet
- Parabola StudentsDocument28 pagesParabola StudentsErika Anne BaravioNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 4: Ellipses and HyperbolasDocument19 pagesPre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 4: Ellipses and HyperbolasAbby Gayle Nacino0% (1)
- CirclesDocument22 pagesCirclesKunal RathoreNo ratings yet
- Curva Parábola Elipse Hipérbola DefinicionesDocument1 pageCurva Parábola Elipse Hipérbola DefinicionesDante FayanásNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Mathematics January Attempt Shift - 2 (10th January, 2019)Document21 pagesJEE Main 2019 Mathematics January Attempt Shift - 2 (10th January, 2019)Resonance Eduventures79% (19)
- PC (2nd) - 1-5 PDFDocument40 pagesPC (2nd) - 1-5 PDFMarvelous VillafaniaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Math 7Document7 pagesWeek 7 Math 7Girlie Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 2 HandoutDocument1 pageIntegral Calculus 2 HandoutJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Parabola Basics and Shortcut FormulaDocument15 pagesParabola Basics and Shortcut FormulaNicole Isabelle BasmayorNo ratings yet
- PARABOLA JEE MAIN Previous Year Q Bank Till 2017Document5 pagesPARABOLA JEE MAIN Previous Year Q Bank Till 2017AnshNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Class: December 1, 2021Document20 pagesSynchronous Class: December 1, 2021Syliviana SylvesterNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 (Guided Notes) - Module 3-Inscribed AnglesDocument10 pagesUnit 4 (Guided Notes) - Module 3-Inscribed AnglesYosief AdaneNo ratings yet
- Summative 2nd Quarter 1 PrecalculusDocument1 pageSummative 2nd Quarter 1 PrecalculusCarlo CutayNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science & Maths-Min (Dragged) 10Document1 pageCBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science & Maths-Min (Dragged) 10Nitya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 - Conic SectionsDocument37 pagesRevision Notes for Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 - Conic SectionsVarnika Arumugam NNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 PBDocument2 pagesSheet 1 PBAaRaV KuShWaHaNo ratings yet
- Laborator 9. Reprezentarea Axonometrică-Izometrică (2 1/2D) Utilizând AutocadDocument6 pagesLaborator 9. Reprezentarea Axonometrică-Izometrică (2 1/2D) Utilizând AutocadAnonymous CX10iTupNo ratings yet
- LeaP Math G5 Week 4 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Math G5 Week 4 Q3Lorefe Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- XII Maths DPP (01) - Prev Chaps - Conic SectionDocument13 pagesXII Maths DPP (01) - Prev Chaps - Conic SectionAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- 2lessons Circle TheoremsDocument29 pages2lessons Circle TheoremsFATMA HINDI / F MOHAMMED HUSSEIN HINDI -No ratings yet